Abstract
Purpose:
Rural residents face higher cancer incidence rates and mortality rates, disparities that could be mitigated with health technology interventions, yet a digital divide is also apparent. This paper systematically and critically examines existing literature to understand how digital technologies have been used to support rural oncology care.
Methods:
PubMed, CINAHL Complete, PsycINFO, and Embase were searched using Medical Subject Headings terms and keywords. Studies were eligible if they presented empirical data investigating the use of technology in rural oncology and were published in English in a peer-reviewed journal within the last decade. The Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool was used to assess methodological quality.
Findings:
Digital health has been less extensively utilized in rural oncology compared with the general cancer population and other chronic diseases. We identified 54 studies that used technology in rural cancer care delivery, a comparatively small number, representing a significant gap in the literature. Studies were classified into 4 categories: Telemedicine (n = 32), phone calls (n = 11), Internet (n = 9), and mobile phone (n = 2). Of the 54 articles, 12 were RCTs, 17 were quasi-experimental, 3 were descriptive, 12 were mixed methods, and 10 were qualitative. Most of the studies involved patients only (n = 31) and were not specific to a cancer type (n = 41).
Conclusions:
Further implementation and expansion of telemedicine and phone-based strategies in rural cancer care delivery are warranted. Rural cancer survivors value digital approaches to their care. However, social and behavioral determinants of health and access to technology must be considered.
Keywords: cancer care delivery, digital health, oncology, rural, telemedicine
BACKGROUND
Cancer remains a leading cause of death in the United States, despite decreasing mortality rates, accounting for more than 600,000 deaths in 2019.1 Of the 15 million cancer survivors in the US, nearly 3 million reside in rural areas and experience 10% higher cancer mortality compared to their non-rural counterparts.2 During 2006–2015, the annual age-adjusted death rates for all cancer sites combined decreased at a slower pace in rural areas versus non-rural areas, widening the disparity in mortality rates.3 Rural cancer survivors tend to be older, have additional comorbidities, and have poorer general health, and as a group has a higher prevalence of lifestyle risk factors that complicate survival, such as smoking, lack of physical activity, and obesity.4–7
Access to care is a major factor driving geographic disparities. Rural areas have a lower county-level physician supply, and importantly, a lower density of specialists like radiation oncologists.8 Less than 3% of medical oncologists practice in rural areas.9 Rural residency has been associated with higher unmet care needs and reduced access to supportive care services among cancer survivors, including social work, palliative care, and hospice services.8,10,11 Access to care issues is further exacerbated by the increased rate of rural hospital closures in recent years.12 Limited local health services mean patients must travel farther for care, with median travel times ranging from 51 to 97 minutes.13 Additionally, poverty creates substantial transportation barriers, making it a challenge for rural residents who are also poor to afford gas for transportation to health care. Furthermore, since over 1.6M rural households do not have cars, transportation to treatment appointments presents a very real challenge.11 Web-based needs assessments have facilitated exploration of unmet rural cancer survivor needs, captured enduring survivorship issues, and recommended the use of technology to better inform and support patients and connect providers.14,15 Digital health can support patient, provider, and system-level needs for distance-based care strategies, which may serve to ultimately mitigate rural disparities in cancer outcomes that arise due to lack of access to care.
Digital health
Digital health can be defined as “using digital information, data, and communication technologies to collect, share, and analyze health information for purposes of improving patient health and health care delivery.”16 Telemedicine, which employs technology to administer distance-based health care, is one of the more widely used subcategories of digital health, while mobile applications (apps) are increasingly used for real-time or regular symptom assessments, health-related reminders, and tailored health feedback with studies reporting significantly improved health outcomes.17,18 While digital health technologies have the potential to optimize health care delivery, key barriers impede broad implementation. Additionally, the rate of health care digitalization and consumer demand has exceeded the health care systems’ ability to modernize its infrastructures and adapt to new workflows.19 Across all disease types and patient populations, there is a need to address these barriers to catch up with the technological curve and implement tools and strategies that are evidence-based.
Digital health in chronic disease management
Previous articles have reviewed the use of digital health technology in the management of a variety of chronic diseases, including hypertension, diabetes mellitus, rheumatology, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, inflammatory bowel disease, and mental illness.20–25 A 2015 scoping review of information and communication technology (ICT) chronic disease interventions identified 350 studies targeting diabetes mellitus (n = 103), cardiovascular disease (n = 89), chronic respiratory disease (n = 73), cancer (n = 67), and stroke (n = 18).26 With respect to cancer, this scoping review found that the use of ICT interventions was most broadly applied in cancer care compared with other chronic diseases, with a wider variety of activities involving self-management and engagement in their health care. Studies were more likely to include ICT interventions for one-way delivery of educational materials versus a patient-centered exchange of information and shared decision-making. Additional articles have reviewed the availability and features of mobile applications related to cancer across the care continuum.27,28 Specific to the cancer treatment phase, Davis categorized apps by the following use cases: Supporting patient-provider communication, patient information management, and managing treatment side effects.28 Digital health strategies have also been examined within subpopulations, including adolescent, young adult, and geriatric cancer survivors, but have yet to be examined within the rural context.29,30
Digital health in rural health care delivery
A 2019 study found that those living in rural areas had reduced odds of having Internet access compared with those residing in non-rural areas (OR 0.75; 95% CI: 0.67-0.84).31 In this paper we will refer to the rural digital divide as the inability of rural populations to access services and information through technology. A key contributor to the rural digital divide and critical to the deployment of digital health strategies is access to the broadband or mobile infrastructure that supports these tools. Over 26% of Americans in rural areas lack broadband coverage that would allow for home Internet access, as compared to only 1.7% of Americans in non-rural areas.32 Deployment of mobile long-term evolution, the pathway to achieving high-speed cellular Internet service, still lags in rural areas. Specifically, only 70% of the rural population has service with a median speed of 10 Mbps/3 Mbps versus 93% of the non-rural population.33 Similarly, 71% of rural residents reported having a smartphone, versus 83% of non-rural residents.34 In addition to infrastructure, social drivers relevant to technology access and use include higher poverty rates, lower educational attainment, and a higher proportion of elderly residents in rural communities.35 Technology tools such as patient portals and mobile apps are being used in the general cancer survivor population,27 yet rural residents are less likely to manage personal health information online or email a health care provider,36 and the extent to which digital health tools are being deployed in rural cancer populations is unknown.
Purpose
Digital health strategies may be used to mitigate rural cancer disparities. Despite progress made in understanding how digital health can enhance cancer care, previous reviews have not focused on their use in rural populations. The aim of this study was to systematically and critically examine existing literature to understand how digital technologies have been used to support rural oncology care.
METHODS
We conducted a systematic literature review in accordance with PRISMA guidelines of technology use in rural oncology research studies. Due to the limited published research on this topic, we did not restrict the search to US-based studies and instead included rural regions worldwide. Studies were eligible for inclusion if they presented empirical data from a human subjects study aimed at investigating the use of technology in rural cancer care delivery and were published between January 2009 and July 2021. Articles were excluded if they did not involve cancer survivors (defined from diagnosis forward), did not include rural participants, or were not available in English in a peer-reviewed journal. Searches were performed in PubMed, CINAHL Complete, PsycINFO, and Embase to identify relevant articles using a combination of Medical Subject Headings terms and keywords determined based on the literature (see Supplementary Material).
Data collection
We first reviewed titles and abstracts of search results. Full text of likely eligible articles was retrieved, screened by one research team member, and then verified by a second. Disagreements between authors were resolved by discussion or consultation with a third author. Reasons for the exclusion of full-text articles were recorded. Data were extracted onto a standardized data abstraction sheet by the first and second authors independently. Discrepancies were discussed and resolved by the study team. The following information was extracted: Publication year, first author, country, study design, study population, rural definition (if provided), rural sample size, total sample size, cancer site(s), type of technology considered, and study outcome(s). Technology type was categorized as telemedicine (video phone visits and telemonitoring systems), phone calls, mobile phone (text messages and phone-based apps), and Internet (websites and web-based applications). These categories were selected to compare the use of digital health in the rural cancer context with general cancer and other chronic disease populations presented by Wildevuur et al.26
Quality appraisal
Each study that met inclusion criteria was assessed for study quality using the mixed methods appraisal tool (MMAT), which allows for the critical appraisal of quantitative, qualitative, and mixed methods studies.37,38 The MMAT was developed to address the challenges of critical appraisal in systematic reviews involving more than 1 study design. Each study type is assessed by 5 quality indicators, items that were developed from the literature, as well as consultations and workshops with experts.38,39 Its efficiency and reliability have been previously demonstrated.38,40
RESULTS
The initial search yielded 661 articles. An additional 5 articles were identified through a review of reference lists. After removing duplicates, there were 581 unique articles remaining. Review of titles and abstracts resulted in 79 articles eligible for full-text screening, and 54 of these articles met study inclusion criteria (Figure 1).
