Abstract
目的
探究补肾化痰方治疗多囊卵巢综合征的主要活性成分、靶点、通路等药理学作用机制。
方法
通过中药系统药理学数据库与分析平台(TCMSP)筛选出补肾化痰方中药物的主要活性成分,使用PubChem和Swiss Target Prediction预测活性成分相关作用靶点;应用GeneCards、OMIM筛选治疗疾病多囊卵巢综合征的作用靶点;将药物靶点与疾病靶点通过Uniprot校正后,取交集靶点;结合STRING构建蛋白-蛋白互作(PPI)网络,并利用Cytoscape3.7.2中的CytoNCA插件对交集靶点进行PPI分析,筛选出核心靶点;采用DAVID数据库进行基因功能GO富集分析和KEGG通路富集分析;利用AutoDock对补肾化痰方中的核心活性成分和核心靶点进行分子对接验证。以动物实验进行验证,24只SPF级雌性C57BL/6J小鼠按随机数字表法分为3组:对照组[n=8,1 mg/(kg·d)生理盐水灌服35 d],模型组[n=8,1 mg/(kg·d)来曲唑溶于1%羧甲基纤维素(CMC)中,连续灌服35 d,并予高脂饲料喂养],治疗组[n=8,造模后予以1 mg/(kg·d)补肾化痰方颗粒剂溶于5%生理盐水中,连续灌服35 d]。小鼠末次给药后,取卵巢组织于-80 ℃保存,Western blot法检测小鼠卵巢组织中核心靶点和核心通路的表达。
结果
补肾化痰方中14味中药共筛选出125个潜在活性成分,990个药物靶点,4759个PCOS靶点,药物与PCOS交集靶点434个;核心活性成分主要为β-谷甾醇、山奈酚、槲皮素等,核心靶点主要为PIK3CA、PIK3R1、APP、AKT1、MAPK1等;GO功能富集主要包括药物反应、凋亡过程的负调控、RNA聚合酶Ⅱ启动子转录的正调控等;KEGG富集通路主要包括癌症通路、HIF-1信号通路、Rap1信号通路、PI3K-Akt信号通路等;分子对接结果显示核心活性成分β-谷甾醇、山奈酚、槲皮素与核心靶点PIK3CA、PIK3R1、APP、AKT1、MAPK1均有强烈的结合能力;动物实验结果表明,补肾化痰方能明显改善多囊卵巢综合征相关症状,并下调PI3K,AKT蛋白表达,上调MAPK1蛋白表达,验证了网络药理学的部分预测结果。
结论
揭示了补肾化痰方多成分、多靶点、多途径的作用特点,预测并通过实验初步验证了补肾化痰方治疗多囊卵巢综合征的可能作用机制。
Keywords: 多囊卵巢综合征, 补肾化痰方, 网络药理学, 分子对接, 作用机制
Abstract
Objective
To explore the pharmacological mechanism of Bushen Huatan (BSHT) recipe in the treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
Methods
The active ingredients in the component drugs of the recipe were screened through TCMSP, and their potential targets were predicted by PubChem and Swiss target prediction. Genecards and OMIM were used to screen the therapeutic targets in the treatment of PCOS. The drug targets and disease targets were corrected using Uniprot, and the intersection targets were obtained. The protein-protein interaction (PPI) network was constructed using STRING, and the intersection targets were analyzed with CytoNCA to screen the core targets. DAVID was used for GO enrichment analysis and KEGG pathway enrichment analysis, and the core components and core targets were verified using AutoDock. Animal experiment was performed to verify the results using a female C57BL/6J mouse model of PCOS, treated daily with 1 mg/kg BSHT recipe granule for 35 days, and the ovarian expressions of the core targets and pathways were detected using Western blotting.
Results
We identified a total of 125 potential active ingredients from the 14 component drugs in the recipe, 990 drug targets, 4759 PCOS targets and 434 intersection targets. The core active ingredients of the recipe included β -Sitosterol, kaempferol, and quercetin, whose core targets included PIK3CA, PIK3R1, APP, AKT1, and MAPK1. GO enrichment analysis highlighted such processes as drug reaction, negative regulation of apoptosis, and positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase Ⅱ promoter. The enriched KEGG pathways included primarily the cancer pathway and PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. Molecular docking showed that the core active ingredients had strong binding ability with the core targets. In the animal experiment, BSHT recipe was shown to improve the symptoms, down-regulate the expressions of PI3K and Akt proteins and up-regulate MAPK1 expression in the ovary of mice with PCOS.
Conclusion
The therapeutic mechanism of BSHT recipe for PCOS involves multiple active ingredients, multiple therapeutic targets and multiple pathways.
Keywords: polycystic ovary syndrome, Bushen Huatan recipe, network pharmacology, molecular docking, mechanism
多囊卵巢综合征(PCOS)是女性最常见的妇科内分泌疾病,伴有生殖功能障碍和代谢异常,影响患者一生的健康及生命质量。如今,PCOS已被视为生殖医学领域不可忽视的重大疾病。现代医学主要采用激素替代、促排卵联合辅助生殖技术进行治疗,但存在妊娠率低、副作用大的风险[1-3]。近年来,中医从宏观辨证入手,采用辨证与辨病相结合的方法进行治疗,取得了一定的疗效,展示了中医药治疗PCOS的优势[4-7]。
补肾化痰方是江苏省中医院生殖医学科临床常用经验方。前期研究表明[8],补肾化痰方能够改善胰岛素抵抗,可能与胰岛素信号传导分子蛋白表达的调控有关。而胰岛素抵抗是PCOS的关键发病机制之一。Zhou等[9]进行了一项用于识别多囊卵巢综合征临床紊乱的非侵入性尿代谢组学研究,表明尿液中小分子代谢物的差异可能反映了多囊卵巢综合征的潜在发病机制,其中PCOS患者的甲基丙二酸水平明显高于健康受试者,维生素B12缺乏引起的甲基丙二酸升高可能与多囊卵巢综合征患者的胰岛素抵抗有关。Zhang等[10]采用气相色谱-质谱联用(GC-MS)血清代谢组学方法,探讨PCOS患者高雄激素血症和胰岛素抵抗患者的代谢紊乱途径,也发现了差异代谢物能反映PCOS的潜在机制,并可作为HA与IR互补诊断的生物标志物。这都提高了对多囊卵巢综合征潜在作用机制的认识。但目前为止,对其作用机制难以提供较为科学、全面、有效的阐释。本课题组基于多年的临床及基础研究,利用与中医药学整体观和辨证论治理论体系相契合的网络药理学方法和分子对接技术,结合动物实验,探究并验证补肾化痰方治疗多囊卵巢综合征的潜在活性成分、作用靶点、信号通路等相关机制,以期为进一步的临床运用和实验研究提供客观科学依据。
