Abstract
Ferroptosis, a new form of programmed necrosis characterized by iron-dependent lethal accumulation of lipid hydroperoxides, is associated with many human diseases. Targeting amino acid (AA) availability can selectively suppress tumor growth and has been a promising therapeutic strategy for cancer therapy. Compelling studies have indicated that AA metabolism is also involved in ferroptosis, closely regulating its initiation and execution. This manuscript systematically summarizes the latest advances of AA metabolism in regulating ferroptosis and discusses the potential combination of therapeutic strategies that simultaneously target AA metabolism and ferroptosis in cancer to eliminate tumors or limit their invasiveness.
Keywords: amino acid metabolism, ferroptosis, cancer, combinatorial therapy
Introduction
Ferroptosis is defined as iron-dependent regulatory necrosis orchestrated by multiple molecular and metabolic pathways 1. Briefly, the regulatory mechanism of ferroptotic cell death mainly involves three parts: lipid peroxides (LPOs) generation, LPOs scavenging, and the repair of damaged plasma membranes 2. In the process of lipid peroxidation, the abundance of free iron, hydrogen peroxide, polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) and PUFA-rich phospholipids control the sensitivity to ferroptosis 2-3; The LPOs eliminating mechanisms mainly involves three pathways, including the cystine-glutamate antiporter transport system (system Xc-)/cysteine (Cys)/glutathione (GSH)/glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4), ferroptosis-suppressor-protein 1 (FSP1)/coenzyme Q (CoQ10), and GTP cyclohydrolase1 (GCH1)/tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) axes 4. Some molecules such as tumor suppressor protein p53, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2), breast cancer gene 1 related protein 1 (BAP1), lncRNAs, etc. can act through regulating the activities of the defense system at the transcriptional or post-transcriptional level to control ferroptosis sensitivity 3-4; Ferroptotic cell death is booted by LPOs-induced membrane rupture. The endosomal sorting complex required for transport III (ESCRT-III) exerts a key part in repairing the damaged plasma membranes and control ferroptosis sensitivity 5. Since definition, ferroptosis has been implicated to be associated with the occurrence and development of various human diseases such as tumorigenesis, infection, immune diseases, neurodegeneration, and tissue ischemia-reperfusion injury 6-8. Especially for drug-resistant cancer cells, multiple experimental cancer models have demonstrated that they can be effectively killed by ferroptosis inducers, such as some small molecules and clinical drugs that target FSP1 and GPX4, deprive GSH or improve the iron pool. Nevertheless, smart cancer cells can always evolve alternative pathways to avoid this disadvantage. Therefore, exploring ferroptosis combination therapy might open up new therapeutic avenues for resensitizing cancer cells and eliminating drug-resistant clones. Studies have confirmed some synergy effects between ferroptosis and current cancer treatments, such as Roh's research 9 found that ferroptosis inducers can work synergistically with cisplatin to suppress the growth of head and neck tumors in mice; Wang's study 10 found that ferroptosis activators and anti-PD-L1 antibody nivolumab synergistically induce melanoma growth inhibition in vitro and in vivo; Moreover, studies have confirmed that ferroptosis inducers enhance radiotherapy sensitivity of melanoma 11, lung cancer and glioma 12-13, breast cancer 14 and nasopharyngeal carcinoma 15.
Studies about tumor metabolic reprogramming have been continually updated recently. As the amino acid (AA) metabolic network is the most complex and highly interconnected with other pathways, AA metabolic reprogramming has garnered considerable attention 16-17. AAs can not only serve as substrates for protein synthesis but also participate in energy production, macromolecular synthesis, signal transduction pathways, and the maintenance of cellular redox homeostasis 18-19. Emerging studies have revealed that AA availability is also involved in ferroptosis process and controls the susceptibility of tumors to ferroptosis. This review focuses on the regulation of ferroptosis by AA metabolism, and explores the potential of the combined strategies that target ferroptosis and AA metabolism to eradicate drug-resistant cancer.
Amino acid metabolism in cancer
As the basis of protein synthesis and the intermediate metabolites that ignite other biosynthetic pathways, cancer cells with AA metabolic addiction have received an increasing attention in recent years 20. Studies have found that tumor cells usually rely on the supply of exogenous AAs, and this is not limited to essential amino acids (EAA) 21. Tumor cells have developed diverse mechanisms to maintain the abundant supply of AAs, including bidirectional transfer 22-23, micropinocytosis 24-25, or utilizing extracellular free AAs 26-27. Abnormal up-regulation of AA uptake and metabolism has been observed in many cancers 17. Therefore, it seems feasible to make tumor cells auxotrophic and then selectively lethal via interfering with AAs availability. Targeting AA metabolism such as interference with AA synthesis, degradation and transfer has been practiced in preclinical and clinical settings of cancer treatment, which provides numerous targets for anti-cancer drug development. For example, a study on colon cancer found 28 that targeting the methionine transporter solute carrier family 43A2 (SLC43A2) improved the expression of dimethylation at lysine 79 of histone H3 (H3K79me2) and signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 (STAT5) in T cells, thereby restoring T cell immunity. Another study 29 also found that elevating L-arginine concentrations promoted the survival ability of CD8+ T cells and their anti-tumor activity in mice. Werner's research 30 also confirmed that the arginine (Arg) transporter human cationic amino acid transporter-1 (hCAT-1) is a key component for activating efficient T cells to regulate the adaptive immune response in tumor immunity. These findings, including but not limited to, suggest that targeting cancer AA metabolism pathways may provide an immunotherapeutic approach. It is worth mentioning that the efficacy of metabolic inhibitor monotherapy may be limited, in that the metabolic changes of cancer cells exposed to AA deprivation may make the cells survive. Therefore, future prospects of AA deprivation therapy may involve combinations with other agents.
Amino acid metabolism and ferroptosis
The trade of metabolites between ferroptosis and cancer cells is increasingly recognized as a critical aspect of tumor metabolism. Evidence has demonstrated that AA metabolism is critical for ferroptosis 31. Here we discuss the most prominent AAs involved in regulating ferroptosis and their possible regulatory mechanisms in cancer.
Cyst(e)ine metabolism
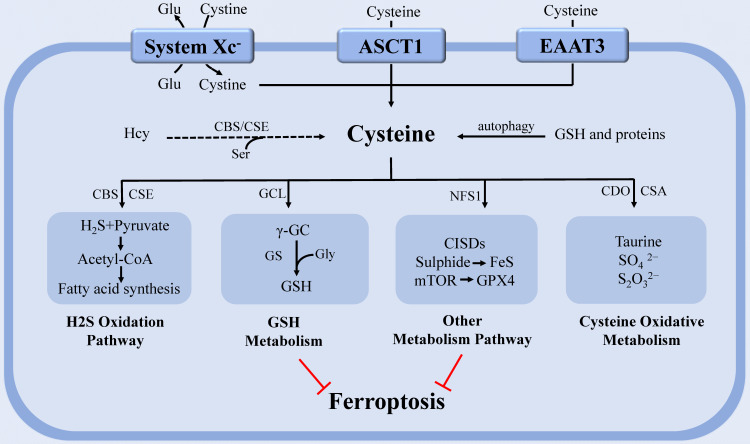
Cys is a sulfur-containing proteinogenic AA whose free thiol group confers unique properties on protein functional sites 32. Cells have developed several mechanisms to keep a ceaseless supply of Cys. Tumor cells obtain Cys primarily via the uptake of cystine, a precursor of Cys, by system Xc- 33. In addition, Cys could be directly assimilated via excitatory amino acid transporter 3 (EAAT3) and SLC1A4 transporter (ASCT1) 34-35. Endogenous Cys is synthesized by the trans-sulfuration pathway, which is mainly catalyzed by cystathionine γ-lyase (CSE) and cystathionine β-synthase (CBS) 36-39. Also, Cys could be obtained through autophagic breakdown of GSH and proteins 40. As a precursor of various biochemical processes, Cys actively participates in diverse metabolic pathways including GSH synthesis, protein s-cysteinylation, hydrogen sulfide (H2S) production, epigenetic regulation, and energy production 36.