FIGURE 1.
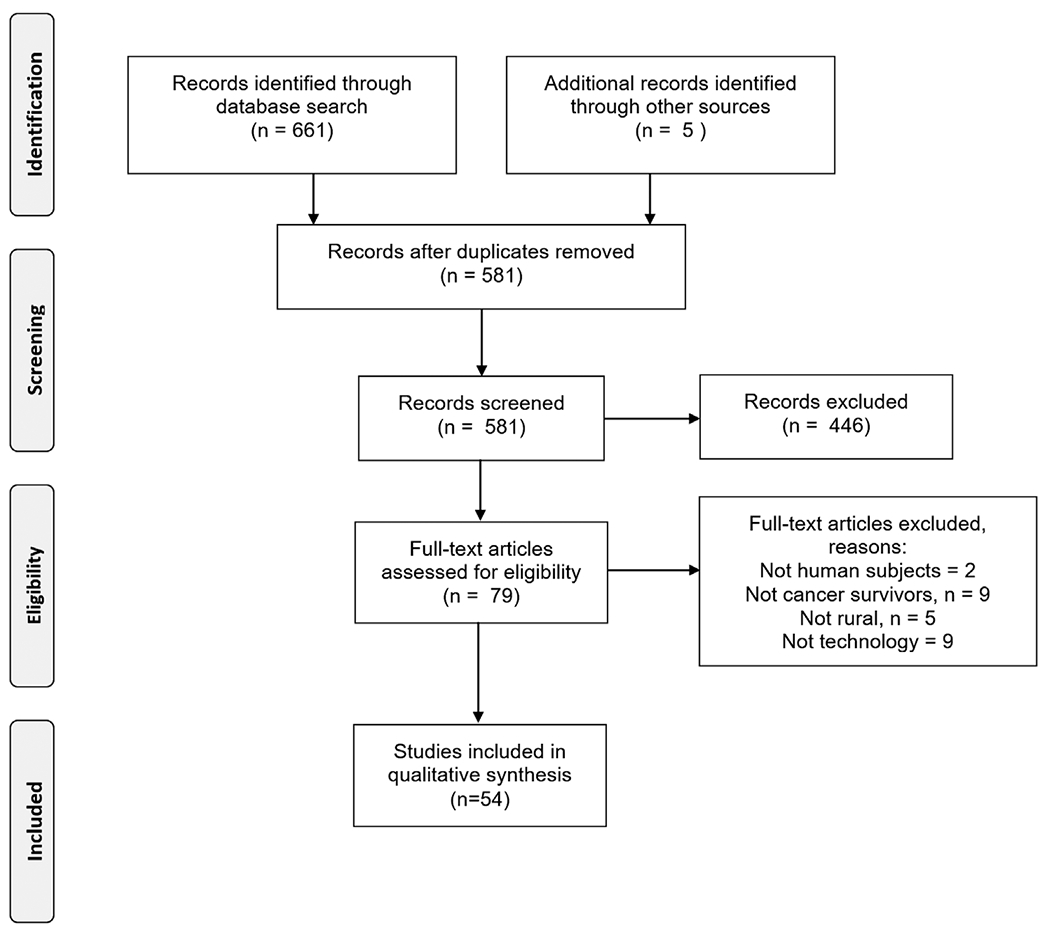
PRISMA flowchart of article review and selection
Study quality
Of the 54 articles that met inclusion criteria, only 22 provided sufficient information for indicators of study quality using a standardized tool (Figure 2). Information was most complete for qualitative studies. Eight out of 10 qualitative studies provided complete MMAT assessment information, while 5 out of 12 randomized controlled trials (RCTs), 3 out of 17 quasi-experimental studies, 2 out of 3 descriptive studies, and 4 out of 12 mixed methods studies provided complete MMAT assessment information. Five qualitative studies and 1 mixed methods study performed the best in quality reporting per the MMAT, meaning that reporting was sufficient to assess all five of the MMAT quality criteria for the respective study type (Figure 3). Quantitative non-randomized studies were the lowest-performing.
FIGURE 2.
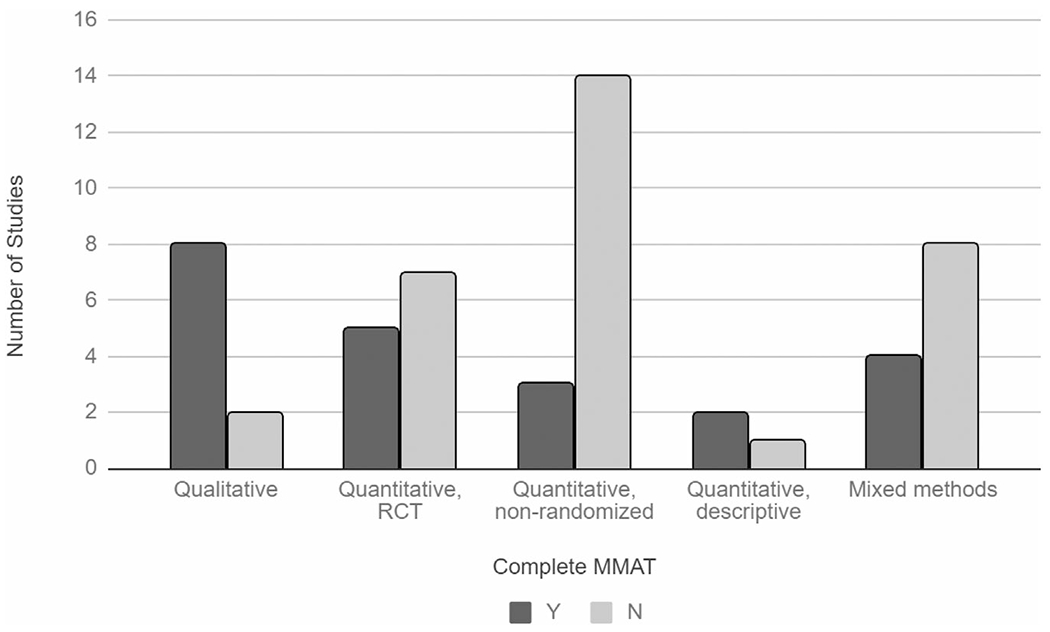
Completeness of manuscript reporting for assessing quality by study type
FIGURE 3.
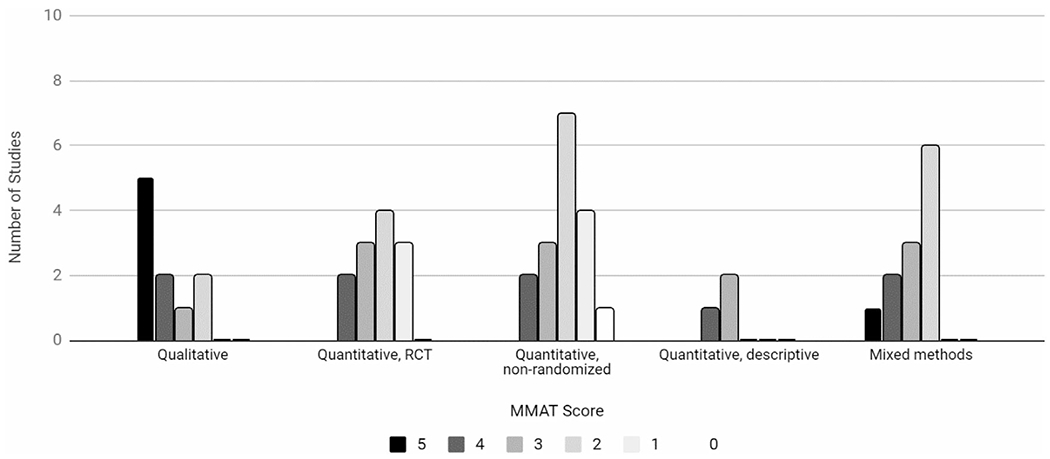
Mixed methods appraisal tool (MMAT) score by study design
Methodological characteristics
Of the 54 articles, 12 were RCTs, 17 were quasi-experimental, 3 were descriptive, 12 were mixed methods, and 10 were qualitative. Most of the studies involved patients only (n = 31), did not provide an explicit definition of “rural” (n = 38), and were not specific to a cancer type (n = 41; Table 1). Of the 12 RCTs, the median sample size was 142 (mean = 181.91 [45-451]). Technology utilized in the 54 articles was categorized as Telemedicine (n = 32), phone calls (n = 11), Internet (n = 9), and mobile phone (n = 2).
TABLE 1.
