Abstract
Background
Intermittent theta burst stimulation (iTBS) is an effective stimulus for long-term potentiation (LTP)-like plasticity. However, iTBS-induced effects varied greatly between individuals. Ample evidence suggested that an initial decrease in local γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) or enhancement in N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) facilitation neurotransmission is of vital importance for allowing LTP-like plasticity to occur. Therefore, we aimed to investigate whether the individual level of GABA or NMDA receptor-mediated activity before stimulation is correlated with the after-effect in cortical excitability induced by iTBS.
Methods
Fifteen healthy volunteers were recruited for the present study. We measured short-interval intracortical inhibitory (SICI), long-interval intracortical inhibitory (LICI), and intracortical facilitation (ICF), which index GABAA receptor-, GABAB receptor-, and glutamate receptor-mediated activity, respectively, in the cortex before conducting iTBS. After iTBS intervention, the changes of motor-evoked potential (MEP) amplitude were taken as a measure for cortical excitability in response to iTBS protocol.
Results
There was a significant negative correlation between the amount of SICI measured before iTBS and the after-effect of iTBS-induced LTP-like plasticity at the time points of 5, 10, and 15 min after inducing iTBS. A multiple linear regression model indicated that SICI was a good predictor of the after-effect in cortical excitability induced by iTBS at 5, 10, and 15 min following stimulation.
Conclusion
The present study found that GABAA receptor-mediated activity measured before stimulation is negatively correlated with the after-effect of cortical excitability induced by iTBS. SICI, as the index of GABAA receptor-mediated activity measured before stimulation, might be a good predictor of iTBS-induced LTP-like plasticity for a period lasting 15 min following stimulation.
Keywords: intermittent theta burst stimulation, LTP-like plasticity, GABAA receptor-mediated activity, GABAB receptor-mediated activity, N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-mediated activity
Introduction
Long-term potentiation (LTP)-like plasticity, defined as the ability of neurons to activity-dependently modify the strength of synaptic transmission, is the most common form of synaptic plasticity (Hebb, 2005; Takeuchi et al., 2014; Llona et al., 2017; Mateos-Aparicio and Rodríguez-Moreno, 2019). It is significant in response to physiological degeneration or brain injury (Wieloch and Nikolich, 2006; Chen et al., 2010; Cramer et al., 2011). LTP has been found to be induced by repetitive electrical stimulation in animal experiments, but recently the introduction of transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) with protocols of repetitive TMS (rTMS) presented the possibility of delivering similar LTP-like plasticity in the human brain (Bliss and Lømo, 1973; Wang et al., 1996; Ziemann et al., 1998b; Siebner and Rothwell, 2003; Cooke, 2006). Therefore, these rTMS-induced synaptic changes might have significant implications for therapeutic opportunities after brain damage via mechanisms of cortical plasticity (Lefaucheur et al., 2020).
Intermittent theta burst stimulation (iTBS) is one such protocol that can result in increases of cortical excitability persisting beyond the period of stimulation (Huang et al., 2005; Di Lazzaro et al., 2008). Compared with traditional rTMS protocols, iTBS requires lower simulation intensity and less stimulation time for inducing similar after-effects (Todd et al., 2009). Although iTBS may be indicative of an appealing technique for modulating cortical plasticity for clinical or therapeutic applications, recent studies observed that the effect varies greatly between individuals (Hamada et al., 2013; Hinder et al., 2014; Schilberg et al., 2017). Ridding and Ziemann (2010) summarized that the interindividual variability may depend on several different factors such as age, genetics, pharmacological influences, and neural activity in the brain before conducting stimulation. Such variability at present limits the therapeutic effectiveness of iTBS for inducing plastic changes.
The present study aimed at testing one such important factor that contributes to the variation of iTBS-induced plastic changes. Accumulating evidence in animal studies suggested that susceptibility to cortical potential-like plasticity is influenced by the level of cortical NMDAergic excitability and GABAergic inhibition (Kano and Iino, 1991; Schwenkreis et al., 2003; Di Lazzaro et al., 2006; Bachtiar and Stagg, 2014). Hess et al. (1996) suggested that LTP was enhanced by blockade of GABAA receptors with antagonist bicuculline in the motor cortex; conversely, the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) antagonist 2-amino-5-phosphonovaleric acid blocked LTP induction. LTP has also been found to be induced through iTBS when GABAA and GABAB receptors were both blocked (Kotak et al., 2017).
In human studies, paired pulse transcranial magnetic stimulation (ppTMS) can be performed to evaluate the level of GABA or NMDA receptor-mediated activity (Kujirai et al., 1993; Ziemann et al., 1998a; Ilić et al., 2002; McDonnell et al., 2006; Rossini et al., 2015). Therefore, we wished to verify whether the after-effect in cortical excitability induced by iTBS is correlated with the level of GABA or NMDA receptor-mediated activity before stimulation. Here, ppTMS was performed to evaluate short-interval intracortical inhibitory (SICI), long-interval intracortical inhibitory (LICI), and intracortical facilitation (ICF), which index GABAA receptor-, GABAB receptor-, and glutamate receptor-mediated activity, respectively.
Materials and Methods
Participants
Fifteen healthy volunteers (13 females) were recruited for the present study. Age ranges from 20 to 23 years (M = 21.07, SD = 1.06). All participants were right-handed (assessed by the Edinburgh Handedness Inventory; Oldfield, 1971) and had normal or correlated-with-normal vision. Exclusion criteria included a history of psychiatric or neurologic diseases, epilepsy, cardiovascular complications, taking any medication on a regular basis, and contraindications to TMS (e.g., taking epileptogenic drugs, implants in the brain, pregnant women). Informed consent was obtained from all participants. The study was performed according to the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of Affiliated Jiangsu Shengze Hospital of Nanjing Medical University (JSSZYY-LLSC-202104). The study was registered with the China Clinical Trial Registration Center1 under the number ChiCTR2100046794.
