Abstract
The exposure-lag response of air temperature on daily COVID-19 incidence is unclear and there have been concerns regarding the robustness of previous studies. Here we present an analysis of high spatial and temporal resolution using the distributed lag non-linear modelling (DLNM) framework. Utilising nearly two years’ worth of data, we fit statistical models to twelve Italian cities to quantify the delayed effect of air temperature on daily COVID-19 incidence, accounting for several categories of potential confounders (meteorological, air quality and non-pharmaceutical interventions). Coefficients and covariance matrices for the temperature term were then synthesised using random effects meta-analysis to yield pooled estimates of the exposure-lag response with effects presented as the relative risk (RR) and cumulative RR (RRcum). The cumulative exposure response curve was non-linear, with peak risk at 15.1 °C and declining risk at progressively lower and higher temperatures. The lowest RRcum at 0.2 °C is 0.72 [0.56,0.91] times that of the highest risk. Due to this non-linearity, the shape of the lag response curve necessarily varied by temperature. This work suggests that on a given day, air temperature approximately 15 °C maximises the incidence of COVID-19, with the effects distributed in the subsequent ten days or more.
Keywords: Air temperature, COVID-19 incidence, Delayed effects, Italy, Time-series, Meta-analysis, Distributed lag non-linear model
1. Introduction
As of October 2021, more than 240 million cases of COVID-19 infections have been confirmed worldwide, and the global death toll has now exceeded 4 million people (World Health Organization, 2021). Aside from the direct impact of COVID-19, healthcare in other fields unrelated to infectious disease have also suffered from its knock-on effects. Woolf et al. (2020) reported a higher number of deaths in the United States than expected when comparing data to previous years and estimated that 35% of the excess mortality is due to conditions not directly attributed to COVID-19. Though difficulty in seeking medical treatment due to movement restriction measures and reluctance to risk exposure in healthcare settings are speculated reasons for the excess mortality, an overwhelmed healthcare system likely played a significant role, especially in the formative stages of the outbreak.
Italy was among the worst affected countries near the start of the pandemic, with daily cases peaking at the end of March 2020. Italy remained within the top ten countries with the highest cumulative number of confirmed cases by June 2020, at more than 240,000 cases, with a recorded case fatality rate exceeding 10% (Worldometer, 2020). Over a year since the start of the pandemic, widespread lockdown was reimposed due to transmission rates rising once more (Day, 2021).
Since the beginning of the outbreak, a number of studies have investigated the relationship between air temperature and COVID-19 incidence, though the evidence is inconclusive (Dong et al., 2021). Studies in Italy are no exception, with reports of both positive (Passerini et al., 2020; Zoran et al., 2020) and negative (De Angelis et al., 2021; Pirouz et al., 2020) associations. Several studies have also attempted to allow for non-linear and delayed effects of meteorological predictors, though until very recently (Nottmeyer and Sera, 2021) these have been limited to select regions (Runkle et al., 2020), relatively narrow temperature ranges (Bashir et al., 2020; Passerini et al., 2020; Tosepu et al., 2020), relatively short time series (Shi et al., 2020) and lag periods (Tobías and Molina, 2020), all of which may induce significant biases. Indeed, a recent review of papers which have investigated the association between air temperature and COVID-19 incidence identified critical methodological flaws in the majority of papers studied (Dong et al., 2021). This is perhaps unsurprising given the urgency for published works. In addition to the limitations mentioned above, concerns highlighted by Dong et al. (2021) included: low spatial resolution, failure to assess and/or account for autocorrelation, and failure to account for various categories of confounding variables (e.g., meteorological, air quality, non-pharmaceutical interventions (NPI)), including their potentially delayed effects.
Here we attempt to address these concerns by performing an analysis of high spatial and temporal resolution using almost two years’ worth of daily data. We fit statistical models to select Italian cities to quantify the delayed effect of air temperature on daily COVID-19 incidence, accounting for confounding variables. Coefficients and covariance matrices for the temperature term are then synthesised using random effects meta-analysis to yield pooled estimates of the exposure-lag response.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Data sources
Twelve Italian cities were included in this analysis, namely: Bologna, Brescia, Firenze, Livorno, Milano, Modena, Napoli, Parma, Prato, Roma, Torino and Trieste, selected based on the availability of daily city level data, between 24 February 2020 and 30 December 2021 inclusive. Daily confirmed COVID-19 cases for each city, with respective populations at risk, were accessed using the COVID-19 R package (Guidotti and Ardia, 2020), an interface to the COVID-19 Data Hub (https://covid19datahub.io/). For daily city-level data, confirmed cases and populations are sourced from Ministero della Salute (Dati COVID-19 Italia, 2021) and Istituto Nazionale di Statistica, Italia (Istituto Nazionale di Statistica, 2018) respectively. Country-level daily values of the stringency index (SI) are sourced from the Oxford Coronavirus Government Response Tracker (OxCGRT) project (Hale et al., 2021). This is a composite metric assessing the number and strictness of government policies and is comprised of nine response indicators including travel bans, workplace closures and school closures (https://www.bsg.ox.ac.uk/research/research-projects/covid-19-government-response-tracker).