Prior studies have indicated that Cystine/Cys depletion increases reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and induces ferroptosis, and certain cancers rely on Cystine/Cys metabolism to avoid ferroptosis 1, 32, 41. In the context of ferroptosis, Cys not only acts as a potent antioxidant by itself but also acts as an element of the major antioxidant GSH to maintain redox homeostasis 42-43. The reducing ability of the thiol group in Cys conferred its protective role against lethal ROS accumulation 44-45. Cys could be catabolized by two main pathways 36. In the first catabolic pathway, Cys could be degraded into compounds such as pyruvate and α-ketoglutarate (α-KG) by CBS and CSE. The former is metabolized to acetyl-coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA) and subsequently enters the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or is utilized to synthesize lipids, whereas the latter acts as an intermediate of TCA cycle or is used to synthesize glutamate (Glu) 46-49. Recently, it was reported that coenzyme A (CoA), a metabolite of Cys, cooperates with GSH to regulate ferroptosis in genetically engineered mice by controlling lipid metabolism 32, 50. However, the precise mechanism of anti-ferroptotic function of CoA is not discussed in the article. Studies have found that CoQ10, the derivative of CoA, also known as ubiquinone can be reduced by the oxidoreductase FSP1 to ubiquinol, a lipophilic radical-trapping antioxidant that halts the propagation of lipid peroxides 51-52. Therefore, CoA might act through generating CoQ10 to perform anti-ferroptotic function.
In the second catabolic pathway, cysteine dioxygenase (CDO1) catalyzes Cys transformation into taurine 53. CDO1 competes for Cys with glutamate-cysteine ligase (GCL), thereby shunting Cys used for GSH synthesis to taurine production 53-54. CDO1 has been demonstrated to decrease the intracellular level of GSH, thus enhancing ROS generation in cancer 55. Silencing or inactivating CDO1 helps to restore cellular GSH contents to avoid ROS and lipid peroxidation, which increases the resistance to ferroptosis, and promotes tumor proliferation 54-56. Therefore, restoring CDO1 function or increasing the expression of CDO1 protein in tumors may render tumor cells more vulnerable to ferroptosis, resulting in decreased tumor viability and growth. Although numerous studies indicate that CDO1 has tumor-suppressive properties, divergent evidence in glioblastoma 55 highlights the necessity for additional research to determine the true impact of Cys-derived compounds on cancer metabolic reconstruction.
Targeting the Xc- system-mediated absorption of cystine is a classical approach to induce cell ferroptosis in basic studies. The clinical development of drugs targeting Cystine/Cys metabolic pathways to treat ferroptosis-related diseases may provide an avenue for future translation of this concept. It is still unknown whether human cancer is also susceptible to Cystine/Cys depletion-induced ferroptosis in clinic practice. A recent study demonstrates that the trans-sulfuration pathway is a direct advantage for cancer cells in maintaining redox equilibrium and evading ferroptosis. The trans-sulfuration pathway can produce endogenous Cys to synthesize GSH when cystine import is inhibited 57-59.
Cysteine persulfide (CysSSH) and cysteine polysulfides (CysSSnH, n > 1), which are Cys derivatives, have been proposed as powerful antioxidants and cytoprotective agents based on their superior nucleophilicity and reducibility 60. Study has found that CysSSnH can up-regulate the transcription of antioxidant genes, including the transcription of enzymes involved in GSH production to increase the level of GSH 61. In light of these findings, we reasonably speculate that CysSSH and CysSSnH are also very likely to participate in the ferroptotic regulation, despite the lack of direct reports on this currently. In this process, the key enzymes 3‐mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase (MPST), CBS, CSE and cysteinyl-tRNA synthetase (CARS) 62 that contribute to the production of CysSSH and CysSSnH may play an important role. Consistently, a screening of genome-wide siRNAs for ferroptosis inhibitors found that knockdown of CARS leads to the activation of trans-sulfuration pathway and ferroptosis resistance 58, 63.
Moreover, mitochondrial cysteine desulfurase (NFS1) can metabolize Cys and produce a sulfur carrier 36. NFS1 degrades Cys and releases sulfide to generate iron-sulfur (Fe-S) clusters, a cofactor of various essential proteins and enzymes in cells. Cells rely on increased NFS1 expression to maintain the continuous supply of Fe-S clusters when exposed to high oxygen concentration, as confirmed in metastatic or primary lung tumors 64. Although NFS1 has been shown to inhibit tumor growth via triggering the iron-starvation response, this state of iron deficiency can also protect cells from ferroptosis 36, 64. Therefore, targeting NFS1 seems to be a promising strategy to trigger ferroptosis for cancer treatment. Homma 65 also discovered a new mechanism by which Cys resists ferroptosis. This study discovered that Cys preservation conferred resistance of GSH depleted cells to ferroptosis through CDGSH iron sulphur domain-containing proteins (CISDs). CISDs exerted anti-ferroptotic function by suppressing free iron toxicity and the subsequent lipid peroxidation with the assistance of Cys. This study revealed a potential therapeutic strategy for eradicating ferroptosis-resistant cells by concurrently inhibiting GSH synthesis and CISDs activity (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
The regulation of cysteine metabolism in ferroptosis. Cysteine regulates ferroptosis through multiple pathways. In the H2S oxidation pathway, cysteine can be degraded into compounds which are used to synthesize fatty acids. PUFAs that undergo lipid peroxidation are involved in ferroptosis. The continuous supply of Fe-S clusters by mitochondrial NFS1 stopped the iron-starvation response. GCL can catalyze cysteine to form the antioxidant GSH. CDO, which catalyzes the conversion of cysteine to taurine, can compete with GCL for cysteine, thereby limiting GSH synthesis and promoting ROS. In addition, Cyst(e)ine could regulate ferroptosis independently of GSH by activating Rag-mTORC1-4EBPs signaling axis and promoting GPX4 protein synthesis. Abbreviations: system Xc-: cystine-glutamate antiporter transport system; ASCT1: solute carrier family 1A4 transporter: EAAT3: excitatory amino acid transporter 3; Glu: glutamate; Ser: serine; Gly: glycine; Hcy: homocysteine; PUFA: polyunsaturated fatty acid; GSH: glutathione; Fe-S: iron-sulfur; NFS1: cysteine desulfurase; GPX4: glutathione peroxidase 4; H2S: gasotransmitter hydrogen sulfide; ROS: reactive oxygen species; GCL: glutamate-cysteine ligase; CDO: cysteine dioxygenase; CBS: cystathionine β-synthase; CSE: cystathionine γ-lyase; GS: glutathione synthase; γ-GC: γ-glutamyl-cysteine; CSA: cysteine sulfinate.
Recent research discovered that cystine/Cys can activate Rag-mTORC1-4EBPs signaling axis and promote GPX4 protein synthesis to prevent cell ferroptosis in a GSH-independent manner. This study elucidated a regulatory mechanism that linked cystine/Cys availability to GPX4 protein synthesis and provided a new idea for using combinatorial therapy of ferroptosis inducers and mTORC1 inhibitors in cancer therapy 66. Cys metabolism is closely connected to that of glutamine (Gln) since serine (Ser), and glycine (Gly) can be derived from Gln and contribute to homocysteine (Hcy) and Cys syntheses through the one-carbon metabolism pathway 67-68. A study on Hcy found that it can promote ferroptosis via enhancing GPX4 methylation 69.
In conclusion, tumor resistance to ferroptosis caused by Cys deprivation can be reversed by concurrently targeting exogenous uptake and endogenous synthesis. It is necessary to explore additional and newer methods of targeting Cys metabolism to kill tumor cells more efficiently in the future. Cystine/Cys and Gln together form a metabolism network of AAs capable of providing the core metabolic pathways underlying key cancer processes. The production of Gln and its role in bioenergetics and signaling are addressed in the next section.
Glutamine metabolism
Gln is the most abundant AA in the human body and the most critical non-toxic carrier in the ammonia cycle 70. In 2011, Hanahan and Weinberg 20 proposed the concept of tumor cell energy metabolic reprogramming in the new ten characteristics of tumor cells. Although glucose metabolic reprogramming plays a crucial biological significance in tumors, some tumor cells do not entirely rely on glucose metabolism to obtain energy 71. Subsequent studies have demonstrated that Gln is an important fuel, and also an important raw material for rapidly growing tumor cells 71-73.