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation and Electromyography Recordings
Single monophasic TMS was performed over the hand region of the left primary motor cortex (LM1) using the Neuro-MS/D stimulator (Neurosoft Llc, Ivanovo, Russia) connected with a figure-of-eight coil (external loop diameters, 70 mm; peak magnetic field, 4 Tesla). The optimal coil position was determined by moving the coil in 1-cm steps around the presumed left M1 of hand until the point of the largest motor-evoked potential (MEP) amplitude of the relaxed abductor pollicis brevis (APB) muscle was reached. The stimulating coil was placed tangentially to the scalp with the handle pointing posteriorly and laterally 45° to the sagittal plane over the LM1 region. The stimulation intensity was determined in relation to the resting motor threshold (RMT) which was defined as the minimum TMS intensity eliciting a peak-to-peak MEP-amplitude of 50 μV or more in resting muscle, in at least 5 out or 10 trials (Groppa et al., 2012; Rossini et al., 2015). To assess the motor cortex excitability, motor-evoked potentials (MEPs) were recorded from the right APB muscle at rest (dominant hand in all participants) by use of silver/carbon-backed electrodes Skintact RT-34 (Fannin Ltd., Dublin, Ireland) with the size of 10.5 mm × 25 mm placed 2 cm apart in a belly-tendon montage (see Figure 1). The Neuro-MEP-Micro software was used to measure the amplitude of MEPs (Neurosoft Llc, Ivanovo, Russia).
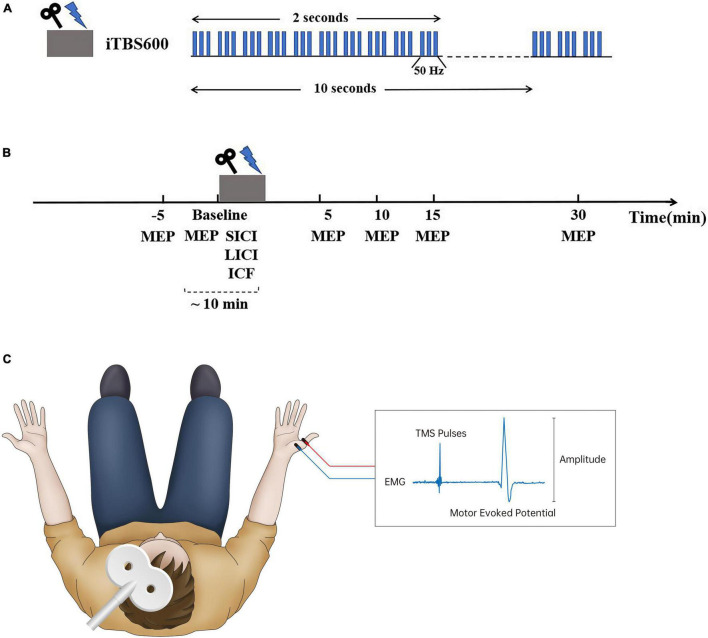
FIGURE 1.
Experimental design. (A) Intermittent theta burst stimulation (iTBS) protocol consisted of bursts containing three pulses given at 50 Hz and repeated every 200 ms; a 2-s train of this stimulating pattern was repeated every 10 s for a total of 190 s (600 pulses). (B) Each subject was assessed motor-evoked potentials (MEPs) and short-interval intracortical inhibitory (SICI), long-interval intracortical inhibitory (LICI), and intracortical facilitation (ICF) successively before iTBS intervention. Following iTBS, MEPs were assessed at 5, 10, 15, and 30 min after stimulation. (C) Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) was performed over the hand region of the left primary motor cortex (LM1) connected with a figure-of-eight coil. The stimulating coil was placed tangentially to the scalp with the handle pointing posteriorly and laterally 45° to the sagittal plane over the LM1 region. MEPs were recorded from the right abductor pollicis brevis (APB) muscle by use of silver/carbon-backed electrodes placed 2 cm apart in a belly-tendon montage to assess cortical excitability.
Intermittent Theta Burst Stimulation
iTBS was delivered over the hotspot of the LM1 using the Neuro-MS/D stimulator (Neurosoft Llc, Ivanovo, Russia). The stimulating protocol was conducted in accordance with the protocol originally described by Huang et al. (2005), which consisted of bursts containing three pulses given at 50 Hz and repeated every 200 ms (see Figure 1A). A 2-s train of this stimulating pattern was repeated every 10 s for a total of 190 s (600 pulses) (Huang et al., 2005). The stimulation intensity was set at 80% of RMT (Bulteau et al., 2017; Fujiki et al., 2020).
Experimental Procedure
Participants were seated in a comfortable chair with a neck support and were asked to relax their right arm entirely. They were also continually reminded to keep their eyes open and fixate forward on throughout each trial. Eyes open and muscle relaxation were observed by visual or electromyography (EMG) monitoring. A hotspot was marked as the optimal coil position where single-pulse TMS produced the largest MEP amplitude of the relaxed APB muscle by moving the coil around the presumed left M1 of hand (Rossini et al., 2015). Single-pulse TMS with intensity of 120% RMT was conducted to assess the excitability of the corticospinal system before and after iTBS. The peak-to-peak amplitude of MEPs evoked by a suprathreshold stimulus with an intensity of 120% RMT was used to probe the excitability of the motor cortex.
