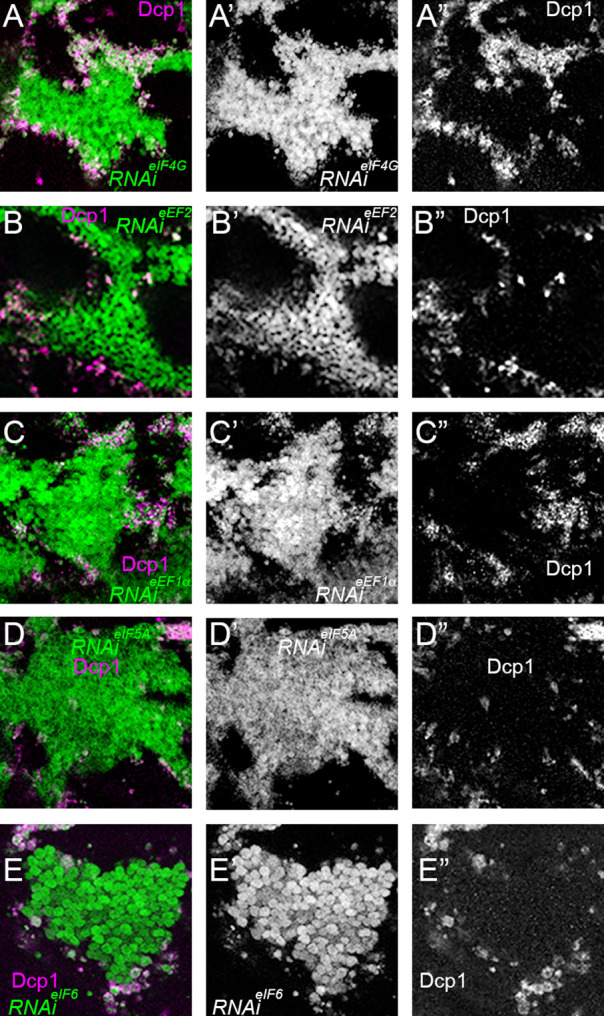
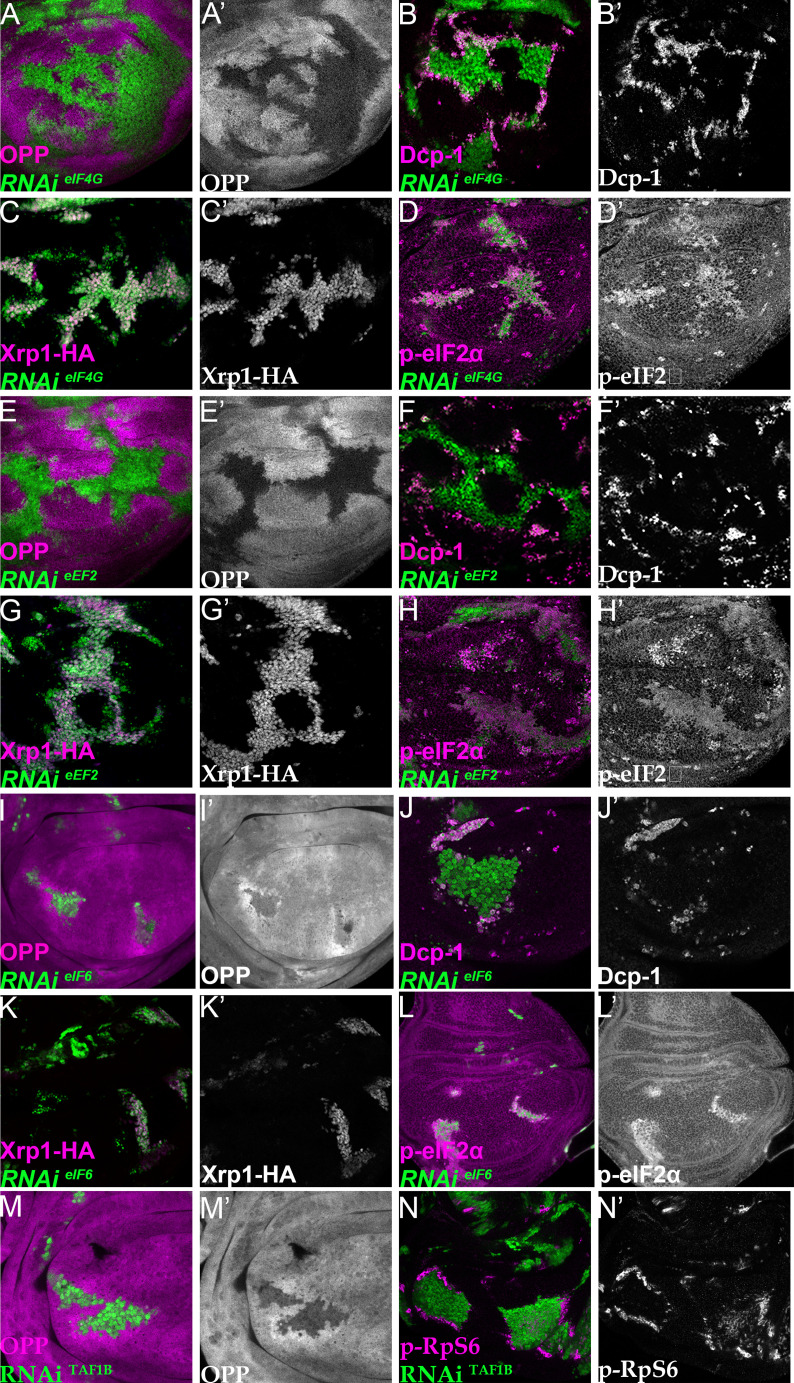
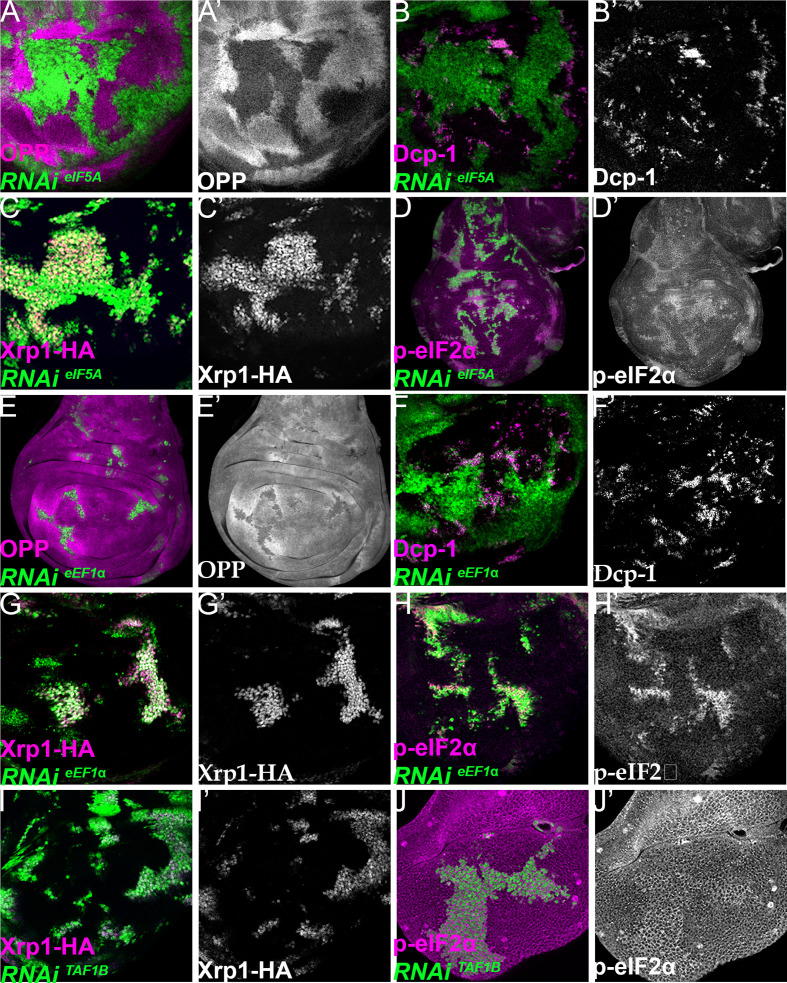
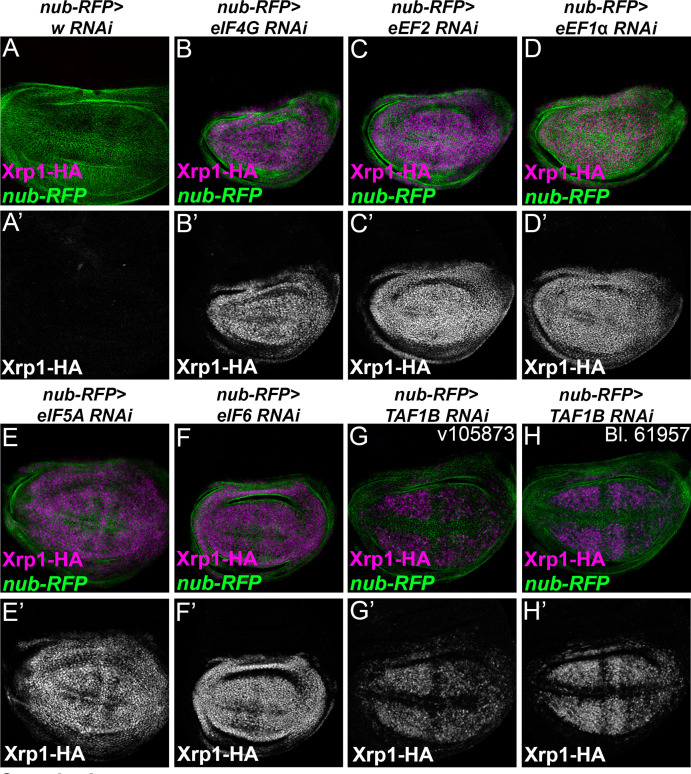
Figure 7. Depletion of translation factors induces Xrp1 expression, eIF2α phosphorylation, reduced translation, and cell competition.
Clones of cells depleted for translation factors are labelled in green. In each case, translation factor depletion reduced translation rate, resulted in competitive cell death at interfaces with wild type cells, induced Xrp1-HA expression, and led to eIF2α phosphorylation. Translation rate, dying cells (activated caspase Dcp1), Xrp1-HA and p-eIF2α are indicated in magenta and in separate channels as labelled. To clarify cell-autonomy, cell death is also shown in higher magnification in Figure 7—figure