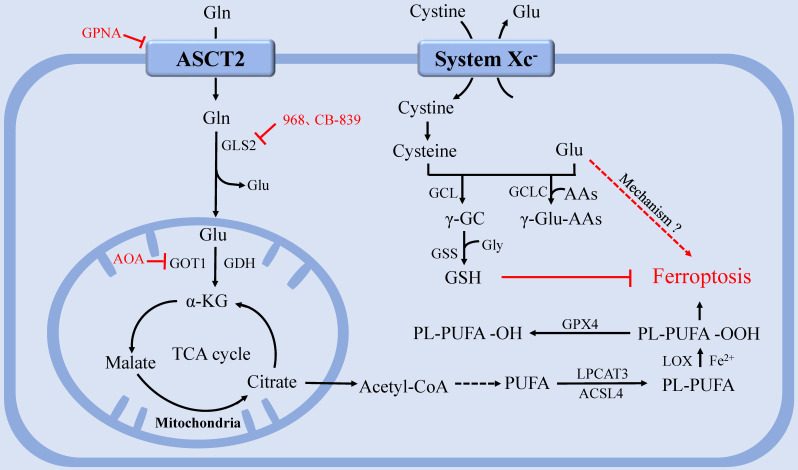
After entering cell via the SLC1A5 (ASCT2), Gln mainly undergoes three metabolic routes 74: first, Gln is converted to Glu catalyzed by glutaminase (GLS), which is used to produce GSH together with Cys and Gly, and the generated GSH and NADPH can be used to maintain redox homeostasis 75; second, Gln acts as a raw material to provide precursors for synthesizing various nucleotides, AAs, proteins, lipids and other biologically important molecules 76-77; third, Gln enters into the mitochondria and is converted into α-KG catalyzed by GLS and glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH). α-KG participates in the TCA cycle to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and replenish TCA cycle intermediates 77-79. While being a non-essential amino acid (NEAA), Gln is essential for rapidly proliferating cells, such as cancer cells 80. In vivo experiments in hepatomas and hepatic fibrosarcoma revealed that cancer cells consume Gln ten times faster than normal hepatocytes 81. In this context of undersupply, many cancer cells reprogram their metabolism pathways to take up more Gln by upregulating Gln transporters or enhancing the expression or activity of Gln key metabolic enzymes 82, shifting Gln utilization from catabolic to anabolic, and facilitating the biosynthesis of macromolecules and organelles required for assembling new cells 20, 83-84.
Gln metabolism is tightly linked to ferroptosis regulation 85. To date, the precise physiological function of Gln in ferroptosis remains unknown. Gao's study 86 found that Gln may be an inducer of ferroptosis, fueling ferroptosis through its specific metabolism, glutaminolysis. Glutaminolysis refers to a series of intracellular biochemical reaction processes driven by Gln, in which Gln is converted to Glu, aspartic acid, carbon dioxide, pyruvate, lactic acid, alanine, citric acid, and other products catalyzed by key enzymes, such as GLS, GDH, and aspartate aminotransferase 2 (GOT2) and subsequently used as a fuel for TCA cycle and lipid biosynthesis 86-87. Gao's research team further demonstrated that L-Gln, but not D-Gln, is responsible for this type of cell death 86. When lack of Gln or glutaminolysis is inhibited, cystine starvation or preventing cystine import cannot induce ferroptosis, ROS accumulation, or lipid peroxidation 86, 88. Meanwhile, high-dose extracellular Gln alone cannot induce ferroptosis. Ferroptosis can be induced only when Gln is available, accompanied by cystine deprivation 86.
Consistent with previous research, deprivation of cystine or Cys or inhibition of the system Xc- induced ferroptosis by depleting cellular GSH and accordingly increasing ROS, and concurrently accelerated the death process through Glu accumulation, the glutaminolysis product 3, 89. The glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit (GCLC) inhibits ferroptosis by participating in the first step of GSH synthesis. However, Yun et al. 89 found that GCLC plays a GSH-independent, non-classical role in preventing ferroptosis by regulating Glu pool under cystine deprivation. GCLC mediates γ-glutamine peptide synthesis, limits Glu accumulation, and thus protects against ferroptosis. In addition, GCLC activity is regulated by NRF2, a pivotal transcriptional regulator. This study indicates how cells save themselves under cystine or Cys starvation conditions, but it does not explain how Glu accumulation promotes ferroptosis.
The function of glutaminolysis in ferroptosis could also be explained by the discovery that α-KG, a product of glutaminolysis, could substitute Gln to function in Cys deprivation-induced lipid ROS accumulation and ferroptosis 75, 88. Furthermore, TCA metabolites downstream of α-KG, including malate, fumarate, and succinate, were all able to substitute the function of Gln in regulating lipid ROS accumulation 87. Notably, compared with Gln status, glucose status has a greater impact on TCA cycle metabolites upstream of α-KG, such as citrate, as the role of glutaminolysis in TCA cycle is primarily to replenish TCA cycle intermediates 79, 88. Interestingly, it has been demonstrated that ferroptosis requires mitochondrial GLS2 rather than cytosolic GLS1, although both enzymes catalyze glutaminolysis 86 (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
The regulation of glutamine metabolism in ferroptosis. After entering the cell via the ASCT2, Gln can be degraded and provide a precursor for TCA and PUFAs biosynthesis. System Xc- inputs cysteine to synthesize GSH and exchange Glu at the same time. GPX4 utilizes GSH to eliminate lipid peroxides that participate in ferroptosis. GCLC maintains the Glu pool homeostasis under cystine starvation by mediating the synthesis of γ-glutamine peptide, thereby limiting the accumulation of Glu and protecting against ferroptosis. Abbreviations: ASCT2: solute carrier family 1A5 transporter; Gln: Glutamine; Glu: glutamate; GLS: glutaminase; GDH: glutamate dehydrogenase; GOT1: aspartate aminotransferase 1; TCA: tricarboxylic acid; PUFAs: polyunsaturated fatty acids; system Xc-: Cystine-glutamate antiporter transport system; GSH: glutathione; GPX4: glutathione peroxidase 4; GCLC: glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit.
At present, studies on Gln starvation therapy have confirmed that Gln transporter inhibitor GPNA 89, GLS inhibitor compound 968 90, CB-839 91-92, and transaminase GOT1 inhibitor aminooxyacetic acid (AOA) 76 can significantly inhibit ferroptosis. Gene interference or pharmacological inhibition of ASCT2 has been shown to decrease the growth of prostate cancer 93, gastric cancer 94, and triple-negative breast cancer 95. However, since compensatory responses are triggered, blocking a single Gln transporter is insufficient to prevent tumor growth 17. Therefore, blocking the uptake or degradation of Gln in multiple ways may become a more viable therapeutic strategy for ferroptosis-associated diseases.
Branched-chain amino acids metabolism
Branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), including leucine, valine, and isoleucine, are a subclass of EAAs whose metabolism has been linked to specific cancer phenotypes 96. BCAA metabolism changes can both affect intrinsic cancer properties of cells and represent systemic metabolic changes correlated with certain cancers 96. After dietary intake, BCAAs are transported by L-type amino acid transporters (LATs) into the cell and are catabolized by highly reversible branched-chain amino acid transaminases (BCATs) 97-98. BCAT exists in two isoforms, BCAT1 and BCAT2 98. BCAT2 is located in mitochondria and is ubiquitously expressed, while BCAT1 is located in cytosol, and its expression is restricted to certain organs, such as the brain 99.
