Abstract
Background: Condom promotion and supply was one the earliest interventions to be mobilized to address the HIV pandemic. Condoms are inexpensive and provide protection against transmission of HIV and other sexually transmitted diseases (STIs) as well as against unintended pregnancy. As many as 16 billion condoms may be used annually in all low- and middle-income countries (LMIC). In recent years the focus of HIV programs as been on testing and treatment and new technologies such as PrEP. Rates of condom use have stopped increasing short of UNAIDS targets and funding from donors is declining.
Methods: We applied a mathematical HIV transmission model to 77 high HIV burden countries to estimate the number of HIV infections that would have occurred from 1990 to 2019 if condom use had remained at 1990 levels.
Results: The results suggest that current levels of HIV would be five times higher without condom use and that the scale-up in condoms use averted about 117 million HIV infections.
Conclusions: HIV programs should ensure that affordable condoms are consistently available and that the benefits of condom use are widely understood.
Keywords: Condoms, HIV prevention, modeling
Introduction
The distribution and promotion of condoms has been a part of efforts to prevent HIV transmission since the beginning of the HIV response. Early programs often focused on ABC (Abstinence, Be faithful, use Condoms). Condoms provide triple protection, against the transmission of HIV and other sexually transmitted infections as well protection against unintended pregnancy 1 . Condom social marketing programs were the first HIV programs to reach national scale in many countries. The number of condoms distributed through social marketing programs increased from about 590 million annually in 1991 to 2.5 billion by 2012 before declining to about 1.7 billion in 2019 2 . Across 55 countries with a recent national household survey as part of the Demographic and Health Surveys (DHS) or AIDS Indicator Surveys (AIS) about 60 percent of men reported using a condom the last time they had sex with a non-marital, non-cohabiting partner and 65 percent report using a condom the last time they visited a sex worker ( Table 1).
Table 1. Reported rates of condom use at last sex with a higher risk partner and with a sex worker.
| Country | Year and
survey |
Percentage
reporting condom use at last higher risk sex |
Percentage
reporting condom use at last paid sex |
Country | Year and
survey |
Percentage
reporting condom use at last higher risk sex |
Percentage
reporting condom use at last paid sex |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Albania | 2017-18 DHS | 58 | 65 | Kenya | 2014 DHS | 76 | 74 |
| Angola | 2015-16 DHS | 53 | 71 | Kyrgyz Republic | 2012 DHS | 83 | 95 |
| Armenia | 2015-16 DHS | 82 | 84 | Lesotho | 2014 DHS | 77 | 90 |
| Azerbaijan | 2006 DHS | 35 | 53 | Liberia | 2013 DHS | 42 | 61 |
| Benin | 2017-18 DHS | 36 | 44 | Madagascar | 2008-09 DHS | 13 | 13 |
| Bolivia | 2008 DHS | 50 | 89 | Malawi | 2015-16 DHS | 73 | 75 |
| Burkina Faso | 2010 DHS | 74 | 33 | Mali | 2018 DHS | 39 | 70 |
| Burundi | 2016-17 DHS | 51 | 55 | Moldova | 2005 DHS | 54 | |
| Cambodia | 2014 DHS | 74 | 82 | Mozambique | 2015 AIS | 47 | 31 |
| Cameroon | 2018 DHS | 63 | 83 | Myanmar | 2015-16 DHS | 77 | 77 |
| Chad | 2014-15 DHS | 42 | 50 | Namibia | 2013 DHS | 80 | 67 |
| Colombia | 2015 DHS | 71 | 85 | Nepal | 2016 DHS | 68 | 93 |
| Comoros | 2012 DHS | 60 | 65 | Niger | 2012 DHS | 64 | |
| Congo | 2011-12 DHS | 58 | 75 | Nigeria | 2018 DHS | 65 | 74 |
| Congo Democratic
Republic |
2013-14 DHS | 31 | 34 | Papua New
Guinea |
2016-18 DHS | 33 | 48 |
| Cote d'Ivoire | 2011-12 DHS | 63 | 63 | Philippines | 2003 DHS | 24 | 36 |