Daily median city-level weather and air quality data were obtained from local meteorological stations (https://aqicn.org/data-platform/covid19/ (Air Quality Open Data Platform, 2022)) and included: (1) air temperature, (2) relative humidity, (3) air pressure, and (4) PM2.5. Daily city level residential mobility data was obtained from https://www.google.com/covid19/mobility/ (COVID-19 community mobility reports, 2020). Finally, daily COVID-19 vaccination administration counts at regional level were obtained from https://raw.githubusercontent.com/italia/covid19-opendata-vaccini/master/dati/somministrazioni-vaccini-latest.csv with corresponding populations from Istituto Nazionale di Statistica, Italia (Istituto Nazionale di Statistica, 2018).
2.2. Study design
We utilised the two-stage time series design (Berhane and Thomas, 2002). In the first stage, a series of city-specific statistical models were fitted, with terms representing the exposure-lag response with respect to air temperature, as well as additional confounding variables. In the second stage, coefficients and covariance matrices from the first stage models were pooled using meta-analysis. This approach controls for city-level confounders, relaxes the strong assumption that the exposure-lag response is not city-specific, and has been deployed in a recent similar study (Nottmeyer and Sera, 2021).
2.3. First stage analysis
In order to model the temporal dependency between daily temperature and COVID-19 incidence, we adopted the Distributed Lag Non-linear Model (DLNM) framework (Gasparrini et al., 2010). For each city, we fitted a Generalized Additive Model (GAM) (Wood, 2011) of the form:
| (1) |
where denotes the number of COVID-19 cases on day t and the model intercept. The logarithm of the population at risk (P) is fitted as a model offset. denotes a cross-basis term for air temperature on day t considering lag l, constructed using natural splines with the corresponding vector of coefficients. For the exposure dimension, internal knots were placed at the 27.5th and 72.5th percentiles, corresponding to 10.4 and 21.9 °C respectively (informed by minimising the AIC over a range of knot placement settings; see R code in the SI). For the lag basis, we pre-specified 3 degrees of freedom, with knots placed at the 33.3rd and 66.7th percentiles (Nottmeyer and Sera, 2021 found that larger values for the degrees of freedom incurred a loss of precision for the estimates). We considered lag range 0 through 10 days inclusive as in recent studies (Lauer et al., 2020; Nottmeyer and Sera, 2021). DOW denotes the day of week fitted as dummy variables, with the corresponding vector of coefficients. denotes additional predictors fitted as penalised smoothing splines, with the degree of smoothing estimated from the data. Time, t, was fitted as a highly flexible penalised natural spline with 20 knots to allow for seasonal and long-term trends, as well as sudden changes such as testing policy. We fitted cross-basis terms for additional confounders using penalised natural splines with 3 degrees of freedom for the exposure and lag dimensions and lag effects up to 10 days. This included: (1) log(daily cases + 1) in order to allow for autocorrelation (Imai et al., 2015, Nottmeyer and Sera, 2021); residential mobility, cumulative percentage of vaccines administered; stringency index, relative humidity, air pressure and PM2.5 (time series plots of these variables are provided in the SI). By fitting these as penalised terms, corresponding parameter estimates can shrink to simple linear effects to avoid over-parameterization (Benedetti and Abrahamowicz, 2004; Chen et al., 2016).
Heteroscedasticity and Autocorrelation Consistent (HAC) estimation of the covariance matrix was performed using the sandwich estimator (Zeileis, 2004, 2006). Parameters were estimated using restricted maximum likelihood (REML). Simulated Quantile-Quantile (Figure SI9) (Hartig, 2021) and partial autocorrelation (Figure SI10) plots are provided as supplementary information. We performed a sensitivity analysis by adjusting the parameterization of the cross-basis term for temperature since this was the predominant term of interest. Accordingly, we assessed the impact of changing the lag period to 5 and 15 days, as well as increasing the degrees of freedom for the lag basis to 4 and 5 respectively.
2.4. Second stage analysis
For each of the city-specific GAM's, the cross-basis term for air temperature, , was reduced to simpler sets of one-dimensional coefficients and corresponding covariance matrices for the exposure- and lag-dimensions respectively (Gasparrini and Armstrong, 2013). These were then pooled using random effects meta-analysis with REML estimation (Sera et al., 2019). We assessed for heterogeneity using the multivariate Cochran's Q test (using pre-specified α = 0.05) and the I2 statistic. The pooled exposure (i.e., air temperature) response summed over the lag period was presented as the cumulative relative risk (RRcum), centred on the temperature of the maximal RRcum. The pooled lag response at select temperatures (i.e., “exposure specific”) was presented as the relative risk (RR) centred on the current day (i.e. lag day 0). We computed 95% confidence intervals for both RR and RRcum to quantify uncertainty in these point estimates.