1. 材料和方法
1.1. 材料
1.1.1. 动物
SPF级雌性C57BL/6J小鼠24只,3周龄,体质量15~20 g。实验动物由南京中医药大学动物中心提供,本实验经南京中医药大学动物护理和使用委员会批准(伦理号:012071002387)。
1.1.2. 药物
补肾化痰方颗粒剂(仙灵脾10 g、仙茅10 g、苍术10 g、半夏6 g、陈皮6 g、九节菖蒲10 g、香附10 g、川芎6 g、泽泻10 g、鹿角霜10 g、胆南星6 g、砂仁3 g、炒白术6 g、淮山药6 g)由南京中医药大学附属医院药剂科提供。
1.1.3. 试剂与仪器
来曲唑(江苏恒瑞医药股份有限公司),BCA蛋白定量检测试剂盒、RIPA裂解液、5×蛋白还原型上样缓冲液、磷酸化蛋白酶抑制剂、β-actin、GAPDH、Histone H3、HRP标记山羊抗兔、HRP标记驴抗山羊、HRP标记山羊抗小鼠、HRP标记山羊抗大鼠(Servicebio),高脂饲料(金益柏生物科技有限公司)。
酶标仪(Rayto),台式高速冷冻离心机(DRAGONLAB),涡旋混合器、磁力搅拌器(Servicebio),超声波细胞破碎仪(宁波新芝生物)。
1.2. 方法
1.2.1. 补肾化痰方活性成分的收集与筛选
利用中药系统药理学数据库与分析平台(TCMSP,<a href="https://tcmspe.com/" target="_blank">https://tcmspe.com/</a>)<sup>[<xref ref-type="bibr" rid="b11">11</xref>]</sup>检索,并查阅已发表的相关文献以补充,收集补肾化痰方(仙灵脾,仙茅,苍术,半夏,陈皮,九节菖蒲,香附,川芎,泽泻,鹿角霜,胆南星,砂仁,炒白术,淮山药)的主要活性成分,以药物成分口服生物利用度(OB)≥30%和类药性(DL)≥0.18<sup>[<xref ref-type="bibr" rid="b12">12</xref>]</sup>为条件作进一步筛选。将最终得到的活性成分导入化学信息数据库Pubchem,检索各个活性成分的规范SMILES结构和化学结构式。
1.2.2. 补肾化痰方潜在靶点的预测
将获得的各个活性成分结构式导入到Swiss Target Prediction(<a href="http://www.swisstargetprediction.ch/" target="_blank">http://www.swisstargetprediction.ch/</a>)数据库,限定物种为人,预测其相关作用靶点,再根据相关性的高低选取潜在作用靶点。
1.2.3. PCOS靶点的预测
以GeneCards数据库(<a href="https://www.genecards.org/" target="_blank">https://www.genecards.org/</a>),OMIM数据库(<a href="https://omim.org/" target="_blank">https://omim.org/</a>)为平台,“Polycystic Ovary Syndrome”为关键词进行搜索,取交集并删除重复靶点,获取PCOS靶标,运用Uniprot(https://www.uniprot.org/)数据库对疾病靶点和药物靶点进行官方校正。通过Draw Venn Diagram网站在线分析,绘制药物-疾病靶点的韦恩图(<a href="http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/Venn/" target="_blank">http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/Venn/</a>),获得其交集靶点。
1.2.4. 补肾化痰方治疗PCOS的PPI网络分析及核心靶点筛选
利用STRING(<a href="http://www.string-db.org/" target="_blank">http://www.string-db.org/</a>)数据库,以“Multiple proteins”为数据分析模式、“Homo Sapiens”为物种限定、Required Confidence(combined score)>0.9为阈值,对交集靶点进行相互作用关系分析。后导入Cytoscape3.7.2并利用CytoNCA<sup>[<xref ref-type="bibr" rid="b13">13</xref>]</sup>插件,以Degree值大小对各靶点进行排序,取排名前十的靶点为核心靶点。
1.2.5. GO富集与KEGG通路分析
通过DAVID(<a href="https://david.ncifcrf.gov/" target="_blank">https://david.ncifcrf.gov/</a>)网站,借助“Functional Annotation Tool”对交集靶点进行GO富集分析,包括生物过程、细胞成分和分子功能3个模块的分析,以<italic>P</italic> < 0.05和FDR < 0.05为标准筛选,根据涉及靶点数目排序,选取前30位;同时对交集靶点进行KEGG通路分析,以<italic>P</italic> < 0.01为筛选标准,根据P值大小排序,选取前20位。
1.2.6. KEGG“通路-靶点”关系网络的构建
根据KEGG通路分析结果,选取前20位,分别建立通路与对应靶点之间的相互作用关系和节点属性与对应靶点之间的相互作用关系,并导入Cytoscape 3.7.2软件中,构建补肾化痰方治疗多囊卵巢综合征的“通路-靶点”关系网络图。
1.2.7. 分子对接验证
选取成分-靶点网络中核心活性成分Degree值排名前3的β-谷甾醇、山奈酚、槲皮素与CytoNCA筛选出来的核心靶点PIK3CA、PIK3R1、APP、AKT1、MAPK1进行分子对接。在PubChem数据库(<a href="https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/" target="_blank">https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/</a>)中下载核心活性成分的三维结构,结合PDB数据库(<a href="https://www.rcsb.org/" target="_blank">https://www.rcsb.org/</a>)中核心靶点的蛋白结构,运用AutoDock Vina对核心活性成分与核心靶点进行分子对接验证,并利用Pymol对部分结果进行可视化。
1.2.8. 动物实验验证
24只SPF级雌性C57BL/6J小鼠按随机数字表法分为3组:对照组、模型组、治疗组,每组8只。适应性喂养1周后,利用来曲唑诱导PCOS小鼠模型。对照组:以1mg/(kgˑd)生理盐水灌服35 d;模型组:来曲唑1 mg/(kgˑd)溶于1%羧甲基纤维素(CMC)中,连续灌服35 d,并予高脂饲料喂养;治疗组:造模结束后,补肾化痰方颗粒剂以1 mg/(kgˑd)溶于5%生理盐水中,连续灌服35 d。小鼠末次给药后,取卵巢组织于-80 ℃保存,以便后续实验进行。
1.2.9. Western blot检测PI3K、AKT、MAPK1蛋白表达
取各组小鼠卵巢组织,使用RIPA裂解液提取总蛋白,BCA法测定蛋白浓度,经凝胶电泳、转模、封闭后,加入一抗4 ℃孵育摇床过夜,TBST洗涤3次,室温孵育二抗30 min,TBST洗涤3次,曝光,显色。
1.2.10. 统计学方法
采用SPSS 24.0统计软件处理,计量资料用均数±标准差表示,组间比较采用单因素方差分析,两两比较采用t检验。P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1. 补肾化痰方活性成分
通过TCMSP数据库检索,并查阅已发表的相关文献进行补充,以药物成分口服生物利用度(OB)≥30%和类药性(DL)≥0.18为条件进一步筛选得到补肾化痰方中14味中药包含125个有效活性成分,其中通过查阅文献所得的九节菖蒲主要活性成分为Palmitic acid、Ferulic acid、Adenosine等;鹿角霜主要活性成分为gamma-Aminobutyric acid、Glutamic acid等;胆南星主要活性成分为Apigenin、Schaftoside、Cholesterol等,其余部分筛选结果如下(表 1)。
1.
