Abstract
mTOR activation is a hallmark of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) and is associated with resistance to glucocorticoid (GC)-based chemotherapy. We previously showed that altering redox homeostasis primes T-ALL cells to GC-induced apoptosis. Here we investigated the connection between the mTOR pathway and redox homeostasis using pharmacological inhibitors and gene silencing.
In vitro studies performed on T-ALL cell lines and CG-resistant patient-derived T-ALL xenograft (PDX) cells showed that the mTOR inhibitor everolimus increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels, augmented lipid peroxidation, and activated the ROS-controlled transcription factor NRF2. These effects were accompanied by a decrease in the levels of NADPH and of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD), the rate-limiting enzyme of the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP), which is a major source of cytosolic NADPH needed for maintaining the cellular ROS-scavenging capacity. The mTOR inhibitor everolimus induced mitochondrial inner membrane depolarization and dose-dependent apoptosis of T-ALL cells, but did not kill normal T-cells. Importantly, the combination of everolimus and the GC dexamethasone had a synergistic effect on killing T-ALL cells. The effects of mTOR inhibition were blunted by ROS scavengers and phenocopied by siRNA-mediated G6PD silencing. In vivo studies of NOD/SCID mice inoculated with refractory T-ALL PDX demonstrated that everolimus overcame dexamethasone resistance in conditions of high tumor burden that mimicked the clinical setting of acute leukemia.
These findings provide insight into the crosstalk between mTOR and ROS homeostasis in T-ALL cells and furnish mechanistic evidence to support the combination of glucocorticoids with mTOR inhibitors as a therapeutic avenue for treating refractory T-ALL.
Keywords: T-ALL, mTOR, G6PD, ROS
Graphical abstract
1. Introduction
T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) is an aggressive neoplasm that accounts for 15% of pediatric lymphoblastic leukemia cases [1]. Although recent risk-adapted therapy protocols have significantly improved the outcome for most T-ALL patients, approximately 25% remain incurable, and the aggressive high-dose chemotherapy regimens employed are burdened with severe acute toxicities and long-term undesired effects [1,2]. Glucocorticoids (GC) are the cornerstone of T-ALL therapy, and response to GC is a predictor of T-ALL patient outcome [3]. Hence, GC resistance is a key hurdle to successful treatment of T-ALL. Primary tumor cells from T-ALL patients frequently harbor increased levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) [4,5] and leukemic T-cells are selectively vulnerable to further increases in ROS [[6], [7], [8]]. We previously showed that the combination of NS1619, a benzimidazolone that increases mitochondrial ROS, with dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), which blunts ROS scavenging through inhibition of the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP), sensitized T-ALL cells to death induced by dexamethasone, without harming normal human thymocytes [9]. DHEA alone produced a long-lasting increase in ROS and efficiently killed T-ALL cells, while NS1619 alone had transient effects on ROS and modest effects on cell death, suggesting that T-ALL cells are highly dependent on PPP fueling for their survival [9].
T-ALL cells often present activation of the mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway [[10], [11], [12], [13]], a key cellular hub connecting nutrient availability and energy sensing, cell growth and survival pathways [14]. Elevated expression of the MTOR gene (coding for mTOR, a serine/threonine kinase that is key to the pathway) is correlated with failure of T-ALL patients to respond to induction chemotherapy [15]. The mTOR kinase participates in two multiprotein complexes termed mTORC1 and mTORC2, which differ in their subunit composition, input signals, substrates controlling downstream effector pathways, and sensitivity to inhibitors [14,16]. Preclinical studies showed that inhibition of the mTOR pathway induces apoptotic death of T-ALL cells and provided an impetus for clinical trials exploring the efficacy of mTOR inhibitors of the rapamycin family in combination with chemotherapy to treat patients with relapsed/refractory disease [17].
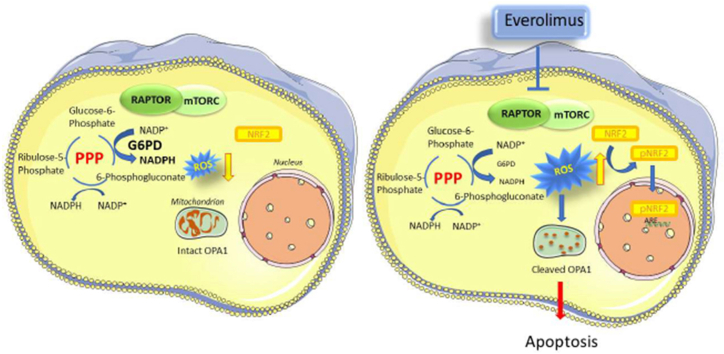
A recent study of tumor cells from relapsed/refractory (R/R) T-ALL patients revealed activation of NRF2 (gene symbol NFE2L2), a transcription factor that controls the cellular responses to oxidative stress [18]. In the present study we investigated the mechanistic links between mTOR and ROS homeostasis in GC-resistant T-ALL cells and found that mTOR inhibition reduced the levels of the PPP enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD), resulting in a decrease in the levels of NADPH, increased ROS levels, and death of T-ALL cells (see Graphical Abstract).
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Bioinformatic analyses
Published gene expression data (GSE87865) obtained with Affymetrix Human Genome U133 Plus 2.0 Arrays for a T-ALL patient cohort [18] were analyzed. After quality control, a total of 17 samples of therapy-resistant (R) T-ALL and 22 samples of therapy-sensitive (S) T-ALL were considered for further analyses. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) was performed on differentially expressed genes as identified by Significance Analysis of Microarrays (SAM) using the default False Discovery Rate (FDR). GSEA included custom gene sets for mTOR/ROS homeostasis and for NRF2 transcriptional targets; the custom NRF2 list was developed by merging the “NRF2_Q4” and “NRF2_01” gene sets (both available on the GSEA web site, www.gsea-msigdb.org) with a list of validated NRF2 target genes [19,20]. A detailed description of the methods, bioinformatic pipeline, custom gene sets, and results is provided in the Supplemental Bioinformatic Analyses section.
2.2. T-ALL samples and cell lines
Primary samples from T-ALL patients were obtained in the context of the AIEOP ALL 2009 protocol in accordance with the Code of Ethics of the World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki. Informed consent was obtained from patients or their legal representatives. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from healthy donors were isolated by Ficoll-Paque Plus (GE Healthcare) gradient centrifugation using a standard protocol. Primary T-ALL cells, PBMC and the T-ALL-derived cell lines Jurkat and TALL-1 were cultured in RPMI 1640 medium (Sigma-Aldrich) supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum (FCS), 2 mM l-glutamine, 100 units/mL penicillin, and 20 units/mL streptomycin (complete RPMI).
Patient-derived xenograft (PDX) cells from primary leukemia cells of pediatric T-ALL patients were propagated in NOD/SCID mice as previously described [21]. PDX cells were re-isolated from spleens of the host mice and either used for short-term in vitro drug testing or re-inoculated into groups of NOD/SCID mice for in vivo experiments (see below). The PDX cells used in the present study are not adapted to growth in vitro and can be cultured for a limited period (2–3 days).
2.3. In vitro drug treatments
Cells (1x106/ml) were treated for 24 h with either ethanol (0.15% final concentration, control), everolimus (Selleck Chemicals), dexamethasone (Sigma-Aldrich) or everolimus plus dexamethasone at the concentrations indicated in the figures, and then analyzed as described below. In some experiments, the cells were pre-incubated with 500 μM N-acetyl-l-cysteine (NAC, Sigma-Aldrich) for 16 h prior to addition of everolimus and/or dexamethasone.
2.4. Analysis of ROS production in living cells
Cells were incubated with 2.6 μM MitoSOX Red (Thermo Fisher Scientific) for 30 min, and analyzed by flow cytometry using a BD FACSCelesta flow cytometer (BD Biosciences). The mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) values in the live-cell gate were determined with Diva software (BD Biosciences). Changes in ROS were expressed as Fx/F0 ratios, where Fx corresponds to the MFI of each sample, and F0 is the MFI of the “no-drug” control.
2.5. Lipid peroxidation assay
Cells were stained with 2 μM Image-iT lipid peroxidation sensor (Thermo Fisher Scientific) for 30 min and then analyzed with a FACSCelesta flow cytometer. Lipid peroxidation was measured as the ratio between the green signal (oxidized probe, fluorescence emission peak at 510 nm) and the red signal (total probe fluorescence emission peak at 590 nm).
2.6. Immunofluorescence analysis
Cells were fixed with 4% formaldehyde, permeabilized with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS)-0.01% NP40, and incubated for 1 h at 37 °C with rabbit anti-phosphoS40-NRF2 antibody (Abcam, 1:100), mouse anti-cytochrome c (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, 1:300) or anti-Hsp60 Alexa Fluor 647 (BD Biosciences, 1:100) followed by Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated chicken anti-rabbit or goat anti-mouse antibody (Thermo Fisher Scientific, 1:1000) for 45 min at 37 °C. Samples were mounted with an anti-fade reagent (Prolong Gold, Molecular Probes) after a 10-min incubation with Vybrant DyeCycle Ruby Stain (Thermo Fisher Scientific, 1:1000 in PBS) to visualize the nucleus. Images were obtained with a Zeiss LSM510 or Zeiss Airyscan LSM900 confocal microscope. Data were analyzed with ZenBlue software.
2.7. NADPH measurements
NADPH levels were measured using the NADP/NADPH-Glo™ Assay (Promega Corporation), according to the manufacturer's instructions. Briefly, 2x106 T-ALL cells were lysed in 0.2 N NaOH with 1% (w/v) dodecyltrimethylammonium bromide (Sigma-Aldrich). NADP+ was decomposed by heating samples at 60 °C for 30 min. Samples were incubated with Detection Reagent for 60 min in black 96-well plates and luminescence was detected using a Victor microplate reader (PerkinElmer).
2.8. Immunoblotting
Cells were collected, washed with PBS, and then lysed in cell disruption buffer (Ambion) containing inhibitors of phosphatases and proteases (PhosphoSTOP and Complete, Roche). Proteins were separated by SDS/PAGE in 4–20% Tris-HEPES gradient gels (BioRad), and transferred to nitrocellulose membranes (GE Healthcare). The membranes were saturated with 3% bovine serum albumin prepared in TBS (50 mM TRIS-Cl, pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl)-0.01% Tween-20 and then incubated overnight with the following antibodies: mouse anti-OPA1 (BD Biosciences, 1:1000), mouse anti-G6PD (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, 1:1000), rabbit anti-phospho-4EBP (Cell Signaling Technology, 1:1000), rabbit anti-non phospho-4EBP (Cell Signaling Technology, 1:1000), rabbit anti-PARP (Cell Signaling Technology, 1:1000) and rabbit anti-GAPDH (GeneTex International Corp., 1:10000). Membranes were then washed twice and incubated for 1 h with an HRP-conjugated anti-mouse or anti-rabbit antibody (Thermo Fisher Scientific, 1:5000). Chemiluminescent signals were detected using Lite Ablot Turbo (EuroClone) and a Cambridge UVITEC imaging system.