All statistical analyses were performed in R studio version 2021.09.0, using R version 4.1.2 (R Core Team, 2013) and relying heavily on the packages ‘dlnm’ (Gasparrini, 2011), ‘mgcv’ (Wood, 2011) and ‘mixmeta’ (Sera et al., 2019). R code and datasets are included in the supplementary material to fully reproduce the analysis.
3. Results
Across all city-specific time series, daily median air temperature ranged from −2.2 to 33.6 °C (Table 1 ). Model checking plots indicated good fit of the first stage models to the observed data (Figures SI9, SI10). Estimates of parameters from the meta-analytic models are provided in SI Table 1. There appeared to be low heterogeneity in meta-analytic models for the exposure and lag responses respectively with all P values for the Multivariate Cochran's Q test non-significant (P > 0.05) and I2 < 0.05% (Table 2 ). This indicated there was very little variation in effects between studies beyond sampling error.
Table 1.
Summary statistics by city for the modelling period.
| City | Total number of confirmed COVID-19 cases | Population at risk | Mean temperature (°C) | Minimum temperature (°C) | Maximum temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bologna | 123,736 | 1,011,291 | 15.3 | −1 | 30.5 |
| Brescia | 139,145 | 1,262,402 | 15 | −1.6 | 30 |
| Firenze | 102,974 | 1,013,260 | 16.2 | 1 | 31.4 |
| Livorno | 27,461 | 336,215 | 15.8 | 1.2 | 28.1 |
| Milano | 397,922 | 3,234,658 | 15.2 | −0.4 | 30.4 |
| Modena | 84,624 | 701,896 | 14.7 | −2.2 | 29.7 |
| Napoli | 337,124 | 3,101,002 | 17.8 | 2.1 | 31 |
| Parma | 37,439 | 450,256 | 15.6 | −1.1 | 30.4 |
| Prato | 31,503 | 256,071 | 15.8 | 1.1 | 31 |
| Roma | 365,339 | 4,355,725 | 17.9 | 3.3 | 31.5 |
| Torino | 255,154 | 2,269,120 | 15.3 | −0.5 | 30.1 |
| Trieste | 37,576 | 234,638 | 16.3 | −0.5 | 33.6 |
*Mean, minimum and maximum temperature are computed using daily median temperatures over the time series'.
Table 2.
Cochran's multivariate Q test and I2 statistic to assess heterogeneity in the meta-analytic models.
| Meta-analytic model | Q | df | P | I2 (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall cumulative response | 18.2 | 33 | 0.983 | <.05 | |
| Lag response | 1 °C | 10.06 | 33 | 1.000 | <.05 |
| 10 °C | 8.36 | 33 | 1.000 | <.05 | |
| 20 °C | 9.09 | 33 | 1.000 | <.05 | |
| 30 °C | 18.42 | 33 | 0.981 | <.05 | |
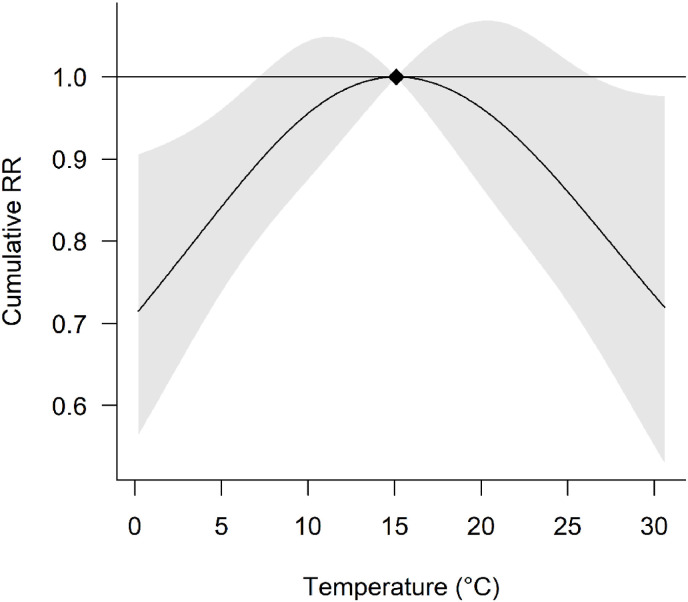
The cumulative exposure response curve was non-linear with peak risk at 15.1 °C, and declining risk at lower and higher temperatures (Fig. 1 ). Cumulative risk at 0.2 °C is 0.72 [0.56,0.91] times that at 15.1 °C. The decline in RRcum at temperature >15.1 °C exhibited slightly more uncertainty than the corresponding effect at temperatures <15.1 °C. The reductions in risk are statistically significant (P < 0.05) at temperatures below approx. 7 °C and above approx. 26 °C.