| Dominican Republic | 2013 DHS | 71 | 80 | Rwanda | 2014-15 DHS | 66 | 65 |
| Eswatini | 2006-07 DHS | 67 | Sao Tome and
Principe |
2008-09 DHS | 61 | 76 | |
| Ethiopia | 2016 DHS | 51 | 81 | Senegal | 2019 DHS | 72 | |
| Gabon | 2012 DHS | 75 | 83 | Sierra Leone | 2019 DHS | 23 | 57 |
| Gambia | 2013 DHS | 67 | 69 | South Africa | 2016 DHS | 73 | 83 |
| Ghana | 2014 DHS | 39 | 44 | Tanzania | 2011-12 AIS | 60 | |
| Guatemala | 2014-15 DHS | 68 | 80 | Timor-Leste | 2016 DHS | 34 | 40 |
| Guinea | 2018 DHS | 50 | 72 | Togo | 2013-14 DHS | 61 | 62 |
| Guyana | 2009 DHS | 72 | 82 | Uganda | 2016 DHS | 62 | 73 |
| Haiti | 2016-17 DHS | 63 | 90 | Ukraine | 2007 DHS | 62 | 84 |
| Honduras | 2011-12 DHS | 61 | 32 | Vietnam | 2005 AIS | 73 | |
| India | 2015-16 DHS | 41 | 48 | Zambia | 2018 DHS | 54 | 56 |
| Indonesia | 2012 DHS | 34 | Zimbabwe | 2015 DHS | 82 | 90 |
Note: ‘Higher risk sex’ refers to sex with a non-marital, non-cohabiting partner. Blank cells represent missing data.
Data accessed on May 24, 2017 through the StatCompiler tool available from the Demographic and Health Survey project at http://www.statcompiler.com/en/.
In all low- and middle-income countries about 16 billion condoms are used annually with about 7.5 billion used primarily for HIV prevention 1 . Since these figures are based on self-reports of condom use, they may over-state actual use. However, it is clear that large numbers of condoms have been procured and/or distributed with the intention of helping users prevent HIV transmission.
Studies have shown condoms to be highly effective against HIV 3 , other sexually transmitted infections 4 and unintended pregnancy 5 . Consistent use is required to maximize an individual’s protection. However, even inconsistent use will provide some benefit that can be large at a population-level 6 .
Across all DHS surveys about three-fifths of people report purchasing commercial brands of condoms at pharmacies and other shops, while about one-fifth report getting condoms from public sources and another one-fifth report obtaining condoms through social marketing programs at subsidized prices. Thus, international donor and national government funding for condom purchase, distribution and promotion plays a large role in supporting the widespread use of condoms.
The purpose of this paper is to investigate the global impact of condoms on the HIV epidemic through both retrospective and prospective analyses.
Methods
We used a publicly available mathematical simulation model, the Goals model 7 , to examine the impact of past and future condom use on the AIDS epidemic in 77 high burden countries. We used version 6.06 of the Goals model, which is available for free download at https://www.avenirhealth.org/software-spectrum.php. The source code for the calculations is available as Extended data 8 .
Goals is a simulation model that calculates HIV transmission among different population risk groups (monogamous heterosexual couples, those with multiple heterosexual partners, female sex workers and clients, men who have sex with men (MSM), and people who inject drugs (PWID)) on the basis of their behaviors (number of partners, contacts per partner, condom use, age at first sex, needle sharing) and characteristics that influence transmission (presence of other sexually transmitted infections, stage of infection, male circumcision, and use of antiretroviral therapy (ART) and pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP)). The model uses data on behaviors drawn from national surveys, such as DHS, and program data on the coverage of ART and programs to prevent mother-to-child transmission, PMTCT, from UNAIDS’ HIV database. The model is fit to official estimates of HIV prevalence trends for each county, also available from UNAIDS.