List of studies included in a systematic review
| Study | Year | First author | Country | Design | Rural definition | Population | n (Rural) | n (Non-rural) | N (Total) | Cancer type | Outcomes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| ||||||||||||
| Telemedicine | ||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||
| A comprehensive program enabling effective delivery of regional genetic counseling | 2018 | Brown J | US | Quasi | Distance from clinic | Patients | – | – | 118 | Multiple | Utilization of genetic counseling (in-person and telemedicine) | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| A pilot trial of a speech pathology telehealth service for head and neck cancer patients | 2012 | Burns CL | Australia | Quasi | Not defined | Multiple | 20 | 0 | 20 | Head and neck | Program evaluation | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| A tele-oncology model replacing face-to-face specialist cancer care: Perspectives of patients in North Queensland | 2014 | Sabesan S | Australia | Qual | Not defined | Patients | 35 | 0 | 35 | Multiple | Exploratory, thematic analysis of interviews | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Acceptability and feasibility of an e-mental health intervention for parents of childhood cancer survivors: “Cascade” | 2016 | Wakefield CE | Australia | RCT | ARIA | Caregivers | 9 | 36 | 45 | Multiple | Feasibility, acceptability | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Assessing the feasibility of a virtual tumor board program: A case study | 2014 | Shea CM | US | Mixed | Not defined | Healthcare providers | 12 | 16 | 28 | Multiple | Acceptability, barriers, value | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Beyond broadband: Digital inclusion as a driver of inequities in access to rural cancer care | 2020 | DeGuzman PB | US | Mixed | Not defined | Patients | – | – | 19 | Head and Neck | Accessibility to the intervention and using borrowed technology equipment, distance to telemedicine site | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Can we use technology to encourage self-monitoring by people treated for melanoma? A qualitative exploration of the perceptions of potential recipients | 2014 | Hall S | Scotland | Qual | Not defined | Patients | 14 | 5 | 19 | Melanoma | Thematic analysis of interviews | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Cost-effectiveness of telecare management for pain and depression in patients with cancer: Results from a randomized trial | 2014 | Choi Yoo SJ | US | RCT | Not defined | Patients | – | – | 405 | Multiple | Intervention costs, depression-free days, QALYs | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Cost savings from a telemedicine model of care in northern Queensland, Australia | 2013 | Thaker DA | Australia | Quasi | Not defined | Patients | 147 | 0 | 147 | Multiple | Cost-savings | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Development of a virtual multidisciplinary lung cancer tumor board in a community setting | 2013 | Stevenson MM | US | Quasi | Not defined | Healthcare providers | 10 | 0 | 10 | Lung | Acceptability, barriers, value | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Do teleoncology models of care enable the safe delivery of chemotherapy in rural towns? | 2015 | Chan BA | Australia | Quasi | Not defined | Patients | 89 | 117 | 206 | Multiple | Dose intensity, toxicity rates | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Enhancing access to cancer education for rural healthcare providers via telehealth | 2011 | Doorenbos AZ | US | Quasi | Not defined | Healthcare providers | 71 | 0 | 71 | Multiple | Program evaluation | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Enhancing chemotherapy capabilities in rural hospitals: Implementation of a telechemotherapy model (QReCS) in North Queensland, Australia | 2018 | Sabesan S | Australia | Quasi | Not defined | Patients | 62 | 0 | 62 | Multiple | Enablers, barriers, provision, Rates of treatment delays, adverse events, and hospital admissions | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Feasibility study: Home telemonitoring for patients with lung cancer in a mountainous rural area | 2014 | Petitte TM | US | Quasi | Not defined | Patients | 10 | 0 | 10 | Lung | Enrollment and retention characteristics, symptoms, program satisfaction | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Identifying the readiness of patients in implementing telemedicine in northern Louisiana for an oncology practice | 2017 | Gurupur V | US | Descr | Not defined | Patients | 78 | 69 | 147 | Multiple | Feasibility | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Improving access to specialist multidisciplinary palliative care consultation for rural cancer patients by videoconferencing: Report of a pilot project | 2013 | Watanabe SW | Canada | Quasi | Not defined | Patients | 44 | 0 | 44 | Multiple | Utilization, symptom management, cost-savings, satisfaction | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Medical oncology clinics through videoconferencing: An acceptable telehealth model for rural patients and health workers | 2012 | Sabesan S | Australia | Mixed | Not defined | Multiple | 68 | 0 | 68 | Multiple | Satisfaction | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Patient perceptions of a mobile cancer support unit in South Wales | 2011 | Iredale R | UK | Mixed | Not defined | Patients | 97 | 0 | 97 | Multiple | Quantitative and qualitative patient satisfaction | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Patients’ experiences of receiving chemotherapy in the outpatient clinic and/or onboard a unique nurse-led mobile chemotherapy unit: A qualitative study | 2013 | Mitchell T | UK | Qual | Not defined | Patients | 20 | 0 | 20 | Multiple | Thematic analysis of interviews | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Randomized controlled trial of a multisite speech pathology telepractice service providing swallowing and communication intervention to patients with head and neck cancer: Evaluation of service outcomes | 2017 | Burns CL | Australia | RCT | Not defined | Multiple | – | – | 82 | Head and neck | Service efficiency, satisfaction | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Randomized trial of telegenetics vs In-person cancer genetic counseling: Cost, patient satisfaction, and attendance | 2015 | Buchanan 2015 | US | RCT | Not defined | Patients | 162 | 0 | 162 | Multiple | Cost, satisfaction, utilization | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Remote chemotherapy supervision model for rural cancer care: Perspectives of health professionals | 2016 | Jhaveri D | Australia | Qualitati | Not defined | Healthcare providers | 19 | 0 | 19 | Multiple | Thematic analysis of interviews | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Role of tele-health/videoconferencing in managing cancer pain in rural American Indian communities | 2012 | Haozous E | US | Quasi | Not defined | Healthcare providers | 52 | 0 | 52 | Multiple | Satisfaction and self-perceived competence | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Safe introduction of laparoscopic colorectal surgery even in remote areas of the world: The value of a comprehensive telementoring training program | 2015 | Forgione A | Russia and Italy | Quasi | Not defined | Healthcare providers | 1 | 0 | 1 | Colorectal | Program evaluation | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Satisfaction with telehealth for cancer support groups in rural American Indian and Alaska Native communities | 2010 | Doorenbos AZ | US | Quasi | Not defined | Patients | 32 | 0 | 32 | Multiple | Satisfaction, distance, time | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Telehealth in radiation oncology at the Townsville Cancer Centre: Service evaluation and patient satisfaction | 2018 | Hamilton E | Australia | Quasi | Distance from clinic | Patients | 311 | 0 | 311 | Multiple | Service evaluation, satisfaction | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Telemedicine for rural cancer care in North Queensland: Bringing cancer care home | 2012 | Sabesan S | Australia | Quasi | Not defined | Patients | 158 | 0 | 158 | Multiple | Service provision | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Teleoncology for indigenous patients: The responses of patients and health workers | 2012 | Mooi JK | Australia | Qual | Not defined | Multiple | 15 | 0 | 15 | Multiple | Satisfaction | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Telepharmacy in a rural Alberta community cancer network | 2012 | Gordon HL | Canada | Mixed | Not defined | Healthcare providers | 47 | 0 | 47 | Multiple | Utilization, satisfaction | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Timely access to specialist medical oncology services closer to home for rural patients: Experience from the Townsville Teleoncology Model | 2014 | Sabesan S | Australia | Quasi | Not defined | Patients | 70 | 0 | 70 | Multiple | Time to specialist review, hospital transfers | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Using telehealth to train providers of a cancer support intervention | 2015 | Brandon AR | US | Mixed | Not defined | Healthcare providers | 3 | 5 | 8 | Multiple | Knowledge, satisfaction, self-confidence | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Using videotelephony to support pediatric oncology-related palliative care in the home: From abandoned RCT to acceptability study | 2009 | Bensink ME | Australia | Quasi | ARIA | Multiple | 10 | 7 | 17 | Multiple | Acceptability, QOL, depression, social support, satisfaction, cost-effectiveness | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Internet | ||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||