Fig. 1.
Overall cumulative exposure-response association. Cumulative RR is computed by summing the log RR over the lag period (0 through 10 days inclusive) before exponentiating. The effects are centred at the reference level (solid diamond = 15.1 °C). Grey shaded area represents 95% confidence intervals.
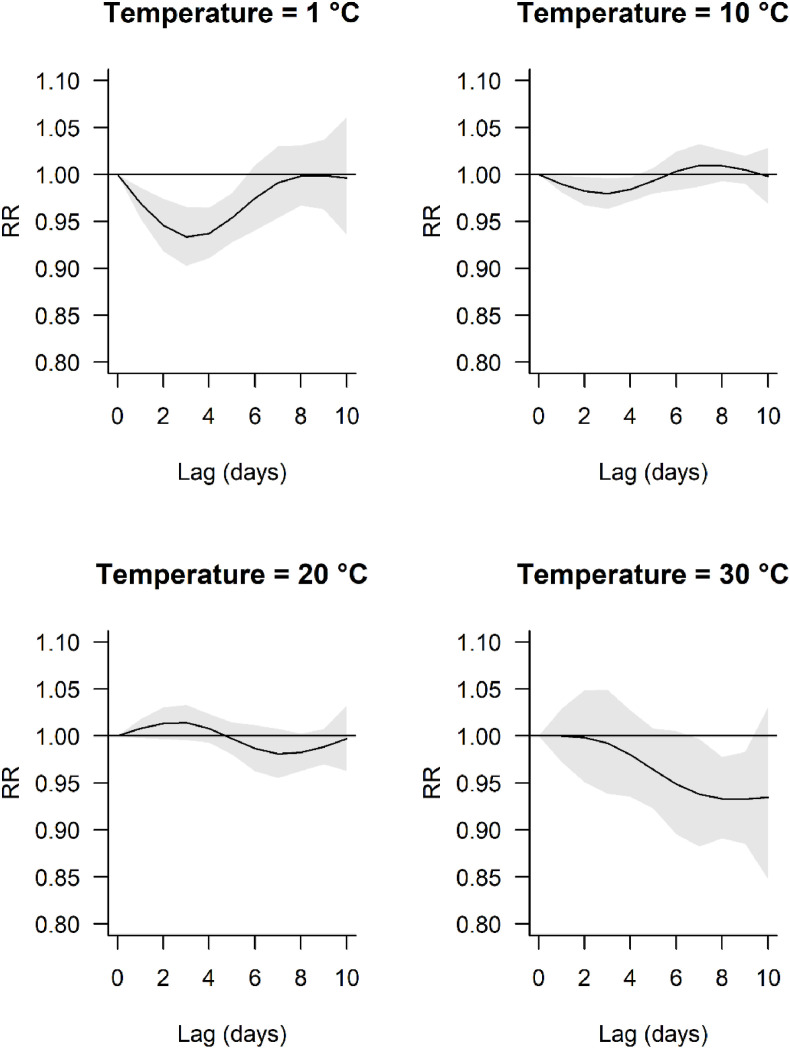
The lag response curves were centred at lag = 0 days and temperature = 15.1 °C (Fig. 2 ). The shape of the lag response necessarily varied by temperature due to the non-linear cumulative exposure response curve (Fig. 2). The magnitude of the effect becomes greater for increasing or decreasing temperatures compared with the reference temperature. Accordingly the lag response curves are relatively flat at temperatures 10 and 20 °C compared with 1 and 30 °C (Fig. 2). At 1 °C (top left Fig. 2) the decline in RRcum is statistically significant (P < 0.05) from day 0 to approx. lag 5.5 days with peak reduction at approx. 3 days lag. In contrast, for 30 °C the reduction in RRcum is delayed, with point estimates <1 only occurring beyond a lag of 2 days, and is significant between approx. 7 and 9.5 days lag. Aside from very high temperatures, the curves retract to the null at the end of the modelled lag (10 days).
Fig. 2.
Exposure-specific lag-response associations. The effects are centred at lag = 0 days and temperature = 15.1 °C. Grey shaded area represents 95% confidence intervals.
Changing the lag period of the cross-basis term for temperature from 10 to either 5 or 15 days in the sensitivity analysis incurred a loss of precision. For lag 5 days, the decline in RRcum above the reference temperature was less certain with confidence intervals that include the null and becoming wider with increasing temperature (Figures SI11). Upon increasing the lag to 15 days, the temperature of the maximum RRcum reduced slightly to approx. 11 °C (Figure SI12). Under this scenario point estimates hint of a possible upward trend at high temperatures, though again confidence intervals are too wide to conclude with any degree of certainty.