HIV transmission is calculated as a function of epidemiological factors and the behavioral factors listed above. For uninfected people in each risk group, the probability of becoming infected in a year is given by the following equation:
P s,r,t = {1-[Prev s’,r,t × (1-r s × S s,r,t × STI s,r,t × MC t × C r,t × PrEP s,r,t × ART s,r,t) a + (1-Prev s’,r,t)] n}
Where:
P s,r,t = Annual probability of becoming infected for a person of sex s in risk group r at time t
Prev s’,r,t = HIV prevalence of the opposite sex in risk group r at time t
r s = probability of transmission per sex act by type of act (heterosexual, homosexual)
S s,r,t = multiplier based on the stage of infection (primary stage, chronic stage or late stage)
MC r,t = multiplier based on male circumcision status
STI r,t = multiplier based on STI prevalence
C r,t = multiplier based on condom use
PrEP r,s,t = multiplier based on the use of PrEP
ART s,t = multiplier based on ART use
a r,t = number of acts per partner per year in risk group g at time t
n r,t = number of partners per year in risk group g at time t
The multipliers on the probability of infection per act (MC, C, PrEP and ART) are based on the probability of circumcision, condom, PrEP or ART use and the effectiveness of each in preventing the transmission of HIV. Effectiveness rates used in this analysis are 0.6 for male circumcision 9– 11 , 0.8 for condoms 4 , 0.8 for PrEP 12– 15 and 0.95 for ART 16 . The probability of infection per act and the STI and stage of infection multipliers are selected from within published ranges to best fit the epidemic in each country. Ranges are 0.0008 – 0.0016 for the probability of infection per act 17, 18 , 2-11 for STIs 19, 20 , 0.8-44 for primary stage infection 21– 23 and 4-12 for symptomatic stage infection 21 . Condom coverage represents the percentage of sexual acts that involve condom use. Since the model does not track individuals separately, it does not distinguish between consistent and inconsistent use. Each condom used has the effect of reducing the probability of transmission for that act. The cumulative impact across all acts is the net effect of condom use.
We applied the Goals model to 77 countries that together account for 94% of new infections globally in 2019 ( https://aidsinfo.unaids.org/) and then scaled-up the result to correspond to the global epidemic. The full list of countries included is in Underlying data 8 . The model is implemented for each individual country by using country-specific data for demographic indicators (base year population, fertility, mortality, and migration) ( https://population.un.org/wpp/), behavioral indicators (number and type of partners, condom use) from national household surveys ( https://www.statcompiler.com/en/), and HIV program data (number of people on ART and number of women receiving prophylaxis to prevent mother-to-child transmission (PMTCT) and number of male circumcisions) ( https://aidsinfo.unaids.org/). The model is fit to data on prevalence from surveys, surveillance, and routine testing by varying the epidemiological parameters within published ranges. The ranges used for the epidemiological parameters and the fitted values by country are provided in the underlying data.
Once the model was fit to each country’s actual epidemic we conducted three analyses: (1) a retrospective analysis that estimates the number of additional HIV infections that would have happened if condom use rates stayed constant from 1990 to 2019, (2) a prospective analysis that compares the number of new HIV infections expected to occur between 2020 and 2030 if condom use rates remain at 2019 levels or increase to reach UNAIDS targets of 95% of casual and sex work contacts protected by condom use by 2025, and (3) a prospective analysis that compares constant condom use rates from 2019 to 2030 with a future where all key HIV interventions increase to UNAIDS targets by 2030 24 for key populations (sex workers, MSM, PWID, transgender people and prisoners), adolescent girls and young women, adolescent boys and young men, adults aged 25+, HIV-positive pregnant women and people living with HIV. Comprehensive services are targeted to the appropriate populations and include testing, treatment, condoms provision, needle and syringe exchange, opioid substitution therapy, PrEP, PEP comprehensive sexuality education, economic empowerment, voluntary medical male circumcision and prevention of mother-to-child transmission. These scenarios are illustrated in Table 2.