补肾化痰方中部分候选活性成分
Some candidate active components in Bushen Huatan recipe
| TCM | MOL ID | Molecule name | OB(%) | DL |
| OB: Oral bioavailability; DL: Drug likeness. | ||||
| XIAN LING PI | MOL001510 | 24-epicampesterol | 37.57681789 | 0.71413 |
| MOL001645 | Linoleyl acetate | 42.10076623 | 0.19845 | |
| MOL001771 | Poriferast-5-en-3beta-ol | 36.91390583 | 0.75034 | |
| MOL001792 | DFV | 32.76272375 | 0.18316 | |
| MOL003044 | Chryseriol | 35.85089483 | 0.27415 | |
| MOL000422 | Kaempferol | 41.88224954 | 0.24066 | |
| MOL004373 | Anhydroicaritin | 45.41193421 | 0.43786 | |
| XIAN MAO | MOL001607 | ZINC03982454 | 36.91390583 | 0.75559 |
| MOL003578 | Cycloartenol | 38.68565906 | 0.78093 | |
| MOL000358 | Beta-sitosterol | 36.91390583 | 0.75123 | |
| MOL004114 | 3, 2', 4, ,6, -Tetrahydroxy-4, 3, -dimethoxy chalcone | 52.69264509 | 0.28064 | |
| CANG ZHU | MOL000173 | Wogonin | 30.68456706 | 0.22942 |
| MOL000179 | 2-Hydroxyisoxypropyl-3-hydroxy-7-isopentene-2, 3 -dihydrobenzofuran-5-carboxylic |
45.19912214 | 0.20496 | |
| BAN XIA | MOL001755 | 24-Ethylcholest-4-en-3-one | 36.08361164 | 0.75703 |
| MOL002670 | Cavidine | 35.64183046 | 0.80513 | |
| MOL002714 | Baicalein | 33.51891869 | 0.20888 | |
| MOL002776 | Baicalin | 40.12360996 | 0.75264 | |
| CHEN PI | MOL004328 | Naringenin | 59.29389773 | 0.21128 |
| MOL005100 | 5, 7-dihydroxy-2-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)chroman-4-one | 47.73643694 | 0.27226 | |
| XIANG FU | MOL004068 | Rosenonolactone | 79.83806452 | 0.37112 |
| MOL004071 | Hyndarin | 73.93668929 | 0.64304 | |
| MOL004077 | Sugeonyl acetate | 45.07648053 | 0.19742 | |
| CHUAN XIONG | MOL001494 | Mandenol | 41.99620045 | 0.19321 |
| MOL002151 | Senkyunone | 47.66394668 | 0.24435 | |
| MOL002135 | Myricanone | 40.5975663252 | 0.51262 | |
| ZE XIE | MOL000832 | Alisol, B, 23-acetate | 32.51621601 | 0.81841 |
| MOL002464 | 1-monolinolein | 37.1766283612 | 0.30249 | |
| SHA REN | MOL000358 | Beta-sitosterol | 36.91390583 | 0.75123 |
| MOL003975 | icosa-11, 14, 17-trienoic acid methyl ester | 44.81361719 | 0.23355 | |
| MOL000449 | Stigmasterol | 43.82985158 | 0.75665 | |
| CHAO BAI ZHU | MOL000028 | a-Amyrin | 39.51208978 | 0.7629 |
| MOL000033 | (3S,8S,9S,10R,13R,14S,17R)-10,13-dimethyl-17-[(2R,5S)-5-propan-2-yloctan-2-yl]-2, 3, 4, 7, 8, 9,1U2,14,15,16,17-dodecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-ol | 36.22847056 | 0.78288 | |
| HUAI SHAN YAO | MOL000310 | Denudatin B | 61.47237606 | 0.37838 |
| MOL000322 | Kadsurenone | 54.72301284 | 0.37829 | |
| MOL005429 | Hancinol | 64.0132681 | 0.37314 | |
2.2. 补肾化痰方成分靶点预测结果
将上述所得125个有效活性成分,依次输入Swiss Target Prediction网站,得到每个成分相对应的药物靶点,以Probability>0为条件进行筛选,导出数据并去重,最终得到990个补肾化痰方成分靶点。
2.3. 多囊卵巢综合征靶点预测结果
利用Genecards数据库和OMIM数据库,以“Polycystic Ovary Syndrome”为关键词进行搜索,合并所得疾病靶点,去重,最终得到4759个疾病靶点。将990个药物靶点和4759个疾病靶点通过Draw Venn Diagram网站在线分析,获得434个交集靶点,绘制韦恩图(图 1)。
1.

药物与疾病共同作用靶点韦恩图
Venn diagram of drug and disease interaction targets.
2.4. 补肾化痰方治疗PCOS的核心靶点筛选
利用STRING(<a href="http://www.string-db.org/" target="_blank">http://www.string-db.org/</a>)数据库,以“Multiple proteins”为数据分析模式、“Homo Sapiens”为物种限定、Required Confidence(combined score)>0.9为阈值,对交集靶蛋白进行相互作用关系分析,后导入Cytoscape3.7.2并利用其中CytoNCA插件分析交集网络中各个节点的属性值,计算Degree值的二倍中位数,筛选出大于其值的靶点,构建核心靶点的筛选策略图(<xref ref-type="fig" rid="Figure2">图 2</xref>)。筛选结果从大到小依次排序,取排名前10的靶点为核心靶点,分别为PIK3CA、PIK3R1、APP、KNG1、SRC、AKT1、TP53、MAPK1、MAPK3、BDKRB2(<xref ref-type="fig" rid="Figure3">图 3</xref>、<xref ref-type="table" rid="Table2">表 2</xref>)。节点分别代表潜在作用靶点,节点大小与颜色代表靶点的度值,节点越大、颜色越深,表明靶点在网络体系中的度值越大;节点间连线表示靶点间存在潜在的相互作用关系<sup>[<xref ref-type="bibr" rid="b14">14</xref>]</sup>。
2.