The shape and precision of the RRcum curve was relatively robust to increasing the degrees of freedom allocated to the lag basis from 3, to 4 and 5 respectively (Figures SI13, SI14).
4. Discussion
In this contribution, we quantified the exposure-lag response of air temperature on daily COVID-19 incidence in Italy. We fitted city-specific statistical models to extended time series accounting for numerous confounders, before pooling the temperature effects using meta-analysis, which was justified by low heterogeneity. We show that the cumulative exposure response curve is non-linear with peak risk at 15.1 °C, and declining risk at progressively lower and higher temperatures.
The decline in RRcum at temperature >12.9 °C was slightly shallower and exhibited more uncertainty than the corresponding effect at temperatures <12.9 °C. The air temperature yielding minimum RRcum was 0.2 °C, i.e., the minimum temperature used in the pooled analysis.
Due to the non-linear cumulative exposure response curve, the shape of the lag response curves necessarily vary by temperature. RR falls below 1 within the lag period, which is consistent with delayed effects of an increase or decrease in temperature (relative to reference) on a given day. Whilst the lag response for low temperatures declines and then returns to the null by day lag 10, this was not observed at high temperatures where the effects seemed further delayed with RR < 1 at lag day 10 (though the effect is not statistically significant). Moreover, our sensitivity analysis suggests effects may be distributed beyond 10 days. It is possible that, at the population level, temperature changes on a given day may affect daily incidence up to and beyond 15 days hence, and further work might consider investigating longer lag periods.
Nottmeyer and Sera (2021) performed a similar study on cities in England. The shape of the non-linear exposure-response relationship reported herein shows a similar trend to their study (though note the different centering temperature), suggesting progressively lower and higher temperatures beyond that at the maximum RRcum, are associated with reduced COVID-19 incidence. However, it appeared as though the temperature at which peak risk occurred was approximately 3.2 °C higher in our study (15.1 °C) compared to theirs (11.9 °C). Moreover, the largest absolute RRcum reported herein (1.39 [95% CI: 1.10; 1.79]) is also slightly smaller than that of the above study, at 1.62 [95% CI: 1.44; 1.81]). The temperature for which risk is minimised was 0.2 °C in the current study compared with 21.8 °C in their study (though confidence intervals widened at higher temperatures in their study).
Experiments on SARS-CoV-2 have demonstrated a temperature-dependent effect on the stability of virus particles on smooth surfaces (Chin et al., 2020). Since SARS-CoV-2 is shown to be capable of surviving in aerosols for at least 3 hours, airborne transmission is highly plausible (Van Doremalen et al., 2020). Aerosol dynamics, and subsequently disease transmission, appear to be affected by air temperature and humidity. Low humidity and low temperature result in smaller infected droplet nuclei that can travel further, remain airborne for a longer duration, and cause delayed virus inactivation (Chen, 2020; Moriyama et al., 2020). Experimental evidence for the effects of climate on transmission dynamics using influenza virus in a guinea pig model lends credence to this hypothesis (Lowen et al., 2007). Low temperature and high humidity favour contact transmission (Lowen et al., 2007; Zhao et al., 2020), whilst high temperature and low humidity promote the accumulation of aerosol particles, increasing the likelihood of inhalation (Moriyama et al., 2020). As highlighted in the above reference, this ambiguity makes non-linear associations plausible. However, not all experimental studies agree that stability of SARS-CoV-2 is greatly affected by temperature (Kratzel et al., 2020). More recent evidence showed that outdoor airborne transmission is unlikely in non-crowded areas (Belosi et al., 2021; Chirizzi et al., 2021; Pivato et al., 2021). Though outdoor air temperature likely has limited direct impact on transmission via virus stability in non-crowded outdoor settings, host factors, such as human behaviour influenced by meteorological variables, may underlie the observed trend. Several studies have suggested an association of human mobility with warmer temperatures (Shao et al., 2021; Xi et al., 2020). An exploratory study in Italy found that mobility correlated with increased spread of COVID-19 (Carta et al., 2021). Although we attempt to control for this confounder by including city level residential mobility, omitted variable bias may have occurred if other mobility indices are confounded with temperature. Furthermore, the stringency index we included is only available on a national level, while restrictions enforced by the Italian government varied across regions depending on the evolving situation of the pandemic. As such, we acknowledge this as a major limitation of our analysis, and, increased human mobility as influenced by temperature remains one plausible explanation for our results.