Table 2. Scenario descriptions.
| Scenario | Condom coverage | Coverage of other
prevention interventions |
|---|---|---|
| Retrospective: 1990-2019 | ||
| - Counterfactual | Constant at 1990 levels | Actual |
| - Actual | Actual | Actual |
| Prospective: 2020-2030 | ||
| - Counterfactual | Constant at 2019 levels | Constant at 2019 levels |
| - Condom scale-up | 95% of casual and sex work contacts
protected by condoms by 2025 |
Constant at 2019 levels |
| - UNAIDS targets | 95% of casual and sex work contacts
protected by condoms by 2025 |
Scale up to all UNAIDS
targets by 2025 |
We tested the sensitivity of the model results to the assumed effective of condoms in averting HIV infection by also running simulations with the effectiveness of condoms set to the low end of the 95% confidence interval (0.50) and with the high end (0.94).
Results
According to UNAIDS estimates, the annual number of new HIV infections worldwide increased to a peak of about 2.8 million around 1998 and then declined to 1.7 (1.2 – 2.2) million by 2019 25 . Model simulations with no increase in condom use rates after 1990 project that the annual number of new HIV infections would have increased to nearly 11 million by 2019 ( Figure 1).
Figure 1. Number of new HIV infections with and without historical scale-up of condom use.
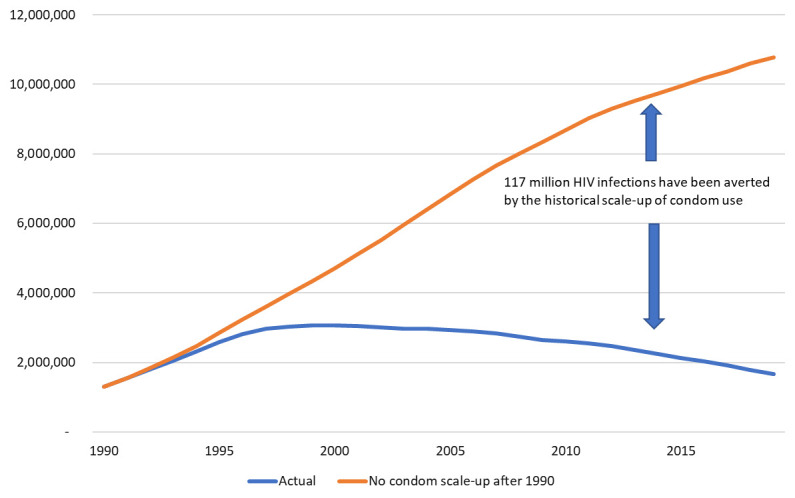
The difference between the lines represents 117 million infections averted from 1990-2019 due to increased condom use. Without the condom scale-up the cumulative number of new infections would have been 160 percent larger. About 45% of the estimated infections averted are in sub-Saharan Africa, 37% in Asia and the Pacific, 10% in Latin America and the Caribbean and 4% each in the Eastern Europe and Central Asia region and the Western and Central Europe and North America region. Impact for each of the modeled countries is shown in the Underlying data 8 . The largest absolute impacts, in terms of infections averted, are seen in the countries with the largest populations or highest prevalence (South Africa, India, China, Kenya and Tanzania) while the highest relative impact occurs in countries with low burden currently where condom use helped to avert a larger epidemic (Guatemala, China, United Kingdom, Italy, Mongolia and Bangladesh).
The sensitivity analysis of condom effectiveness indicates that the estimate of 117 million infections averted could be as low as 70 million or as high as 130 million.
We do not know how many condoms were used globally between 1990 and 2019 but if we assume that condom use was very low in 1990 and scaled up to near today’s rates by 2010 and remained approximately constant from 2010 to 2019, then total condom consumption for HIV prevention would have been around 160 billion for that period. This implies a global average of about 1300 condoms per infection averted. At an average cost per condom distributed of about $0.18 26 the cost per infection averted by condoms during 1990–2019 is about $230.