Before conducting iTBS, each participant received two sessions of single-pulse TMS with 20 consecutive pulses of each with an interval of 5 min at baseline to confirm intraindividual reliability of cortical excitability; the following trials could begin until the difference between average MEPs in two sessions of measurement was no more than 20% (Yu et al., 2020). To quantify the level of GABA or NMDA receptor-mediated activity before stimulation, we measured SICI, LICI, and ICF successively before conducting iTBS using a paired pulse paradigm at rest (Kujirai et al., 1993) (see Figure 1). SICI and ICF were delivered with an intensity of 90% RMT for the conditioning stimulus (CS) and 120% RMT for the testing stimulus (TS), with an interstimulus interval (ISI) of 2.5 and 12 ms, respectively, for 10 consecutive trials (Ozdemir et al., 2017; Tran et al., 2020). The CS and TS delivered in LICI were both set at 120% RMT, with an ISI of 150 ms for 10 consecutive trials (Mancheva et al., 2017). Paired pulse TMS results were based on 10 trials with single pulses (unconditioned) and 10 trials with paired pulses (conditioned) as previously recommended (Rossini et al., 2015).
Statistical Analysis
All analyses were performed using IBM SPSS version 22 (Armonk, NY, United States), and statistical significance was set at p < 0.05. Data were first tested to evaluate the normal distribution using the Shapiro–Wilk test. The MEPs were normalized to baseline MEP amplitude for each participant to calculate the after-effect of iTBS-induced LTP-like plasticity. Paired-pulse TMS protocols were expressed as the ratio of conditioned MEPs to unconditioned MEPs. A one-way within-subject ANOVA was conducted on the LTP-like after-effect induced by iTBS among different time points (baseline, 5, 10, 15, 30 min). The Mauchly test was used to verify the sphericity. A two-sided Pearson correlation test was used to examine relationships between SICI/LICI/ICF measured before stimulation and the after-effect of iTBS-induced LTP-like plasticity at 5, 10, 15, and 30 min after conducting iTBS, respectively. Multiple tests were corrected using the false discovery rate (FDR) method (Benjamini and Yekutieli, 2001) for ANOVA and Pearson correlation. To examine whether iTBS-induced plasticity can be predicted by SICI, LICI, or ICF, we also performed multiple regression analysis using the stepwise method. The multicollinearity test was performed based on the variance inflation factor (VIF) to examine whether our data met the assumption of collinearity.
Results
Intermittent Theta Burst Stimulation-Induced Plasticity
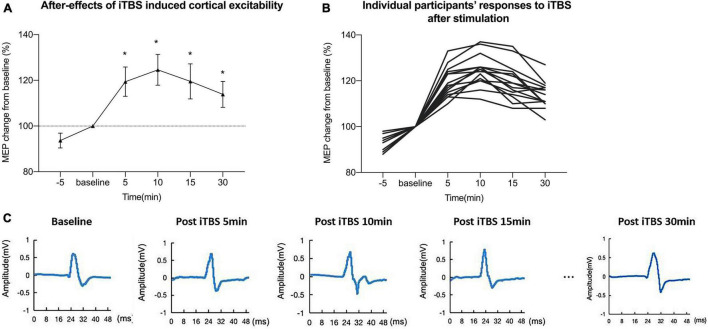
Figure 2 shows an iTBS-induced increase in cortical excitability at different time points after inducing iTBS and individual participants’ responses to iTBS. Figure 2C shows representative changes in MEPs recorded at 5, 10, 15, and 30 min after stimulation. The data indicated that the MEP amplitude began to increase after conducting iTBS. A one-way within-subject ANOVA was conducted on the LTP-like after-effect induced by iTBS. There was a significant effect of the after-effect of iTBS-induced LTP-like plasticity among different time points (baseline, 5, 10, 15, 30 min): F(4,56) = 123.9, p < 0.001 (FDR corrected), ηp2 = 0.87.
FIGURE 2.
Intermittent theta burst stimulation (iTBS) induced increase in cortical excitability at different time points. (A) iTBS induced a mean increase in motor-evoked potential (MEP) amplitude at different time points after intervention. (B) Individual responses to iTBS after stimulation of each participant. (C) Representative traces in motor-evoked potentials (MEPs) recorded at 5, 10, 15, and 30 min after stimulation. The data indicated that the MEP amplitude began to increase after conducting iTBS.