Both BCAT1 and BCAT2 are highly active and reversible enzymes that catalyze all three types of BCAAs and their corresponding branched-chain keto acids (BCKAs) 100. BCAT produces Gln and designated BCKA by transferring nitrogen to a-KG, and the produced Glu can be used to support AA and nucleotide pools 101. In addition, the generated keto acids are further metabolized by several steps to acetyl-CoA and/or succinyl-CoA, which were used to replenish TCA cycle intermediates and participate in synthesizing fatty acids 98. BCAAs at high concentrations have been demonstrated to increase ROS production and mitochondrial dysfunction by activating Akt-mTOR signaling pathway 102. However, a recent study demonstrated that BCAT1 could mediate EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) resistance by producing GSH to counteract ROS accumulation 103. Furthermore, another study also identified BCAT2 as a novel suppressor of ferroptosis, whose activation of ectopic expression could specifically antagonize system Xc- inhibition and protect liver cancer and pancreatic cancer cells from ferroptosis. Therefore, BCAT2 could serve to predict the responsiveness of cancer cells to the ferroptosis-inducing therapy 104. Together, reprogramming of BCAA metabolism could change mitochondrial functions as well as gene expression, redraw other metabolic pathways, and change the levels of essential metabolites, including Glu, α-KG, BCAAs and ROS, therefore elevating cancer cell proliferation and enhancing drug resistance capacity 98.
Tryptophan metabolism
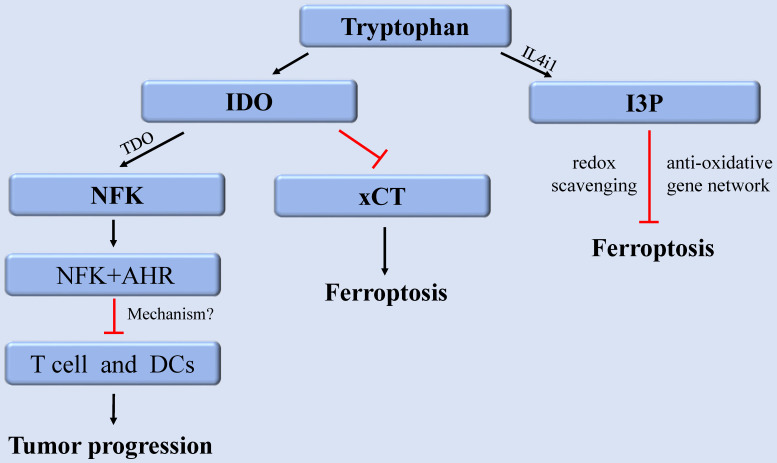
As EAA, tryptophan (Trp) and its metabolites perform various nutritional and physiological roles and are intimately linked to regulating cancer, neurodegeneration, and other diseases 105. As a building block of proteins, Trp is required for cell growth and maintenance. As a neurotransmitter and signaling molecule, Trp is required to transmit organismal responses to dietary and environmental signals 106. The content of internal free Trp depends on the external food intake and the activity of Trp metabolic pathway. Among them, more than 95% of free Trp functions as a substrate to participate in the kynurenine (Kyn) pathway, which produces various metabolites with different biological activities. The rate-limiting step in the Kyn pathway is performed by three enzymes indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1), IDO2, and tryptophan-2,3-dioxygenase (TDO). They consume Trp by converting Trp into N-formylkynurenine (NFK), which accordingly has a fundamental impact on cellular function and survival 106. In cancer, aberrant activation of IDO1 and TDO results in suppression of anti-tumor immunity 107. Therefore, drugs combining IDO1 inhibitors and immune checkpoint inhibitors have been developed for enhancing anti-tumor immunity 108. Although there are few reports about the metabolites or key enzymes of the Kyn pathway involved in regulating ferroptosis, a recent study revealed that IDO1 deficiency contribute to ferroptosis resistance by activating the expression of SLC7A11, (xCT), while IDO1 overexpression could exacerbate the classical ferroptosis events 109.
Furthermore, recent research discovered that Trp metabolite, indole-3-pyruvate (I3P) can regulate ferroptosis 110. Trp can be metabolized to I3P catalyzed by interleukin 4 induction 1 (IL4i1), a FAD-dependent oxidoreductase that metabolizes AAs and is linked to immune suppression in cancer. I3P protects against ferroptosis in at least two distinct ways: by directly scavenging free radicals and activating anti-oxidative stress pathways 110. I3P can up-regulate the protein levels of SLC7A11, NQO1, ATF4, CYP1B1, and the AKR1C family at the transcriptional level. These proteins are all involved in oxidative stress response, which can induce cell resistant to ferroptosis-induced oxidative damage. Furthermore, compared with the metabolites derived from the catalyzation of other AAs by IL4il, I3P exhibited the highest radical scavenging potency against the exogenous stable radical diphenyl-2-pyridohydrazine (DPPH). Therefore, I3P might also be able to trap lipid peroxyl radicals directly to prevent ferroptosis 110. Given that IL4i1 activates anti-ferroptosis pathways through I3P and possibly other indoles, we speculate that blocking IL4i1-mediated Trp metabolism could be a useful anti-cancer therapeutic strategies (Figure 3).
Figure 3.
The regulation of tryptophan metabolism in ferroptosis. Trp can be converted into NFK under the catalysis of IDO and TDO to regulate tumor growth. IDO aggravates ferroptosis by inhibiting xCT. In addition, Trp can also be metabolized to I3P under the catalysis of IL4i1 to prevent ferroptosis. Abbreviations: Trp: tryptophan; IDO: indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase; TDO: tryptophan-2,3-dioxygenase; NFK: N-formylkynurenine; AHR: aryl hydrocarbon receptor; xCT: solute carrier family 7 member 11; I3P: indole-3-pyruvate; IL4i1: nterleukin 4 induction 1.
Other amino acids metabolism
Other AAs, such as Arg, Ser, Gly, lysine (Lys), etc., also play a critical role in cell metabolism and cancer development. Arg could serve as a precursor of many biomolecules, such as creatine, nitric oxide, polyamines, proteins, and other AAs 10. In recent years, Arg starvation has become a potential and novel clinical strategy for cancer therapy 111-112. There is currently a lack of research on Arg metabolism in regulating ferroptosis. But numerous evidences indicate that Arg consumption is intimately linked to ROS production 113. A study exploring the effect of Arg on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced oxidative stress found that the intracellular GPX content was significantly increased after the addition of Arg, accompanied by a decrease in ROS and malondialdehyde (MDA) content, and this process was realized at least partially through arginase-1 signaling pathway 114. These findings indirectly imply that Arg metabolism is likely to participate in the regulation of ferroptosis.
The de novo synthesis of Cys fails to perform without considering Ser and Gly in the one-carbon pathway 16. Activating Ser synthesis pathway is directly correlated with GSH synthesis 115, as Ser itself participates in Cys synthesis, and serine-derived Gly is a component of GSH 19,116. Along with its anabolic function in nucleotide synthesis and protein translation, Ser catabolism in mitochondria is crucial to maintain NADPH production and redox balance 117. Therefore, it can be inferred that Ser and Gly might be able to regulate ferroptosis by participating in GSH synthesis and redox reactions. Many studies have noted that tumors, such as melanoma, breast cancer, lung cancer, and Ewing's sarcoma could activate the serine-glycine biosynthetic pathway to support their growth 118-121. The de novo synthesis of serine-glycine has been established as an important factor in tumorigenesis. And the inhibition of serine-glycine biosynthesis could interfere with their redox state, leading to the ROS accumulation and cell death 121. Nevertheless, there is still a lack of direct evidence that Ser or Gly can regulate ferroptosis.
A recent study showed that Lys was also involved in the regulation of ferroptosis, which found that L-lysine α-oxidase, a member of the L-amino acid oxidase family, activates ferroptotic signal by catalyzing the oxidative deamination of L-lysine and ROS production 122. The most updated situation of key enzymes/transporters or genes of AA metabolism that possibly participates in the regulation of ferroptosis are presented in Table 1.
Table 1.