supplement 2. (A–D) Clones expressing RNAi for eIF4G. (E–H) Clones expressing RNAi for eEF2. (I–L) Clones expressing RNAi for eIF6. In all cases (panels A,E,I), wild-type cells near to cells depleted for translation factors show higher translation rate than other wild type cells. (M) Clones of cells depleted for TAF1B (green) also showed a cell-autonomous reduction in translation rate and non-autonomous increase in nearby wild-type cells (translation rate in magenta, see also M’). (N) Clones of cells depleted for TAF1B (green) showed a non-autonomous increase in RpS6 phosphorylation in nearby cells (magenta, see also N’). Additional data relevant to this Figure is shown in Figure 7—figure supplement 1 and Figure 7—figure supplement 2. Genotypes: A, B, D: {hs:FLP}/+; UAS – RNAieIF4G /+; act> CD2> Gal4, UAS-GFP /+ (line: v17002), C:{hs:FLP}/+; UAS – RNAieIF4G /+; act> CD2> Gal4, UAS-GFP /Xrp1-HA (line: v17002), E, F, H: {hs:FLP}/+; UAS – RNAieEF2 /+; act> CD2> Gal4, UAS-GFP /+ (line: v107268), G: {hs:FLP}/+; UAS – RNAieEF2 /+; act> CD2> Gal4, UAS-GFP / Xrp1-HA (line: v107268), I, J, L:{hs:FLP}/+; UAS – RNAi eIF6 /+; act> CD2> Gal4, UAS-GFP / + (line: v108094), K: {hs:FLP}/+; UAS – RNAieIF6 /+; act> CD2> Gal4, UAS-GFP / Xrp1-HA(line: v108094), M, N: p{hs:FLP}/+; UAS-RNAiTAF1B/+;act> CD2> Gal4, UAS- GFP /+ (line: Bl 61957).
Figure 7—figure supplement 1. Xrp1 expression, eIF2α phosphorylation, reduced translation, and cell competition after depletion of additional translation factors.
Figure 7—figure supplement 2. Cell-autonomy of cell death after translation factor depletion.