After-Effect of Intermittent Theta Burst Stimulation-Induced Potential-Like Plasticity Correlates With the Level of Short-Interval Intracortical Inhibitory Before Stimulation
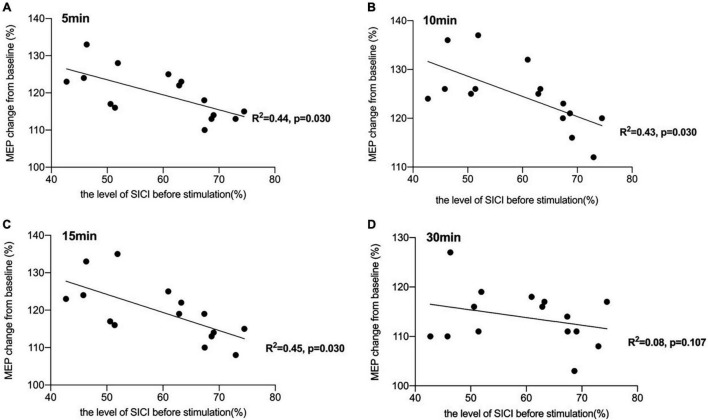
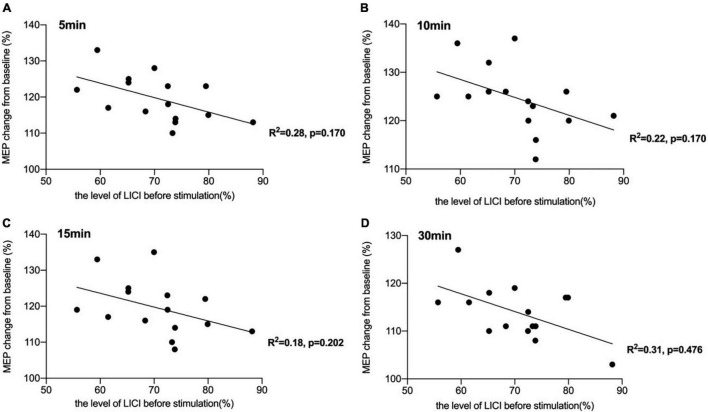
There was a significant negative correlation between the amount of SICI measured before iTBS and the after-effect of iTBS-induced LTP-like plasticity at the time points of 5 min (R2 = 0.44, p < 0.05, FDR corrected), 10 min (R2 = 0.43, p < 0.05, FDR corrected), and 15 min (R2 = 0.45, p < 0.05, FDR corrected) following conduction of iTBS (Figure 3). Post hoc power analysis indicated that the power to detect the observed effects at the 0.05 level was 0.742, 0.760, and 0.807 at the time points of 5, 10, and 15 min, respectively, while there is no significant correlation between SICI before stimulation and iTBS effect at 30 min (R2 = 0.08, p = 0.107, FDR corrected). No correlation between iTBS after-effect and the level of LICI was found at all time points 5, 10, 15, and 30 min after stimulation (Figure 4). Similarly, the iTBS after-effect was not correlated with the level of ICF measured before iTBS at all time points (Figure 5). Table 1 shows all R2 and p-values before and after applying the FDR correction.
FIGURE 3.
Correlation between short-interval intracortical inhibitory (SICI) and the after-effect of intermittent theta burst stimulation (iTBS)-induced long-term potentiation (LTP)-like plasticity. (A) There was a significant negative correlation between the amount of SICI measured before iTBS and the after-effect of iTBS-induced LTP-like plasticity at the time point of 5 min [R2 = 0.44, p < 0.05, false discovery rate (FDR) corrected]. (B) The correlation between the level of SICI before stimulation and iTBS-induced after-effects at 10 min after conducting iTBS was also significant (R2 = 0.43, p < 0.05, FDR corrected). (C) A significant negative correlation was also reported between the amount of SICI before stimulation and the iTBS-induced effects at 15 min after stimulation (R2 = 0.45, p < 0.05, FDR corrected). (D) There was no significant correlation between SICI before stimulation and iTBS effect at 30 min (R2 = 0.08, p = 0.107, FDR corrected).
FIGURE 4.
Correlation between long-interval intracortical inhibitory (LICI) and the after-effect of intermittent theta burst stimulation (iTBS)-induced long-term potentiation (LTP)-like plasticity. (A) No significant correlation was reported between the amount of LICI measured before iTBS and the iTBS after-effect at the time point of 5 min [R2 = 0.28, p = 0.170, false discovery rate (FDR) corrected]. (B) No significant correlation was also reported between the amount of LICI before stimulation and the iTBS-induced effects at 10 min after stimulation (R2 = 0.22, p = 0.170, FDR corrected). (C) The correlation between the level of LICI before stimulation and iTBS-induced after-effects at 15 min after conducting iTBS was also not significant (R2 = 0.18, p = 0.202, FDR corrected). (D) There was also no significant correlation between the level of LICI and the after-effect of iTBS-induced LTP-like plasticity at the time point of 30 min (R2 = 0.31, p = 0.476, FDR corrected).
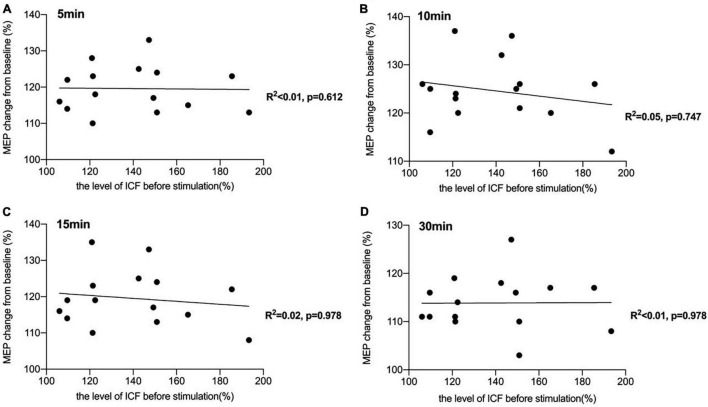
FIGURE 5.
Correlation between intracortical facilitation (ICF) and the after-effect of intermittent theta burst stimulation (iTBS)-induced long-term potentiation (LTP)-like plasticity. (A) No significant correlation was reported between the amount of ICF measured before iTBS and the iTBS after-effect at the time point of 5 min [R2 < 0.01, p = 0.612, false discovery rate (FDR) corrected]. (B) There was also no significant correlation between the level of ICF and the after-effect of iTBS-induced LTP-like plasticity at the time point of 10 min (R2 = 0.05, p = 0.747, FDR corrected). (C) A non-significant correlation was also reported between the amount of ICF before stimulation and the iTBS-induced effects at 15 min after stimulation (R2 = 0.02, p = 0.978, FDR corrected). (D) There was no significant correlation between ICF before stimulation and iTBS-effect at 30 min (R2 < 0.01, p = 0.978, FDR corrected).
TABLE 1.