Key enzymes/transporters or genes that may participate in the regulation of ferroptosis in amino acid metabolism
| Compound/Drug | Target | Mechanism | Phase (status) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| sorafenib | system Xc- | Prevents cystine import, causes GSH depletion | Approval | 123 |
| erastin | system Xc- | Prevents cystine import, causes GSH depletion | Phase I | 1 |
| sulfasalazine | system Xc- | Prevents cystine import, causes GSH depletion | Approval | 1 |
| BSO | GCL | Inhibits GCL, inhibits GSH synthesis. | Phase I | 124 |
| artesunate | glutathione S-transferase | Inhibits glutathione S-transferase, causes GSH depletion | Approval | 125 |
| cyst(e)inase | Cyst(e)ine | Induces cyst(e)ine depletion | 32 | |
| CB-839, BPTES 968 |
GLS | Inhibits the conversion of Gln to Glu | Phase I/II | 87, 91 |
| AOA | GOT1 | Inhibits the conversion of Glu to a-KG |
87 | |
| ADI-PEG20 | Arginine | degrades and consumes Arg | Phase III | 126 |
| CB-1158 | Arginase | Inhibiting arginase | Phase II | 127 |
| GPNA, Tamoxifen Raloxifene |
ASCT2 | Inhibits glutamine uptake | 91, 128 | |
| Gene | Protein | Mechanism | Phase (status) | Reference |
| CDO1 | cysteine dioxygenase | enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of cysteine to taurine and reduces GSH synthesis | 53 | |
| CISD1 | CDGSH iron-sulfur domain 1 | Inhibits mitochondrial iron transport into the matrix | 129 | |
| SLC7A11 | Solute carrier family 7 member A11, xCT | a component of system Xc-, requires for cystine import | 82 | |
| CARS | cysteinyl-tRNA synthetase | knockdown causes increased transsulfuration pathway activity, and resistance to ferroptosis | 58 | |
| NFS1 | cysteine desulfurase | enzyme involves in synthesizing iron-sulfur clusters using sulfur from cysteine |
64 | |
| SLC1A5 | solute carrier family 1 member 5 |
amino acid transporter feeding glutaminolysis | 86 | |
| GCLC | glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit |
enzyme involves in GSH synthesis |
124 | |
| BCAT2 | branched-chain amino acid transaminase-2 | activation could antagonize system Xc- inhibition and protect from ferroptosis. | 104 | |
| I3P | indole-3-pyruvate | scavenges free radicals and activates anti-oxidative stress pathways | 110 | |
| LO | L-lysine α-oxidase | enzyme catalyzes the oxidative deamination of L-lysine to activate ferroptosis | 122 |
Perspectives and Conclusions
Since the concept of “ferroptosis” was defined, people have continuously explored its therapeutic potential in lipid peroxidation diseases. In fact, it has been confirmed in many cancers that they are more susceptible to this iron-catalyzed necrosis. However, working hard to develop tolerance and escape various forms of death seems to be the eternal hallmark of cancer cells, and ferroptosis is no exception. The sensitivity of cell to ferroptosis is correlated with numerous biological processes, including AA metabolism.
As basic nutrients and energy sources, AAs contribute significantly to tumor proliferation and homeostasis by acting as intermediates in the metabolism of glucose, lipids and nucleotides. As new functions continue to be discovered, AA metabolism has exerted an increasing part in cancers. Numerous cancers exhibit a high requirement for specific AAs acquired exogenously or released endogenously. Thus, specific AA deprivation could shut down nutrient supply, resulting in AA starvation and cell death. Some AA starvation therapies designed according to the high demand of tumor cells for specific AAs have been introduced into clinical practice or are undergoing clinical evaluation, such as Arg, asparagine, Lys, methionine, phenylalanine, tyrosine and so on 130. However, although AA depletion therapy has broad applicability in cancer treatment, metabolic inhibitor monotherapy may render cancer cells drug-resistant due to compensatory activation and cross-interference of metabolism pathway or reactivation of the silenced genes.
Targeting AA metabolism is currently moving towards combinatorial studies based on the synergistic drug interactions, such as the study of combining immunotherapy and metabolic inhibitors. Although the current research on the regulation of ferroptosis by AA metabolism is limited, the combinatorial targeting of AA metabolism and ferroptosis has shown great promise in cancer treatment. While there are still some thorny issues for this mode of therapy that urgently need to be further studied. For example, it is necessary to clarify the metabolic dependence in specific cancer type, so as to select an appropriate AA target. Attention should also be paid to the crosstalk of AA metabolism between cancer cells and immune cells as well as normal cells in the surrounding environment, as ferroptosis may affect cancer immune surveillance in a dual way. A full understanding of metabolic flexibility and diversity of ferroptosis in cancers will help better guide drugs usage and cancer treatment.
Acknowledgments
Funding
Funding was obtained from 1.3.5 project for disciplines of excellence, West China Hospital, Sichuan University (ZYGD18005); the Sichuan Provincial Department of Science and Technology (2019YJ0056); the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82073059); and Science Fund for Creative Research Groups of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81621003).
Author Contributions
Jian Yang and Feng Bi drafted the original article and prepared the figures; Xinyu Dai, Huanji Xu, and Qiulin Tang critically revised the article for intellectual content, and Feng Bi approved the final version to be submitted.
References
- 1.Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR. et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell. 2012;149:1060–72. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Xu H, Ye D, Ren M. et al. Ferroptosis in the tumor microenvironment: perspectives for immunotherapy. Trends in molecular medicine. 2021;27:856–67. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2021.06.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Tang D, Chen X, Kang R. et al. Ferroptosis: molecular mechanisms and health implications. Cell research. 2021;31:107–25. doi: 10.1038/s41422-020-00441-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hassannia B, Vandenabeele P, Vanden Berghe T. Targeting Ferroptosis to Iron Out Cancer. Cancer cell. 2019;35:830–49. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2019.04.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Pedrera L, Espiritu RA, Ros U. et al. Ferroptotic pores induce Ca(2+) fluxes and ESCRT-III activation to modulate cell death kinetics. Cell death and differentiation. 2021;28:1644–57. doi: 10.1038/s41418-020-00691-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ju J, Song YN, Wang K. Mechanism of Ferroptosis: A Potential Target for Cardiovascular Diseases Treatment. Aging and disease. 2021;12:261–76. doi: 10.14336/AD.2020.0323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Yuan H, Pratte J, Giardina C. Ferroptosis and its potential as a therapeutic target. Biochemical pharmacology. 2021;186:114486. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chen X, Kang R, Kroemer G. et al. Broadening horizons: the role of ferroptosis in cancer. Nature reviews Clinical oncology. 2021;18:280–96. doi: 10.1038/s41571-020-00462-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Roh JL, Kim EH, Jang HJ. et al. Induction of ferroptotic cell death for overcoming cisplatin resistance of head and neck cancer. Cancer letters. 2016;381:96–103. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.07.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wang W, Green M, Choi JE. et al. CD8(+) T cells regulate tumour ferroptosis during cancer immunotherapy. Nature. 2019;569:270–4. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1170-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lang X, Green MD, Wang W. et al. Radiotherapy and Immunotherapy Promote Tumoral Lipid Oxidation and Ferroptosis via Synergistic Repression of SLC7A11. Cancer discovery. 2019;9:1673–85. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-19-0338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ye LF, Chaudhary KR, Zandkarimi F. et al. Radiation-Induced Lipid Peroxidation Triggers Ferroptosis and Synergizes with Ferroptosis Inducers. ACS chemical biology. 2020;15:469–84. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.9b00939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Pan X, Lin Z, Jiang D. et al. Erastin decreases radioresistance of NSCLC cells partially by inducing GPX4-mediated ferroptosis. Oncology letters. 2019;17:3001–8. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.9888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Zhang Z, Lu M, Chen C. et al. Holo-lactoferrin: the link between ferroptosis and radiotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer. Theranostics. 2021;11:3167–82. doi: 10.7150/thno.52028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Li HL, Deng NH, Xiao JX. et al. Cross-link between ferroptosis and nasopharyngeal carcinoma: New approach to radiotherapy sensitization. Oncology letters. 2021;22:770. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.13031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Li Z, Zhang H. Reprogramming of glucose, fatty acid and amino acid metabolism for cancer progression. Cellular and molecular life sciences: CMLS. 2016;73:377–92. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-2070-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Wei Z, Liu X, Cheng C. et al. Metabolism of Amino Acids in Cancer. Frontiers in cell and developmental biology. 2020;8:603837. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.603837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Shanware NP, Mullen AR, DeBerardinis RJ. et al. Glutamine: pleiotropic roles in tumor growth and stress resistance. Journal of molecular medicine (Berlin, Germany) 2011;89:229–36. doi: 10.1007/s00109-011-0731-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Vettore L, Westbrook RL, Tennant DA. New aspects of amino acid metabolism in cancer. British journal of cancer. 2020;122:150–6. doi: 10.1038/s41416-019-0620-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–74. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Choi BH, Coloff JL. The Diverse Functions of Non-Essential Amino Acids in Cancer. Cancers. 2019. 11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 22.Bertero T, Oldham WM, Grasset EM. et al. Tumor-Stroma Mechanics Coordinate Amino Acid Availability to Sustain Tumor Growth and Malignancy. Cell metabolism. 2019;29:124–40.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.09.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Tajan M, Hock AK, Blagih J. et al. A Role for p53 in the Adaptation to Glutamine Starvation through the Expression of SLC1A3. Cell metabolism. 2018;28:721–36.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.07.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Bloomfield G, Kay RR. Uses and abuses of macropinocytosis. Journal of cell science. 2016;129:2697–705. doi: 10.1242/jcs.176149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Commisso C, Davidson SM, Soydaner-Azeloglu RG. et al. Macropinocytosis of protein is an amino acid supply route in Ras-transformed cells. Nature. 2013;497:633–7. doi: 10.1038/nature12138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Elia I, Broekaert D, Christen S. et al. Proline metabolism supports metastasis formation and could be inhibited to selectively target metastasizing cancer cells. Nature communications. 2017;8:15267. doi: 10.1038/ncomms15267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Olivares O, Mayers JR, Gouirand V. et al. Collagen-derived proline promotes pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cell survival under nutrient limited conditions. Nature communications. 2017;8:16031. doi: 10.1038/ncomms16031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Bian Y, Li W, Kremer DM. et al. Cancer SLC43A2 alters T cell methionine metabolism and histone methylation. Nature. 2020;585:277–82. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2682-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Geiger R, Rieckmann JC, Wolf T. et al. L-Arginine Modulates T Cell Metabolism and Enhances Survival and Anti-tumor Activity. Cell. 2016;167:829–42.e13. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.09.031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Werner A, Amann E, Schnitzius V. et al. Induced arginine transport via cationic amino acid transporter-1 is necessary for human T-cell proliferation. European journal of immunology. 2016;46:92–103. doi: 10.1002/eji.201546047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Angeli JPF, Shah R, Pratt DA. et al. Ferroptosis Inhibition: Mechanisms and Opportunities. Trends in pharmacological sciences. 2017;38:489–98. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2017.02.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Badgley MA, Kremer DM, Maurer HC. et al. Cysteine depletion induces pancreatic tumor ferroptosis in mice. Science (New York, NY) 2020;368:85–9. doi: 10.1126/science.aaw9872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lewerenz J, Hewett SJ, Huang Y. et al. The cystine/glutamate antiporter system x(c)(-) in health and disease: from molecular mechanisms to novel therapeutic opportunities. Antioxidants & redox signaling. 2013;18:522–55. doi: 10.1089/ars.2011.4391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Bianchi MG, Bardelli D, Chiu M. et al. Changes in the expression of the glutamate transporter EAAT3/EAAC1 in health and disease. Cellular and molecular life sciences: CMLS. 2014;71:2001–15. doi: 10.1007/s00018-013-1484-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Scalise M, Console L, Cosco J. et al. ASCT1 and ASCT2: Brother and Sister? SLAS discovery: advancing life sciences R & D. 2021;26:1148–63. doi: 10.1177/24725552211030288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Bonifácio VDB, Pereira SA, Serpa J. et al. Cysteine metabolic circuitries: druggable targets in cancer. British journal of cancer. 2021;124:862–79. doi: 10.1038/s41416-020-01156-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Davidson SM, Jonas O, Keibler MA. et al. Direct evidence for cancer-cell-autonomous extracellular protein catabolism in pancreatic tumors. Nature medicine. 2017;23:235–41. doi: 10.1038/nm.4256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Mosharov E, Cranford MR, Banerjee R. The quantitatively important relationship between homocysteine metabolism and glutathione synthesis by the transsulfuration pathway and its regulation by redox changes. Biochemistry. 2000;39:13005–11. doi: 10.1021/bi001088w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Stipanuk MH, Dominy JE Jr, Lee JI. et al. Mammalian cysteine metabolism: new insights into regulation of cysteine metabolism. The Journal of nutrition. 2006;136:1652s–9s. doi: 10.1093/jn/136.6.1652S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Hanigan MH, Ricketts WA. Extracellular glutathione is a source of cysteine for cells that express gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. Biochemistry. 1993;32:6302–6. doi: 10.1021/bi00075a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Poursaitidis I, Wang X, Crighton T. et al. Oncogene-Selective Sensitivity to Synchronous Cell Death following Modulation of the Amino Acid Nutrient Cystine. Cell reports. 2017;18:2547–56. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.02.054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Pompella A, Visvikis A, Paolicchi A. et al. The changing faces of glutathione, a cellular protagonist. Biochemical pharmacology. 2003;66:1499–503. doi: 10.1016/s0006-2952(03)00504-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Paul BD, Sbodio JI, Snyder SH. Cysteine Metabolism in Neuronal Redox Homeostasis. Trends in pharmacological sciences. 2018;39:513–24. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2018.02.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Yu X, Long YC. Crosstalk between cystine and glutathione is critical for the regulation of amino acid signaling pathways and ferroptosis. Scientific reports. 2016;6:30033. doi: 10.1038/srep30033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Wu G, Fang YZ, Yang S. et al. Glutathione metabolism and its implications for health. The Journal of nutrition. 2004;134:489–92. doi: 10.1093/jn/134.3.489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Zou S, Shimizu T, Shimizu S. et al. Possible role of hydrogen sulfide as an endogenous relaxation factor in the rat bladder and prostate. Neurourology and urodynamics. 2018;37:2519–26. doi: 10.1002/nau.23788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Kohl JB, Mellis AT, Schwarz G. Homeostatic impact of sulfite and hydrogen sulfide on cysteine catabolism. British journal of pharmacology. 2019;176:554–70. doi: 10.1111/bph.14464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Pascale RM, Peitta G, Simile MM, Alterations of Methionine Metabolism as Potential Targets for the Prevention and Therapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Medicina (Kaunas, Lithuania) 2019. 55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 49.Adeva-Andany MM, López-Maside L, Donapetry-García C. et al. Enzymes involved in branched-chain amino acid metabolism in humans. Amino acids. 2017;49:1005–28. doi: 10.1007/s00726-017-2412-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Shimada K, Skouta R, Kaplan A. et al. Global survey of cell death mechanisms reveals metabolic regulation of ferroptosis. Nature chemical biology. 2016;12:497–503. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.2079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Bersuker K, Hendricks JM, Li Z. et al. The CoQ oxidoreductase FSP1 acts parallel to GPX4 to inhibit ferroptosis. Nature. 2019;575:688–92. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1705-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Doll S, Freitas FP, Shah R. et al. FSP1 is a glutathione-independent ferroptosis suppressor. Nature. 2019;575:693–8. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1707-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Kang YP, Torrente L, Falzone A, Cysteine dioxygenase 1 is a metabolic liability for non-small cell lung cancer. eLife. 2019. 8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 54.Dominy JE Jr, Hwang J, Stipanuk MH. Overexpression of cysteine dioxygenase reduces intracellular cysteine and glutathione pools in HepG2/C3A cells. American journal of physiology Endocrinology and metabolism. 2007;293:E62–9. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00053.2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Jeschke J, O'Hagan HM, Zhang W. et al. Frequent inactivation of cysteine dioxygenase type 1 contributes to survival of breast cancer cells and resistance to anthracyclines. Clinical cancer research: an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. 2013;19:3201–11. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-3751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Hao S, Yu J, He W. et al. Cysteine Dioxygenase 1 Mediates Erastin-Induced Ferroptosis in Human Gastric Cancer Cells. Neoplasia (New York, NY) 2017;19:1022–32. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2017.10.