Abstract
Administration of high concentrations of oxygen (hyperoxia) is one of few available options to treat acute hypoxemia-related respiratory failure, as seen in the current coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic. Although hyperoxia can cause acute lung injury through increased production of superoxide anion (O2•−), the choice of high-concentration oxygen administration has become a necessity in critical care. The objective of this study was to test the hypothesis that UCP2 (uncoupling protein 2) has a major function of reducing O2•− generation in the lung in ambient air or in hyperoxia. Lung epithelial cells and wild-type; UCP2−/−; or transgenic, hTrx overexpression–bearing mice (Trx-Tg) were exposed to hyperoxia and O2•− generation was measured by using electron paramagnetic resonance, and lung injury was measured by using histopathologic analysis. UCP2 expression was analyzed by using RT-PCR analysis, Western blotting analysis, and RNA interference. The signal transduction pathways leading to loss of UCP2 expression were analyzed by using IP, phosphoprotein analysis, and specific inhibitors. UCP2 mRNA and protein expression were acutely decreased in hyperoxia, and these decreases were associated with a significant increase in O2•− production in the lung. Treatment of cells with rhTrx (recombinant human thioredoxin) or exposure of Trx-Tg mice prevented the loss of UCP2 protein and decreased O2•− generation in the lung. Trx is also required to maintain UCP2 expression in normoxia. Loss of UCP2 in UCP2−/− mice accentuated lung injury in hyperoxia. Trx activates the MKK4–p38MAPK (p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase)–PGC1α (PPARγ [peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor γ] coactivator 1α) pathway, leading to rescue of UCP2 and decreased O2•− generation in hyperoxia. Loss of UCP2 in hyperoxia is a major mechanism of O2•− production in the lung in hyperoxia. rhTrx can protect against lung injury in hyperoxia due to rescue of the loss of UCP2.
Keywords: hyperoxia, lung injury, UCP2, thioredoxin, PGC1α
Clinical Relevance
Hyperoxia-mediated acute lung injury is a major impediment to much-needed oxygen therapy to treat respiratory distress. Here, we have shown that loss of UCP2 (uncoupling protein 2) is a major mechanism in the hyperoxia-mediated increase in reactive oxygen species generation. Rescue of UCP2 by thiol reductants or other agents would decrease reactive oxygen species and reduce lung injury due to hyperoxia.
High concentrations of oxygen (hyperoxia) are routinely administered to patients with acute hypoxemia to counter respiratory distress (1–3). However, prolonged breathing of high concentrations of oxygen can cause acute lung injury (ALI) and thereby increase morbidity and mortality. Although hyperoxia can cause ALI (4, 5), no medicinal treatment exists to alleviate hyperoxia-mediated damage. Therefore, pulmonary toxicity remains a potential complication of supplemental oxygen therapy. Although mitochondria are major producers of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in hyperoxia, the precise mechanism remains unclear. Hence, better understanding the exact mechanism by which hyperoxia induces superoxide anion (O2•−) generation in the mitochondria could facilitate our therapeutic approach to acute respiratory distress and might decrease the necessity of our use of more aggressive therapies such as extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.
UCPs (uncoupling proteins) are expressed in the inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM) and are involved in uncoupling respiration from ATP synthesis by inducing regulated proton leaks (6, 7). Leakage of protons to the matrix disrupts the proton gradient, causing increased respiration to compensate for energy demand. Increased oxygen use to pump protons to the IMM space decreases oxygen tension in the mitochondria and therefore decreases electron acceptance by oxygen, resulting in decreased O2•− production (7, 8). UCP2 is a member of the anion transporter proteins, and it differs from the thermogenic UCP1 but is similar to the UCP3 expressed in other tissues (7). Although UCP2 is expressed in many organs, it is the only UCP expressed in the lung (9). The exact function of UCP2 in the lung remains incompletely understood. Breathing of ambient air (20–21% oxygen) is known to generate significant amounts of O2•− during oxidative phosphorylation in the mitochondria. Therefore, robust antioxidant enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase 2, exist in the mitochondrial matrix, where the O2•− is produced as a result of normal electron leakage from respiratory electron transfer. In addition, UCP2 in the IMM could also decrease O2•− generation by slightly uncoupling the proton gradient from ATP production (8). However, the role of UCP2 in pulmonary oxygen toxicity remains unclear.