Correlation between the level of short-interval intracortical inhibitory (SICI), long-interval intracortical inhibitory (LICI), and intracortical facilitation (ICF) measured before stimulation and the after-effect of intermittent theta burst stimulation (iTBS)-induced long-term potentiation (LTP)-like plasticity (all R2 and p-values before and after applying the FDR correction).
| ppTMS protocol | Time points after iTBS (min) | R2 | p-value before FDR correction | p-value after FDR correction | Results after FDR correction |
| SICI | 5 | 0.44 | 0.005 | 0.030 | Significant |
| 10 | 0.43 | 0.006 | 0.030 | Significant | |
| 15 | 0.45 | 0.008 | 0.030 | Significant | |
| 30 | 0.08 | 0.036 | 0.107 | Not significant | |
| LICI | 5 | 0.28 | 0.078 | 0.170 | Not significant |
| 10 | 0.22 | 0.085 | 0.170 | Not significant | |
| 15 | 0.18 | 0.118 | 0.202 | Not significant | |
| 30 | 0.31 | 0.317 | 0.476 | Not significant | |
| ICF | 5 | 0.00036 | 0.459 | 0.612 | Not significant |
| 10 | 0.05 | 0.623 | 0.747 | Not significant | |
| 15 | 0.02 | 0.916 | 0.978 | Not significant | |
| 30 | 0.000064 | 0.978 | 0.978 | Not significant |
Short-Interval Intracortical Inhibitory as a Good Predictor of Effectiveness of Intermittent Theta Burst Stimulation-Induced Cortical Plasticity
To assess predictive values for iTBS-induced cortical plasticity, we performed the multiple linear regression analysis with the levels of SICI, LICI, and ICF before iTBS as independent variables, and the dependent variable the after-effects of iTBS-induced cortical plasticity. Results from multicollinearity tests showed that the data met the assumption of collinearity with VIF = 1. Results from stepwise linear regression indicated that the model, with SICI as the only predictor, was significant at the time point of 5 min following iTBS conduction [F(1,13) = 10.144, p = 0.007, R2 = 0.40] and with beta coefficient = –0.4 for influence of SICI on the iTBS-induced cortical plasticity. In addition, SICI also remained as the only predictor in the models of 10 min [F(1,13) = 9.952, p = 0.008, R2 = 0.40] and 15 min [F(1,13) = 10.733, p = 0.006, R2 = 0.41] after conducting iTBS, with beta coefficients = –0.42 and –0.48 for influence of SICI on the iTBS-induced after-effect at 10 and 15 min after stimulation, respectively. Post hoc power analysis revealed that coefficients of –0.4, –0.42, and –0.48 could be detected at 0.05 at a power of greater than 0.90.
Discussion
The current study aimed at providing a direct investigation of the relationship between LTP-like plasticity induced by iTBS in the human motor cortex and the level of GABA or NMDA receptor-mediated activity before stimulation. We used a series of paired-pulse TMS protocols including SICI, LICI, and ICF to assess GABAA receptor-, GABAB receptor-, and glutamate receptor-mediated activity, respectively. Our findings showed that (i) GABAA receptor-mediated activity assessed before stimulation was significantly negatively correlated with LTP-like plasticity induced by iTBS following 5, 10, and 15 min after conduction of stimulation; (ii) there was no significant correlation between LTP-like plasticity induced by iTBS and GABAB receptor- or glutamate receptor-mediated activity before stimulation as assessed by the TMS protocol of LICI and ICF; and (iii) SICI, as the index of GABAA receptor-mediated activity measured before stimulation, is a good predictor of iTBS-induced LTP-like plasticity for a period lasting 15 min following stimulation.
Cortical inhibition is essential for regulating neuronal excitability, and a decrease in local inhibitory signaling is necessary for LTP-like plasticity to occur. In the present study, we found that GABAA receptor-mediated activity before stimulation was significantly negatively correlated with LTP-like plasticity induced by iTBS. This is consistent with previous evidence indicating that reduced GABAergic inhibition can facilitate induction of LTP-like plasticity (Castro-Alamancos et al., 1995; Trepel and Racine, 2000; Chen et al., 2010; Bachtiar and Stagg, 2014). Similar findings have also been observed in patients during chronic stages of stroke recovery that GABAA receptor-mediated activity is reduced compared with healthy controls (Blicher et al., 2009). Furthermore, we also found that SICI measured before stimulation is a good predictor of iTBS-induced LTP-like plasticity for a period lasting 15 min. Our findings might add evidence to the suggestion that SICI in the early recovery phase can be a predictor of LTP-like plasticity in the later recovery stage for patients after stroke (McDonnell et al., 2007; Liuzzi et al., 2014).
In addition to GABAA receptors, GABAB receptors are also thought to have an important role in induction of LTP (Larson and Munkácsy, 2015). In the present study, GABAB receptor-mediated activity before stimulation as assessed by LICI was found not significantly correlated with the after-effects of LTP-like plasticity induced by iTBS. This suggested that the interplay between GABAB receptor-mediated inhibition and plasticity is complex. In addition, metabotropic GABAB receptors have been found to modulate inhibitory neural circuits by mediating long-lasting inhibitory postsynaptic potentials or involve presynaptic autoinhibition of interneurons through GABAA receptors to inhibit GABA release (McDonnell et al., 2006; McDonnell et al., 2007). The former postsynaptic inhibition hyperpolarizes target neurons and reduces LTP-like plasticity, whereas the latter one depolarizes target neurons and results in facilitation of LTP (Mott and Lewis, 1991; Stäubli et al., 1999). In the current study, LICI was used to measure GABAB receptor-mediated effects without distinguishing postsynaptic and presynaptic GABAB effects. On the other hand, McDonnell et al. (2006) and Cash et al. (2010) suggested that these two different GABAB effects should be measured using LICI protocol and induce SICI in the presence of LICI in the human motor cortex. Therefore, although no significant correlation between postsynaptic GABAB effects measured by LICI- and iTBS-induced LTP was found in the present study, future studies need to further investigate the relationship between presynaptic GABAB effects and LTP-like plasticity.