| The quality of cancer patient experience: Perspectives of patients, family members, providers, and experts | 2010 | Wagner EH | US | Qual | not defined | Multiple | – | – | 54 | Multiple | Barriers, facilitators | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| The experiences of participants in an innovative online resource designed to increase regular walking among rural cancer survivors: A qualitative pilot feasibility study | 2014 | Frensham LJ | Australia | Qual | not defined | Patients | 8 | 0 | 8 | Multiple | Feasibility, acceptability | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| The consumer-driven development and acceptability testing of a website designed to connect rural cancer patients and their families, carers, and health professionals with appropriate information and psychosocial support | 2017 | Fennel KM | Australia | Mixed | ARIA | Multiple | 111 | 0 | 111 | Multiple | Acceptability, perceived impact, utilization | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Reaching further with online education? The development of an effective online program in palliative oncology | 2010 | Koczwara B | Australia | Mixed | Not defined | Healthcare providers | 90 | 0 | 90 | Multiple | Utilization and satisfaction | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Evaluation of cancer chat Canada: A program of online support for Canadians affected by cancer | 2013 | Stephen J | Canada | Mixed | Population size | Multiple | 77 | 274 | 351 | Multiple | Program evaluation | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Evaluating adaptation of a cancer clinical trial decision aid for rural cancer patients: A mixed-methods approach | 2018 | Pathak S | US | Mixed | RUCA | Patients | 46 | 0 | 46 | Multiple | Decisional conflict, decision self-efficacy, knowledge, communication self-efficacy, attitudes | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Engaging stakeholders in the development of an eHealth intervention for cancer symptom management for rural residents | 2018 | Gilbertson-White S | US | Mixed | Population size | Multiple | 26 | 0 | 26 | Multiple | Useability | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Engagement with INSPIRE, an online program for hematopoietic cell transplantation survivors | 2018 | Syrjala KL | US | RCT | ZIP codes using cms.gov categories | Patients | 95 | 356 | 451 | Multiple | Engagement, utilization | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Assessing cancer survivors’ needs using web-based technology: A pilot study | 2012 | Lavoie Smith EM | US | Descr | Not defined | Patients | 318 | 229 | 547 | Multiple | Symptoms, needs assessment | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Phone calls | ||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||
| A qualitative evaluation of a group phone-based weight loss intervention for rural breast cancer survivors: Themes and mechanisms of success | 2016 | Fazzino TL | US | Qual | Not defined | Patients | 186 | 0 | 186 | Breast | Thematic analysis of interviews | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Change in physical activity during a weight management intervention for breast cancer survivors: Association with weight outcomes | 2017 | Fazzino TL | US | Quasi | Population density | Patients | 142 | 0 | 142 | Breast | Physical activity | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Outcomes of a weight loss intervention among rural breast cancer survivors | 2012 | Befort CA | US | Quasi | RUCA | Patients | 35 | 0 | 35 | Breast | Weight, diet, physical activity, serum biomarkers, QOL | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Weight loss maintenance strategies among rural breast cancer survivors: The rural women connecting for better health trial | 2016 | Befort CA | US | RCT | RUCA | Patients | 172 | 0 | 172 | Breast | Weight loss maintenance, cost-effectiveness | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Cost-benefit analysis of decision support methods for patients with breast cancer in a rural community | 2013 | Wilson L | US | RCT | Not defined | Patients | 68 | 0 | 68 | Breast | Program delivery costs and willingness-to-pay | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Decision support by telephone: Randomized controlled trial in a rural community setting | 2012 | Belkora J | US | RCT | population density | Patients | 67 | 0 | 67 | Breast | Decisional self-efficacy, anxiety, satisfaction, preparation for decision-making | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Benefits of early versus delayed palliative care to informal family caregivers of patients with advanced cancer: Outcomes from the ENABLE III randomized controlled trial | 2015 | Dionne-Odom JN | US | RCT | RUCA | Multiple | – | – | 122 | Multiple | QOL, depression, and burden | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Adapting an early palliative care intervention to family caregivers of persons with advanced cancer in the rural deep south: A qualitative formative evaluation | 2018 | Dionne-Odom JN | US | Qual | RUCA | Multiple | 64 | 0 | 64 | Multiple | Thematic analysis of interviews | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Family caregiver depressive symptom and grief outcomes from the ENABLE III randomized controlled trial | 2016 | Dionne-Odom JN | US | RCT | Not defined | Multiple | – | – | 123 | Multiple | Depressive symptoms and complicated grief | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| The project ENABLE II randomized controlled trial to improve palliative care for rural patients with advanced cancer: Baseline findings, methodological challenges, and solutions | 2009 | Bakitas MA | US | RCT | RUCA | Patients | 147 | 132 | 279 | Multiple | Symptoms, QOL, mood, and functional status | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Early vs delayed initiation of concurrent palliative oncology care: Patient outcomes in the ENABLE III randomized controlled trial | 2015 | Bakitas MA | US | RCT | RUCA | Multiple | – | – | 207 | Multiple | QOL, symptom impact, mood, 1-year survival, and resource use | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| Mobile | ||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||
| Developing NaviCanPlan: A mobile web resource locator for cancer providers and survivors | 2015 | Dahlke DV | US | Mixed | Not defined | Multiple | – | – | 150 | Multiple | Needs assessment | |
|
| ||||||||||||
| A mobile breast cancer survivorship care app: Pilot study | 2017 | Baseman J | US | Qual | Not defined | Multiple | 4 | 7 | 11 | Breast | Thematic analysis of interviews | |
Types of technology
Telemedicine
Telemedicine articles focused on care delivery (n = 23), training (n = 4), multidisciplinary cancer teleconferences (ie, tumor boards, n = 2), telemonitoring (n = 2), and cancer support (n = 1). The most thoroughly described rural tele-oncology model is the Townsville Cancer Centre (TCC) tele-oncology program established in 2007 for rural cancer care delivery, totaling 974 participants.41 Medical oncologists at TCC provide their services via videoconference with rural-based doctors, chemotherapy-competent nurses, allied health workers, and patients in consultation. Initially, patients were required to attend at least 1 face-to-face appointment at TCC, which became optional in 2009. The program was expanded to radiation oncology in 2011.42 The studies conducted were able to establish that tele-oncology was feasible, acceptable to patients and health care workers, and cost-effective.43–47 High patient satisfaction was reported with the quality of the video consultation and in establishing rapport with the specialist over video conference. Patients overall preferred video conferences to face-to-face consultations and were very satisfied with the care received via the tele-oncology program.42,44,48 Health care professionals similarly reported high satisfaction in the program, including patient convenience, interprofessional communication, expanded scope of practice, continuity of care, and maintenance of patient safety.47 Thaker determined that the TCC model resulted in a net savings of $320,118 over 56 months and that costs would have to increase by 72% to negate the savings.45
The singular US-based publication eligible for inclusion in this systematic review took place among rural Virginia head and neck cancer survivors.49 This feasibility study examined broadband access, driving time to a satellite telemedicine site, and the ability to utilize a borrowed cellular-enabled tablet to evaluate an intervention connecting rural cancer survivors with their care team at an academic medical center. The intervention included an in-person end-of-treatment visit to discuss survivorship care planning. Eligible patients who consented were then scheduled for a nurse telemedicine visit via 1 of 3 routes based on access: 1) survivors with broadband access and a device with videoconferencing capabilities were provided a link to a videoconferencing application installed using HIPAA-compliant technology; 2) survivors lacking either broadband access or a device but who were able to travel attended the visit at a satellite clinic; or 3) survivors without technology access or ability to travel were mailed a tablet with cellular service to attend the visit from home. Of the 19 study participants, 58% were male and 84% were non-Hispanic White, with an average age of 59 years old. Eleven participants received the intervention at home on their own device, 3 traveled to a satellite site, and 5 used borrowed tablets. The average driving time to a satellite clinic was 30 minutes. Utilizing borrowed equipment proved challenging. The cellular signal was sufficient for 3 of the 5 participants, with one only able to utilize the audio portion similar to a phone call and the other being unable to connect at all without a research team member setting up a cellular hot spot. Despite upfront instruction on using the tablets, 3 of the 5 participants had never used a tablet before and all but one participant required supplemental instruction and an additional research team member phone call. Participants also relied on family member support to navigate the technology. The study also found that only 58% of households within the areas the study participants lived in had the broadband access and/or speed necessary to support telemedicine videoconferencing, creating a significant disparity in access as health care shifts to virtual-based care delivery in the post-Covid-19 era.
Two additional telemedicine studies examined the use of mobile chemotherapy units in rural areas of the United Kingdom.50,51 Specialty care delivery examined via the use of telemedicine in rural areas included speech pathology services for head and neck cancer patients, pharmacy services, mental health care, pain management, genetic counseling, and palliative care.52–61 These studies were in agreement that telehealth is less expensive, equal quality, more efficient, and had high satisfaction for delivering rural oncology care.
Telemedicine as a training platform was examined in the rural cancer setting in 4 studies and was a feasible and satisfactory means of delivering real-time, interactive training to providers who might not otherwise have access to such programs. Training included continuing medical education, training on a cancer support intervention, and surgical oncology telementoring.57,62–64 Connecting community oncologists with multidisciplinary cancer conferences (tumor boards) via teleconference was considered in 2 articles.65,66 These articles demonstrated the initial feasibility of providing oncologists in rural areas and at smaller institutions access to tumor boards to improve the quality and continuity of care.