2.9. Measurement of G6PD protein half-life
Jurkat cells were treated with either 10 μM cycloheximide (Sigma-Aldrich) alone, 10 μM cycloheximide + 15 μM everolimus or with 10 μM cycloheximide + 15 μM everolimus + 1 μM Vps34-IN1 (Selleck Chemicals). Cells were harvested in cell disruption buffer at 0, 1, 4, 8 and 12 h after indicated treatments. Lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting to detect G6PD and GAPDH as described above. The G6PD signals measured at the 4 timepoints were scaled against the value at 0 h; resulting values represented the fraction of protein remaining. Protein half-life was calculated through best fitting equations to the data.
2.10. RNA extraction and quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR)
Total RNA was isolated using TRIzol (Thermo Fisher Scientific). RNA samples were treated with DNase I (Thermo Fisher Scientific) for 15 min at room temperature followed by addition of EDTA and incubation at 65 °C for 10 min to inactivate the enzyme. The RNA was reverse-transcribed using Prime Script RT Master Mix (Takara-Bio Inc.). Aliquots of the resulting cDNA were PCR-amplified by using TaqMan Gene Expression Assays (Thermo Fisher Scientific) to detect G6PD and GAPDH mRNAs. The PCR reactions were performed in a LightCycler 480 thermal cycler (Roche) according to the manufacturer's protocol. Relative quantification (RQ) values were calculated using GAPDH as a housekeeper mRNA.
2.11. RNA-seq analysis
Total RNA was isolated from Jurkat and TALL-1 cells after 24 h of treatment with 10 μM everolimus or drug vehicle. The RNA was processed at the University of Padova CRIBI Biotechnology Center for poly-A-enrichment and RNA-seq using an Illumina platform. Approximately 20 million reads per sample were obtained.
The Wald statistical test was performed using DeSeq2 and APEGLM shrinkage [22,23] to identify transcripts whose expression changed upon everolimus treatment (the two cell lines were analyzed separately). Further analyses were carried out only on sequences with statistically and quantitatively significant differences (fold change >2 and adjusted p value < 0.05, Benjamini-Hochberg correction). After annotating sequences with BioMart [24,25], we focused on protein coding genes and discarded the following categories: long intergenic non-protein coding RNA (lncRNA), uncharacterized open reading frames, microRNA, families with sequence similarity, small nucleolar RNA, pseudogenes, divergent transcripts, novel proteins, intronic transcripts, competing endogenous lncRNA, overlapping transcripts.
GSEA [26] was performed after scaling and centering of the data in order to correct for potential differences due to cell line specificity; results indicated enrichment of gene sets for mTOR inhibition, NRF2 and apoptosis.
2.12. Oxygen consumption and mitochondrial membrane potential measurements
Oxygen consumption rates (OCR) were measured using a Seahorse XFe24 Extracellular Flux Analyzer (Agilent). Briefly, 2x105 cells were collected, washed, and suspended in Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium lacking phenol red (DMEM no. D5030, Sigma-Aldrich) supplemented with 10 mM sodium pyruvate (Lonza), 25 mM d-glucose (Sigma-Aldrich), 31 mM NaCl (Sigma-Aldrich), and 2 mM glutamine (EuroClone). The cells were seeded at 100 μl per well in XF cell culture microplates pre-coated with 500 μg/ml poly-l-lysine (Sigma-Aldrich) for 20 min, pelleted at 300 rpm for 2 min without brake to allow adhesion, and preincubated for 30 min at 37 °C with atmospheric CO2 concentration. Before starting the assay, 400 μl of the aforementioned medium were added to each well.
To measure mitochondrial inner membrane potential, cells were incubated with 5 nM tetramethylrhodamine methyl ester (Image-iT TMRM, Invitrogen) for 15 min and then analyzed with a FACSCelesta flow cytometer and Kaluza software (Beckman Coulter Life Sciences).
2.13. Cell viability and death assays
Cell viability was measured using the MTT [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide] conversion assay and a standard protocol. For cell death assays, 2x105 cells were suspended in 200 μl complete RPMI and stained with 400 ng propidium iodide (PI, Sigma-Aldrich) alone or together with 1 μl of Annexin-V tagged with Alexa Fluor 633 or 647 (Thermo Fisher Scientific). After 10 min’ incubation at room temperature, the cells were analyzed by flow cytometry using a FACSCelesta flow cytometer and Kaluza software. Ten thousand ungated events were analyzed. Specific cell death (SCD) was calculated using the following formula: [(% of dead cells in drug-treated sample - % of dead cells in mock-treated control)/(100 - % of dead cells in mock-treated control)] x 100.
2.14. siRNA-mediated knockdown of G6PD, mTOR, Rictor and Raptor
Jurkat cells (5x106) were mixed with 312.5 pmol of Silencer Select siRNA (G6PD#S5446, RAPTOR# S33216, RICTOR#S226000, MTOR/FRAP1#S603 or Silencer Negative Control 1 #4390843, Thermo Fisher Scientific) and electroporated with a Neon transfection system (Thermo Fisher Scientific) using a single 1410 V-30 msec pulse. The electroporated cells were analyzed following overnight culture in complete RPMI containing 30% FCS.
2.15. G6PD complementation assay
Jurkat cells (5x106) were mixed with 3 μg G6PD/pRK5 [a gift from Xiaolu Yang (Addgene plasmid #41521; http://n21.net/addgene:41521:RRID:Addgen_41521) [27]] or pBlueScript plasmid as control and electroporated with a Neon transfection system using a single 1410 V-30 msec pulse. Following overnight culture in complete RPMI containing 30% FCS, cells were treated with everolimus for 24 h and then analyzed for cell death and G6PD expression by immunoblot.
2.16. In vivo experiments using T-ALL PDX in NOD/SCID mice
All procedures involving animals and their care were authorized by the ethics committees of the University of Padova and the Italian Ministry of Health (Authorization n. 876/2018-PR) in compliance with the ARRIVE guidelines and in accordance with European Union directives (86/609/EEC and 2010/63/EU). In vivo experiments were performed on NOD/SCID mice housed in a specific pathogen-free (SPF) facility. The mice were raised in an in-facility breeding colony and maintained in groups of maximum 5 individuals in cages (Allentown IVC, floor area 542 cm2) furnished with sawdust bedding and cardboard tubes to enrich the animals’ environment. Mice received food and water ad libitum. The room temperature was maintained at 22 °C and the light/night cycle was of 12 h. Mice were anesthetized with isoflurane prior to blood sampling and injections. Manipulations were performed by selecting mice in random order. During the experiments, mice were examined daily for signs of distress (e.g. decrease in physical activity or symptoms of drug toxicity).
In vivo experiments were performed with 3 genetically distinct PDX chosen for their in vitro resistance to dexamethasone (PDX9, PDX13 and PDX19, Supplemental Fig. S1). Mice (6-8-week-old females, weighing approximately 20 g) were inoculated with 1x106 PDX cells by injection into the tail vein on day T = 0. One week later, mice were randomized, assigned in blind to the experimental group, tagged to allow their identification, and injected intraperitoneally (IP) with either 50% polyethylene glycol (PEG)/50% H2O (vehicle control), dexamethasone (15 mg/kg), everolimus (4 mg/kg), or with dexamethasone (15 mg/kg) + everolimus (4 mg/kg); treatments were repeated every second day. Blood samples were obtained from the submandibular plexus. The experimental endpoint was chosen to minimise animal suffering. Euthanasia was carried out by administration of CO2 after anaesthesia with isoflurane.
For non-invasive in vivo tracking of tumor cells, 5x106 PDX19 cells were transduced in vitro with a lentiviral vector coding for luciferase and, after 24 h of culture, inoculated into the tail vein of a NOD/SCID mouse. After 15 days, 106 PDX19-luc cells isolated from the spleen were injected into the tail veins of NOD/SCID mice. One week later, the mice were randomly divided into two groups of 10 each and injected intraperitoneally (IP) with dexamethasone or with dexamethasone plus everolimus. Tumor growth was monitored weekly following IP inoculation of a luciferin solution using a Xenogen bioluminescence imaging system.
The initial number of animals required for experiments comparing the effects of dexamethasone, everolimus, and the drug combination was estimated by assuming an effect size = 0.8 for the main effect of each treatment and combinations. Inoculating 8 mice per group, this difference would have been significant with 80% power and 5% significance (three-way ANOVA). Numbers of animals in experiments presented in the study are indicated in the figure legends. The Kaplan-Meier Log-Rank Survival analysis method was applied to data from in vivo experiments. Multiple comparisons were performed using the Bonferroni correction method. Some of the animals inoculated with PDX9 did not engraft the tumour cells and were therefore excluded from the remainder of the experiment.
2.17. In situ analyses of tissue sections from spleens of mice inoculated with T-ALL PDX
Spleens of mice from in vivo experiments were snap-frozen, cryo-sectioned into 5-μm sections, air-dried for 30 min, fixed in 4% formaldehyde for 10 min, rinsed twice in PBS, and permeabilized with PBS-0.01% NP40 for 5 min. G6PD was detected by immunofluorescence using rabbit anti-G6PD antibody (GeneTex International Corp.) followed by Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG (Invitrogen); PI was added to stain nuclei. Images were obtained with a Zeiss LSM510 microscope and a 20X PlanFluo objective; 4-μm optical slices were analyzed.
Apoptosis in spleen sections prepared as described above was detected using the DeadEnd Fluorometric TUNEL System (Promega Corporation). In brief, sections were incubated with 50 μL of the kit's equilibration buffer at room temperature for 10 min, and then with 50 μl of TdT reaction mix (45 μl equilibration buffer, 5 μl nucleotides and 1 μl of rTdT enzyme) at 37 °C for 1 h. The reaction was terminated by immersing the slides in 2X SSC solution for 15 min followed by 2 rinses in PBS. Samples were counterstained with PI solution (1 μg/ml) and immediately analyzed with a Zeiss LSM510 microscope.
2.18. Statistical analysis and graphics
Data from in vitro experiments were analyzed using the Mann-Whitney rank sum test. The Kaplan-Meier Log-Rank Survival analysis method was applied to data from in vivo experiments. Multiple comparisons were performed using the Bonferroni correction method. Statistically significant differences are indicated in the figures (*** indicate p values < 0.001, ** <0.01 and * < 0.05). Graphs were generated using SigmaPlot version 13.0 (Systat Software Inc.). Figures were generated using CorelDraw. The graphical abstract was generated using images from Servier Medical Art (http://smart.servier.com).