Our study has several strengths which we believe make it a valuable contribution to the literature, particularly in the light of criticisms raised by Dong et al. (2021). First, we employ the DLNM framework to simultaneously assess non-linear and delayed dependencies of air temperature in the exposure and lag dimensions (Gasparrini et al., 2010). Second, we used city-level daily data for COVID-19 incidence and several confounders providing high spatial resolution. Third, we used the powerful two-stage design; this allows for both the background risk and the exposure-lag response functions to vary by city which would otherwise incur ecologic bias. Forth, we account for many confounders, including meteorological, air quality and NPI variables, and allow for delayed dependencies in these effects. Fifth, analysing data from a single country, Italy, which has coordinated nationwide COVID-19 interventions, as compared to analysis using data from different countries, allows for better control over confounding variables. This is especially significant, because confounders, such as government interventions, likely have a greater influence over an immunologically naïve population more than meteorological factors (Baker et al., 2020). For the later period of the study, we have also accounted for vaccination efforts by including the cumulative percentage of vaccine doses administered in each region. Sixth, we have accounted for and assessed autocorrelation and model fit in each of the city level models. Finally, we controlled for potential overfitting using shrinkage estimators for confounding variables. In sum, we have addressed the major concerns highlighted in a recent review of the relationship between air temperature and COVID-19 incidence (Dong et al., 2021).
Our work has several limitations. The first concerns the accuracy of the estimated daily counts of COVID-19. In addition to varying rates of testing, it is postulated that estimates are biased low due to undocumented infections (Li et al., 2020) or other reporting errors (De Natale et al., 2020). Secondly, our study is limited to the lag effects of median daily temperature. It has been reported that extremes of daily temperature might be a better predictor of COVID-19 incidence (Babin, 2020); this would be a worthy avenue for future research. Third, our analysis was based on a smaller number of cities (albeit longer time series and more confounders considered) than similar work (Nottmeyer and Sera, 2021; Shi et al., 2020); this was a direct consequence of the availability of good quality city-level data for confounders which we considered a key feature of our analysis. Although meta-analysing 12 cities in this framework is valid (the example in Gasparini and Armstrong (Gasparrini and Armstrong, 2013) used 10 regions), further work might consider a larger sample size of cities, increasing statistical power and yielding more precise effect estimates. Forth, although meteorological, air quality and residential mobility data were city level, vaccine data was regional, whilst SI data was country level policy; this may incur some aggregation bias and presents a limitation for our analysis. Fifth, we also had not considered the possible change in virus infectivity throughout the course of the study period.
In conclusion, our results support recent works of a non-linear cumulative exposure-response of air temperature on COVID-19 incidence. Peak risk for daily incidence is 15.1 °C, with the effects seen over the subsequent 10 days or more due to the delayed response. It should be stressed that risks presented herein are population level risks since the statistical units analysed are population groups. This information is particularly useful for policy makers assessing population level trends, though might not necessarily correspond to individual level risk due to the ecological fallacy.
Credits
Fang Chyi Fong: Conceptualization; Data curation; Investigation; Methodology; Writing – original draft; Writing – review & editing. Daniel Robert Smith: Conceptualization; Data curation; Formal analysis; Investigation; Methodology; Software; Supervision; Validation; Visualization; Writing – original draft; Writing – review & editing.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Footnotes
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
This study used publicly available datasets and did not involve human subjects or experimental animals.
Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.113099.
Appendix A. Supplementary data
The following are the Supplementary data to this article:
References
- Air Quality Open Data Platform [Internet] World Air Quality Index project. 2021 [cited 31 Dec 2021]. https://aqicn.org/data-platform/covid19/ Available from: [Google Scholar]
- Babin S. Use of weather variables in SARS-CoV-2 transmission studies. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020;100:333–336. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker R.E., Yang W., Vecchi G.A., Metcalf C.J.E., Grenfell B.T. Susceptible supply limits the role of climate in the early SARS-CoV-2 pandemic. Science. 2020;369:315–319. doi: 10.1126/science.abc2535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bashir M.F., Ma B., Bilal Komal B., Bashir M.A., Tan D., Bashir M. Correlation between climate indicators and COVID-19 pandemic in New York, USA. Sci. Total Environ. 2020;728:138835. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belosi F., Conte M., Gianelle V., Santachiara G., Contini D. On the concentration of SARS-CoV-2 in outdoor air and the interaction with pre-existing atmospheric particles. Environ. Res. 2021;193:110603. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2020.110603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benedetti A., Abrahamowicz M. Using generalized additive models to reduce residual confounding. Stat. Med. 2004;23:3781–3801. doi: 10.1002/sim.2073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berhane K., Thomas D.C. A two-stage model for multiple time series data of counts. Biostatistics. 