核心靶点的筛选策略图
Screening strategy of the core targets.
3.

补肾化痰方治疗PCOS的核心靶点图
Core targets of Bushen Huatan Recipe in the treatment of PCOS.
2.
补肾化痰方治疗PCOS的核心靶点
Core targets of Bushen Huatan recipe in the treatment of PCOS
| Name | Degree |
| PIK3CA | 82 |
| PIK3R1 | 76 |
| APP | 68 |
| KNG1 | 59 |
| SRC | 58 |
| AKT1 | 54 |
| TP53 | 54 |
| MAPK1 | 52 |
| MAPK3 | 52 |
| BDKRB2 | 50 |
2.5. GO功能富集分析
通过DAVID(<a href="https://david.ncifcrf.gov/" target="_blank">https://david.ncifcrf.gov/</a>)网站,借助“Functional Annotation Tool”对434个交集靶点进行GO富集分析,包括生物过程、细胞成分和分子功能等3个模块的分析,以<italic>P</italic> < 0.05和FDR < 0.05为标准筛选,根据涉及靶点数目排序,选取前30个GO条目:其中BP相关条目8个,CC相关条目14个,MF相关条目8个,结果显示补肾化痰方治疗多囊卵巢综合征主要靶点的生物过程主要富集在药物反应、凋亡过程的负调控、RNA聚合酶Ⅱ启动子转录的正调控、蛋白质磷酸化、细胞增殖的正调控、氧化还原过程等;细胞组成主要富集在细胞质、细胞膜、胞质溶胶、线粒体、内质网膜等;分子功能主要富集在蛋白质结合、ATP结合、酶结合、锌离子结合等(<xref ref-type="table" rid="Table3">表 3</xref>),并借助微生信(<a href="http://www.bioinformatics.com.cn/" target="_blank">http://www.bioinformatics.com.cn/</a>)在线网站作GO富集BP CC MF三合一图(<xref ref-type="fig" rid="Figure4">图 4</xref>)。
3.
GO功能富集分析
GO functional enrichment analysis
| Sub group | GO term | Number of genes |
| BP: Biological process; CC: Cellular component; MF: Molecular function. | ||
| BP | Signal transduction | 83 |
| BP | Protein phosphorylation | 67 |
| BP | Positive regulation of transcription from rna polymerase ii promoter | 65 |
| BP | Response to drug | 57 |
| BP | Negative regulation of apoptotic process | 56 |
| BP | Positive regulation of cell proliferation | 54 |
| BP | Negative regulation of transcription from rna polymerase ii promoter | 44 |
| BP | Oxidation-reduction process | 42 |
| CC | Plasma membrane | 213 |
| CC | Cytoplasm | 175 |
| CC | Cytosol | 169 |
| CC | Integral component of membrane | 154 |
| CC | Nucleoplasm | 112 |
| CC | Integral component of plasma membrane | 106 |
| CC | Membrane | 105 |
| CC | Extracellular exosome | 105 |
| CC | Mitochondrion | 54 |
| CC | Extracellular space | 54 |
| CC | Perinuclear region of cytoplasm | 52 |
| CC | Intracellular | 49 |
| CC | Cell surface | 48 |
| CC | Endoplasmic reticulum membrane | 44 |
| MF | Protein binding | 303 |
| MF | Atp binding | 117 |
| MF | Protein kinase activity | 61 |
| MF | Protein serine/threonine kinase activity | 52 |
| MF | Identical protein binding | 50 |
| MF | Protein homodimerization activity | 49 |
| MF | Enzyme binding | 48 |
| MF | Zinc ion binding | 47 |
4.
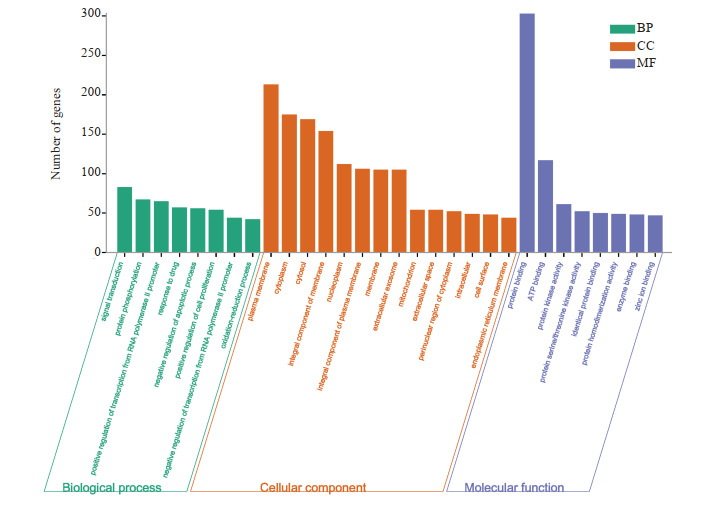
GO功能富集分析
GO functional enrichment analysis.
2.6. KEGG通路富集分析
通过DAVID(<a href="https://david.ncifcrf.gov/" target="_blank">https://david.ncifcrf.gov/</a>)网站,借助“Functional Annotation Tool”对434个共同靶基因进行KEGG富集分析,得141条信号通路,设置<italic>P</italic> < 0.01为筛选标准,根据P值大小进行排序,选取前20位为主要信号通路如癌症通路、HIF-1信号通路、Rap1信号通路、PI3K-Akt信号通路、雌激素信号通路等(<xref ref-type="table" rid="Table4">表 4</xref>)。借助微生信(<a href="http://www.bioinformatics.com.cn/" target="_blank">http://www.bioinformatics.com.cn/</a>)在线网站作KEGG通路富集气泡图(<xref ref-type="fig" rid="Figure5">图 5</xref>)。
4.
KEGG通路富集分析
KEGG pathway enrichment analysis
| Pathway | P | Count |
| Pathways in cancer | 7.9038E-28 | 84 |
| Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | 2.16567E-21 | 62 |
| Proteoglycans in cancer | 5.86175E-21 | 52 |
| Prostate cancer | 1.59199E-19 | 34 |
| Pancreatic cancer | 1.94634E-16 | 27 |
| HIF-1 signaling pathway | 2.90563E-16 | 32 |
| Rap 1 signaling pathway | 2.16931E-15 | 46 |
| Hepatitis B | 1.33093E-14 | 37 |
| Central carbon metabolism in cancer | 1.76555E-14 | 25 |
| Prolactin signaling pathway | 2.73225E-14 | 26 |
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | 6.12596E-14 | 58 |
| Non-small cell lung cancer | 7.23434E-14 | 23 |
| Steroid hormone biosynthesis | 1.70959E-13 | 23 |
| Glioma | 2.69896E-13 | 24 |
| Estrogen signaling pathway | 3.99392E-13 | 29 |
| VEGF signaling pathway | 5.75002E-13 | 23 |
| cAMP signaling pathway | 6.71883E-13 | 41 |
| ErbB signaling pathway | 6.84991E-13 | 27 |
| Colorectal cancer | 8.45564E-13 | 23 |
| Neurotrophin signaling pathway | 1.94753E-12 | 31 |
5.