3. Results
3.1. T-ALL cells from therapy-resistant patients exhibit an enrichment of transcripts related to mTOR signaling and redox homeostasis
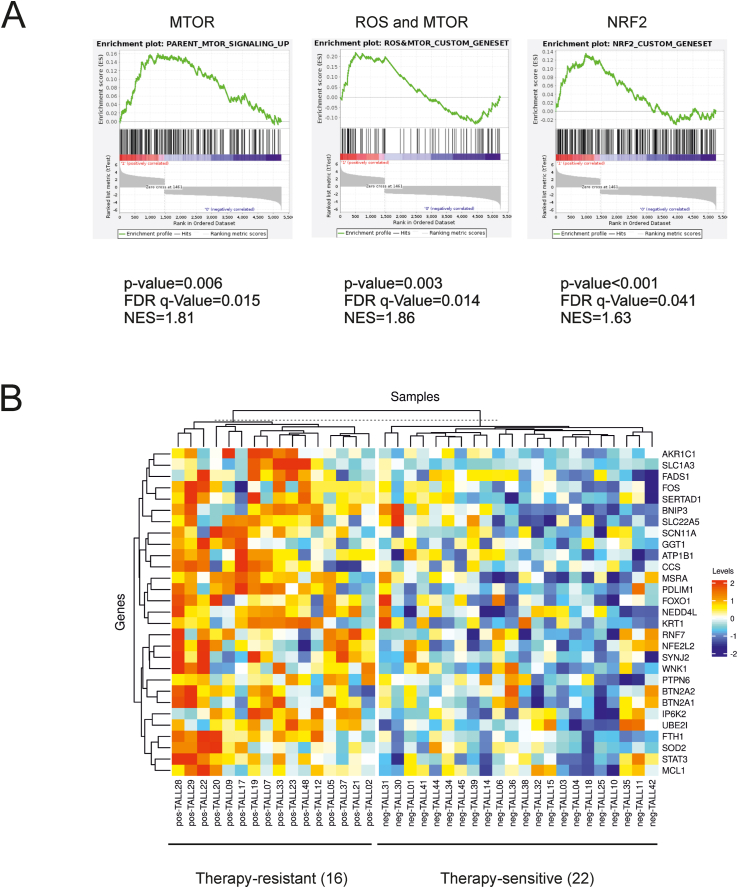
As a first step in investigating a possible link between the mTOR pathway and redox homeostasis in T-ALL, we queried a published gene expression data set [18] of pediatric T-ALL patients who had been identified as responsive or resistant to standard chemotherapy. Following data normalization, quality control, and removal of batch effects, dimensionality-reduction algorithms revealed a clear separation of the two groups of samples (see Supplemental Bioinformatic Analyses). GSEA was then performed with the addition of two custom lists of genes related to mTOR/ROS homeostasis and NRF2 target genes (see Tables 1 and 2 in Supplemental Bioinformatic Analyses). Results showed that gene sets related to mTOR, mTOR/ROS and NRF2 were enriched in samples from therapy-resistant patients (Fig. 1A). Consistent with these findings, many genes belonging to the mTOR/ROS custom gene set were differentially expressed in the two subsets of patients (Fig. 1B).
Fig. 1.
Enrichment of mTOR- and ROS-related transcripts in therapy-resistant T-ALL samples. A published gene expression data set [18] of tumor samples from pediatric T-ALL patients was queried to investigate their transcriptional signatures in relation to their response to therapy. (A) GSEA revealed that gene sets related to mTOR signaling, mTOR/ROS (custom gene set) and NRF2 (custom gene set) were enriched in the samples from therapy-resistant patients. (B) The heatmap shows differentially expressed genes (included in the mTOR/ROS custom geneset) with FDR q-value< 20% and FC > 1.16, corresponding to the 3rd quartile in the distribution of fold changes. Probes were collapsed per gene based on median values. Clustering was performed using metric “Manhattan” and method “complete”.
3.2. mTORC1 inhibition alters redox homeostasis
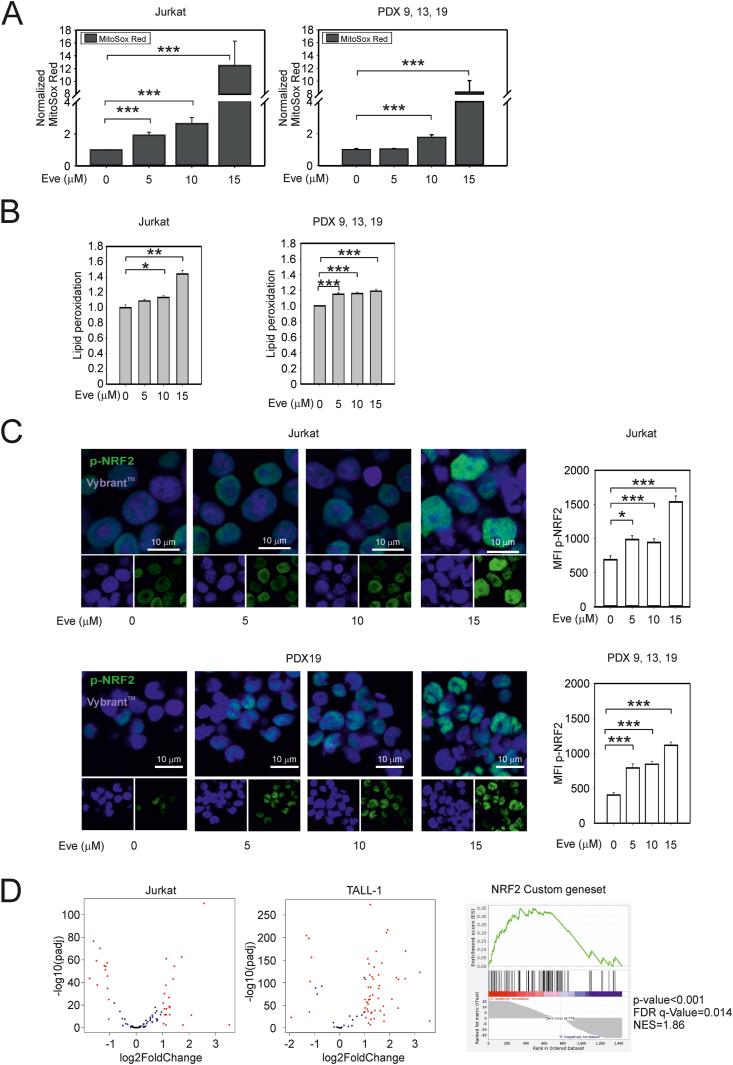
To investigate the links between mTOR and ROS homeostasis, we first tested the effects of the rapamycin analogue everolimus in the T-ALL cell lines Jurkat and TALL-1 (which are highly GC-resistant) and in cultures of 3 patient-derived T-ALL xenografts (PDX9, PDX13, and PDX19) selected from a total of 12 T-ALL PDX for their resistance to dexamethasone (Fig. S1A). The effects of everolimus on ROS were tested using the fluorescent probe MitoSOX Red. Results showed that 24 h’ treatment with everolimus produced an increase in MitoSOX Red fluorescence in Jurkat, TALL-1, and the 3 T-ALL PDX (Fig. 2A and Fig. S1B). Everolimus-treated cells also exhibited an increase in lipid peroxidation (Fig. 2B and Fig. S1B) and nuclear accumulation of phospho-NRF2 (Fig. 2C), a ROS-controlled transcription factor that drives the expression of a roster of genes regulating antioxidant responses [28].
Fig. 2.
Effects of mTORC1 inhibition on redox homeostasis in T-ALL cells. (A) Levels of ROS in everolimus-treated T-ALL cells. The graphs show mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) values for MitoSOX Red fluorescent probe measured after 24 h of everolimus treatment and scaled against MFI values measured in the untreated cells. The left-hand graph shows the mean values and standard error bars of 3 independent experiments, 3 replicates each obtained in Jurkat cells. The right-hand graph shows the mean values and standard error bars of 3 independent experiments, 3 replicates each obtained in T-ALL PDX9, PDX13 and PDX19 cells. (B) Lipid peroxidation in Jurkat cells (left) and PDX cells (right, PDX9, PDX13 and PDX19) treated for 24 h with everolimus. Shown are mean lipid peroxidation values (measured with the Image-iT Lipid peroxidation sensor) and standard error bars from 6 experiments. (C) Nuclear accumulation of phospho-NRF2 in Jurkat cells and PDX19 cells treated for 24 h with everolimus. NRF2 phosphorylated on serine-40 was detected by immunofluorescence (green signal, measured as MFI); Vybrant DyeCycle Ruby Stain (blue signal) was used to visualize the nuclei. The bar graphs show the means of the phosphoS40-NRF2 MFI values and standard error bars from at least 100 cells for each treatment. In Panels A–C, statistically significant differences determined using the Mann-Whitney rank sum test are as follows: ***p value < 0.001; ** <0.01; * <0.05. (D) RNA-Seq data for Jurkat and TALL-1 cell lines after treatment with everolimus. The volcano plots show genes included in the NRF2 custom gene set with a fold change (FC) > 2 and p < 0.05 (Benjamini-Hochberg correction) (everolimus-treated versus control) in at least one of the two cell lines. The right-hand panel shows GSEA of the same custom gene set. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)
RNA-seq analysis of control- and everolimus-treated Jurkat and TALL-1 cells indicated that everolimus induced a broad change in gene expression, and GSEA showed that the custom NRF2 gene set was enriched in the everolimus-treated samples (Fig. 2D). Genes that were differentially expressed in both cell lines were analyzed with the Pathway Commons platform (https://www.pathwaycommons.org; [29]). Results of this analysis showed that many NRF2-related genes controlling antioxidant pathways were upregulated upon treatment with everolimus, while a more restricted subset of NRF2-related genes was downregulated (Table S1). Interestingly, most of the downregulated genes were identified as regulators of the cell cycle, a finding that is consistent with recent studies connecting NRF2 with cell cycle arrest [30].
