Figure 1. ROS modulation of signaling pathways in bone cells.
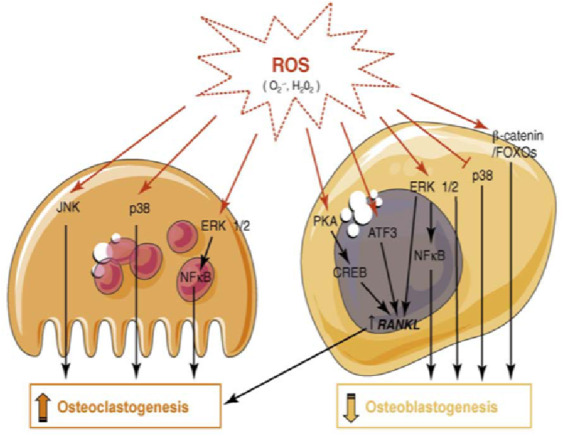
ROS promote bone loss by inhibiting osteoblast differentiation and enhancing osteoclastogenesis. ROS induced bone resorption occurs directly or indirectly (increased RANKL expression) through the modulation of kinases and transcription factor activities in both osteoclasts and osteoblasts. Figure reprinted from Trends in Molecular Medicine, Vol 15, Wauquier F, Leotoing L, Coxam V, Guicheux J, Wittrant Y., Oxidative stress in bone remodelling and disease, 2009 Oct;15(10):468-77. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2009.08.004.
