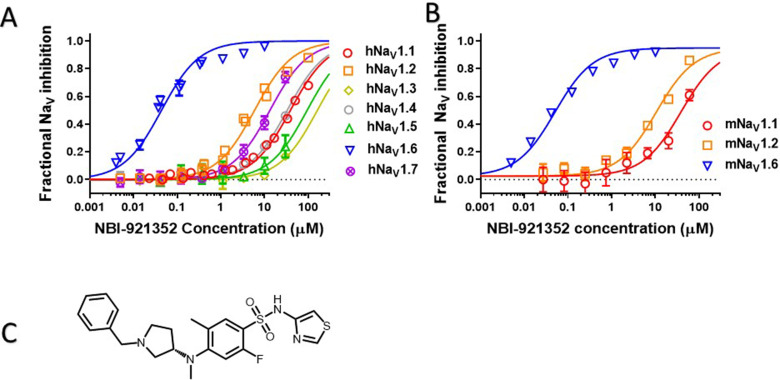
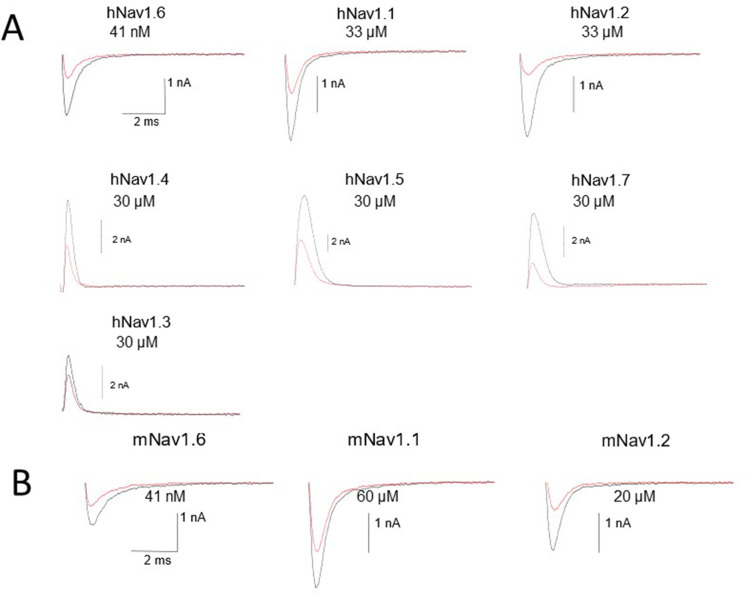
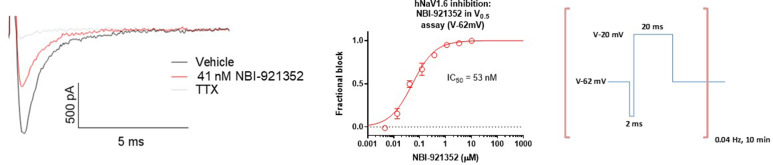
Figure 1. Potency and isoform selectivity of NBI-921352 for human and mouse NaV channels.
Concentration-response curves were generated by automated patch-clamp electrophysiology using the SophionQube. Concentration-response curves were generated for human (A) or mouse (B) NaV channel isoforms heterologously expressed in HEK293 cells. The analysis included only those cells that met pre-specified acceptance criteria for seal quality, current amplitude, and series resistance. Normalized data from all cell recordings at a concentration were grouped together and plotted with GraphPad Prism 8. Details regarding the number of cells analyzed for each NaV channel and concentration can be found in the source data sheet. Error bars indicating the standard error of the mean fraction were plotted for all points, but, in some cases, they were smaller than the data point symbols and, therefore, not visible. The chemical structure of NBI-921352 is shown (C).