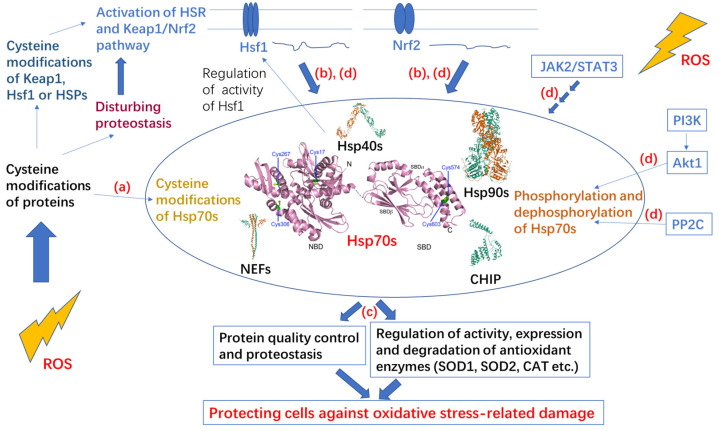
Figure 1.
Scheme of Hsp70 in redox homeostasis. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) often cause extensive cysteine modifications of proteins and disturb proteostasis, which can activate the heat shock response (HSR) and Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1)/nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) pathways by activation of heat shock transcription factor 1 (Hsf1) and redox-sensitive transcription factor Nrf2. ROS also widely modify different cellular signaling pathways. Hsp70s are involved in redox homeostasis in several aspects: (a) ROS can cause cysteine modifications of Hsp70s to modify their functions; (b) activation of Hsf1 and Nrf2 elevate expression of HSP70s; (c) Hsp70s work as central hubs in the protein quality control network to maintain proteostasis, including eliminating oxidized proteins and regulating activity, expression and degradation of antioxidant enzymes to contribute to redox homeostasis; and (d) Hsp70s are involved in redox-related signaling pathways, leading to phosphorylation or upregulated expression of Hsp70s.