The feasibility of telemonitoring for rural cancer patients was considered in 2 articles, with the first determining that the potential exists for melanoma follow-up telemonitoring if the technology is tailored by age, skill level, area of residence, and time since diagnosis.67 Petitte and colleagues remotely collected physiologic data in lung cancer patients who were post-hospital discharge.68 Despite the low sample size, telemonitored data transmission was feasible in rural areas with high satisfaction. Last, 1 study considered the acceptability of telehealth support group services for rural American Indian and Alaskan Native communities and found that participants valued the opportunity to connect with other similar survivors living in remote areas.69
Phone calls
Telephone studies (n = 11) were composed of a group or individual phone calls. Studies largely focused on cancer survivorship issues and included weight loss (n = 4), palliative care (n = 2), caregiver support (n = 3), and decision support (n = 2). Weekly group phone sessions have been utilized in addition to a specified reduced-calorie diet and physical activity plan that resulted in significantly improved clinical outcomes and quality of life among rural breast cancer survivors.70 The second phase of the study involved a 12-month intervention in which participants were randomized to either continued biweekly phone-based group counseling or mailed newsletters.71 The study concluded that the technology intervention improved the magnitude of weight loss maintained over 18 months, increased the proportion of participants who maintained clinically significant weight loss, and was successful in improving physical activity outcomes over 18 months, as measured by accelerometer.72 A follow-up qualitative study revealed technology-related themes of the group phone counseling sessions provided benefits of accountability and connectedness, as well as the feedback to adjust scheduling and the length of the sessions (1 hour).73
Individual phone call interventions have also been employed, such as the ENABLE II RCT that was designed to facilitate early integration of palliative care.74 Rural patients with advanced cancer were randomly assigned to a phone-based, nurse-led educational and care coordination palliative care intervention or to receive usual care. Patients receiving the technology intervention were found to have a significantly higher self-reported quality of life and mood, while comparisons of symptom intensity, days in the hospital, and ICU and emergency department visits were not significantly different.74 When the intervention was applied using a waitlist control, patients receiving the technology intervention upon enrollment versus 3 months later had higher 1-year survival rates.75 The ENABLE intervention was extended to caregivers in the ENABLE III RCT, which was found to lower depression scores among caregivers.76 Caregivers perceived intervention delivery via phone calls to be acceptable, while there was concern that Internet-based technologies may have limited use due to lower skill and access.77
Remote delivery of consultation planning provides a second example of individual phone call interventions, which stems from the constraints of providing treatment decision support within a fast-paced clinic environment. Two studies included in this review examined treatment decision support via coaching patients to develop a list of personalized questions to bring to their next clinic appointment. These studies found that remote consultation planning was equally effective, with comparable quality, cost, and value as in-person consultation planning, while increasing accessibility of decision support services in rural communities.78,79
Internet
Studies utilizing websites (n = 9) included in this review examined educational, symptom management, and lifestyle support programs delivered in an online format to address access issues in the rural setting. For example, Fennell et al reported on a website developed with community involvement to address psychosocial information needs that are relevant, accessible, and acceptable to increase rates of support service use among rural cancer survivors.80 Website design not only incorporated information targeted to rural populations but also sought to address attitudinal barriers to service use (eg, medical mistrust, belief that help is unnecessary or shows weakness, finding help is too hard) and tailored information by stage of change and level of distress. Survey results documented that participants were more willing to access professional and peer support after using the website, were more motivated and confident in accessing resources, and felt less isolated after utilizing the website.
Rural engagement is notable across this category of studies. Studies highlighted that while not all patients used technology, they often had family members and caregivers who did and that less access to health care did not preclude engagement in digital health-based studies. For example, support groups have been shown to improve psychosocial symptoms associated with cancer and improve quality of life, yet access is an issue for rural residents.81,82 CancerChatCanada provided 55 professional-led live-chat support groups for 351 cancer patients and caregivers that were held weekly over the course of 10-12 weeks. Participants reported high satisfaction and psychosocial benefit, with any initial discomfort in communicating online in a live chat group being outweighed by access to support at home. Typing versus talking was viewed as a benefit by giving added time for reflection, organizing thoughts, and not impending emotional expression (eg, being able to cry while typing but not while talking).
Mobile phone
Only 2 studies focused on using a mobile app among rural cancer survivors. The first study used a mixed-methods approach and developed a health services locator app for both providers and cancer survivors. However, additional studies are needed to evaluate the feasibility, acceptability, and effectiveness of implementing this app on a broader scale.83 Second, Baseman et al developed a breast cancer survivorship care app called SmartSurvivor.84 Components of the app included a medical profile, a journal section with a tracking tool for self-monitoring, calendar links for reminders and appointments, tailored survivor tips and tools, and the ability to audio record for documenting notes and appointment questions. Qualitative results highlighted key features and utility of the app, while also discussing the need for it to be tailored for rural users. Overall, the app was found to be both feasible and acceptable as a breast cancer survivorship tool and could serve as a foundation for developing a tool to support rural breast cancer survivors.
DISCUSSION
While there have been other reviews focused on digital technology use in cancer care delivery, this is the first within the rural cancer setting.27–30,85 The overall aim of this study was to systematically and critically examine existing literature to understand how digital technologies have been used to support rural oncology care. Rurality is associated with higher cancer incidence and mortality rates, and rural residents face significant challenges influencing access to health care. Health technologies may serve to address some of these disparities, yet the 54 studies included in this review make up a comparatively small number, representing a significant gap in the literature. The limited number of studies is surprising since digital health strategies could improve access to care issues faced by rural cancer survivors. However, mobile and broadband availability remains an issue in rural areas.32–34 Despite the shift in focus to telehealth approaches due to the Covid-19 pandemic, only 1 study included in the present review was from the pandemic era, a US-based telemedicine study published in 2020. Notably, this is the only US-based telemedicine study for rural cancer care in contemporary literature, highlighting the urgent need for additional work in this area.
Across all studies was the consensus that rural cancer survivors value digital technology approaches to their care, with results varying by type of technology. Telemedicine was the most common type of technology considered. While the designs and approaches differed across these studies, it was generally concluded that telemedicine is a feasible and acceptable approach to improving care delivery. Telemedicine studies were able to demonstrate both improved patient outcomes and improved access to care. Specifically, an RCT examining telecare management on pain and depression outcomes among rural and non-rural cancer patients found a significant increase of 60 depression-free days, as well as an increase in quality-adjusted life-years compared to the usual care group.56 A palliative care telemedicine study found significantly improved anxiety and appetite at the first follow-up visit among rural cancer patients.60 Implementing a comprehensive program of telemedicine and patient navigation, genetic counseling for ovarian cancer patients increased from 37% to 96% and for triple-negative breast cancer patients from 69% to 91%. Genetic testing doubled for ovarian cancer patients and increased from 59% to 86% in triple-negative breast cancer patients.59 These studies speak to the utility of telemedicine approaches to address cancer survivorship in rural settings.
While telemedicine represented the largest category of studies in the present review, phone-based studies had the most RCTs for both quantity and percentage (7/11, 64%). Phone-based interventions supported weight loss in cancer survivors and improved patient outcomes in palliative care. Phone-based strategies increased survivors’ feelings of connectedness and facilitated access to care, and, as noted by the ENABLE team, were preferred over Internet-based technologies that may have limited use due to lower skill and access.77 Future studies should focus on implementation strategies to optimize these programs for long-term sustainability.
Internet-based digital health approaches involving patients may emerge as being useful but may also pose a potential challenge for implementation in rural populations. Beyond the pure infrastructure limitation of access to the Internet, it is important to consider device requirements and behavioral skills needed to utilize Internet-based technology. Applications or “apps” can be desktop, mobile, and/or Internet-based. Desktop apps usually have all the features of a program, whereas the mobile equivalent is a simpler and easier-to-use version. Internet or web apps can have extensive features too, but they must leverage the capabilities of the Internet connection and the web browser program. Participants have reported concern with using Internet-based interventions for palliative care due to lower comfort with technology and access to the Internet.77 Patients may be more likely to attend in-person counseling, attributed to a significant association found between decreased computer comfort and attendance rate in telegenetics.58 Other telemedicine studies did not support this finding, but the discord may be attributed to the skills and technology needed to virtually attend a genetic counseling appointment from home versus teleconference with an oncology specialist from a cancer clinic or primary care facility closer to home. Only 2 studies involved a mobile app, yet the more streamlined format may be preferred over web-based versions in rural populations. To this point, a prior secondary analysis of the National Cancer Institute’s Health Information National Trends Survey found that rurality was associated with the use of mHealth applications for making treatment decisions, indicating mobile phone apps as a means to increase access to health information.86 Cell phone ownership has increased significantly among rural populations, with 94% of US adults reporting cell phone ownership in 2021. However, 14% report owning a cell phone that is not a smartphone,87 precluding the use of apps as a point of the study intervention. There is a need to further expand this area of research.