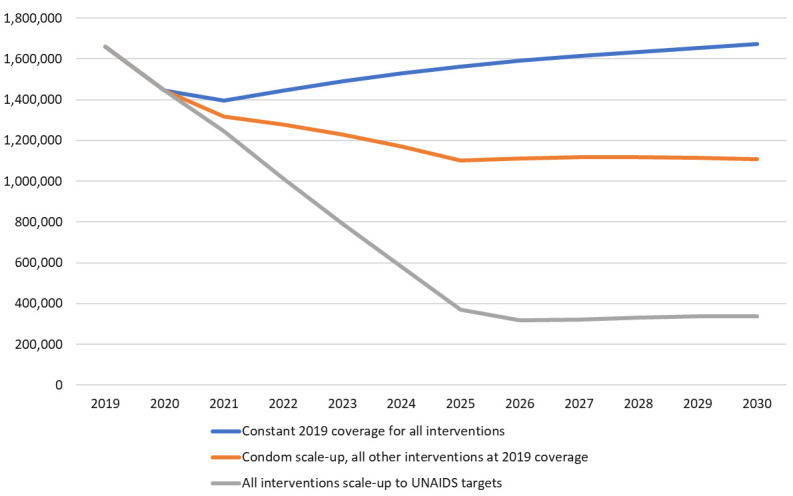
Figure 2 shows the two projections from 2019 to 2030. If condom use rates remained at their 2019 levels and all other interventions also had constant coverage, then the annual number of new HIV infections would rise slowly due to constant incidence and a growing population. If condom use rates scaled-up everywhere to the UNAIDS target of 95% of all risky sex acts and all other prevention interventions remained at 2019 coverage levels, then the number of new infections would decline to 1.1 million 2030. The difference between these two lines indicates that condom scale-up would avert about 3.6 million HIV infections over that period, about 20% of those that would occur without condom scale-up. Figure 2 also shows that the rapid scale-up of condom use could produce about one-third the impact as the full UNAIDS strategy, which scales up all the intervention mentioned above to UNAIDS targets.
Figure 2. Number of new HIV infections in the future under three scenarios.
Discussion
Condom use has increased dramatically since the beginning of the HIV epidemic. Today, approximately 16 billion condoms are used annually to prevent infections and unintended pregnancies. Condom use has impacted the HIV epidemic and avoided a much worse HIV epidemic than has actually evolved. Condoms can play a key role in future efforts, such as the Fast-Track initiative to end AIDS as a public health threat by 2030 27 .
The number of HIV new infections under the retrospective counterfactual scenario of no increase in condom use after 1990, which reaches 11million by 2019, is quite high compared to the actual level of about 1.7 million. But this just illustrates the benefits of early intervention. Early increases in condom use among key populations, in particular sex workers and their clients, as well as with non-regular partners has slowed early transmission and helped to avert a much larger epidemic in the general population.
There are several limitations to this analysis. We rely on self-reports of condom use in national surveys that may over-state actual use. The effectiveness of condoms depends on correct and consistent use but our measures of these factors are not well developed. Our modeling estimates the impact of condom use in aggregate population groups but does not model individual behavior. Using these data our models can replicate historical epidemic trends in the countries modeled but that does not ensure that they are correct. Findings of this analysis are, however, broadly consistent with other mathematical modelling analyses of the impact of condom use 28, 29 . In spite of above-mentioned limitations, the case for the importance of condoms as an ongoing component of HIV programming is compelling.
Condoms are a good investment. The total cost to prevent one new HIV infection with condoms is small compared to life-time costs of treatment meaning that condom investments now will save future expenditures on treatment. Since many people rely on free or subsidized condoms, it is crucial to ensure adequate funding for condom programs, including demand creation activities and frequent behavioral data collection.