KEGG通路富集分析
KEGG pathway enrichment analysis.
2.7. KEGG“通路-靶点”关系网络的构建
根据KEGG通路分析结果,选取前20位,分别建立通路与对应靶点之间的相互作用关系和节点属性与对应靶点之间的相互作用关系,并导入Cytoscape 3.7.2软件中,对“通路-靶点”关系网络进行可视化分析,构建补肾化痰方治疗多囊卵巢综合征的“通路-靶点”关系网络图(图 6)。
6.

KEGG"通路-靶点"关系网络图
KEGG pathway-target relationship network diagram.
2.8. 分子对接验证
根据网络拓扑结构分析结果选取核心活性成分Degree值排名前3的β-谷甾醇、山奈酚、槲皮素与CytoNCA筛选出来的核心靶点PIK3CA、PIK3R1、APP、AKT1、MAPK1分别进行分子对接。一般认为结合能 < -4.25 kcal/mol表示配体小分子与受体蛋白之间有一定的结合活性;结合能 < -5.0 kcal/mol表明二者之间有较好的结合活性;结合能 < -7.0 kcal/mol表明配体与受体具有强烈的结合活性[15]。分子对接结果(表 5)可见核心活性成分β-谷甾醇、山奈酚、槲皮素与核心靶点PIK3CA、PIK3R1、APP、AKT1、MAPK1之间的结合能均小于-5.0 kcal/mol,说明两者之间有较好的结合活性;并且β-谷甾醇与PIK3CA、PIK3R1、APP、AKT1、MAPK1,山奈酚与PIK3CA、APP、MAPK1,槲皮素与PIK3CA、PIK3R1、APP、MAPK1之间的结合能均小于-7.0 kcal/mol,说明两者具有强烈的结合活性。依据自由结合能的大小,选取部分对接结果进行可视化,利用PyMOL软件绘图(图 7)。由图可见,β-谷甾醇能稳定地对接到PIK3CA蛋白结构6GVF的活性口袋中,二者通过氨基酸残基LYS-271发生氢键作用;山奈酚能稳定地对接到AKT1蛋白结构1UNQ的活性口袋中,二者通过氨基酸残基AGR-48和ASN-54发生氢键作用;槲皮素能稳定地对接到MAPK1蛋白结构2Y9Q的活性口袋中,二者通过氨基酸残基GLU-33和LYS-114发生氢键作用。
5.
补肾化痰方核心活性成分与核心靶点的分子对接结果
Molecular docking results of core active components and core targets of Bushen Huatan recipe
| Core active component | Core target | Binding energy/kcal·mol-1 |
| PIK3CA(6GVF) | -10.1 | |
| PIK3R1(7CIO) | -7.7 | |
| Beta-sitosterol | APP(5onQ) | -8.6 |
| AKT1(1UNQ) | -7.9 | |
| MAPK1(2Y9Q) | -8.5 | |
| PIK3CA(6GVF) | -8.6 | |
| PIK3R1(7CIO) | -6.9 | |
| Kaempferol | APP(5onQ) | -7.2 |
| AKT1(1UNQ) | -6.0 | |
| MAPK1(2Y9Q) | -8.8 | |
| PIK3CA(6GVF) | -8.9 | |
| PIK3R1(7CIO) | -7.6 | |
| Quercetin | APP(5onQ) | -7.4 |
| AKT1(1UNQ) | -6.2 | |
| MAPK1(2Y9Q) | -8.9 |
7.

部分核心活性成分与核心靶点相互作用的分子对接示意图
Schematic diagram of molecular docking of interaction between some core active components and core targets.A: Docking site between β-sitosterol and PIK3CA.B: Docking site between kaempferoll and AKT1. C: Docking site between quercetin and MAPK1.
2.9. 补肾化痰方对PI3K、AKT、MAPK1蛋白表达的影响
Western blot检测PI3K、AKT、MAPK1蛋白表达,其中,MAPK1编码ERK1/2。结果表明,与对照组比较,模型组PI3K蛋白、AKT蛋白表达升高,ERK1/2蛋白(P < 0.01)表达降低;与模型组比较,治疗组PI3K蛋白(P < 0.01)、AKT蛋白(P < 0.05)表达降低,ERK1/2蛋白表达升高(图 8)。
8.

各组小鼠卵巢组织PI3K、AKT、MAPK1蛋白表达
Expression of PI3K, AKT and MAPK1 proteins in ovarian tissue of the mice in each group detected by Western blotting (A) and quantitative analysis of the results (B-D). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs model group; ##P < 0.01 vs control group.