While medical mistrust was not a theme that emerged in the articles examined in the present review, it is relevant to the discussion of rural health care delivery. Trust in the provider and health care system has been documented as impacting rural health care seeking behaviors,88–92 and there is emerging evidence that trust plays a role in digital health intervention utilization as well.93–95 For instance, rural residents have reported concern that not being able to visually see the provider when communicating health information could result in individuals other than qualified medical professionals reviewing their information.93 Therefore, strategies to enhance trust, such as the preference of voice-over text messages and using familiar voices when delivering voice messages,94 should be considered in the design and implementation of studies and health care interventions among rural populations.
The majority of studies (38/54) did not provide a definition of “rural.” There are a number of ways that geography can be classified for the purposes of rural research and policy (Table 2). In the US, the main classifications are provided by the US Census Bureau,96 the US Office of Management and Budget,97 and the US Department of Agriculture.98,99 Australia, from which a number of the telemedicine studies presented in this review were published, uses the Accessibility/Remoteness Index of Australia.100 Aside from the broad implication of complicating comparisons across studies, the definition chosen can result in different areas being classified or not classified as rural, such that estimates of the rural US population range from 15.0%-19.3% and estimates of rural land range from 72%-95%.
TABLE 2.
Comparison of main geographic classification systems
| US Census Bureau96 | Office of Management and Budget97 | USDA RUCA99 | USDA RUCC98 | ARIA100 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| |||||
| Categories | Urban Area (UA), Urban Cluster, Rural | Metro and non-metro (micro and non-core) | 1-10 | 1-9 | 0 - 15 |
|
| |||||
| Defining attributes | Population size and density in census areas | Population size in counties | Population density, proximity to a UA, daily commuting patterns | Population size, proximity to a UA, adjacency to a metro area | Distance via road access to urban (“service”) centers by population size |
|
| |||||
| Category definitions |
Urban Area: Census areas with at least 50,000 people, a population density of at least 1,000 individuals/sq mile and may include surrounding census blocks with an overall density of at least 500 individuals/sq mile; Urban Cluster: At least 2,500 but <50,000 people; Rural Area: <2,500 people and population density <500 people/sq mile |
Metro: At least one central county with an UA (population at least 50,000); Non-Metro: Counties that are outside the boundaries of a Metro area, with Micro being urban clusters of 10,000-<50,000 people and Non-core being all remaining counties |
1: Metro area core; 2: Metro high commuting; 3: Metro low commuting; 4: Micro area core; 5: Micro high commuting; 6: Micro low commuting; 7: Small town core; 8: Small town high commuting; 9: Small town low commuting; 10: Rural |
1: Counties in metro area with 1M+ population; 2: Counties in metro area 250,000-<1M; 3: Counties in metro area <250,000; 4: Urban population 20,000+ adjacent to metro area; 5: Urban population 20,000+ not adjacent to metro area; 6: Urban population 2,500-<20,000 adjacent to metro area; 7: Urban population 2,500-<20,000 not adjacent to metro area; 8: Completely rural or <2,500 urban population adjacent to metro area; 9: Completely rural or <2,500 urban population not adjacent to metro area |
0-0.2: Service to Category A (250,000+ population service area); >0.2-2.4: Service to Category B (48,000 -<250,000 pop service area); >2.4-5.92: Service to Category C (18,000- <48,000 pop service area); >5.92-10.53: Service to Category D (5,000-<18,000 pop service area); >10.53: Service to Category E (1,000-<5,000 population service area) |
Limitations
As evident by the present review and assessed by the MMAT, there are limitations to the state of the science. Despite the availability of standardized reporting guidelines by study design like CONSORT and STROBE, there is room for improvement in practice in terms of both study design and reporting results. Overall, there were few randomized trials and samples sizes were low. Most studies restricted participants to those with Internet access without reporting on how many potential participants were excluded due to access. Few studies measured access to care variables. No studies examined the use of interactive voice response, electronic health records, patient portals, or social media in the context of rural cancer survivors. Despite the benefits of text messaging as an intervention strategy, including reach, engagement, low cost, and documented effectiveness in directly supporting behavior change, no studies using text messaging were identified for inclusion in this study.101 Additionally, this review is not without some limitations. We could not measure quality in every study and were restricted to evaluating the information reported. Broad variation in study design prevented us from performing meta-analyses. Varying definitions of rurality led to difficulty in generating comparisons across studies. As is the case with other systematic reviews, there may be publication bias present, with studies finding null results being less likely to be published and therefore included in this review. Despite the limitations, our study synthesizes lessons learned thus far on designing and implementing digital health studies among rural cancer survivors and highlights the gap in knowledge on technology use in this population.
CONCLUSIONS
To conclude, unique challenges faced by rural cancer survivors require targeted approaches. More research is needed involving studies of high scientific and methodological rigor and employing cutting-edge technology to support this underserved population. Critical to reducing the rural digital divide and the deployment of digital health strategies are increasingly mobile, Internet, or broadband service in rural areas. While steps are being taken to address this geographic disparity, the fact remains that nearly 30% of Americans live in areas that lack the coverage needed for home Internet. Ease of use and technological requirements are important considerations in rural populations. Given the study limitations and knowledge gaps identified in this review, we recommend the following: Investigators should take advantage of available guidelines like CONSORT at both the study design and reporting phase to improve the quality of literature in this research area. Future rural cancer control studies would benefit from the use of mixed methodology and a theoretical framework to guide study development. Finally, studies should continue to build upon and expand telemedicine and phone-based interventions as digital health strategies at a more widespread scale, yet also consider innovative or under-utilized strategies.
Supplementary Material
Funding information
National Cancer Institute F99CA245799 (PI: Morris)
Footnotes
SUPPORTING INFORMATION
Additional supporting information may be found in the online version of the article at the publisher’s website.
DISCLOSURES
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
REFERENCES
- 1.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. An Update on Cancer Deaths in the United States. Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Division of Cancer Prevention and Control; 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/dcpc/research/update-on-cancer-deaths/index.htm Accessed February 23, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Blake KD, Moss JL, Gaysynsky A, Srinivasan S, Croyle RT. Making the case for investment in rural cancer control:An analysis of rural cancer incidence, mortality, and funding trends. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2017;26(7):992–997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Henley SJ, Anderson RN, Thomas CC, Massetti GM, Peaker B, Richardson LC. Invasive cancer incidence, 2004–2013, and deaths, 2006–2015, in nonmetropolitan and metropolitan counties-United States. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2017;66(14):1–13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Weaver KE, Palmer N, Lu L, Case LD, Geiger AM. Rural-urban differences in health behaviors and implications for health status among US cancer survivors. Cancer Causes Control. 2013;24(8):1481–1490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bolin JN, Bellamy GR, Ferdinand AO, et al. Rural healthy people 2020: New decade, same challenges. J Rural Health. 2015;31(3):326–333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Jones CA, Kandel W, Parker T. Population dynamics are changing the profile of rural areas. J Rural Mental Health. 2007;31(3):46–53. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Levit LA, Byatt L, Lyss AP, et al. Closing the rural cancer care gap: Three institutional approaches. JCO Oncol Pract. 2020;16(7):422–430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Singh R, Goebel LJ. Rural disparities in cancer care: A review of its implications and possible interventions. W V Med J. 2016;112(3):76–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kirkwood MK, Bruinooge SS, Goldstein MA, Bajorin DF, Kosty MP. Enhancing the American Society of Clinical Oncology workforce information system with geographic distribution of oncologists and comparison of data sources for the number of practicing oncologists. J Oncol Pract. 2014;10(1):32–38. 10.1200/jop.2013.001311 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Harrison JD, Young JM, Price MA, Butow PN, Solomon MJ. What are the unmet supportive care needs of people with cancer? A systematic review. Support Care Cancer. 2009;17(8):1117–1128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.USDA ERS. Rural Transportation at a Glance. Washington, DC: US Department of Agriculture, Economic Research Service; 2005. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kaufman BG, Thomas SR, Randolph RK, et al. The rising rate of rural hospital closures. J Rural Health. 2016;32(1):35–43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Onega T, Duell EJ, Shi X, Wang D, Demidenko E, Goodman D. Geographic access to cancer care in the U.S. Cancer. 2008;112(4):909–918. 