While condoms are not a magic bullet that alone can control the HIV epidemic, they remain a critical part of the prevention response. Unfortunately, support for condom social marketing programs has been decreasing in recent years 30 . International and domestic financing should continue to support general population condom programs even as new technologies are introduced that are targeted to the highest risk populations. Condom programs remain among the most cost-effective interventions in the response and provide other health benefits including prevention of other sexually transmitted infections and protection against unwanted pregnancies 1 . Past experience has shown that we do know how to promote and distribute condoms and that many people will use them if they are available. Recent declines in condom investments especially around demand creation implies that the younger generation have not been exposed to relevant condom promotion and condom use skills, a worrisome trend given the relative size of young populations in low- and middle-income countries.
Data availability
Underlying data
Zenodo: JGStover/Data-for-condom-impact-paper-on-Gates-Open-Research: Impact of condoms. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4898086 8 .
This project contains the following underlying data:
Appendix Table 1.csv (number of new HIV infections by country from 1990-2019 according to actual trends or a counterfactual scenario in which rates of condom use remain at 1990 levels)
Zenodo: JGStover/Data-for-condom-impact-paper-on-Gates-Open-Research: Impact of condoms. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4898086 8 .
This project contains the following extended data:
-
-
Parameter ranges used for model fitting.docx (the ranges for key epidemiological factors used in model fitting)
-
-
Fitted parameter values by county.docx (final fitted values for key epidemiological parameters for each country)
-
-
Calculation code (the Delphi code for the simulation calculations in the Goals in .PAS format)
Data are available under the terms of the Creative Commons Zero "No rights reserved" data waiver (CC0 1.0 Public domain dedication).
Acknowledgements
The authors express their appreciation to Gina Dallabetta, Clemens Benedikt and Bidia Deperthes for their review and comments on the first draft.
Funding Statement
This work was supported by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation [OPP1191665].
The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
[version 1; peer review: 2 approved with reservations]
References
- 1. Stover J, Rosen JE, Carvalho MN, et al. : The case for investing in the male condom. PLoS One. 2017;12(5):e0177108. 10.1371/journal.pone.0177108 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. DKT: Contraceptive Social Marketing Statistics. accessed on April 13, 2021. Reference Source [Google Scholar]
- 3. Weller S, Davis K: Condom effectiveness in reducing heterosexual HIV transmission. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002; (1):CD003255. 10.1002/14651858.CD003255 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Holmes KK, Levine R, Weaver M: Effectiveness of condoms in preventing sexually transmitted infections. Bull World Health Organ. 2004;82(6):454–61. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Trussell J: Contraceptive Efficacy. In Hatcher RA, Trussell J, Nelson AL, Cates W, Kowal D, Policar M. Contraceptive Technology: Twentieth Revised Edition. New York NY: Ardent Media, Table 3-2.2011. 10.3843/GLOWM.10375 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Rutenberg N: The fertility impact of inconsistent use of contraception. Washington, DC: The Futures Group International.1993. [Google Scholar]
- 7. Stover J, Hallett TB, Wu Z, et al. : How Can We Get Close to Zero? The Potential Contribution of Biomedical Prevention and the Investment Framework towards an Effective Response to HIV. PLoS One. 2014;9(11):e111956. 10.1371/journal.pone.0111956 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. JGStover: JGStover/Data-for-condom-impact-paper-on-Gates-Open-Research: Impact of condoms (Version v1.0). Zenodo. 2021. 10.5281/zenodo.4898086 [DOI]