Further, it is not consistent with our expectation that no significant correlation was found between iTBS after-effects and NMDA receptor-mediated activity before iTBS as assessed by ICF. Plentiful studies have shown that the NMDA receptor plays an important role in the development of rapid cortical plastic changes and activation of NMDA receptors is necessary to induce LTP-like plasticity (Hunt and Castillo, 2012; Hasan et al., 2013), while this phenomenon was not confirmed by others (Liao et al., 1995; Selig et al., 1995). Besides, previous work indicated that although LTP is induced by activation of NMDA receptors at synapses, these mechanisms are mediated by AMPA receptors trafficking in postsynaptic neurons (Park et al., 2018; Sumi and Harada, 2020). Further studies need to explore the role the AMPA receptor plays in iTBS-induced LTP-like plasticity and how to separate the effect of the NMDA and AMPA receptors on iTBS-induced after-effects. In addition, it may also be due to the fact that ICF is not an ideal measurement of NMDA receptor-mediated activities as more than one possible neural circuit contribute to ICF (Hanajima et al., 1998). Recent studies combining TMS–MRS methods showed that there was no significant relationship between the ICF protocol with ISI of 12 ms and MRS-glutamate, which questioned ICF as an effective tool to measure the level of NMDA-type glutamate receptor-mediated activity (Stagg et al., 2011; Dyke et al., 2017).
In conclusion, the present study found that GABAA receptor-mediated activity measured before stimulation is negatively correlated with the after-effect of cortical excitability induced by iTBS. SICI, as an index of GABAA receptor-mediated activity measured before stimulation, is a good predictor of iTBS-induced LTP-like plasticity for a period lasting 15 min following stimulation. However, there are several limitations in our study. First, we measured cortical excitability only within 30 min following iTBS protocols; it is unclear what happens after 30 min. In addition, a limited number of TMS pulses were applied to LM1, with only 10 trials for each condition (i.e., SICI, ICF, and LICI). Although we have ensured intraindividual reliability of cortical excitability by performing two sessions of single-pulse TMS with an interval of 5 min, the optimal number of trials was required to reduce interindividual differences in order to make the results more reliable. Furthermore, as a pilot study, the sample size is small and the sex of participants was not very balanced. Although no previous work has reported a sex difference in the iTBS-induced after-effects, further studies are still required to investigate sex differences in iTBS-induced LTP-like plasticity to make our findings more generalized to the entire population.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics Statement
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of Affiliated Jiangsu Shengze Hospital of Nanjing Medical University. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author Contributions
YS, T-FY, and CH had full access to all the data in the study, took responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis, designed the trial, and provided critical revisions to the manuscript. XD wrote the original draft as well as review and editing of the current manuscript. QL performed the data analysis. QL, LQ, and XD performed the study procedures. YS was responsible for the funding acquisition. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Acknowledgments
We thank all volunteers for their participation in this study. We express our gratitude to Xinyu Zhang for assistance with recruitment and testing of study participants.
Footnotes
Funding
This research was supported by the Introduced Project of Suzhou Clinical Medical Expert Team (Number SZYJTD201725), the Nanjing Municipal Science and Technology Bureau (Number 2019060002), and the National Key R&D Program of China (Numbers 2018YFC2001600 and 2018YFC2001603).
References
- Bachtiar V., Stagg C. J. (2014). The role of inhibition in human motor cortical plasticity. Neuroscience 278 93–104. 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.07.059 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamini Y., Yekutieli D. (2001). The control of the false discovery rate in multiple testing under dependency. Ann. Statistics 29 1165–1188. [Google Scholar]
- Blicher J. U., Jakobsen J., Andersen G., Nielsen J. F. (2009). Cortical excitability in chronic stroke and modulation by training: a TMS study. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair. 23 486–493. 10.1177/1545968308328730 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bliss T. V., Lømo T. (1973). Long-lasting potentiation of synaptic transmission in the dentate area of the anaesthetized rabbit following stimulation of the perforant path. J. Physiol. 232 331–356. 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010273 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulteau S., Sébille V., Fayet G., Thomas-Ollivier V., Deschamps T., Bonnin-Rivalland A., et al. (2017). Efficacy of intermittent Theta Burst Stimulation (iTBS) and 10-Hz high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) in treatment-resistant unipolar depression: study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials 18 1–10. 10.1186/s13063-016-1764-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cash R. F. H., Ziemann U., Murray K., Thickbroom G. W. (2010). Late cortical disinhibition in human motor cortex: a triple-pulse transcranial magnetic stimulation study. J. Neurophysiol. 103 511–518. 10.1152/jn.00782.2009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castro-Alamancos A., Donoghue P., Connors W. (1995). Different forms of synaptic plasticity in somatosensory areas of the neocortex. J. Neurosci. 15(7 Pt 2), 5324–5333. 10.1523/jneurosci.15-07-05324.1995 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen H., Epstein J., Stern E. (2010). Neural plasticity after acquired brain injury: evidence from functional neuroimaging. PMR 2 S306–S312. 10.1016/j.pmrj.2010.10.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke S. F. (2006). Plasticity in the human central nervous system. Brain 129 1659–1673. 