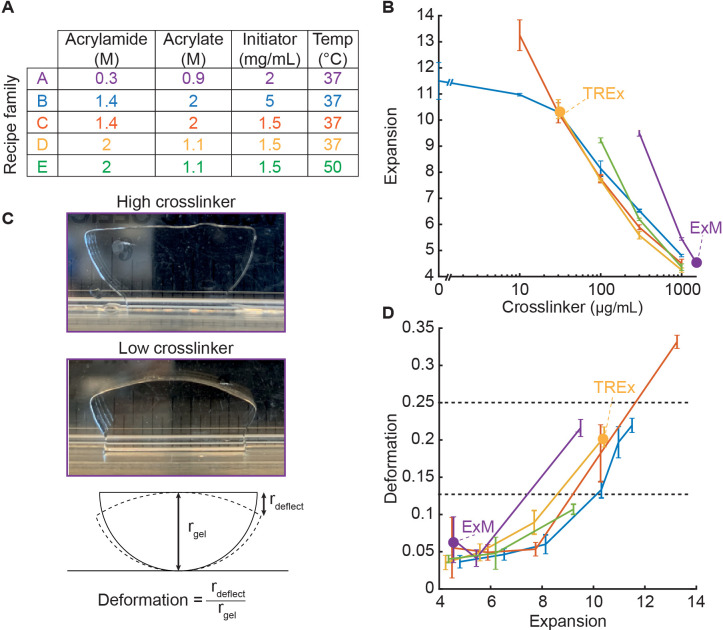
Figure 1. Development of Ten-fold Robust Expansion Microscopy (TREx) gel recipe.
(A) Parameters of gel recipe families explored, including component concentrations and gelation temperature. Each family was characterized by keeping these conditions constant while systematically varying the crosslinker concentration. (B) Expansion factor (mean ± SD, n = 3) versus crosslinker concentration (log scale) for each gel recipe family without biological specimens. Line colors correspond to recipe families as in (A). Specific recipes are indicated with a filled purple dot (original expansion microscopy [ExM] recipe) and yellow dot (TREx). All recipe families were tested with crosslinker concentrations of 0, 10, 30, 100, 300, and 1000 µg/mL, plus an additional condition for family A with 1500 µg/mL, corresponding to the original ExM recipe. Only conditions in which gels formed are plotted. (C) Definition of gel deformation index. Example gels from recipe family A with high crosslinker and low deformation (top panel, 1.5 mg/mL), and low crosslinker and high deformation (middle panel, 300 µg/mL). Bottom panel: schematic illustrating deformation index measurement. (D) Deformation index (mean ± SD, n = 3) versus expansion factor for each gel recipe family without biological specimens, with line colors and dots corresponding to specific recipes as in (A) and (B). Horizontal gray lines indicate thresholds for gels with mechanical quality deemed perfect (deformation < 0.125) and acceptable (deformation < 0.25). Ideal recipes would occupy the lower-right quadrant, corresponding to high expansion and low deformability.