10.1002/cncr.23229 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wagner EH, Aiello Bowles EJ, Greene SM, et al. The quality of cancer patient experience: perspectives of patients, family members, providers and experts. Qual Saf Health Care. 2010;19(6):484–489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Smith EML, Skalla K, Li Z, et al. Assessing cancer survivors’ needs using web-based technology: A pilot study. Comput Inform Nurs. 2012;30(2):71–81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sharma A, Harrington RA, McClellan MB, et al. Using digital health technology to better generate evidence and deliver evidence-based care. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;71(23):2680–2690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Lee J-A, Choi M, Lee SA, Jiang N. Effective behavioral intervention strategies using mobile health applications for chronic disease management: A systematic review. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2018;18(1):12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Rathbone AL, Prescott J. The use of mobile apps and SMS messaging as physical and mental health interventions: Systematic review. FOCUS. 2018;16(4):456–465. 10.1176/appi.focus.16406 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Meskó B, Drobni Z, Bényei É, Gergely B, Győrffy Z. Digital health is a cultural transformation of traditional healthcare. Mhealth. 2017;3:38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Parati G, Pellegrini D, Torlasco C. How digital health can be applied for preventing and managing hypertension. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2019;21(5):40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Cahn A, Akirov A, Raz I. Digital health technology and diabetes management. J Diabetes. 2018;10(1):10–17. 10.1111/1753-0407.12606 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kataria S, Ravindran V. Digital health: A new dimension in rheumatology patient care. Rheumatol Int. 2018;38(11):1949–1957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ding H, Fatehi F, Maiorana A, Bashi N, Hu W, Edwards I. Digital health for COPD care: The current state of play. J Thorac Dis. 2019;11(Suppl 17):S2210–S2220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Yin AL, Hachuel D, Pollak JP, Scherl EJ, Estrin D. Digital health apps in the clinical care of inflammatory bowel disease: Scoping review. J Med Internet Res. 2019;21(8):e14630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Batra S, Baker RA, Wang T, Forma F, DiBiasi F, Peters-Strickland T. Digital health technology for use in patients with serious mental illness: A systematic review of the literature. Med Devices. 2017;10:237–251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Wildevuur SE, Simonse LWL. Information and communication technology-enabled person-centered care for the “big five” chronic conditions: Scoping review. J Med Internet Res. 2015;17(3):e77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Geng Y, Myneni S. Patient engagement in cancer survivorship care through mHealth: A consumer-centered review of existing mobile applications. AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2015;2015:580–588. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Davis SW, Oakley-Girvan I. mHealth education applications along the cancer continuum. J Cancer Educ. 2015;30(2):388–394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Fallahzadeh R, Rokni SA, Ghasemzadeh H, Soto-Perez-de-Celis E, Shahrokni A. Digital health for geriatric oncology. JCO Clin Cancer Inform. 2018;2:1–12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Devine KA, Viola AS, Coups EJ, Wu YP. Digital health interventions for adolescent and young adult cancer survivors. JCO Clin Cancer Inform. 2018;(2):1–15. 10.1200/cci.17.00138 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Greenberg-Worisek AJ, Kurani S, Rutten LJF, Blake KD, Moser RP, Hesse BW. Tracking Healthy People 2020 Internet, broad-band, and mobile device access goals: An update using data from the Health Information National Trends Survey. J Med Internet Res. 2019;21(6):e13300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Federal Communications Commission. 2018 Broadband Deployment Report. 2018. https://www.fcc.gov/reports-research/reports/broadband-progress-reports/2018-broadband-deployment-report Accessed August 8, 2020.
- 33.Wicker RF. Broadband Deployment Accuracy and Technological Availability Act or the Broadband DATA Act. 2020. In Proceedings of H.R.4229–116th Congress (2019–2020). https://www.congress.gov/bill/116th-congress/house-bill/4229/text. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Perrin A Digital Gap Between Rural and Nonrural America Persists. Pew Research Center. 2017. https://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2019/05/31/digital-gap-between-rural-and-nonrural-america-persists/ [Google Scholar]
- 35.Rural Health Information Hub. Selected Rural Statistics for the United States. 2021. https://www.ruralhealthinfo.org/states/united-states Accessed March 4, 2021.
- 36.Greenberg AJ, Haney D, Blake KD, Moser RP, Hesse BW. Differences in access to and use of electronic personal health information between rural and urban residents in the United States. J Rural Health. 2018;34 Suppl 1:s30–s38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Hong QN, Gonzalez-Reyes A, Pluye P. Improving the usefulness of a tool for appraising the quality of qualitative, quantitative and mixed methods studies, the mixed methods appraisal tool (MMAT). J Eval Clin Pract. 2018;24(3):459–467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Pace R, Pluye P, Bartlett G, et al. Testing the reliability and efficiency of the pilot mixed methods appraisal tool (MMAT) for systematic mixed studies review. Int J Nurs Stud. 2012;49(1):47–53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Pluye P, Gagnon M-P, Griffiths F, Johnson-Lafleur J. A scoring system for appraising mixed methods research, and concomitantly appraising qualitative, quantitative and mixed methods primary studies in mixed studies reviews. Int J Nurs Stud. 2009;46(4):529–546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Souto RQ, Khanassov V, Hong QN, Bush PL, Vedel I, Pluye P. Systematic mixed studies reviews: Updating results on the reliability and efficiency of the mixed methods appraisal tool. Int J Nurs Stud. 2015;52(1):500–501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Sabesan S, Brennan S. TeleOncology for cancer care in rural Australia. In: Graschew G, Rakowsky S, eds. Telemedicine Techniques and Applications. London: IntechOpen; 2011:289–306. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Hamilton E, Van Veldhuizen E, Brown A, Brennan S, Sabesan S. Telehealth in radiation oncology at the Townsville Cancer Centre: Service evaluation and patient satisfaction. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2019;15:20–25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Sabesan S, Larkins S, Evans R, et al. Telemedicine for rural cancer care in North Queensland: Bringing cancer care home. Aust J Rural Health. 2012;20(5):259–264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Mooi JK, Whop LJ, Valery PC, Sabesan SS. Teleoncology for indigenous patients: The responses of patients and health workers. Aust J Rural Health. 2012;20(5):265–269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Thaker DA, Monypenny R, Olver I, Sabesan S. Cost savings from a telemedicine model of care in northern Queensland, Australia. Med J Aust. 2013;199(6):414–417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Sabesan S, Senko C, Schmidt A, et al. Enhancing chemotherapy capabilities in rural hospitals: Implementation of a telechemotherapy model (QReCS) in North Queensland, Australia. J Oncol Pract. 2018;14(7):e429–e437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Jhaveri D, Larkins S, Kelly J, Sabesan S. Remote chemotherapy supervision model for rural cancer care: Perspectives of health professionals. Eur J Cancer Care. 2016;25(1):93–98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Sabesan S, Kelly J, Evans R, Larkins S. A tele-oncology model replacing face-to-face specialist cancer care: Perspectives of patients in North Queensland. J Telemed Telecare. 2014;20(4):207–211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.DeGuzman PB, Bernacchi V, Cupp CA, et al. Beyond broadband: Digital inclusion as a driver of inequities in access to rural cancer care. J Cancer Surviv. 2020. Oct;14(5):643–652. 10.1007/s11764-020-00874-y. Epub 2020 May 11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Iredale R, Hilgart J, Hayward J. Patient perceptions of a mobile cancer support unit in South Wales. Eur J Cancer Care. 2011;20(4):555–560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Mitchell T Patients’ experiences of receiving chemotherapy in outpatient clinic and/or onboard a unique nurse-led mobile chemotherapy unit: A qualitative study. Eur J Cancer Care. 2013;22(4):430–439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Burns CL, Ward EC, Hill AJ, et al. A pilot trial of a speech pathology telehealth service for head and neck cancer patients. J Telemed Telecare. 2012;18(8):443–446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Burns CL, Ward EC, Hill AJ, Kularatna S, Byrnes J, Kenny LM. Randomized controlled trial of a multisite speech pathology telepractice service providing swallowing and communication intervention to patients with head and neck cancer: Evaluation of service outcomes. Head Neck. 2017;39(5):932–939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Gordon HL, Hoeber M, Schneider A. Telepharmacy in a rural Alberta Community Cancer Network. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2012;18(3):366–376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Wakefield CE, Sansom-Daly UM, McGill BC, et al. Acceptability and feasibility of an e-mental health intervention for parents of childhood cancer survivors: “Cascade.” Support Care Cancer. 2016;24(6):2685–2694. 10.1007/s00520-016-3077-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Choi Yoo SJ, Nyman JA, Cheville AL, Kroenke K. Cost effectiveness of telecare management for pain and depression in patients with cancer: Results from a randomized trial. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2014;36(6):599–606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Haozous E, Doorenbos AZ, Demiris G, et al. Role of telehealth/videoconferencing in managing cancer pain in rural American Indian communities. Psychooncology. 2012;21(2):219–223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Buchanan AH, Datta SK, Skinner CS, et al. Randomized trial of telegenetics vs. in-person cancer genetic counseling: Cost, patient satisfaction and attendance. J Genet Couns. 2015;24(6):961–970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Brown J, Athens A, Tait DL, et al. A comprehensive program enabling effective delivery of regional genetic counseling. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2018;28(5):996–1002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Watanabe SM, Fairchild A, Pituskin E, Borgersen P, Hanson J, Fassbender K. Improving access to specialist multidisciplinary palliative care consultation for rural cancer patients by videoconferencing: Report of a pilot project. Support Care Cancer. 2013;21(4):1201–1207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Bensink ME, Armfield NR, Pinkerton R, et al. Using videotelephony to support paediatric oncology-related palliative care in the home: From abandoned RCT to acceptability study. Palliat Med. 2009;23(3):228–237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Doorenbos AZ, Kundu A, Eaton LH, et al. Enhancing access to cancer education for rural healthcare providers via telehealth. J Cancer Educ. 2011;26(4):682–686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Brandon AR, Song L, Deal AM, et al. Using telehealth to train providers of a cancer support intervention. Telemed J E Health. 2015;21(10):793–800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Forgione A, Kislov V, Guraya SY, Kasakevich E, Pugliese R. Safe introduction of laparoscopic colorectal surgery even in remote areas of the world: The value of a comprehensive telementoring training program. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2015;25(1):37–42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Stevenson MM, Irwin T, Lowry T, et al. Development of a virtual multidisciplinary lung cancer tumor board in a community setting. J Oncol Pract. 2013;9(3):e77–e80. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Shea CM, Haynes-Maslow L, McIntyre M, et al. Assessing the feasibility of a virtual tumor board program: A case study. J Healthc Manag. 2014;59(3):177–193. 10.1097/00115514-201405000-00005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Hall S, Murchie P. Can we use technology to encourage self-monitoring by people treated for melanoma? A qualitative exploration of the perceptions of potential recipients. Support Care Cancer. 2014;22(6):1663–1671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Petitte TM, Narsavage GL, Chen Y-J, Coole C, Forth T, Frick KD. Feasibility study: Home telemonitoring for patients with lung cancer in a mountainous rural area. Oncol Nurs Forum. 2014;41(2):153–161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Doorenbos AZ, Eaton LH, Haozous E, Towle C, Revels L, Buchwald D. Satisfaction with telehealth for cancer support groups in rural American Indian and Alaska Native communities. Clin J Oncol Nurs. 2010;14(6):765–770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Befort CA, Klemp JR, Austin HL, et al. Outcomes of a weight loss intervention among rural breast cancer survivors. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012;132(2):631–639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Befort CA, Klemp JR, Sullivan DK, et al. Weight loss maintenance strategies among rural breast cancer survivors: The rural women connecting for better health trial. Obesity. 2016;24(10):2070–2077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Fazzino TL, Fabian C, Befort CA. Change in physical activity during a weight management intervention for breast cancer survivors: Association with weight outcomes. Obesity. 2017;25 Suppl 2:S109–S115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Fazzino TL, Sporn NJ, Befort CA. A qualitative evaluation of a group phone-based weight loss intervention for rural breast cancer survivors: Themes and mechanisms of success. Support Care Cancer. 2016;24(7):3165–3173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Bakitas M, Lyons KD, Hegel MT, et al.The project ENABLE II randomized controlled trial to improve palliative care for rural patients with advanced cancer: Baseline findings, methodological challenges, and solutions. Palliat Support Care. 2009;7(1):75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Bakitas MA, Tosteson TD, Li Z, et al. Early versus delayed initiation of concurrent palliative oncology care: Patient outcomes in the ENABLE III randomized controlled trial. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(13): 1438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Dionne-Odom JN, Azuero A, Lyons KD,et al. Benefits of early versus delayed palliative care to informal family caregivers of patients with advanced cancer: Outcomes from the ENABLE III randomized controlled trial. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(13):1446–1452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Dionne-Odom JN, Taylor R, Rocque G, et al. Adapting an early palliative care intervention to family caregivers of persons with advanced cancer in the rural deep south: A qualitative formative evaluation. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2018;55(6):1519–1530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Belkora J,Stupar L, O’Donnell S, et al. Decision support by telephone: Randomized controlled trial in a rural community setting. Patient Educ Couns. 2012;89(1):134–142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Wilson L, Loucks A, Stupar L. Cost-benefit analysis of decision support methods for patients with breast cancer in a rural community. Commun Oncol . 2013;10(2):47–57. [Google Scholar]
- 80.Fennell KM, Turnbull DA, Bidargaddi N, McWha J, Davies M, Olver I. The consumer-driven development and acceptability testing of a website designed to connect rural cancer patients and their families, carers and health professionals. Eur J Cancer Care. 2017;26:e12533. 10.1111/ecc.12533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Rehse B, Pukrop R. Effects of psychosocial interventions on quality of life in adult cancer patients: Meta analysis of 37 published controlled outcome studies. Patient Educ Couns. 2003;50(2):179–186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Gottlieb BH,Wachala ED. Cancer support groups: A critical review of empirical studies. Psychooncology. 2007;16(5):379–400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Vollmer Dahlke D, Kellstedt D, Weinberg AD. Developing NaviCanPlan: A mobile web resource locator for cancer providers and survivors. J Cancer Educ. 2015;30(4):670–676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Baseman J, Revere D, Baldwin L-M. A mobile breast cancer survivorship care app: Pilot study. JMIR Cancer. 2017;3(2):e14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Rao R, Shukla BM, Saint-Cyr M, Rao M, Teotia SS. Take two and text me in the morning: Optimizing clinical time with a short messaging system. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2012;130(1):44–49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Jiang Y, West BT, Barton DL, Harris MR. Acceptance and use of eHealth/mHealth applications for self-management among cancer survivors. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2017;245:131–135. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Pew Research Center. Mobile Fact Sheet. 2021. https://www.pewresearch.org/internet/fact-sheet/mobile/ Accessed July 12, 2021.
- 88.Statz M, Evers K. Spatial barriers as moral failings: What rural distance can teach us about women’s health and medical mistrust. Health Place. 2020. Jul;64:102396. 10.1016/j.healthplace.2020.102396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Oakley LP, López-Cevallos DF, Harvey SM. The association of cultural and structural factors with perceived medical mistrust among young adult latinos in rural Oregon. Behav Med. 2019;45(2):118–127. 10.1080/08964289.2019.1590799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Hall MB, Vos P, Bess JJ, Reburn KL, Locklear GD, McAlister J, et al. Cervical cancer screening behaviors and perceptions of medical mistrust among rural black and white women. J Health Care Poor Underserved. 2018;29(4):1368–1385. 10.1353/hpu.2018.0101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.López-Cevallos DF, Harvey SM, Warren JT. Medical mistrust, perceived discrimination, and satisfaction with health care among young-adult rural latinos. J Rural Health. 2014;30(4):344–351. 10.1111/jrh.12063. Epub 2014 Feb 27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Connell CL, Wang SC, Crook L, Yadrick K. Barriers to healthcare seeking and provision among African American adults in the rural Mississippi delta region: Community and provider perspectives. J Community Health. 2019;44(4):636–645. 10.1007/s10900-019-00620-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Peprah P, Abalo EM, Agyemang-Duah W, Budu HI,Appiah-Brempong E, Morgan AK, et al. Lessening barriers to healthcare in rural Ghana: Providers and users’ perspectives on the role of mHealth technology. A qualitative exploration. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2020;20(1):27. 10.1186/s12911-020-1040-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Steinman L, Heang H, van Pelt M, Ide N, Cui H, Rao M, et al. Facilitators and barriers to chronic disease self-management and mobile health interventions for people living with diabetes and hypertension in Cambodia: Qualitative study. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2020;8(4):e13536. 10.2196/13536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Willis K, Baxter J. Trusting technology: Women aged 40–49 years participating in screening for breast cancer–An exploratory study. Aust N Z J Public Health. 2003;27(3):282–6. 10.1111/j.1467-842x.2003.tb00395.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.US Census Bureau. Urban and Rural. 2021. https://www.census.gov/programs-surveys/geography/guidance/geo-areas/urban-rural.html Accessed June 16, 2021.
- 97.Health Resources & Services Administration. Defining Rural Population. 2017. https://www.hrsa.gov/rural-health/about-us/definition/index.html Accessed April 13, 2021.
- 98.USDA ERS. Rural-Urban Continuum Codes. 2020. https://www.ers.usda.gov/data-products/rural-urban-continuum-codes.aspx Accessed April 13,2021.
- 99.USDA ERS. Rural-Urban Commuting Area Codes. 2020. https://www.ers.usda.gov/data-products/rural-urban-commuting-area-codes/ Accessed April 13,2021.
- 100.Glover JD , Tennant SK. Remote Areas Statistical Geography in Australia: Notes on the Accessibility/Remoteness Index for Australia (ARIA+ Version). Adelaid: Public Health Information Development Unit; 2003. [Google Scholar]
- 101.Willcox JC, Dobson R, Whittaker R. Old-fashioned technology in the era of “Bling”: Is there a future for text messaging in health care? J Med Internet Res. 2019;21(12):e16630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