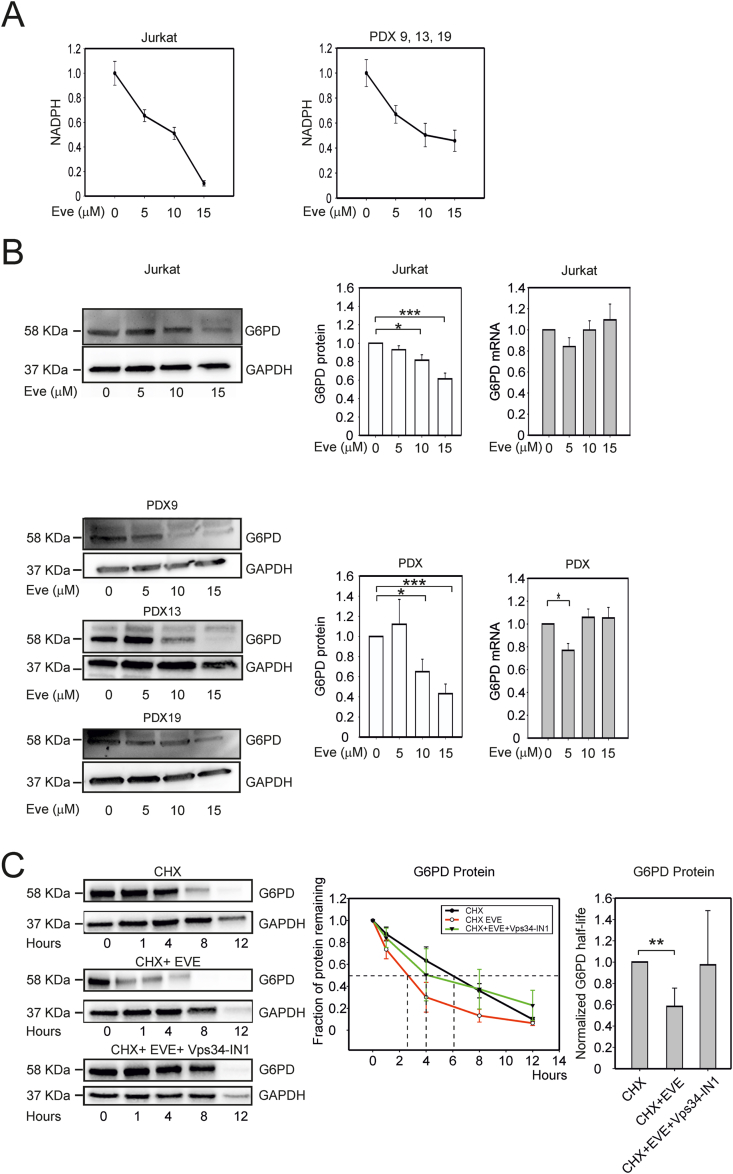
3.3. Inhibition of mTORC1 results in a decrease in the levels of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase and NADPH
Despite upregulation of NRF2-regulated genes, everolimus-treated cells (Jurkat, TALL-1 and PDX) exhibited a dose-dependent depletion of NADPH (Fig. 3A and Fig. S1C). Immunoblotting assays revealed a decrease in the levels of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD; Fig. 3B and Fig. S1D), the key rate-limiting enzyme of the PPP, which is a major contributor to the cytosolic pool of NADPH [31]. Interestingly, the decrease in G6PD protein abundance was not mirrored by a consistent reduction in levels of G6PD mRNA determined by quantitative RT-PCR (Figs. 3B and S1D, right-hand graphs). The G6PD mRNA also did not emerge as differentially expressed in the RNA-Seq analyses, supporting the hypothesis that the decrease in G6PD expression reflected a post-transcriptional effect.
Fig. 3.
Effects of mTORC1 inhibition on NADPH and G6PD levels in T-ALL cells. (A) Changes in NADPH levels upon 24 h' treatment with 5, 10 or 15 μM everolimus in Jurkat cells (left-hand graph) and T-ALL PDX9, PDX13, and PDX19 cells (right-hand graph). NADPH measurements (pmol NADPH per 106 cells) in treated cells were normalized against values measured in untreated cells. Graphs show mean values and standard error bars from 4 independent experiments, 4 replicates each. (B) G6PD expression in Jurkat (upper panels) and PDX cells (lower panels) treated as described in (A). Shown are immunoblots from representative experiments and plots of the mean G6PD/GAPDH ratios and standard error bars from 6 independent experiments. The right-hand graphs show results of qRT-PCR to measure G6PD mRNA; fold changes in G6PD mRNA in treated versus untreated cells (Eve = 0) were calculated using GAPDH as a housekeeping mRNA. Mean values and standard error bars from 6 experiments are shown. (C) Degradation rates of the G6PD and GAPDH proteins after blocking protein synthesis. Jurkat cells were treated with 10 μM cycloheximide (CHX) alone, with 10 μM cycloheximide + 15 μM everolimus (EVE) or with 10 μM cycloheximide + 15 μM everolimus + 1 μM Vps34-IN1 and harvested for immunoblotting to detect G6PD and GAPDH after 0, 1, 4, 8 and 12 h. The left panel shows immunoblots from a representative experiment. The line graph (middle panel) shows G6PD signals scaled against the value measured in the control (t = 0); resulting values represent the fraction of protein remaining in cells treated with cycloheximide alone (black line), cycloheximide + everolimus (red line) or with cycloheximide + everolimus + Vps34-IN1 (green line). The bar graph (right panel) shows mean values (5 experimental repeats) of G6PD half-life in the different treatments scaled against half-life measured in the cycloheximide alone samples; standard error bars are shown. The indicated pairwise comparisons were statistically significant with the Mann-Whitney test; *** indicates p values < 0.001, ** <0.01 and * < 0.05. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)
Consistent with this notion, a comparison of the levels of G6PD after addition of cycloheximide to block de novo protein translation revealed faster turnover of the protein in everolimus-treated cells (half-life 2 h) compared to the control (half-life 6 h) (Fig. 3C). Treatment with the autophagy inhibitor Vps34-IN1 counteracted this effect, suggesting that G6PD degradation induced by everolimus is at least in part mediated by induction of autophagy (Fig. 3C).
Cancer cells from pediatric T-ALL patients frequently carry loss-of-function mutations of PTEN, the main negative regulator of PI3K/AKT [32], a pathway that is tightly connected with mTOR signaling [33]. However, the effects of everolimus on T-ALL cells did not appear to be related to PTEN status, as they were observed both in cells with undetectable levels of PTEN (Jurkat, PDX9 and PDX13) and in PTEN-positive cells (TALL-1 and PDX19) (Fig. S1E and S1F). Interestingly, everolimus did not have major effects on ROS, G6PD or death in normal T-cells (Fig. S1G).
3.4. mTORC1 inhibition reduces T-ALL cell viability
We next investigated the effects of everolimus on T-ALL cell viability using the MTT test, which measures the overall NAD(P)H-dependent oxidoreductase activity, and the propidium iodide (PI) exclusion assay, which tests plasma membrane integrity. These assays thus provide a readout of overall cell viability/metabolic activity and cell death, respectively.
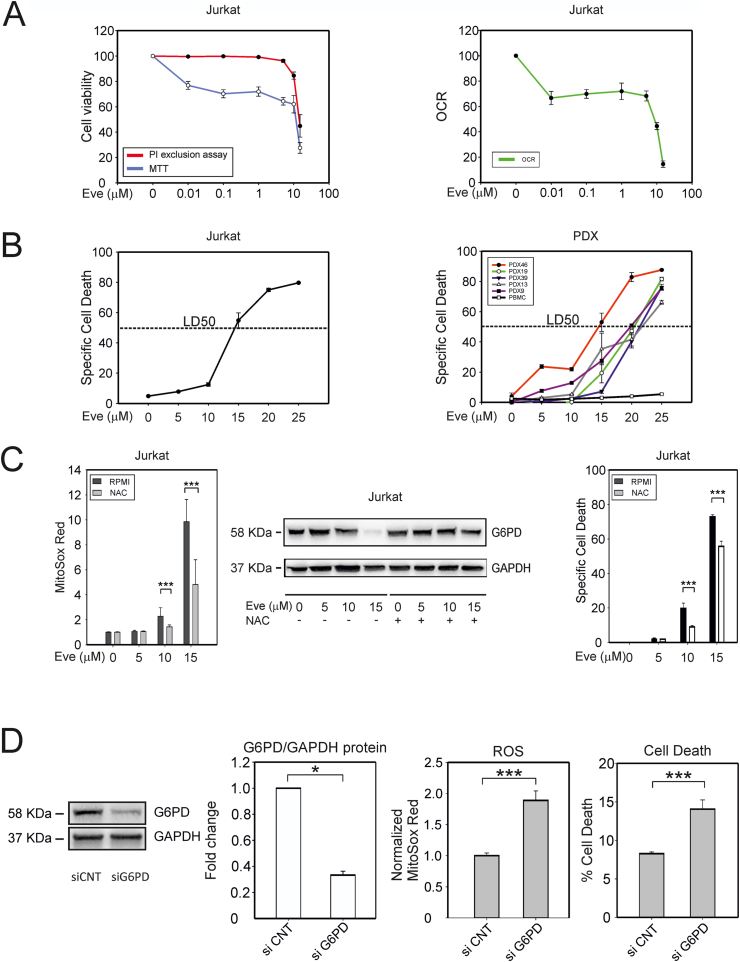
Analyses of Jurkat cells revealed substantial inhibition of MTT conversion with 0.01 μM everolimus (Fig. 4A, left panel), an effect that was paralleled by a reduction in the oxygen consumption rate (OCR) measured with a Seahorse XF Analyzer (Fig. 4A, right panel, Fig. S1H). A higher concentration of everolimus (10 μM) was required to induce Jurkat cell death measured with the PI exclusion test (Fig. 4A, left panel). Quantitative evaluation of the response to different doses of everolimus revealed a lethal dose 50 (LD50) of approximately 15 μM in Jurkat cells (Fig. 4B, left panel). Similar results were obtained for a panel of GC-resistant T-ALL PDX, which exhibited LD50 values ranging from 15 to 20 μM (Fig. 4B, right panel). Importantly, peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) obtained from healthy donors were not killed by everolimus (Fig. 4B, right panel). The effects of everolimus on G6PD protein levels and cell viability/death were largely recapitulated using Torin 1, another mTOR inhibitor (Fig. S2A).
Fig. 4.
Dose-dependent effects of everolimus on T-ALL cell viability. (A) Effects of 24 h' treatment with everolimus on Jurkat cell viability and oxygen consumption rate. The left-hand graph shows cell viability assessed with the MTT assay (which measures NAD(P)H-dependent oxidoreductases; blue line), and the PI exclusion test, which tests plasma membrane integrity (red line). The right-hand graph shows the basal oxygen consumption rate (OCR, a proxy of mitochondrial OXPHOS activity) measured with a Seahorse XF Analyzer. (B) Quantitative evaluation of cell death in response to 24 h' treatment with different doses of everolimus revealed a lethal dose 50 (LD50) of approximately 15 μM in Jurkat (left) and PDX (right) cells. (C) Effects of the ROS scavenger NAC in everolimus-treated Jurkat cells. NAC (500 μM) was added to the cultures 16 h before addition of the indicated concentrations of everolimus; cells were analyzed 24 h later. The left-hand graph shows ROS measured with MitoSOX Red and flow cytometry. Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) data were normalized against the MFI of the control. Shown are mean values and standard error bars from 3 independent experiments, 3 replicates each. The middle panel shows representative immunoblots to detect G6PD and GAPDH proteins. The right-hand graph shows specific cell death detected by PI staining and flow cytometry (3 independent experiments, 3 replicates each). (D) Jurkat cells were electroporated with siRNA against G6PD or with control siRNA, cultured for 24 h, and analyzed for the expression levels of G6PD protein, ROS accumulation using MitoSox Red, and cell death measured as percentages of PI-positive cells.