10.1093/brain/awl082 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramer S. C., Sur M., Dobkin B. H., O’brien C., Sanger T. D., Trojanowski J. Q., et al. (2011). Harnessing neuroplasticity for clinical applications. Brain 134 1591–1609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Lazzaro V., Pilato F., Dileone M., Profice P., Oliviero A., Mazzone P., et al. (2008). The physiological basis of the effects of intermittent theta burst stimulation of the human motor cortex: Theta-burst rTMS of the human motor cortex. J. Physiol. 586 3871–3879. 10.1113/jphysiol.2008.152736 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Lazzaro V., Pilato F., Dileone M., Ranieri F., Ricci V., Profice P., et al. (2006). GABAA receptor subtype specific enhancement of inhibition in human motor cortex. J. Physiol. 575 721–726. 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.114694 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyke K., Pépés S. E., Chen C., Kim S., Sigurdsson H. P., Draper A., et al. (2017). Comparing GABA-dependent physiological measures of inhibition with proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy measurement of GABA using ultra-high-field MRI. Neuroimage 152 360–370. 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.03.011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiki M., Kawasaki Y., Fudaba H. (2020). Continuous theta-burst stimulation intensity dependently facilitates motor-evoked potentials following focal electrical stimulation of the rat motor cortex. Front. Neural Circuits 14:585624. 10.3389/fncir.2020.585624 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groppa S., Oliviero A., Eisen A., Quartarone A., Cohen L. G., Mall V., et al. (2012). A practical guide to diagnostic transcranial magnetic stimulation: report of an IFCN committee. Clin. Neurophysiol. 123 858–882. 10.1016/j.clinph.2012.01.010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada M., Murase N., Hasan A., Balaratnam M., Rothwell J. C. (2013). The role of interneuron networks in driving human motor cortical plasticity. Cereb. Cortex 23 1593–1605. 10.1093/cercor/bhs147 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanajima R., Ugawa Y., Terao Y., Sakai K., Furubayashi T., Machii K., et al. (1998). Paired-pulse magnetic stimulation of the human motor cortex: differences among I waves. J. Physiol. 509(Pt 2), 607–618. 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1998.607bn.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasan M. T., Hernández-González S., Dogbevia G., Trevino M., Bertocchi I., Gruart A., et al. (2013). Role of motor cortex NMDA receptors in learning-dependent synaptic plasticity of behaving mice. Nat. Commun. 4:2258. 10.1038/ncomms3258 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebb D. O. (2005). The Organization of Behavior: A Neuropsychological Theory. Hove: Psychology Press. [Google Scholar]
- Hess G., Aizenman C. D., Donoghue J. P. (1996). Conditions for the induction of long-term potentiation in layer II/III horizontal connections of the rat motor cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 75 1765–1778. 10.1152/jn.1996.75.5.1765 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinder M. R., Goss E. L., Fujiyama H., Canty A. J., Garry M. I., Rodger J., et al. (2014). Inter- and intra-individual variability following intermittent theta burst stimulation: implications for rehabilitation and recovery. Brain Stimulation 7 365–371. 10.1016/j.brs.2014.01.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang Y. Z., Edwards M. J., Rounis E., Bhatia K. P., Rothwell J. C. (2005). Theta burst stimulation of the human motor cortex. Neuron 45 201–206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt D. L., Castillo P. E. (2012). Synaptic plasticity of NMDA receptors: mechanisms and functional implications. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 22 496–508. 10.1016/j.conb.2012.01.007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilić T. V., Meintzschel F., Cleff U., Ruge D., Kessler K. R., Ziemann U. (2002). Short-interval paired-pulse inhibition and facilitation of human motor cortex: the dimension of stimulus intensity. J. Physiol. 545 153–167. 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.030122 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kano M., Iino K. (1991). Functional reorganization of adult cat somatosensory cortex is dependent on NMDA receptors. NeuroReport 2 77–80. 10.1097/00001756-199102000-00003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotak V. C., Mirallave A., Mowery T. M., Sanes D. H. (2017). GABAergic inhibition gates excitatory LTP in perirhinal cortex. Hippocampus 27 1217–1223. 10.1002/hipo.22799 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kujirai T., Caramia M. D., Rothwell J. C., Day B. L., Thompson P. D., Ferbert A., et al. (1993). Corticocortical inhibition in human motor cortex. J. Physiol. 471 501–519. 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019912 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson J., Munkácsy E. (2015). Theta-burst LTP. Brain Res. 1621 38–50. 10.1016/j.brainres.2014.10.034 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefaucheur J.-P., Aleman A., Baeken C., Benninger D. H., Brunelin J., Di Lazzaro V., et al. (2020). Evidence-based guidelines on the therapeutic use of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS): an update (2014–2018). Clin. Neurophysiol. 131 474–528. 10.1016/j.clinph.2019.11.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao D., Hessler N. A., Malinow R. (1995). Activation of postsynaptically silent synapses during pairing-induced LTP in CA1 region of hippocampal slice. Nature 375 400–404. 10.1038/375400a0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liuzzi G., Hörniß V., Lechner P., Hoppe J., Heise K., Zimerman M., et al. (2014). Development of movement-related intracortical inhibition in acute to chronic subcortical stroke. Neurology 82 198–205. 10.1212/WNL.0000000000000028 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llona I., Farías P., Troc-Gajardo J. L. (2017). Early postnatal development of somastostatinergic systems in brainstem respiratory network. Plastic Brain 1015 131–144. 10.1007/978-3-319-62817-2_8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancheva K., Stephanova D. I., Wolf W., Kossev A. (2017). “Long-Latency intracortical inhibition during unilateral muscle activity,” in CMBEBIH 2017, ed. Badnjevic A. (Singapore: Springer; ). 10.1152/japplphysiol.01016.2017 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Mateos-Aparicio P., Rodríguez-Moreno A. (2019). The impact of studying brain plasticity. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 13:66. 