3. 讨论
多囊卵巢综合征是临床上常见的妇科内分泌疾病,好发于育龄期女性,以持续无排卵、卵巢多囊样变、高雄激素血症为特征,临床常表现为月经紊乱、不孕、肥胖、多毛、黑棘皮症等[16]。痰湿证、血瘀证、湿热证是PCOS的主要证候,痰、瘀壅滞胞宫表现为闭经、不孕、卵巢呈多囊样改变;化热则表现出痤疮、多毛等现象。以此长期不断积累,则成为多囊卵巢综合征的发病重要因素。本课题组基于多年的临床及基础研究,采用补肾化痰方以治疗多囊卵巢综合征。补肾化痰方是临床经验方,由苍附导痰汤化载而来。方中仙灵脾、仙茅、鹿角霜补肾益气;苍术、炒白术、半夏、陈皮、九节菖蒲、泽泻、胆南星、砂仁健脾化痰,利水渗湿;淮山药补脾益肾;香附、川芎活血化瘀,调经助孕。全方补肾健脾,化痰逐瘀通经,是临床治疗多囊卵巢综合征的有效方剂。
本研究通过TCMSP数据库筛选得到补肾化痰方中共包含125个有效活性成分,对应990个药物靶点,多囊卵巢综合征的相关作用靶点4759个,将药物靶点和疾病靶点通过Draw Venn Diagram网站在线分析,获得434个交集靶点。根据上述所筛选出的结果,可知β-谷甾醇、山奈酚、槲皮素可能是补肾化痰方治疗多囊卵巢综合征的核心活性成分。β-谷甾醇是四环三萜类化合物,有抗炎、抗氧化、免疫调节、降糖、降脂、降低雄激素等作用[17-18]。赵帅等[19]发现β-谷甾醇可促进颗粒细胞增殖,抑制凋亡,其机制与PI3K/AKT信号通路有关。山柰酚是黄酮类化合物,有抗炎、抗氧化、降低血脂、扩张血管、抗肿瘤等作用[20-23]。有研究发现卵泡生长发育异常可能是引起多囊卵巢综合征无排卵及临床内分泌改变的病理基础[24]。而山奈酚可以在绵羊次级卵泡的体外培养过程中保持卵泡存活率,增加活性线粒体水平并通过介导PI3K信号通路促进卵母细胞减数分裂[25]。槲皮素是黄酮类化合物,有抗炎、抗氧化、控制葡萄糖稳态、抑制胰岛素分泌等作用[26-27]。研究证实槲皮素具有降低卵巢直径和体质量,促进卵泡腺外层和黄体功能恢复的作用,还可减轻PCOS患者性激素和代谢紊乱的作用[28]。经网络拓扑属性分析筛选出MAPK1、AKT1、PIK3CA等核心靶点,推测可能是补肾化痰方治疗多囊卵巢综合征的主要作用靶点。PIK3CA是PI3K家族中唯一存在肿瘤特异性突变的基因[29]。在人体各个组织中均有表达的PIK3CA对PI3K/AKT信号通路有激活作用。MAPK1,MAPK3等属于MAPK家族,MAPK通路能负反馈调节PI3K通路,导致PCOS胰岛素抵抗的形成,而胰岛素抵抗是PCOS重要发病机制[30]。GO富集分析显示补肾化痰方治疗多囊卵巢综合征主要靶点的生物过程主要富集在药物反应、凋亡过程的负调控、RNA聚合酶Ⅱ启动子转录的正调控、蛋白质磷酸化、细胞增殖的正调控、氧化还原过程等;细胞组成主要富集在细胞质、细胞膜、胞质溶胶、线粒体、内质网膜等;分子功能主要富集在蛋白质结合、ATP结合、酶结合、锌离子结合等。KEGG富集分析得141条信号通路,根据P值大小进行排序,选取前二十位为主要信号通路如癌症通路、HIF-1信号通路、Rap1信号通路、PI3K-Akt信号通路、雌激素信号通路等。其中,PI3K-Akt信号通路与多囊卵巢综合征密切相关。PI3K-Akt信号通路与胰岛素抵抗(IR)、糖尿病和代谢疾病密切相关。PI3K通路障碍是PCOS引起IR的主要因素,PI3K通过变构并激活磷酸酰肌醇的激酶进而激活靶蛋白Akt;活化的胰岛素受体β亚基的酪氨酸激酶通过激活胰岛素受体底物,进一步激活PI3K通路,激活后的PI3K使其下游靶蛋白Akt多个残基位点发生磷酸化进而激活Akt,导致卵泡膜细胞增生、卵泡异常发育或无排卵等[31]。Qiu等[32]运用六味地黄丸治疗PCOS,发现PI3K-Akt信号通路可通过上调CYP19A1,将雄激素转化为雌激素,减轻IR和卵巢多囊样改变,恢复卵泡的发育,减少闭锁卵泡。可以推测未来将会有更多的PCOS患者受益于PI3K-Akt信号通路的研究。
分子对接结果显示核心活性成分β-谷甾醇、山奈酚、槲皮素均能与核心靶点PIK3CA、PIK3R1、APP、AKT1、MAPK1稳定结合并形成氢键,初步揭示了补肾化痰方通过多靶点,多通路治疗多囊卵巢综合征的作用特点,可为后期进一步探究其机制提供依据。
为进一步验证补肾化痰方治疗多囊卵巢综合征的作用机制的网络药理学分析结果,结合以上分析最终选取了核心靶点MAPK1和核心通路PI3K-AKT进行动物实验研究。结果表明,补肾化痰方能明显改善多囊卵巢综合征相关症状,并下调PI3K,AKT蛋白表达,上调MAPK1蛋白表达,提示了补肾化痰方可能通过β-谷甾醇、山奈酚、槲皮素等活性成分作用于MAPK1等关键靶点,并通过介导PI3K-Akt等信号通路发挥抗炎、改善胰岛素抵抗、促进卵泡发育、调节激素水平等药理作用来治疗多囊卵巢综合征。
综上所述,本研究采用网络药理学方法和分子对接技术,结合动物实验初步验证了补肾化痰方治疗多囊卵巢综合征的具体作用靶点和通路,表现了中药、多成分、疾病、多靶点协同作用的药理机制,为进一步探究其作用机制提供了一定的参考依据,为临床上中药治疗多囊卵巢综合征的药效物质基础和作用机制提供了重要理论和实验依据。
Biography
高梦雅,硕士,E-mail:gaomengya54@163.com
Funding Statement
国家自然科学基金(81774357,81904237,82074479);江苏省中医院创新发展基金(Y2018CX40);2019年高层次卫生人才“六个一工程”拔尖人才科研项目(LGY2019070);2021年度江苏省中医药科技发展计划专题研究项目(ZT202107)
Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (81774357, 81904237, 82074479)
Contributor Information
高 梦雅 (Mengya GAO), Email: gaomengya54@163.com.
聂 晓伟 (Xiaowei NIE), Email: fsyy00636@njucm.edu.cn.
