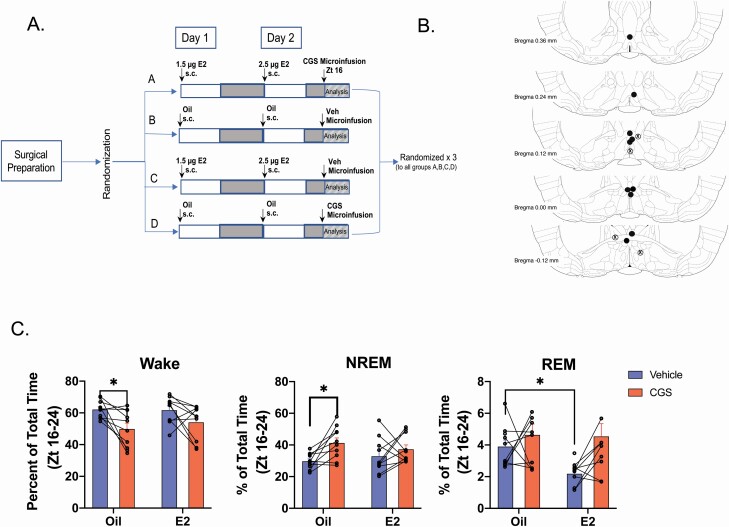
Figure 7.
A2A receptor agonist CGS-21680 decreased wake and increases NREM sleep following oil but not E2 treatment. Experimental timeline. Sprague–Dawley rats (n = 10) were OVX, fitted with telemeters and implanted with infusion guide cannula targeted to the MnPO. Following recovery from surgery, animals were randomly placed into one of four treatment arms where they received two subcutaneous injections of either oil or a subthreshold dose of E2 (that does not affect sleep–wake behavior) and at Zt16 on Day 2 infusion into the MnPO of either the A2A receptor agonist CGS-21680 (CGS; 24 nmol) or DMSO vehicle. The EEG/EMG recordings began immediately after the MnPO infusions. At the end of the recording period, the animals were allowed a 7-day washout period before being randomly assigned to another treatment arm. This protocol was repeated until all animals had been run through each treatment arm. The EEG/EMG traces from Zt 16 to 0 (8 h total) were scored and analyzed for changes in sleep–wake states. As CGS was predicted to increase NREM sleep at the expense of wake, the dark phase was chosen to maximize the probability of detecting changes in these two vigilant states. (B) Cannula Placement. Cannula placement was determined visually using neutral red staining. Representation of guide cannula placements (including misses). Placements were deemed a hit when they fell within the POA boundary defined by Bregma −0.3 mm to Bregma +0.4 mm and within with boundary of the MnPO (as marked by the box Figure 6B). Black circles = hits; Circled X = misses. (C) Effects of CGS on wake, NREM, and REM sleep in the presence and absence of E2. Local infusion of CGS into the MnPO significantly decreased wake following oil treatment, but not in the presence of E2 (repeated measures two-way ANOVA; main effect of CGS F1,9 = 15.16; p = 0.0037; no effect of E2; F1,9 = 0.2983, p = 0.5982; Šídák’s multiple comparison test, Adjusted p value *p = 0.0474). The decrease in wake was accompanied by an increase in NREM sleep following oil treatment only (repeated measures two-way ANOVA; main effect of CGS F1,9 = 8.822; p = 0.0157; no effect of E2; F1,9 = 0.0178, p = 0.8969; Šídák’s multiple comparison test, Adjusted p value *p = 0.0312). Curiously, REM sleep showed a significant effect of E2 but not CGS (repeated measures two-way ANOVA; main effect of E2 F1,9 = 5.576; p = 0.0425; no effect of CGS; F1,9 = 2.233, p = 0.1693; Šídák’s multiple comparison test, Adjusted p value *p = 0.0246). Individual lines represent paired measurements from the same animal. Data are the mean + SEM.