10.3389/fncel.2019.00066 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell M. N., Orekhov Y., Ziemann U. (2006). The role of GABA B receptors in intracortical inhibition in the human motor cortex. Exp. Brain Res. 173 86–93. 10.1007/s00221-006-0365-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell M. N., Orekhov Y., Ziemann U. (2007). Suppression of LTP-like plasticity in human motor cortex by the GABAB receptor agonist baclofen. Exp. Brain Res. 180 181–186. 10.1007/s00221-006-0849-840 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mott D., Lewis D. (1991). Facilitation of the induction of long-term potentiation by GABAB receptors. Science 252 1718–1720. 10.1126/science.1675489 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldfield R. C. (1971). The assessment and analysis of handedness: the Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia 9 97–113. 10.1016/0028-3932(71)90067-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozdemir Z., Sirin G., Kayki Y., Acar E., Soysal A. (2017). P226 The effect of interstimulus interval between the conditioning and test stimulus on inhibition and fascilitation: a transcranial magnetic stimulation study. Clin. Neurophysiol. 128:e251. [Google Scholar]
- Park P., Kang H., Sanderson T. M., Bortolotto Z. A., Georgiou J., Zhuo M., et al. (2018). The role of calcium-permeable AMPARs in long-term potentiation at principal neurons in the rodent hippocampus. Front. Synaptic Neurosci. 10:42. 10.3389/fnsyn.2018.00042 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridding M. C., Ziemann U. (2010). Determinants of the induction of cortical plasticity by non-invasive brain stimulation in healthy subjects. J. Physiol. 588 2291–2304. 10.1113/jphysiol.2010.190314 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossini P. M., Burke D., Chen R., Cohen L. G., Daskalakis Z., Di Iorio R., et al. (2015). Non-invasive electrical and magnetic stimulation of the brain, spinal cord, roots and peripheral nerves: basic principles and procedures for routine clinical and research application. an updated report from an IFCN Committee. Clin. Neurophysiol. 126 1071–1107. 10.1016/j.clinph.2015.02.001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schilberg L., Schuhmann T., Sack A. T. (2017). Interindividual variability and intraindividual reliability of intermittent theta burst stimulation-induced neuroplasticity mechanisms in the healthy brain. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 29 1022–1032. 10.1162/jocn_a_01100 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwenkreis P., Maier C., Pleger B., Mansourian N., Dertwinkel R., Malin J. P., et al. (2003). NMDA-mediated mechanisms in cortical excitability changes after limb amputation. Acta Neurol. Scand. 108 179–184. 10.1034/j.1600-0404.2003.00114.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selig D. K., Hjelmstad G. O., Herron C., Nicoll R. A., Malenka R. C. (1995). Independent mechanisms for long-term depression of AMPA and NMDA responses. Neuron 15 417–426. 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90045-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebner H., Rothwell J. (2003). Transcranial magnetic stimulation: new insights into representational cortical plasticity. Exp. Brain Res. 148 1–16. 10.1007/s00221-002-1234-1232 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stagg C. J., Bestmann S., Constantinescu A. O., Moreno Moreno L., Allman C., Mekle R., et al. (2011). Relationship between physiological measures of excitability and levels of glutamate and GABA in the human motor cortex. J. Physiol. 589 5845–5855. 10.1113/jphysiol.2011.216978 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stäubli U., Scafidi J., Chun D. (1999). GABA B receptor antagonism: facilitatory effects on memory parallel those on LTP induced by TBS but not HFS. J. Neurosci. 19 4609–4615. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-11-04609.1999 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumi T., Harada K. (2020). Mechanism underlying hippocampal long-term potentiation and depression based on competition between endocytosis and exocytosis of AMPA receptors. Sci. Rep. 10:14711. 10.1038/s41598-020-71528-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi T., Duszkiewicz A. J., Morris R. G. M. (2014). The synaptic plasticity and memory hypothesis: encoding, storage and persistence. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci. 369:20130288. 10.1098/rstb.2013.0288 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd G., Flavel S. C., Ridding M. C. (2009). Priming theta-burst repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation with low- and high-frequency stimulation. Exp. Brain Res. 195 307–315. 10.1007/s00221-009-1791-1798 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tran D. M., Chowdhury N. S., McNair N. A., Harris J. A., Livesey E. J. (2020). Linking cortical and behavioural inhibition: testing the parameter specificity of a transcranial magnetic stimulation protocol. Brain Stimulation 13 1381–1383. 10.1016/j.brs.2020.07.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trepel C., Racine R. J. (2000). GABAergic modulation of neocortical long-term potentiation in the freely moving rat. Synapse 35 120–128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H., Wang X., Scheich H. (1996). LTD and LTP induced by transcranial magnetic stimulation in auditory cortex. Neuroreport 7 521–525. 10.1097/00001756-199601310-00035 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieloch T., Nikolich K. (2006). Mechanisms of neural plasticity following brain injury. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 16 258–264. 10.1016/j.conb.2006.05.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu F., Tang X., Hu R., Liang S., Wang W., Tian S., et al. (2020). The After-Effect of accelerated intermittent theta burst stimulation at different session intervals. Front. Neurosci. 14:576. 10.3389/fnins.2020.00576 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziemann U., Corwell B., Cohen L. G. (1998b). Modulation of plasticity in human motor cortex after forearm ischemic nerve block. J. Neurosci. 18 1115–1123. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-03-01115.1998 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziemann U., Chen R., Cohen L. G., Hallett M. (1998a). Dextromethorphan decreases the excitability of the human motor cortex. Neurology 51 1320–1324. 10.1212/wnl.51.5.1320 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.