References
- 1.马 堃. 补肾活血中药在卵巢功能障碍(排卵障碍性不孕不育)中提高卵巢对促性腺激素反应性机制的现状、问题及展望. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZY201117034.htm. 中国中药杂志. 2011;36(17):2441–4. [马堃. 补肾活血中药在卵巢功能障碍(排卵障碍性不孕不育)中提高卵巢对促性腺激素反应性机制的现状、问题及展望[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2011, 36(17): 2441-4.] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Beltadze K, Barbakadze L. Diagnostic features of polycystic ovary syndrome in adolescents (review) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26598450. Georgian Med News. 2015;(238):32–4. [Beltadze K, Barbakadze L. Diagnostic features of polycystic ovary syndrome in adolescents (review)[J]. Georgian Med News, 2015 (238): 32-4.] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ren LN, Guo LH, Ma WZ, et al. A meta-analysis on acupuncture treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2014;39(3):238–46. [Ren LN, Guo LH, Ma WZ, et al. A meta-analysis on acupuncture treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome[J]. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu, 2014, 39(3): 238-46.] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.沈 文娟, 尤 天娇, 金 宝, et al. 多囊卵巢综合征中西医病因病机及治疗研究进展. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJZY201904041.htm. 辽宁中医杂志. 2021;48(12):196–9. [沈文娟, 尤天娇, 金宝, 等. 多囊卵巢综合征中西医病因病机及治疗研究进展[J]. 辽宁中医杂志, 2021, 48(12): 196-9.] [Google Scholar]
- 5.周 雨禾, 刘 婷, 马 宏博. 黄连温胆汤合少腹逐瘀汤加减治疗痰瘀互结证多囊卵巢综合征致排卵障碍的临床疗效. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSFX202116016.htm. 中国实验方剂学杂志. 2021;27(16):96–101. [周雨禾, 刘婷, 马宏博. 黄连温胆汤合少腹逐瘀汤加减治疗痰瘀互结证多囊卵巢综合征致排卵障碍的临床疗效[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2021, 27(16): 96-101.] [Google Scholar]
- 6.周 桂瑶, 冉 雪梦. 中医药治疗肥胖型多囊卵巢综合征研究进展. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDZY202104005.htm. 现代中医药. 2021;41(4):12–6. [周桂瑶, 冉雪梦. 中医药治疗肥胖型多囊卵巢综合征研究进展[J]. 现代中医药, 2021, 41(4): 12-6.] [Google Scholar]
- 7.洪 莲, 林 诗彬, 符 娇文, et al. 补肾调经汤治疗对多囊卵巢综合征患者卵巢超声影像学及预后的影响. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYHS202111043.htm. 中华中医药学刊. 2021;39(11):186–8. [洪莲, 林诗彬, 符娇文, 等. 补肾调经汤治疗对多囊卵巢综合征患者卵巢超声影像学及预后的影响[J]. 中华中医药学刊, 2021, 39(11): 186-8.] [Google Scholar]
- 8.洪 艳丽, 吴 飞. 补肾化痰方对多囊卵巢综合征胰岛素抵抗Akt通路调控的实验研究. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZXJ201402029.htm. 中国中西医结合杂志. 2014;34(2):230–4. [洪艳丽, 吴飞. 补肾化痰方对多囊卵巢综合征胰岛素抵抗Akt通路调控的实验研究[J]. 中国中西医结合杂志, 2014, 34(2): 230-4.] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Zhou W, Hong YL, Yin AL, et al. Non-invasive urinary metabolomics reveals metabolic profiling of polycystic ovary syndrome and its subtypes. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2020;185:113262. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2020.113262. [Zhou W, Hong YL, Yin AL, et al. Non-invasive urinary metabolomics reveals metabolic profiling of polycystic ovary syndrome and its subtypes[J]. J Pharm Biomed Anal, 2020, 185: 113262.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Zhang ZH, Hong YL, Chen MM, et al. Serum metabolomics reveals metabolic profiling for women with hyperandrogenism and insulin resistance in polycystic ovary syndrome. Metabolomics. 2020;16(2):20. doi: 10.1007/s11306-020-1642-y. [Zhang ZH, Hong YL, Chen MM, et al. Serum metabolomics reveals metabolic profiling for women with hyperandrogenism and insulin resistance in polycystic ovary syndrome[J]. Metabolomics, 2020, 16 (2): 20.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ru JL, Li P, Wang JN, et al. TCMSP: a database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines. J Cheminform. 2014;6:13. doi: 10.1186/1758-2946-6-13. [Ru JL, Li P, Wang JN, et al. TCMSP: a database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines[J]. J Cheminform, 2014, 6: 13.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Li JS, Zhao P, Li Y, et al. Systems pharmacology-based dissection of mechanisms of Chinese medicinal formula Bufei Yishen as an effective treatment for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Sci Rep. 2015;5:15290. doi: 10.1038/srep15290. [Li JS, Zhao P, Li Y, et al. Systems pharmacology-based dissection of mechanisms of Chinese medicinal formula Bufei Yishen as an effective treatment for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. Sci Rep, 2015, 5: 15290.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Tang Y, Li M, Wang JX, et al. CytoNCA: a cytoscape plugin for centrality analysis and evaluation of protein interaction networks. Biosystems. 2015;127:67–72. doi: 10.1016/j.biosystems.2014.11.005. [Tang Y, Li M, Wang JX, et al. CytoNCA: a cytoscape plugin for centrality analysis and evaluation of protein interaction networks [J]. Biosystems, 2015, 127: 67-72.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.夏 亚飞, 潘 博宇, 阎 姝. 基于网络药理学探究黄芪-桂枝药对防治化疗引起的神经毒性的作用机制. 中草药. 2021;52(12):3611–8. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2021.12.018. [夏亚飞, 潘博宇, 阎姝. 基于网络药理学探究黄芪-桂枝药对防治化疗引起的神经毒性的作用机制[J]. 中草药, 2021, 52(12): 3611-8.] [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 15.裴 超, 邵 霖霖, 刘 晶, et al. 基于网络药理学与分子对接技术探讨红花治疗视网膜静脉阻塞的作用机制研究. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRCW202011006.htm. 天然产物研究与开发. 2020;32(11):1844–51, 1865. [裴超, 邵霖霖, 刘晶, 等. 基于网络药理学与分子对接技术探讨红花治疗视网膜静脉阻塞的作用机制研究[J]. 天然产物研究与开发, 2020, 32(11): 1844-51, 1865.] [Google Scholar]
- 16.马 堃, 宫 林娟, 陈 燕霞, et al. 基于网络药理学和分子对接研究补肾促卵方治疗多囊卵巢综合征不孕的分子机制. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZY202111006.htm. 中国中药杂志. 2021;46(11):2650–9. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20210312.501. [马堃, 宫林娟, 陈燕霞, 等. 基于网络药理学和分子对接研究补肾促卵方治疗多囊卵巢综合征不孕的分子机制[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2021, 46(11): 2650-9.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ponnulakshmi R, Shyamaladevi B, Vijayalakshmi P, et al. In silico and in vivo analysis to identify the antidiabetic activity of beta sitosterol in adipose tissue of high fat diet and sucrose induced type- 2 diabetic experimental rats. Toxicol Mech Methods. 2019;29(4):276–90. doi: 10.1080/15376516.2018.1545815. [Ponnulakshmi R, Shyamaladevi B, Vijayalakshmi P, et al. In silico and in vivo analysis to identify the antidiabetic activity of beta sitosterol in adipose tissue of high fat diet and sucrose induced type- 2 diabetic experimental rats[J]. Toxicol Mech Methods, 2019, 29 (4): 276-90.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Novel Foods and Food Allergens (NDA) E F S A Panel on Nutrition, Turck D, Castenmiller J, et al. A combination of beta-sitosterol and beta-sitosterol glucoside and normal function of the immune system: evaluation of a health claim pursuant to Article 13(5) of Regulation (EC) No1924/2006. http://efsa.