2002;3:21–32. doi: 10.1093/biostatistics/3.1.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carta M.G., Minerba L., Demontis R., Orrù G., Romano F., Scano A., Restivo A., Del Giacco S., Deidda S., Firnu D., Campagna M., Meloni F., Cossu G., Sancassiani F., Chessa L., Kalcev G., Littera R., Zorcolo L., Aviles-Gonzale C.I., Usai P. The COVID-19 incidence in Italian regions correlates with low temperature, mobility and PM10 pollution but lethality only with low temperature. J. Publ. Health Res. 2021 doi: 10.4081/jphr.2021.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L.D. Effects of ambient temperature and humidity on droplet lifetime - a perspective of exhalation sneeze droplets with COVID-19 virus transmission. Int. J. Hyg Environ. Health. 2020;229:113568. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheh.2020.113568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Q., Nian H., Zhu Y., Talbot H.K., Griffin M.R., Harrell F.E., Jr. Too many covariates and too few cases? - a comparative study. Stat. Med. 2016;35:4546–4558. doi: 10.1002/sim.7021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin A.W.H., Chu J.T.S., Perera M.R.A., Hui K.P.Y., Yen H.L., Chan M.C.W., Peiris M., Poon L.L.M. Stability of SARS-CoV-2 in different environmental conditions. Lancet Microb. 2020;1:e10. doi: 10.1016/S2666-5247(20)30003-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirizzi D., Conte M., Feltracco M., Dinoi A., Gregoris E., Barbaro E., La Bella G., Ciccarese G., La Salandra G., Gambaro A., Contini D. SARS-CoV-2 concentrations and virus-laden aerosol size distributions in outdoor air in north and south of Italy. Environ. Int. 2021;146:106255. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.106255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Google LLC . Google COVID-19 Community Mobility Reports. 2020. https://www.google.com/covid19/mobility/ [Google Scholar]
- Dati COVID-19 Italia . Dipartimento della Protezione Civile. 2021 [30 Dec 2021]. https://github.com/pcm-dpc/COVID-19 Available from: [Google Scholar]
- Day M. Covid-19: Italy reimposes widespread lockdown as transmission rate rises again. Bmj. 2021;372:n726. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Angelis E., Renzetti S., Volta M., Donato F., Calza S., Placidi D., Lucchini R.G., Rota M. COVID-19 incidence and mortality in Lombardy, Italy: an ecological study on the role of air pollution, meteorological factors, demographic and socioeconomic variables. Environ. Res. 2021;195:110777. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.110777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Natale G., Ricciardi V., De Luca G., De Natale D., Di Meglio G., Ferragamo A., Marchitelli V., Piccolo A., Scala A., Somma R., Spina E., Troise C. The COVID-19 infection in Italy: a statistical study of an abnormally severe disease. J. Clin. Med. 2020;9 doi: 10.3390/jcm9051564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong Z., Fan X., Wang J., Mao Y., Luo Y., Tang S. Data-related and methodological obstacles to determining associations between temperature and COVID-19 transmission. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021;16 [Google Scholar]
- Gasparrini A. Distributed lag linear and non-linear models in R: the package dlnm. J. Stat. Software. 2011;43:1–20. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasparrini A., Armstrong B. Reducing and meta-analysing estimates from distributed lag non-linear models. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2013;13:1. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-13-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasparrini A., Armstrong B., Kenward M.G. Distributed lag non-linear models. Stat. Med. 2010;29:2224–2234. doi: 10.1002/sim.3940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti E., Ardia D. COVID-19 data Hub. J. Open Sour. Software. 2020;5:2376. [Google Scholar]
- Hale T., Angrist N., Goldszmidt R., Kira B., Petherick A., Phillips T., Webster S., Cameron-Blake E., Hallas L., Majumdar S., Tatlow H. A global panel database of pandemic policies (Oxford COVID-19 Government Response Tracker) Nat. Hum. Behav. 2021;5:529–538. doi: 10.1038/s41562-021-01079-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartig F. 2021. DHARMa: Residual Diagnostics for Hierarchical (Multi-Level/Mixed) Regression Models. R package version 0.4.4. [Google Scholar]
- Imai C., Armstrong B., Chalabi Z., Mangtani P., Hashizume M. Time series regression model for infectious disease and weather. Environ Res. 2015;142:319–327. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2015.06.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Istituto Nazionale Di Statistica I. 2018. Population and Household: Data and Microdata.https://www.istat.it/en/population-and-households?data-and-indicators [Online]. Available. 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kratzel A., Steiner S., Todt D., V'kovski P., Brueggemann Y., Steinmann J., Steinmann E., Thiel V., Pfaender S. Temperature-dependent surface stability of SARS-CoV-2. J. Infect. 2020;81:452–482. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.05.074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauer S.A., Grantz K.H., Bi Q., Jones F.K., Zheng Q., Meredith H.R., Azman A.S., Reich N.G., Lessler J. The incubation period of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) from publicly reported confirmed cases: estimation and application. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020;172:577–582. doi: 10.7326/M20-0504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li R., Pei S., Chen B., Song Y., Zhang T., Yang W., Shaman J. Substantial undocumented infection facilitates the rapid dissemination of novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) Science. 