The indicated pairwise comparisons were statistically significant with the Mann-Whitney test (*** indicates p values < 0.001 and * < 0.05). (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)
Notably, the effects of everolimus on ROS, G6PD protein expression and cell death were counteracted by the ROS scavenger N-acetyl-l-cysteine (NAC), demonstrating their ROS-dependence (Fig. 4C).
To further test the role of G6PD in T-ALL cells, we suppressed its expression by siRNA-mediated knock-down in Jurkat cells. G6PD silencing resulted in significantly increased levels of ROS and cell death (Fig. 4D). Interestingly, silencing of mTOR or Raptor (a component of the mTORC1 complex) likewise resulted in a reduction in G6PD expression and an increase in ROS and cell death, whereas silencing of the mTORC2 component Rictor had no effect (Fig. S2B). Taken together, these observations suggest that the observed effects on the PPP and cell death in Jurkat cells are mediated through mTORC1. Importantly, Jurkat cells transfected with a G6PD expression plasmid were less sensitive to everolimus compared to mock-transfected cells (Fig. S2C). Furthermore, Jurkat cells treated with H2O2 for 24 h exhibited a dose-dependent decrease in G6PD levels that was paralleled by an increase in cell death (Fig. S2D), a finding that reinforces the critical role of ROS in perturbing G6PD levels and triggering cell death.
3.5. mTOR inhibition induces OPA1 cleavage and apoptosis in T-ALL cells
Mitochondria play a central role in controlling intrinsic apoptosis [34]. Given the finding that mTORC1 inhibition by everolimus induced a substantial increase in mitochondrial ROS, we analyzed everolimus-treated cells for apoptosis using bi-parametric AnnexinV/PI labeling and immunoblotting to detect poly ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP), a target of effector caspases. Results showed that everolimus induced a dose-dependent increase in cleavage of PARP (Fig. S4B, left-hand panels) and Annexin V/PI-positive cells (Figs. 5C and S4C) indicating full engagement of the apoptotic machinery.
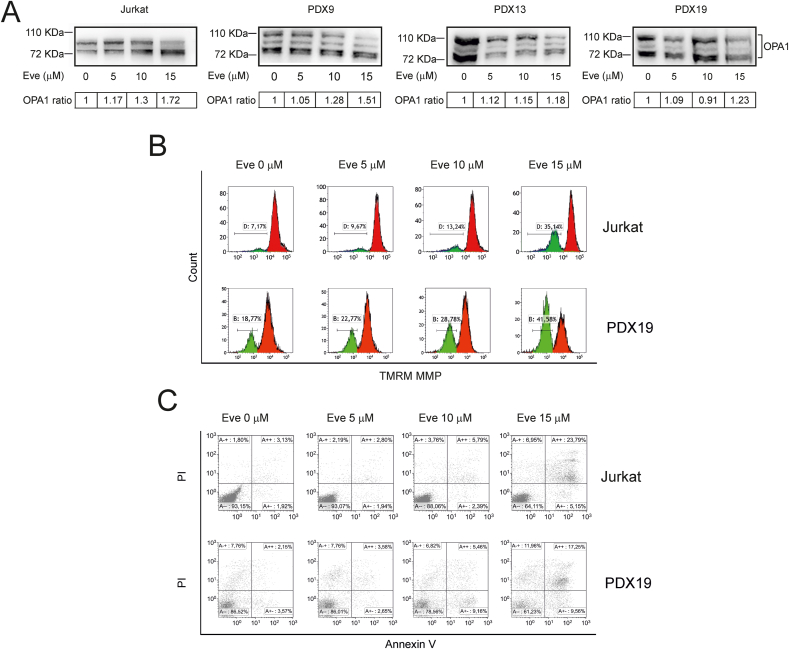
We previously showed that pharmacological inhibition of the PPP primes T-ALL cells to apoptosis by inducing ROS-dependent cleavage of OPA1, a mitochondrial protein that controls mitochondrial fusion, cristae remodeling, respiration and apoptosis [9,35]. Consistent with these findings, everolimus increased mitochondrial fragmentation (Fig. S3A) and cleavage of OPA1 in Jurkat cells and in the GC-resistant T-ALL PDX (Fig. 5A). These effects were accompanied by mitochondrial depolarization measured using the fluorescent probe tetramethylrhodamine methyl ester (TMRM) (Fig. 5B and Fig. S3B).
Fig. 5.
OPA1 cleavage and apoptotic death of T-ALL cells induced by everolimus. Jurkat and T-ALL PDX cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of everolimus for 24 h. (A) Detection of OPA1 cleavage. Shown are representative immunoblots of OPA1 isoforms in Jurkat cells and PDX cells; OPA1 ratios were calculated by dividing the intensity of the cleaved OPA1 bands by the intensity of all OPA1 bands and scaled against the value obtained for the untreated sample. (B) Changes in mitochondrial membrane potential. Control and everolimus-treated Jurkat and PDX19 cells were incubated with 5 nM TMRM for 15 min and analyzed by flow cytometry. Resulting histograms show a dose-dependent increase in the number of depolarized cells (gate B). (C) Apoptosis measurements. Scatter plots show flow cytometry analyses of Jurkat and PDX19 cells stained with Annexin V/PI.
A time course analysis indicated that the rate of OPA1 cleavage was maximal in the first hour, while release of cytochrome c from mitochondria reached its maximum rate between 2 and 4 h (Fig. S4A), thus supporting the notion that proteolytic processing of OPA1 precedes massive cytochrome c release and commitment to apoptosis.
As a control to monitor the extent of mTORC1 inhibition, we measured phosphorylation of 4EBP, one of the principal targets of this complex [36,37]. Results showed substantial loss of 4EBP phosphorylation at the highest concentration of everolimus tested (15 μM) (Fig. S4B, right-hand panels). This observation suggests that the effect of everolimus on cell death is likely to be due to inhibition of mTORC1 rather than to off-target effects.
Furthermore, cell-cycle analysis of Jurkat cells showed that everolimus also produced a reduction in the S-phase fraction (Fig. S4D).
3.6. Everolimus overcomes dexamethasone resistance in vitro
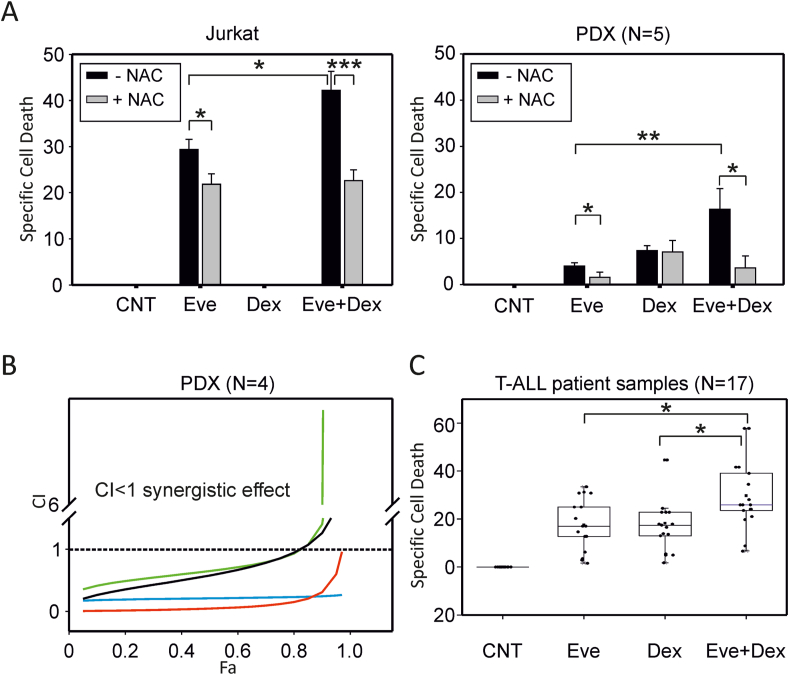
As resistance to GC is a major hurdle to the success of T-ALL chemotherapy, we next investigated whether everolimus may overcome resistance to dexamethasone in our panel of T-ALL cells. Results showed that while Jurkat cells were entirely refractory to dexamethasone, they did respond to everolimus, and the combination of dexamethasone and everolimus resulted in a significant increase in cell death (Fig. 6A, left panel; Fig. S5). Consistent with these findings, knockdown of G6PD resulted in a small but statistically significant increase in death of Jurkat cells exposed to dexamethasone (Fig. S6).
Fig. 6.
Everolimus overcomes dexamethasone resistance in vitro. (A) Specific cell death after 24 h' treatment with everolimus (Eve, 10 μM), dexamethasone (Dex, 1 μM) or both drugs (Eve + Dex) in the presence (+) or absence (−) of NAC (500 μM) measured in Jurkat cells (3 independent experiments, 3 replicates each) and PDX 9, 13, 19, 39 and 46 (3 replicates each); mean values and standard error bars are shown. (B) The combination index of everolimus and dexamethasone in PDX 9, 19, 39 and 46 (black, red, blue and green line, respectively) was calculated using CompuSyn software. The FA (fraction affected) was calculated using specific cell death values measured as percentages of PI-positive cells. It was not possible to calculate the combination index for PDX13, as it was refractory to dexamethasone-induced cell death. (C) Specific cell death after 24 h' treatment with everolimus (Eve, 10 μM), dexamethasone (Dex, 1 μM) or both drugs (Eve + Dex) in primary tumor cells from T-ALL patients (N = 17); mean values and standard error bars are shown. The indicated pairwise comparisons were statistically significant with the Mann-Whitney test; *** indicate p values < 0.001, ** <0.01 and * < 0.05. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)
T-ALL PDX exhibited a weak response to dexamethasone and everolimus as single agents, but their combination resulted in a significant increase in cell death (Fig. 6A, right panel). Pre-exposure to NAC blunted the response of Jurkat and PDX cells to the drug combination (Fig. 6A, compare grey and black bars). Isobologram analysis [38,39] indicated the synergy of dexamethasone and everolimus in T-ALL PDX cells (Fig. 6B). As Jurkat cells are refractory to dexamethasone alone, it was not possible to carry out isobologram analysis on these cells.
Importantly, the effects of everolimus and dexamethasone were confirmed using primary leukemia cells isolated from T-ALL patients (Fig. 6C).