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.2903/j.efsa.2019.5776. EFSA J. 2019;17(7):e05776. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2019.5776. [Novel Foods and Food Allergens (NDA) E F S A Panel on Nutrition, Turck D, Castenmiller J, et al. A combination of beta-sitosterol and beta-sitosterol glucoside and normal function of the immune system: evaluation of a health claim pursuant to Article 13(5) of Regulation (EC) No1924/2006[J]. EFSA J, 2019, 17(7): e05776.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.赵 帅, 陈 冬梅, 虎 娜, et al. β-谷甾醇通过PI3K/AKT通路影响颗粒细胞增殖及凋亡. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNXY202104004.htm. 宁夏医科大学学报. 2021;43(4):339–44. [赵帅, 陈冬梅, 虎娜, 等. β-谷甾醇通过PI3K/AKT通路影响颗粒细胞增殖及凋亡[J]. 宁夏医科大学学报, 2021, 43(4): 339-44.] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Nam SY, Jeong HJ, Kim HM. Kaempferol impedes IL-32-induced monocyte-macrophage differentiation. Chem Biol Interact. 2017;274:107–15. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2017.07.010. [Nam SY, Jeong HJ, Kim HM. Kaempferol impedes IL-32-induced monocyte-macrophage differentiation[J]. Chem Biol Interact, 2017, 274: 107-15.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Torres-Villarreal D, Camacho A, Castro H, et al. Anti-obesity effects of kaempferol by inhibiting adipogenesis and increasing lipolysis in 3T3-L1 cells. J Physiol Biochem. 2019;75(1):83–8. doi: 10.1007/s13105-018-0659-4. [Torres-Villarreal D, Camacho A, Castro H, et al. Anti-obesity effects of kaempferol by inhibiting adipogenesis and increasing lipolysis in 3T3-L1 cells[J]. J Physiol Biochem, 2019, 75(1): 83-8.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Mahobiya A, Singh TU, Rungsung S, et al. Kaempferol-induces vasorelaxation via endothelium-independent pathways in rat isolated pulmonary artery. Pharmacol Rep. 2018;70(5):863–74. doi: 10.1016/j.pharep.2018.03.006. [Mahobiya A, Singh TU, Rungsung S, et al. Kaempferol-induces vasorelaxation via endothelium-independent pathways in rat isolated pulmonary artery[J]. Pharmacol Rep, 2018, 70(5): 863-74.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Imran M, Salehi B, Sharifi-Rad J, et al. Kaempferol: a key emphasis to its anticancer potential. Molecules. 2019;24(12):2277. doi: 10.3390/molecules24122277. [Imran M, Salehi B, Sharifi-Rad J, et al. Kaempferol: a key emphasis to its anticancer potential[J]. Molecules, 2019, 24(12): 2277.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Rafa L, Dessein AF, Devisme L, et al. REG4 acts as a mitogenic, motility and pro-invasive factor for colon cancer cells. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000039644811010_70c1.html. Int J Oncol. 2010;36(3):689–98. doi: 10.3892/ijo_00000544. [Rafa L, Dessein AF, Devisme L, et al. REG4 acts as a mitogenic, motility and pro-invasive factor for colon cancer cells[J]. Int J Oncol, 2010, 36(3): 689-98.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Santos JMS, Monte APO, TLBGLins, et al. Kaempferol can be used as the single antioxidant in the in vitro culture medium, stimulating sheep secondary follicle development through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling pathway. Theriogenology. 2019;136:86–94. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2019.06.036. [Santos JMS, Monte APO, TLBGLins, et al. Kaempferol can be used as the single antioxidant in the in vitro culture medium, stimulating sheep secondary follicle development through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling pathway[J]. Theriogenology, 2019, 136: 86-94.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Yuan K, Zhu QQ, Lu QY, et al. Quercetin alleviates rheumatoid arthritis by inhibiting neutrophil inflammatory activities. J Nutr Biochem. 2020;84:108454. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2020.108454. [Yuan K, Zhu QQ, Lu QY, et al. Quercetin alleviates rheumatoid arthritis by inhibiting neutrophil inflammatory activities[J]. J Nutr Biochem, 2020, 84: 108454.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Wang YY, Chang CY, Lin SY, et al. Quercetin protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion and oxygen glucose deprivation/ reoxygenation neurotoxicity. J Nutr Biochem. 2020;83:108436. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2020.108436. [Wang YY, Chang CY, Lin SY, et al. Quercetin protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion and oxygen glucose deprivation/ reoxygenation neurotoxicity[J]. J Nutr Biochem, 2020, 83: 108436.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Jahan S, Abid A, Khalid S, et al. Therapeutic potentials of Quercetin in management of polycystic ovarian syndrome using Letrozole induced rat model: a histological and a biochemical study. J Ovarian Res. 2018;11(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s13048-018-0400-5. [Jahan S, Abid A, Khalid S, et al. Therapeutic potentials of Quercetin in management of polycystic ovarian syndrome using Letrozole induced rat model: a histological and a biochemical study[J]. J Ovarian Res, 2018, 11(1): 26.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Samuels Y, Wang ZH, Bardelli A, et al. High frequency of mutations of the PIK3CA gene in human cancers. Science. 2004;304(5670):554. doi: 10.1126/science.1096502. [Samuels Y, Wang ZH, Bardelli A, et al. High frequency of mutations of the PIK3CA gene in human cancers[J]. Science, 2004, 304 (5670): 554.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.张 飞祥, 李 雪莲. 多囊卵巢综合征胰岛素抵抗机制研究进展. 国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志. 2018;37(2):167–71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1889.2018.02.019. [张飞祥, 李雪莲. 多囊卵巢综合征胰岛素抵抗机制研究进展[J]. 国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志, 2018, 37(2): 167-71.] [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 31.洪 金妮, 黎 巍威, 张 宁, et al. 中药降糖复方水提物通过PI3K/Akt/NF- κB信号通路抑制KK-Ay小鼠糖尿病肾病炎症. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YWPJ201710005.htm. 药物评价研究. 2017;40(10):1389–96. [洪金妮, 黎巍威, 张宁, 等. 中药降糖复方水提物通过PI3K/Akt/NF- κB信号通路抑制KK-Ay小鼠糖尿病肾病炎症[J]. 药物评价研究, 2017, 40(10): 1389-96.] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Qiu ZX, Dong JJ, Xue C, et al. Liuwei Dihuang Pills alleviate the polycystic ovary syndrome with improved insulin sensitivity through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020;250:111965. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.111965. [Qiu ZX, Dong JJ, Xue C, et al. Liuwei Dihuang Pills alleviate the polycystic ovary syndrome with improved insulin sensitivity through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2020, 250: 111965.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