- 9. Auvert B, Taljaard D, Lagarde E, et al. : Randomized, Controlled Intervention Trial of Male Circumcision for Reduction of HIV Infection Risk: The ANRS 1265 Trial. PLoS Med. 2005;2(11):e298. 10.1371/journal.pmed.0020298 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Gray RH, Kigozi G, Serwadda D, et al. : Male circumcision for HIV prevention in men in Rakai, Uganda: a randomised trial. Lancet. 2007;369(9562):657–66. 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60313-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Bailey RC, Moses S, Parker CB, et al. : Male circumcision for HIV prevention in young men in Kisumu, Kenya: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2007;369(9562):643–56. 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60312-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Abdool Karim Q, Abdool Karim SS, Frohlich JA, et al. : Effectiveness and safety of tenofovir gel, an antiretroviral microbicide, for the prevention of HIV infection in women. Science. 2010;329(5996):1168–1174. 10.1126/science.1193748 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Grant RM, Lama JR, Anderson PL, et al. : Preexposure Chemoprophylaxis for HIV Prevention in Men Who Have Sex with Men. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(27):2587–2599. 10.1056/NEJMoa1011205 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Baeten JM, Donnell D, Ndase P, et al. : Antiretroviral Prophylaxis for HIV Prevention in Heterosexual Men and Women. N Engl J Med. 2012;367(5):399–410. 10.1056/NEJMoa1108524 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Thigpen MC, Kebaabetswe PM, Paxton LA, et al. : Antiretroviral Preexposure Prophylaxis for Heterosexual HIV Transmission in Botswana. N Engl J Med. 2012;367(5):423–34. 10.1056/NEJMoa1110711 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Cohen MS, Chen YQ, McCauley M, et al. : Prevention of HIV-1 Infection with Early Antiretroviral Therapy. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(6):493–505. 10.1056/NEJMoa1105243 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Baggaley RF, Fraser C: Modelling sexual transmission of HIV: testing the assumptions, validating the predictions. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2010;5(4):269–76. 10.1097/COH.0b013e32833a51b2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Gray RH, Wawer MJ, Brookmeyer R, et al. : Probability of HIV-1 transmission per coital act in monogamous, heterosexual, HIV-1-discordant couples in Rakai, Uganda. Lancet. 2001;357(9263):1149–53. 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)04331-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Galvin SR, Cohen MS: The Role of Sexually Transmitted Diseases in HIV Transmission. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2004;2(1):33–42. 10.1038/nrmicro794 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Powers KA, Poole C, Pettifor AE, et al. : Rethinking the heterosexual infectivity of HIV-1: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2008;8(9):553–63. 10.1016/S1473-3099(08)70156-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Boily MC, Baggaley RF, Wang L, et al. : Heterosexual risk of HIV-1 infection per sexual act: systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Lancet Infect Dis. 2009;9(2):118–29. 10.1016/S1473-3099(09)70021-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Pinkerton SD: Probability of HIV transmission during acute infection in Rakai, Uganda. AIDS Behav. 2008;12(5):677–84. 10.1007/s10461-007-9329-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Blaser N, Wettstein C, Estill J, et al. : Impact of viral load and the duration of primary infection on HIV transmission: systematic review and meta-analysis. AIDS. 2014;28(7):1021–1029. 10.1097/QAD.0000000000000135 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. UNAIDS: Prevailing Against Pandemics by Putting People at the Centre.United Nations Joint Programme on HIV/AIDS, Geneva, Switzerland.2020. Reference Source [Google Scholar]
- 25. UNAIDS: UNAIDS Data 2020.Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS,2020. Reference Source [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. PSI: Annual Cost Effectiveness Report.2009. Reference Source [Google Scholar]
- 27. Stover J, Bollinger L, Izazola JA, et al. : What is Required to End the AIDS Epidemic as a Public Health Threat by 2030? The Cost and Impact of the Fast-Track Approach. PLoS One. 2016;11(5):e0154893. 10.1371/journal.pone.0154893 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Chiu C, Johnson LF, Jamieson L, et al. : Designing an optimal HIV programme for South Africa: Does the optimal package change when diminishing returns are considered? BMC Public Health. 2017;17(1):143. 10.1186/s12889-017-4023-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Johnson LF, Hallett TB, Rehle TM, et al. : The effect of changes in condom usage and antiretroviral treatment coverage on human immunodeficiency virus incidence in South Africa: a model-based analysis. J R Soc Interface. 2012;9(72):1544–1554. 10.1098/rsif.2011.0826 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Smith B, Mann C, Jones C, et al. : Challenged and Recommendations for Reaching “Fast-Track” Targets for Condom Use.Mann Global Health,2019. Reference Source [Google Scholar]