3.7. Everolimus overcomes dexamethasone resistance in vivo
To test the effects of everolimus in vivo, we employed a preclinical model based on NOD/SCID mice inoculated with GC-resistant T-ALL PDX (PDX9, PDX13 and PDX19). When the percentage of circulating CD5+/CD7+ tumor cells reached at least 1% of the PBMC, mice were randomized into 4 groups and treated 3 times/week by intraperitoneal (IP) inoculation of (i) vehicle, (ii) dexamethasone, (iii) everolimus, or (iv) everolimus + dexamethasone. Tumor growth was assessed weekly by measuring the percentage of CD5+/CD7+ tumor cells in the peripheral blood. Mice were sacrificed when the percentage of circulating CD5+/CD7+ cells was >60% of the total PBMC population, and Kaplan–Meier plots were generated considering this endpoint to calculate the event-free survival time (EFS). Results of this analysis showed that the EFS in the everolimus + dexamethasone-treated group was significantly increased compared with the other experimental groups (Fig. S7A). To better visualize their in vivo growth and homing, PDX19 cells were engineered to express luciferase by transduction with a lentiviral vector. Results of in vivo imaging analyses indicated that, in addition to the effect on circulating leukemia cells, the overall tumor burden of mice treated with everolimus + dexamethasone was also greatly reduced compared to mice treated with dexamethasone alone (Fig. S7B).
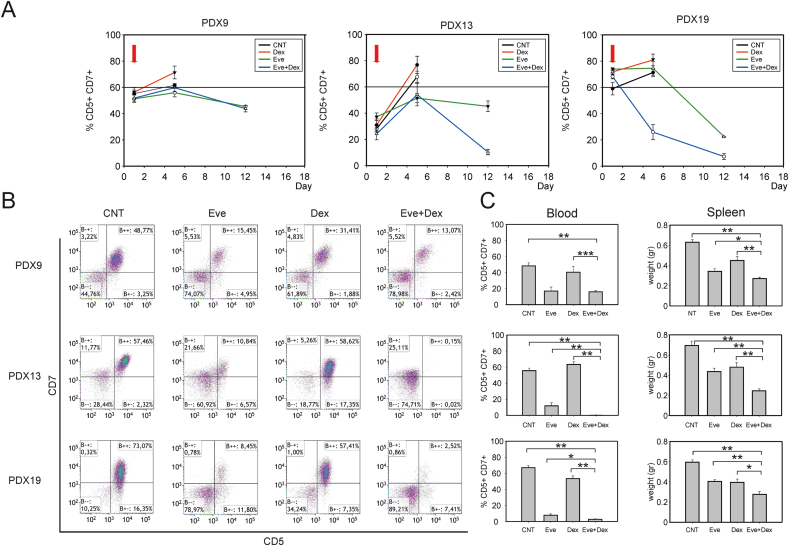
We then modified the in vivo model to mimic the setting of full-blown leukemia by starting the drug treatments when PDX cells in the peripheral blood were more than 30% of the PBMC. As shown in Fig. 7A, everolimus + dexamethasone produced a substantial reduction in circulating CD5+/CD7+ tumor cells. This reduction in tumor burden was paralleled by differences observed at the time of sacrifice, with fewer circulating leukemia cells and lower spleen weights (Fig. 7B and C). Furthermore, the combination of everolimus + dexamethasone substantially increased the time-to-humane endpoint in the full-blown leukemia model (Fig. S7C). To our knowledge, these data provide the first preclinical evidence that this treatment may be effective for debulking full-blown T-ALL.
Fig. 7.
Effects of everolimus on advanced leukemia in vivo. Mice were injected in the tail vein with 1x106 PDX9, PDX13, or PDX19 cells (totals of 24, 20, and 24 mice, respectively). When PDX cells in the peripheral blood reached ≥30% of the PBMC, the mice were treated with either drug vehicle, dexamethasone (15 mg/kg), everolimus (4 mg/kg), or with dexamethasone (15 mg/kg) plus everolimus (4 mg/kg); treatments were repeated every second day. (A) Effects of drug treatments on numbers of circulating PDX cells. The graphs show the percentages of CD5+/CD7+ PDX cells in total PBMC measured over the course of the experiment. The red arrows indicate the beginning of the treatment. (B) Scatter plots show results of flow cytometry analyses to detect tumor cells in peripheral blood at the time of sacrifice. Each scatter plot shows results for one mouse; a reduction in the percentage of events in the B++ quadrant indicates an inhibitory effect of the drug treatment. (C) Bar graphs show the percentages of CD5+/CD7+ PDX cells in total PBMC (left) and spleen weights (right), an indicator of the tumor burden in lymphoid organs. Plotted are mean values and standard error bars from 6 mice in each group. The indicated pairwise comparisons were statistically significant with the Mann-Whitney test (*** indicates p values < 0.001, ** <0.01 and * < 0.05). (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)
Notably, also in this in vivo model, everolimus, alone or in combination with dexamethasone, downregulated G6PD protein expression in tumor cells infiltrating the spleens of inoculated mice (see immunofluorescence analyses of spleen sections in Fig. S8), and induced apoptosis (see TUNEL assay of spleen sections in Fig. S9).
4. Discussion
The present study extends previous investigations of mTOR in T-ALL [17,[40], [41], [42], [43]] by demonstrating its functional intersection with redox homeostasis and cell death pathways. Treatment of T-ALL cells with the mTOR inhibitor everolimus led to accumulation of ROS (Fig. 2), a reduction in the levels of NADPH (Fig. 3A) as well as the crucial PPP enzyme G6PD (Fig. 3B), and enhanced sensitivity to killing by the GC dexamethasone, both in vitro and in vivo (Fig. 6, Fig. 7).
To our knowledge, the data presented here provide the first evidence for the central role of the mTOR pathway in rewiring redox homeostasis through the inhibition of the PPP in T-ALL cells (cell lines, as well as PDX and primary patients’ samples). These findings are supported by results of studies in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) showing a connection between mTOR and G6PD [44].
A connection between mTOR and the PPP was also indicated by results of genomic and gene set enrichment analyses carried out in mouse fibroblasts; these studies identified PPP genes as potential mTOR targets in Tsc1 −/− cells [45]. In this murine model, mTORC1 was shown to activate HIF1α- and SREBP-mediated transcriptional programs, leading to increased levels of the G6PD mRNA [45]. A subsequent study in human prostate cancer cell lines highlighted a central role for androgen receptor signaling in engaging the mTORC-G6PD axis and controlling tumor cell growth and a correlation between G6PD expression and survival in mouse models of prostate cancer driven by PTEN loss [46]. Effects of mTORC1 on G6PD expression were also suggested by a study of glioma cell lines that showed increased expression of G6PD upon shRNA-mediated silencing of Tsc2; while rapamycin did not produce significant effects, Torin 1 reduced G6PD levels in one of the two cell lines under study [47].
Our study shows that blockade of the mTOR pathway led to a reduction in the half-life of G6PD protein, but did not change the levels of G6PD mRNA (Fig. 3B). The reduction in G6PD half-life induced by everolimus was blocked by the autophagy inhibitor Vps34-IN1 (Fig. 3C), a finding that is consistent with the well-established role of mTORC1 in the control of autophagy [16]. A recent study demonstrated the involvement of the ubiquitin ligase TRIM21 in regulation of G6PD protein levels, and a negative correlation between TRIM21 expression and PI3K/AKT activity in several cancer histotypes [48]; the activity and targets of TRIM21 in the context of T-ALL remain to be studied. The mTOR pathway has also been implicated in a mechanism that allows glycolysis-addicted cancer cell lines to escape 2-deoxyglucose-induced blockage of glycolysis by redirecting glucose flux from the PPP back to glycolysis [49].
The present study builds on earlier investigations that employed the mTORC1 inhibitor rapamycin [50] or the dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor BEZ235 [51,52] to overcome GC resistance of T-ALL cells. Gu et al. [50] showed that, in vitro, rapamycin induces G0/G1 cell cycle arrest in GC-resistant T-ALL cell lines and sensitizes the cells to dexamethasone, resulting in a more pronounced cell cycle block and apoptotic death. Schult et al. [51] showed that BEZ235 reduces the metabolic activity and induces cell cycle arrest at G0/G1 in Jurkat cells, without substantial effects on apoptosis, but induces death when combined with dexamethasone. Hall et al. confirmed the synergistic effects of BEZ235 plus dexamethasone in T-ALL cell lines (5 out of 7 tested), 3 primary T-ALL samples, and in an in vivo model that employed a T-ALL cell line and a PDX derived from the same primary T-ALL cells as the cell line [52]. The synergism between BEZ235 and dexamethasone was traced to BEZ235-triggered downregulation of MCL1 and was independent of PI3K/AKT pathway activation or PTEN status [52].
To our knowledge, the present study is the first to indicate a mechanistic link between mTORC1 and redox homeostasis as the basis for the therapeutic synergy between everolimus and glucocorticoids in T-ALL. Our experiments with everolimus, which is specific for mTORC1, combined with experiments to silence RICTOR and RAPTOR, verified a direct connection between mTORC1, G6PD and redox homeostasis. Importantly, the effects of everolimus on G6PD expression were confirmed in our preclinical model that employed 3 PDX that were selected for their pronounced resistance to dexamethasone. Furthermore, our study is the first to demonstrate the in vivo efficacy of everolimus plus dexamethasone in a setting mimicking full-blown leukemia.
An important consequence of ROS accumulation in everolimus-treated T-ALL cells is the proteolytic cleavage of OPA1 (Fig. 5A), an inner mitochondrial membrane protein that controls mitochondrial dynamics, cristae remodeling and apoptosis [35]. This finding builds on results of a previous study in which we showed that increasing ROS in T-ALL cells results in the activation of the ROS-sensitive protease OMA1 which cleaves OPA1, priming cells to proapoptotic stimuli [9].
It is noteworthy that the effects of everolimus on T-ALL cell death were evident in the 10–15 μM concentration range, while inhibition of NAD(P)H-dependent oxidoreductase activity and mitochondrial respiration (measured with the MTT assay and OCR, respectively, Fig. 4A) were observed at much lower concentrations (0.01 μM). These differences suggest a hierarchical engagement of mTOR targets depending on the level of activity of the complex. Such “low-dose” effects of everolimus were also reported in other studies [53,54] where the MTT assay was employed as a readout of viability. However, our results clearly indicate that, in the context of T-ALL cells, at these concentrations of everolimus the cells are not dead (as indicated by PI exclusion assays), and the mTOR pathway is not fully inhibited (as indicated by the detection of phospho-4EBP, Fig. S4B). The “high-dose” effects of everolimus are not likely to be due to off-target effects as they were mimicked by genetic silencing (Figs. 4D and S2B), and were required to reduce the levels of 4EBP phosphorylation (Fig. S4B).