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Cao J, Chen X, Jiang L. et al. DJ-1 suppresses ferroptosis through preserving the activity of S-adenosyl homocysteine hydrolase. Nature communications. 2020;11:1251. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15109-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Hayano M, Yang WS, Corn CK. et al. Loss of cysteinyl-tRNA synthetase (CARS) induces the transsulfuration pathway and inhibits ferroptosis induced by cystine deprivation. Cell death and differentiation. 2016;23:270–8. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2015.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Zhu J, Berisa M, Schwörer S. et al. Transsulfuration Activity Can Support Cell Growth upon Extracellular Cysteine Limitation. Cell metabolism. 2019;30:865–76.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2019.09.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Sawa T, Motohashi H, Ihara H, Enzymatic Regulation and Biological Functions of Reactive Cysteine Persulfides and Polysulfides. Biomolecules. 2020. 10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 61.Koike S, Ogasawara Y, Shibuya N. et al. Polysulfide exerts a protective effect against cytotoxicity caused by t-buthylhydroperoxide through Nrf2 signaling in neuroblastoma cells. FEBS letters. 2013;587:3548–55. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2013.09.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Kimura H. Signalling by hydrogen sulfide and polysulfides via protein S-sulfuration. British journal of pharmacology. 2020;177:720–33. doi: 10.1111/bph.14579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Shimada K, Stockwell BR. tRNA synthase suppression activates de novo cysteine synthesis to compensate for cystine and glutathione deprivation during ferroptosis. Molecular & cellular oncology. 2016;3:e1091059. doi: 10.1080/23723556.2015.1091059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Alvarez SW, Sviderskiy VO, Terzi EM. et al. NFS1 undergoes positive selection in lung tumours and protects cells from ferroptosis. Nature. 2017;551:639–43. doi: 10.1038/nature24637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Homma T, Kobayashi S, Fujii J. Cysteine preservation confers resistance to glutathione-depleted cells against ferroptosis via CDGSH iron sulphur domain-containing proteins (CISDs) Free radical research. 2020;54:397–407. doi: 10.1080/10715762.2020.1780229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Zhang Y, Swanda RV, Nie L. et al. mTORC1 couples cyst(e)ine availability with GPX4 protein synthesis and ferroptosis regulation. Nature communications. 2021;12:1589. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21841-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Muir A, Danai LV, Gui DY, Environmental cystine drives glutamine anaplerosis and sensitizes cancer cells to glutaminase inhibition. eLife. 2017. 6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 68.Lian G, Gnanaprakasam JR, Wang T, Glutathione de novo synthesis but not recycling process coordinates with glutamine catabolism to control redox homeostasis and directs murine T cell differentiation. eLife. 2018. 7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 69.Zhang X, Huang Z, Xie Z. et al. Homocysteine induces oxidative stress and ferroptosis of nucleus pulposus via enhancing methylation of GPX4. Free radical biology & medicine. 2020;160:552–65. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.08.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Zhang J, Pavlova NN, Thompson CB. Cancer cell metabolism: the essential role of the nonessential amino acid, glutamine. The EMBO journal. 2017;36:1302–15. doi: 10.15252/embj.201696151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Le A, Lane AN, Hamaker M. et al. Glucose-independent glutamine metabolism via TCA cycling for proliferation and survival in B cells. Cell metabolism. 2012;15:110–21. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2011.12.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Zhdanov AV, Waters AH, Golubeva AV. et al. Availability of the key metabolic substrates dictates the respiratory response of cancer cells to the mitochondrial uncoupling. Biochimica et biophysica acta. 2014;1837:51–62. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2013.07.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Metallo CM, Gameiro PA, Bell EL. et al. Reductive glutamine metabolism by IDH1 mediates lipogenesis under hypoxia. Nature. 2011;481:380–4. doi: 10.1038/nature10602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Bernfeld E, Foster DA. Glutamine as an Essential Amino Acid for KRas-Driven Cancer Cells. Trends in endocrinology and metabolism: TEM. 2019;30:357–68. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2019.03.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Hensley CT, Wasti AT, DeBerardinis RJ. Glutamine and cancer: cell biology, physiology, and clinical opportunities. The Journal of clinical investigation. 2013;123:3678–84. doi: 10.1172/JCI69600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Bode BP, Fuchs BC, Hurley BP. et al. Molecular and functional analysis of glutamine uptake in human hepatoma and liver-derived cells. American journal of physiology Gastrointestinal and liver physiology. 2002;283:G1062–73. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00031.2002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Daye D, Wellen KE. Metabolic reprogramming in cancer: unraveling the role of glutamine in tumorigenesis. Seminars in cell & developmental biology. 2012;23:362–9. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2012.02.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Matés JM, Segura JA, Martín-Rufián M. et al. Glutaminase isoenzymes as key regulators in metabolic and oxidative stress against cancer. Current molecular medicine. 2013;13:514–34. doi: 10.2174/1566524011313040005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Yang L, Venneti S, Nagrath D. Glutaminolysis: A Hallmark of Cancer Metabolism. Annual review of biomedical engineering. 2017;19:163–94. doi: 10.1146/annurev-bioeng-071516-044546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Lacey JM, Wilmore DW. Is glutamine a conditionally essential amino acid? Nutrition reviews. 1990;48:297–309. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.1990.tb02967.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Medina MA. Glutamine and cancer. The Journal of nutrition. 2001;131:2539S–42S. doi: 10.1093/jn/131.9.2539S. discussion 50S-1S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Koppula P, Zhuang L, Gan B. Cystine transporter SLC7A11/xCT in cancer: ferroptosis, nutrient dependency, and cancer therapy. Protein & cell. 2021;12:599–620. doi: 10.1007/s13238-020-00789-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Son J, Lyssiotis CA, Ying H. et al. Glutamine supports pancreatic cancer growth through a KRAS-regulated metabolic pathway. Nature. 2013;496:101–5. doi: 10.1038/nature12040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Toda K, Nishikawa G, Iwamoto M, Clinical Role of ASCT2 (SLC1A5) in KRAS-Mutated Colorectal Cancer. International journal of molecular sciences. 2017. 18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 85.Gao M, Jiang X. To eat or not to eat-the metabolic flavor of ferroptosis. Current opinion in cell biology. 2018;51:58–64. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2017.11.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Gao M, Monian P, Quadri N. et al. Glutaminolysis and Transferrin Regulate Ferroptosis. Molecular cell. 2015;59:298–308. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.06.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Wang H, Liu C, Zhao Y. et al. Mitochondria regulation in ferroptosis. European journal of cell biology. 2020;99:151058. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2019.151058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Gao M, Yi J, Zhu J. et al. Role of Mitochondria in Ferroptosis. Molecular cell. 2019;73:354–63.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.10.042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Chen L, Cui H. Targeting Glutamine Induces Apoptosis: A Cancer Therapy Approach. International journal of molecular sciences. 2015;16:22830–55. doi: 10.3390/ijms160922830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Wang JB, Erickson JW, Fuji R. et al. Targeting mitochondrial glutaminase activity inhibits oncogenic transformation. Cancer cell. 2010;18:207–19. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2010.08.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Zimmermann SC, Duvall B, Tsukamoto T. Recent Progress in the Discovery of Allosteric Inhibitors of Kidney-Type Glutaminase. Journal of medicinal chemistry. 2019;62:46–59. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b00327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Huang Q, Stalnecker C, Zhang C. et al. Characterization of the interactions of potent allosteric inhibitors with glutaminase C, a key enzyme in cancer cell glutamine metabolism. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2018;293:3535–45. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.810101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Wang Q, Hardie RA, Hoy AJ. et al. Targeting ASCT2-mediated glutamine uptake blocks prostate cancer growth and tumour development. The Journal of pathology. 2015;236:278–89. doi: 10.1002/path.4518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Lu J, Chen M, Tao Z. et al. Effects of targeting SLC1A5 on inhibiting gastric cancer growth and tumor development in vitro and in vivo. Oncotarget. 2017;8:76458–67. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.19479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.van Geldermalsen M, Wang Q, Nagarajah R. et al. ASCT2/SLC1A5 controls glutamine uptake and tumour growth in triple-negative basal-like breast cancer. Oncogene. 2016;35:3201–8. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Sivanand S, Vander Heiden MG. Emerging Roles for Branched-Chain Amino Acid Metabolism in Cancer. Cancer cell. 2020;37:147–56. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2019.12.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Kim DK, Kim IJ, Hwang S. et al. System L-amino acid transporters are differently expressed in rat astrocyte and C6 glioma cells. Neuroscience research. 2004;50:437–46. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2004.08.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Peng H, Wang Y, Luo W. Multifaceted role of branched-chain amino acid metabolism in cancer. Oncogene. 2020;39:6747–56. doi: 10.1038/s41388-020-01480-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Hall TR, Wallin R, Reinhart GD. et al. Branched chain aminotransferase isoenzymes. Purification and characterization of the rat brain isoenzyme. The Journal of biological chemistry. 1993;268:3092–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Hattori A, Tsunoda M, Konuma T. et al. Cancer progression by reprogrammed BCAA metabolism in myeloid leukaemia. Nature. 2017;545:500–4. doi: 10.1038/nature22314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Raffel S, Falcone M, Kneisel N. et al. BCAT1 restricts αKG levels in AML stem cells leading to IDHmut-like DNA hypermethylation. Nature. 2017;551:384–8. doi: 10.1038/nature24294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Zhenyukh O, Civantos E, Ruiz-Ortega M. et al. High concentration of branched-chain amino acids promotes oxidative stress, inflammation and migration of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells via mTORC1 activation. Free radical biology & medicine. 2017;104:165–77. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.01.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Wang Y, Zhang J, Ren S. et al. Branched-Chain Amino Acid Metabolic Reprogramming Orchestrates Drug Resistance to EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Cell reports. 2019;28:512–25.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.06.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Wang K, Zhang Z, Tsai HI. et al. Branched-chain amino acid aminotransferase 2 regulates ferroptotic cell death in cancer cells. Cell death and differentiation. 2021;28:1222–36. doi: 10.1038/s41418-020-00644-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Platten M, Nollen EAA, Röhrig UF. et al. Tryptophan metabolism as a common therapeutic target in cancer, neurodegeneration and beyond. Nature reviews Drug discovery. 2019;18:379–401. doi: 10.1038/s41573-019-0016-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Cervenka I, Agudelo LZ, Ruas JL. Kynurenines: Tryptophan's metabolites in exercise, inflammation, and mental health. Science (New York, NY) 2017. 357. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 107.Opitz CA, Wick W, Steinman L. et al. Tryptophan degradation in autoimmune diseases. Cellular and molecular life sciences: CMLS. 2007;64:2542–63. doi: 10.1007/s00018-007-7140-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Prendergast GC, Malachowski WJ, Mondal A. et al. Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase and Its Therapeutic Inhibition in Cancer. International review of cell and molecular biology. 2018;336:175–203. doi: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2017.07.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Zeng T, Deng G, Zhong W. et al. Indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase 1enhanceshepatocytes ferroptosis in acute immune hepatitis associated with excess nitrative stress. Free radical biology & medicine. 2020;152:668–79. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.01.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Zeitler L, Fiore A, Meyer C, Anti-ferroptotic mechanism of IL4i1-mediated amino acid metabolism. eLife. 2021. 10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 111.Qiu F, Huang J, Sui M. Targeting arginine metabolism pathway to treat arginine-dependent cancers. Cancer letters. 2015;364:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.04.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Xiong L, Teng JL, Botelho MG. et al. Arginine Metabolism in Bacterial Pathogenesis and Cancer Therapy. International journal of molecular sciences. 2016;17:363. doi: 10.3390/ijms17030363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Zhou L, Sun CB, Liu C. et al. Upregulation of arginase activity contributes to intracellular ROS production induced by high glucose in H9c2 cells. International journal of clinical and experimental pathology. 2015;8:2728–36. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Qiu Y, Yang X, Wang L, L-Arginine Inhibited Inflammatory Response and Oxidative Stress Induced by Lipopolysaccharide via Arginase-1 Signaling in IPEC-J2 Cells. International journal of molecular sciences. 2019. 20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 115.Sun L, Song L, Wan Q. et al. cMyc-mediated activation of serine biosynthesis pathway is critical for cancer progression under nutrient deprivation conditions. Cell research. 2015;25:429–44. doi: 10.1038/cr.2015.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Nikiforov MA, Chandriani S, O'Connell B. et al. A functional screen for Myc-responsive genes reveals serine hydroxymethyltransferase, a major source of the one-carbon unit for cell metabolism. Molecular and cellular biology. 2002;22:5793–800. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.16.5793-5800.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Ye J, Fan J, Venneti S. et al. Serine catabolism regulates mitochondrial redox control during hypoxia. Cancer discovery. 2014;4:1406–17. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-14-0250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Locasale JW, Grassian AR, Melman T. et al. Phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase diverts glycolytic flux and contributes to oncogenesis. Nature genetics. 2011;43:869–74. doi: 10.1038/ng.890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Possemato R, Marks KM, Shaul YD. et al. Functional genomics reveal that the serine synthesis pathway is essential in breast cancer. Nature. 2011;476:346–50. doi: 10.1038/nature10350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.DeNicola GM, Chen PH, Mullarky E. et al. NRF2 regulates serine biosynthesis in non-small cell lung cancer. Nature genetics. 2015;47:1475–81. doi: 10.1038/ng.3421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Sen N, Cross AM, Lorenzi PL. et al. EWS-FLI1 reprograms the metabolism of Ewing sarcoma cells via positive regulation of glutamine import and serine-glycine biosynthesis. Molecular carcinogenesis. 2018;57:1342–57. doi: 10.1002/mc.22849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Chepikova OE, Malin D, Strekalova E. et al. Lysine oxidase exposes a dependency on the thioredoxin antioxidant pathway in triple-negative breast cancer cells. Breast cancer research and treatment. 2020;183:549–64. doi: 10.1007/s10549-020-05801-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Louandre C, Ezzoukhry Z, Godin C. et al. Iron-dependent cell death of hepatocellular carcinoma cells exposed to sorafenib. International journal of cancer. 2013;133:1732–42. doi: 10.1002/ijc.28159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Yang WS, SriRamaratnam R, Welsch ME. et al. Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4. Cell. 2014;156:317–31. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.12.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Lisewski AM, Quiros JP, Ng CL. et al. Supergenomic network compression and the discovery of EXP1 as a glutathione transferase inhibited by artesunate. Cell. 2014;158:916–28. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.07.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Ji JX, Cochrane DR, Tessier-Cloutier B. et al. Arginine Depletion Therapy with ADI-PEG20 Limits Tumor Growth in Argininosuccinate Synthase-Deficient Ovarian Cancer, Including Small-Cell Carcinoma of the Ovary, Hypercalcemic Type. Clinical cancer research: an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. 2020;26:4402–13. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-1905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Steggerda SM, Bennett MK, Chen J. et al. Inhibition of arginase by CB-1158 blocks myeloid cell-mediated immune suppression in the tumor microenvironment. Journal for immunotherapy of cancer. 2017;5:101. doi: 10.1186/s40425-017-0308-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Todorova VK, Kaufmann Y, Luo S. et al. Tamoxifen and raloxifene suppress the proliferation of estrogen receptor-negative cells through inhibition of glutamine uptake. Cancer chemotherapy and pharmacology. 2011;67:285–91. doi: 10.1007/s00280-010-1316-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Yuan H, Li X, Zhang X. et al. CISD1 inhibits ferroptosis by protection against mitochondrial lipid peroxidation. Biochemical and biophysical research communications. 2016;478:838–44. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.08.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Pokrovsky VS, Chepikova OE, Davydov DZ. et al. Amino Acid Degrading Enzymes and their Application in Cancer Therapy. Current medicinal chemistry. 2019;26:446–64. doi: 10.2174/0929867324666171006132729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]