2020;368:489–493. doi: 10.1126/science.abb3221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowen A.C., Mubareka S., Steel J., Palese P. Influenza virus transmission is dependent on relative humidity and temperature. PLoS Pathog. 2007;3:1470–1476. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0030151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriyama M., Hugentobler W.J., Iwasaki A. Seasonality of respiratory viral infections. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2020;7:83–101. doi: 10.1146/annurev-virology-012420-022445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nottmeyer L.N., Sera F. Influence of temperature, and of relative and absolute humidity on COVID-19 incidence in England - a multi-city time-series study. Environ. Res. 2021;196:110977. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.110977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passerini G., Mancinelli E., Morichetti M., Virgili S., Rizza U. A preliminary investigation on the statistical correlations between SARS-CoV-2 spread and local meteorology. Int. J. Environ. Res. Publ. Health. 2020;17 doi: 10.3390/ijerph17114051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirouz B., Shaffiee Haghshenas S., Pirouz B., Shaffiee Haghshenas S., Piro P. Development of an assessment method for investigating the impact of climate and urban parameters in confirmed cases of COVID-19: a new challenge in sustainable development. Int. J. Environ. Res. Publ. Health. 2020;17 doi: 10.3390/ijerph17082801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pivato A., Amoruso I., Formenton G., Di Maria F., Bonato T., Vanin S., Marion A., Baldovin T. Evaluating the presence of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in the particulate matters during the peak of COVID-19 in Padua, northern Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 2021;784:147129. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runkle J.D., Sugg M.M., Leeper R.D., Rao Y., Matthews J.L., Rennie J.J. Short-term effects of specific humidity and temperature on COVID-19 morbidity in select US cities. Sci. Total Environ. 2020;740:140093. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sera F., Armstrong B., Blangiardo M., Gasparrini A. An extended mixed-effects framework for meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2019;38:5429–5444. doi: 10.1002/sim.8362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shao W., Xie J., Zhu Y. Mediation by human mobility of the association between temperature and COVID-19 transmission rate. Environ. Res. 2021;194:110608. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2020.110608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi P., Dong Y., Yan H., Zhao C., Li X., Liu W., He M., Tang S., Xi S. Impact of temperature on the dynamics of the COVID-19 outbreak in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020;728:138890. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobías A., Molina T. Is temperature reducing the transmission of COVID-19. Environ. Res. 2020;186:109553. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2020.109553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosepu R., Gunawan J., Effendy D.S., Ahmad O.A.I., Lestari H., Bahar H., Asfian P. Correlation between weather and covid-19 pandemic in Jakarta, Indonesia. Sci. Total Environ. 2020;725:138436. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Doremalen N., Bushmaker T., Morris D.H., Holbrook M.G., Gamble A., Williamson B.N., Tamin A., Harcourt J.L., Thornburg N.J., Gerber S.I., Lloyd-Smith J.O., De Wit E., Munster V.J. Aerosol and surface stability of SARS-CoV-2 as compared with SARS-CoV-1. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020;382:1564–1567. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2004973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood S.N. Fast stable restricted maximum likelihood and marginal likelihood estimation of semiparametric generalized linear models. J. Roy. Stat. Soc. B. 2011;73:3–36. [Google Scholar]
- Woolf S.H., Chapman D.A., Sabo R.T., Weinberger D.M., Hill L. Excess deaths from COVID-19 and other causes, march-april 2020. JAMA. 2020;324:510–513. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.11787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization . 2021. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard [Online]https://covid19.who.int/ Available: [Google Scholar]
- Worldometer . 2020. Italy Coronavirus [Online]https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/country/italy/ Available. [Google Scholar]
- Xi T., Wang Q., Qin H., Jin H. Influence of outdoor thermal environment on clothing and activity of tourists and local people in a severely cold climate city. Build. Environ. 2020;173:106757. [Google Scholar]
- Zeileis A. Econometric computing with HC and HAC covariance matrix estimators. J. Stat. Software. 2004;1(Issue 10) 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Zeileis A. vol. 16. 2006. p. 16. (Object-oriented Computation of Sandwich Estimators). 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao L., Qi Y., Luzzatto-Fegiz P., Cui Y., Zhu Y. COVID-19: effects of environmental conditions on the propagation of respiratory droplets. Nano Lett. 2020;20:7744–7750. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.0c03331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoran M.A., Savastru R.S., Savastru D.M., Tautan M.N. Assessing the relationship between surface levels of PM2.5 and PM10 particulate matter impact on COVID-19 in Milan, Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 2020;738:139825. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Further reading
- Hartig F. 2020. DHARMa: Residual Diagnostics for Hierarchical (Multi-level/mixed) Regression Models. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.