The micromolar doses of everolimus that killed T-ALL cells in vitro in our experiments are considerably higher than the therapeutic plasma levels of everolimus measured in humans, which are in the 10–20 nM range [55]. Notably, other studies of B-acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells employed similar micromolar doses of everolimus in short-term in vitro experiments [56,57]. In their discussion of the in vitro vs in vivo everolimus concentrations, the authors of these studies suggested the importance of considering peak plasma levels of everolimus when investigating its antineoplastic effects [57] and proposed that higher drug concentrations might be present in the local tumor microenvironment [56]. The apparently higher potency of everolimus in vivo may also be influenced by other peculiar conditions in the tumor microenvironment, e.g., limited nutrients and oxygen supply, or to metabolic activation of the drug in vivo. We would also like to point out that in vivo treatments are carried out for prolonged periods of time and may thus reflect additive effects of the drug, while in vitro studies are usually carried out for one to a few days.
Aside from this apparent discrepancy, it is noteworthy that our experiments in mice confirmed a reduction in G6PD expression, induction of apoptosis and antitumor effects using a standard 10 mg/kg dose, which is known to produce plasma levels of approximately 500 nM after 24 h [58]. The basis for the apparently enhanced sensitivity of the PDX cells to everolimus when propagated in vivo merits further investigation.
The effects of G6PD silencing on ROS and cell death were smaller compared to those obtained with pharmacological inhibition of mTOR (compare Fig. 2, Fig. 3, Fig. 4A with Fig. 4D), and implies that everolimus might also affect the expression/function of other enzymes controlling redox homeostasis.
Our in vivo experiments confirmed the efficacy of everolimus in reducing the rate of T-ALL growth described in other studies [41]. In addition, we provide novel evidence of the efficacy of this treatment in the context of high tumor burden (Fig. 7). The in vivo studies also indicated that PDX9, PDX13 and PDX19 responded differently to the combined treatment with everolimus + dexamethasone, a finding that is in line with the variable response observed in patients treated with everolimus in association with HyperCVAD chemotherapy [43,59,60]. Our PDX-based preclinical model may thus prove useful for future studies aimed at identifying molecular markers for selecting those patients who are most likely to benefit from an everolimus plus GC-based induction regimen [61].
5. Conclusions
mTOR activation is a hallmark of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) and is associated with resistance to glucocorticoid (GC)-based chemotherapy. Our findings provide insight into the crosstalk between mTOR and ROS homeostasis in T-ALL cells and furnish mechanistic evidence to support the combination of glucocorticoids with mTOR inhibitors as a therapeutic avenue to treat refractory T-ALL by depowering G6PD, the rate-limiting enzyme of the pentose phosphate pathway.
Declarations of interest
None.
Funding information
The study was funded by the Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (AIRC) Investigator Grant #24935 (VC) and by the University of Padova (Department of Surgery, Oncology and Gastroenterology DOR 2021 funds, to VC, and Department of Biomedical Sciences grant no. BIRD204551/20, to DMD). VR and FC were supported by fellowships from the Veneto Institute of Oncology IOV-IRCCS. The funding agencies were not involved in the study design, collection, analysis or interpretation of data, writing of the manuscript or in the decision to submit the study for publication.
Author contributions
MSB designed and performed experiments. VR, IC, ES and FC helped with the in vitro experiments. LU, GS, and SM helped with the in vivo experiments, GB, BB and SF provided patients’ samples and were responsible for the clinico-pathological management of the patients. SI and DMD contributed to the experimental design and manuscript preparation, AC performed bioinformatic analyses and prepared the supplemental bioinformatics section. HK assisted with gene expression analyses. VC designed experiments and wrote the manuscript. All the authors contributed to the discussion and interpretation of the data.
Acknowledgments
We thank Nazareno Paolocci, Riccardo Dalla-Favera and Luigi Chieco-Bianchi for discussions, and Anna Michelotto and Andrea Saponeri for their technical support and Paola Del Bianco for advice on statistical analysis of in vivo experiments. The co-authors dedicate the present study to the late Giuseppe Basso in memory of his enthusiastic support and collaborative spirit.
Footnotes
Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2022.102268.
Appendix A. Supplementary data
The following are the Supplementary data to this article:
References
- 1.Karrman K., Johansson B. Pediatric T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2017;56:89–116. doi: 10.1002/gcc.22416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Hunger S.P., Mullighan C.G. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015;373:1541–1552. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1400972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bhadri V.A., Trahair T.N., Lock R.B. Glucocorticoid resistance in paediatric acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. J. Paediatr. Child Health. 2012;48:634–640. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1754.2011.02212.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Silva A., Yunes J.A., Cardoso B.A., Martins L.R., Jotta P.Y., Abecasis M., Nowill A.E., Leslie N.R., Cardoso A.A., Barata J.T. PTEN posttranslational inactivation and hyperactivation of the PI3K/Akt pathway sustain primary T cell leukemia viability. J. Clin. Invest. 2008;118:3762–3774. doi: 10.1172/JCI34616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Silva A., Gírio A., Cebola I., Santos C.I., Antunes F., Barata J.T. Intracellular reactive oxygen species are essential for PI3K/Akt/mTOR-dependent IL-7-mediated viability of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Leukemia. 2011;25:960–967. doi: 10.1038/leu.2011.56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Silic-Benussi M., Cavallari I., Vajente N., Vidali S., Chieco-Bianchi L., Di Lisa F., Saggioro D., D'Agostino D.M., Ciminale V. Redox regulation of T-cell turnover by the p13 protein of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1: distinct effects in primary versus transformed cells. Blood. 2010;116:54–62. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-07-235861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Silic-Benussi M., Cannizzaro E., Venerando A., Cavallari I., Petronilli V., La Rocca N., Marin O., Chieco-Bianchi L., Di Lisa F., D'Agostino D.M., Bernardi P., Ciminale V. Modulation of mitochondrial K(+) permeability and reactive oxygen species production by the p13 protein of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2009;1787:947–954. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2009.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Silic-Benussi M., Biasiotto R., Andresen V., Franchini G., D'Agostino D.M., Ciminale V. HTLV-1 p13, a small protein with a busy agenda. Mol. Aspect. Med. 2010;31:350–358. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2010.03.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Silic-Benussi M., Scattolin G., Cavallari I., Minuzzo S., Del Bianco P., Francescato S., Basso G., Indraccolo S., D'Agostino D.M., Ciminale V. Selective killing of human T-ALL cells: an integrated approach targeting redox homeostasis and the OMA1/OPA1 axis. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9:822. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0870-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wei G., Twomey D., Lamb J., Schlis K., Agarwal J., Stam R.W., Opferman J.T., Sallan S.E., den Boer M.L., Pieters R., Golub T.R., Armstrong S.A. Gene expression-based chemical genomics identifies rapamycin as a modulator of MCL1 and glucocorticoid resistance. Cancer Cell. 2006;10:331–342. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2006.09.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Laplante M., Sabatini D.M. mTOR signaling in growth control and disease. Cell. 2012;149:274–293. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Martelli A.M., Paganelli F., Fazio A., Bazzichetto C., Conciatori F., McCubrey J.A. The key roles of PTEN in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia development, progression, and therapeutic response. Cancers. 2019;11 doi: 10.3390/cancers11050629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Moharram S.A., Shah K., Kazi J.U. T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells display activation of different survival pathways. J. Cancer. 2017;8:4124. doi: 10.7150/jca.21725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Szwed A., Kim E., Jacinto E. Regulation and metabolic functions of mTORC1 and mTORC2. Physiol. Rev. 2021;101:1371–1426. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00026.2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Khanna A., Bhushan B., Chauhan P.S., Saxena S., Gupta D.K., Siraj F. High mTOR expression independently prognosticates poor clinical outcome to induction chemotherapy in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Clin. Exp. Med. 2018;18:221–227. doi: 10.1007/s10238-017-0478-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Liu G.Y., Sabatini D.M. mTOR at the nexus of nutrition, growth, ageing and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020;21:183–203. doi: 10.1038/s41580-019-0199-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Evangelisti C., Chiarini F., McCubrey J.A., Martelli A.M. Therapeutic targeting of mTOR in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: an update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018;19 doi: 10.3390/ijms19071878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bortolozzi R., Bresolin S., Rampazzo E., Paganin M., Maule F., Mariotto E., Boso D., Minuzzo S., Agnusdei V., Viola G., Te Kronnie G., Cazzaniga G., Basso G., Persano L. AKR1C enzymes sustain therapy resistance in paediatric T-ALL. Br. J. Cancer. 2018;118:985–994. doi: 10.1038/s41416-018-0014-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Zhang Q., Liu W., Zhang H.M., Xie G.Y., Miao Y.R., Xia M., Guo A.Y. hTFtarget: a comprehensive database for regulations of human transcription factors and their targets. Dev. Reprod. Biol. 2020;18:120–128. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2019.09.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lacher S.E., Slattery M. Gene regulatory effects of disease-associated variation in the NRF2 network. Curr Opin Toxicol. 2016;1:71–79. doi: 10.1016/j.cotox.2016.09.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Agnusdei V., Minuzzo S., Frasson C., Grassi A., Axelrod F., Satyal S., Gurney A., Hoey T., Seganfreddo E., Basso G., Valtorta S., Moresco R.M., Amadori A., Indraccolo S. Therapeutic antibody targeting of Notch1 in T-acute lymphoblastic leukemia xenografts. Leukemia. 2014;28:278–288. doi: 10.1038/leu.2013.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Love M.I., Huber W., Anders S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014;15:550. doi: 10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Zhu A., Ibrahim J.G., Love M.I. Heavy-tailed prior distributions for sequence count data: removing the noise and preserving large differences. Bioinformatics. 2019;35:2084–2092. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Durinck S., Moreau Y., Kasprzyk A., Davis S., De Moor B., Brazma A., Huber W. BioMart and Bioconductor: a powerful link between biological databases and microarray data analysis. Bioinformatics. 2005;21:3439–3440. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Durinck S., Spellman P.T., Birney E., Huber W. Mapping identifiers for the integration of genomic datasets with the R/Bioconductor package biomaRt. Nat. Protoc. 2009;4:1184–1191. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2009.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Subramanian A., Tamayo P., Mootha V.K., Mukherjee S., Ebert B.L., Gillette M.A., Paulovich A., Pomeroy S.L., Golub T.R., Lander E.S., Mesirov J.P. Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2005;102:15545–15550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0506580102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Jiang P., Du W., Wang X., Mancuso A., Gao X., Wu M., Yang X. p53 regulates biosynthesis through direct inactivation of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011;13:310–316. doi: 10.1038/ncb2172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Leinonen H.M., Kansanen E., Polonen P., Heinaniemi M., Levonen A.L. Role of the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway in cancer. Adv. Cancer Res. 2014;122:281–320. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-420117-0.00008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Rodchenkov I., Babur O., Luna A., Aksoy B.A., Wong J.V., Fong D., Franz M., Siper M.C., Cheung M., Wrana M., Mistry H., Mosier L., Dlin J., Wen Q., O'Callaghan C., Li W., Elder G., Smith P.T., Dallago C., Cerami E., Gross B., Dogrusoz U., Demir E., Bader G.D., Sander C. Pathway Commons 2019 Update: integration, analysis and exploration of pathway data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020;48:D489–D497. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Márton M., Tihanyi N., Gyulavári P., Bánhegyi G., Kapuy O. NRF2-regulated cell cycle arrest at early stage of oxidative stress response mechanism. PLoS One. 2018;13 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0207949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ciccarese F., Ciminale V. Escaping death: mitochondrial redox homeostasis in cancer cells. Front. Oncol. 2017;7:1–16. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2017.00117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Gutierrez A., Sanda T., Grebliunaite R., Carracedo A., Salmena L., Ahn Y., Dahlberg S., Neuberg D., Moreau L.A., Winter S.S., Larson R., Zhang J., Protopopov A., Chin L., Pandolfi P.P., Silverman L.B., Hunger S.P., Sallan S.E., Look A.T. High frequency of PTEN, PI3K, and AKT abnormalities in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2009;114:647–650. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-02-206722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Martelli A.M., Evangelisti C., Chappell W., Abrams S.L., Bäsecke J., Stivala F., Donia M., Fagone P., Nicoletti F., Libra M., Ruvolo V., Ruvolo P., Kempf C.R., Steelman L.S., McCubrey J.A. Targeting the translational apparatus to improve leukemia therapy: roles of the PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR pathway. Leukemia. 2011;25:1064–1079. doi: 10.1038/leu.2011.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Bock F.J., Tait S.W.G. Mitochondria as multifaceted regulators of cell death. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020;21:85–100. doi: 10.1038/s41580-019-0173-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Pernas L., Scorrano L. Mito-morphosis: mitochondrial fusion, fission, and cristae remodeling as key mediators of cellular function. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2016;78:505–531. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-021115-105011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Yanagiya A., Suyama E., Adachi H., Svitkin Y.V., Aza-Blanc P., Imataka H., Mikami S., Martineau Y., Ronai Z.A., Sonenberg N. Translational homeostasis via the mRNA cap-binding protein, eIF4E. Mol. Cell. 2012;46:847–858. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.04.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Martin D., Nguyen Q., Molinolo A., Gutkind J.S. Accumulation of dephosphorylated 4EBP after mTOR inhibition with rapamycin is sufficient to disrupt paracrine transformation by the KSHV vGPCR oncogene. Oncogene. 2014;33:2405–2412. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Chou T.C., Talalay P. Quantitative analysis of dose-effect relationships: the combined effects of multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv. Enzym. Regul. 1984;22:27–55. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(84)90007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Chou T.C. Drug combination studies and their synergy quantification using the Chou-Talalay method. Cancer Res. 2010;70:440–446. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-1947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Pikman Y., Alexe G., Roti G., Conway A.S., Furman A., Lee E.S., Place A.E., Kim S., Saran C., Modiste R., Weinstock D.M., Harris M., Kung A.L., Silverman L.B., Stegmaier K. Synergistic drug combinations with a CDK4/6 inhibitor in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017;23:1012–1024. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-2869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Simioni C., Martelli A.M., Zauli G., Melloni E., Neri L.M. Targeting mTOR in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cells. 2019;8 doi: 10.3390/cells8020190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Silva A., Girio A., Cebola I., Santos C.I., Antunes F., Barata J.T. Intracellular reactive oxygen species are essential for PI3K/Akt/mTOR-dependent IL-7-mediated viability of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Leukemia. 2011;25:960–967. doi: 10.1038/leu.2011.56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Daver N., Boumber Y., Kantarjian H., Ravandi F., Cortes J., Rytting M.E., Kawedia J.D., Basnett J., Culotta K.S., Zeng Z., Lu H., Richie M.A., Garris R., Xiao L., Liu W., Baggerly K.A., Jabbour E., O'Brien S., Burger J., Bendall L.J., Thomas D., Konopleva M. A phase I/II study of the mTOR inhibitor everolimus in combination with HyperCVAD chemotherapy in patients with relapsed/refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015;21:2704–2714. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-2888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Poulain L., Sujobert P., Zylbersztejn F., Barreau S., Stuani L., Lambert M., Palama T.L., Chesnais V., Birsen R., Vergez F., Farge T., Chenevier-Gobeaux C., Fraisse M., Bouillaud F., Debeissat C., Herault O., Récher C., Lacombe C., Fontenay M., Mayeux P., Maciel T.T., Portais J.C., Sarry J.E., Tamburini J., Bouscary D., Chapuis N. High mTORC1 activity drives glycolysis addiction and sensitivity to G6PD inhibition in acute myeloid leukemia cells. Leukemia. 2017;31:2326–2335. doi: 10.1038/leu.2017.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Düvel K., Yecies J., Menon S., Raman P., Lipovsky A., Souza A., Triantafellow E., Ma Q., Gorski R., Cleaver S., Vander H.M.G., MacKeigan J., Finan P., Clish C., Murphy L., Manning B. Activation of a metabolic gene regulatory network downstream of mTOR complex 1. Mol. Cell. 2010;39 doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.06.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Tsouko E., Khan A.S., White M.A., Han J.J., Shi Y., Merchant F.A., Sharpe M.A., Xin L., Frigo D.E. Regulation of the pentose phosphate pathway by an androgen receptor-mTOR-mediated mechanism and its role in prostate cancer cell growth. Oncogenesis. 2014;3:e103. doi: 10.1038/oncsis.2014.18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Thiepold A.L., Lorenz N.I., Foltyn M., Engel A.L., Divé I., Urban H., Heller S., Bruns I., Hofmann U., Dröse S., Harter P.N., Mittelbronn M., Steinbach J.P., Ronellenfitsch M.W. Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 activation sensitizes human glioma cells to hypoxia-induced cell death. Brain. 2017;140:2623–2638. doi: 10.1093/brain/awx196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Cheng J., Huang Y., Zhang X., Yu Y., Wu S., Jiao J., Tran L., Zhang W., Liu R., Zhang L., Wang M., Wang M., Yan W., Wu Y., Chi F., Jiang P., Zhang X., Wu H. TRIM21 and PHLDA3 negatively regulate the crosstalk between the PI3K/AKT pathway and PPP metabolism. Nat. Commun. 2020;11:1–16. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15819-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Pusapati R.V., Daemen A., Wilson C., Sandoval W., Gao M., Haley B., Baudy A.R., Hatzivassiliou G., Evangelista M., Settleman J. mTORC1-Dependent metabolic reprogramming underlies escape from glycolysis addiction in cancer cells. Cancer Cell. 2016;29:548–562. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2016.02.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Gu L., Zhou C., Liu H., Gao J., Li Q., Mu D., Ma Z. Rapamycin sensitizes T-ALL cells to dexamethasone-induced apoptosis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010;29:150. doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-29-150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Schult C., Dahlhaus M., Glass A., Fischer K., Lange S., Freund M., Junghanss C. The dual kinase inhibitor NVP-BEZ235 in combination with cytotoxic drugs exerts anti-proliferative activity towards acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Anticancer Res. 2012;32:463–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Hall C.P., Reynolds C.P., Kang M.H. Modulation of glucocorticoid resistance in pediatric T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia by increasing BIM expression with the PI3K/mTOR inhibitor BEZ235. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016;22:621–632. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-0114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Bressanin D., Evangelisti C., Ricci F., Tabellini G., Chiarini F., Tazzari P.L., Melchionda F., Buontempo F., Pagliaro P., Pession A., McCubrey J.A., Martelli A.M. Harnessing the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: eliminating activity by targeting at different levels. Oncotarget. 2012;3:811–823. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Kuwatsuka Y., Minami M., Minami Y., Sugimoto K., Hayakawa F., Miyata Y., Abe A., Goff D.J., Kiyoi H., Naoe T. The mTOR inhibitor, everolimus (RAD001), overcomes resistance to imatinib in quiescent Ph-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Blood Cancer J. 2011;1:e17. doi: 10.1038/bcj.2011.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Thiery-Vuillemin A., Mouillet G., Nguyen Tan Hon T., Montcuquet P., Maurina T., Almotlak H., Stein U., Montange D., Foubert A., Nerich V., Pivot X., Royer B. Impact of everolimus blood concentration on its anti-cancer activity in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2014;73:999–1007. doi: 10.1007/s00280-014-2435-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Baraz R., Cisterne A., Saunders P.O., Hewson J., Thien M., Weiss J., Basnett J., Bradstock K.F., Bendall L.J. mTOR inhibition by everolimus in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia induces caspase-independent cell death. PLoS One. 2014;9 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0102494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Saunders P., Cisterne A., Weiss J., Bradstock K.F., Bendall L.J. The mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor RAD001 (everolimus) synergizes with chemotherapeutic agents, ionizing radiation and proteasome inhibitors in pre-B acute lymphocytic leukemia. Haematologica. 2011;96:69–77. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2010.026997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Majumder P.K., Febbo P.G., Bikoff R., Berger R., Xue Q., McMahon L.M., Manola J., Brugarolas J., McDonnell T.J., Golub T.R., Loda M., Lane H.A., Sellers W.R. mTOR inhibition reverses Akt-dependent prostate intraepithelial neoplasia through regulation of apoptotic and HIF-1-dependent pathways. Nat. Med. 2004;10:594–601. doi: 10.1038/nm1052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Martelli A.M., Lonetti A., Buontempo F., Ricci F., Tazzari P.L., Evangelisti C., Bressanin D., Cappellini A., Orsini E., Chiarini F. Targeting signaling pathways in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia initiating cells. Adv. Biol. Regul. 2014;56:6–21. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2014.04.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Place A.E., Pikman Y., Stevenson K.E., Harris M.H., Pauly M., Sulis M.L., Hijiya N., Gore L., Cooper T.M., Loh M.L., Roti G., Neuberg D.S., Hunt S.K., Orloff-Parry S., Stegmaier K., Sallan S.E., Silverman L.B. Phase I trial of the mTOR inhibitor everolimus in combination with multi-agent chemotherapy in relapsed childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr. Blood Cancer. 2018;65 doi: 10.1002/pbc.27062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Cooper S., Brown P. Treatment of pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr. Clin. 2015:62. doi: 10.1016/j.pcl.2014.09.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.