Cytosolic Trx or Trx1 or TXN1 (thioredoxin) is a 12-kD multifunctional antioxidant protein with a redox-active disulfide/dithiol within the conserved active site Cys32–Gly–Pro–Cys35. The Trx system composed of Trx and TrxR1 (Trx reductase) is an effective protein disulfide reductase that regulates the redox status of the cell in normoxia as well as hyperoxia. Because UCPs decrease mitochondrial O2•− production (7, 8), we hypothesized that modulation of UCP2 expression in hyperoxia may regulate O2•− generation in the mitochondria. PGC1α (PPARγ [peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor γ] coactivator 1α) is the master regulator of mitochondrial oxidative metabolism and is involved in mitochondrial biogenesis (10, 11). PGC1α is a strong inducer of UCP2; however, the exact mechanism of the PGC1α-mediated increase in UCP2 remains unclear. In this report, we demonstrate that exposure of lung cells in vitro or mice in vivo to hyperoxia severely decreased UCP2 expression. Furthermore, loss of UCP2 expression resulted in significant O2•− generation during hyperoxia in the lung. We show that Trx is required for maintaining baseline UCP2 expression in the lung during normoxia. In addition, overexpression of Trx in transgenic, hTrx overexpression–bearing (Trx-Tg) mice or treatment of cells with rhTrx (recombinant human Trx) rescued UCP2 expression in hyperoxia. Trx induced MKK4 activation, which, in turn, phosphorylated p38 MAPK (p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase), resulting in activation of p38MAPK in hyperoxia that phosphorylated PGC1α, promoting its nuclear translocation and resulting in PPARγ-mediated UCP2 expression and rescue of UCP2 in hyperoxia.
Experimental Procedure
Cell Culture and Oxygen Exposure
MLE-12 cells were cultured in hydrocortisone, insulin, transferrin, estradiol, and selenium medium (12) supplemented with 2% FBS. Actively growing MLE-12 cells were exposed to normoxia (21% oxygen, room air) or hyperoxia (95% oxygen) in a modular incubator chamber (Billups-Rothenberg, Inc.).
Exposure of Mice to Hyperoxia
C57BL/6J UCP2−/− (stock number 005934) (12–14 wk old) and C57BL/6J wild-type (WT) mice were purchased from Charles River Laboratories and used in this study. Trx-Tg mice were bred and maintained in the animal facility of Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center and have been described previously (4, 13). All procedures were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at the Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, Lubbock, and were consistent with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals published by the National Institutes of Health. Mice were exposed to 21% O2 or 90% O2 for 24–72 hours, followed by thoracotomy. The lungs were perfused with PBS via right ventricular puncture, dissected free, and processed immediately.
Antibodies and Reagents
Anti-UCP2 (catalog number [cat. no.] 89326), anti–phospho–p38 MAPK (Thr180/Tyr182) (cat. no. 4511), anti–p38 MAPK (cat. no. 9212), anti–phospho-ERK1/2 (Thr202/Tyr204) (cat. no. 9101), phospho-SAPK/JNK (Thr183/Tyr185) (cat. no. 9251), phospho-SEK1/MKK4 (Thr261) (cat. no. 9151), SEK1/MKK4 (cat. no. 9152), MKK7 (cat. no. 4172), anti-PARP (cat. no. 9542), anti–cleaved caspase 3 (Asp175), and Trx1 (cat. no. 2298) antibodies were procured from Cell Signaling Technology. Antiphosphoserine antibodies (cat. no. P5747), antiphosphothreonine antibodies (cat. no. P6623), N5,N6-bis(2-fluorophenyl)[1,2,5]oxadiazolo[3,4-b]pyrazine-5,6-diamine (BAM15) (cat. no. SML1760), and deferoxamine mesylate salt (cat no. D9533) were purchased from Sigma. Anti–nuclear matrix protein p84 (cat. no. GTX70220), JNK1/3 (sc-474), NRF-1 (sc-33771), ERK 2 (sc-153), and Tom40 (sc-11414) antibodies were purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology. PGC1α antibodies (NBP1-04676) were purchased from Novus Biologicals. Anti-Sirt1 antibodies (09-844) were obtained from Millipore. Niclosamide and ethanolamine (cat no. AG-CR1-3644-M025) were obtained from AdipoGen. rhTrx protein was obtained from Thermo Fisher Scientific. siRNA with a concentration of 100 nM was transfected by using lipofectamine RNAiMAX reagent obtained from Thermo Fisher Scientific. Anti–phospho–PGC1α–Ser571 (cat. no. AF6650) was obtained from R&D Systems.
IP and Western Blotting Analysis
Immunoprecipitates and protein extracts were analyzed for Western blotting by using their specific antibodies as previously described (14–17).
Flow Cytometry and Annexin V Apoptosis Assay
MLE-12 cells were exposed to 21% or 95% O2 for 24 hours, and an apoptosis assay was performed as described previously (16).
Detection of O2•− by Using Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Spectrometry
Superoxide generation in MLE-12 cells was detected through electron paramagnetic resonance spectrometry by using spin-probe 1-hydroxy-3-methoxycarbonyl-2,2,5,5-tetramethylpyrrolidine hydrochloride as described in our previous publication (16).
Statistical Analysis
Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM. Multiple experimental groups were compared by using ANOVA with a Tukey post hoc test comparison of means in GraphPad Prism software. The Student’s t test was used when comparing means from two experimental groups. A value of P ⩽ 0.05 was considered to indicate statistical significance. Unless otherwise stated, the figures represent a minimum of N = 3 for cell culture as well as mouse experiments.
Results
Hyperoxia Decreases UCP2 Expression, and Loss of UCP2 Increases O2•− Generation in Lung Cells
Although hyperoxia generates O2•− in the mitochondria, the exact mechanism of O2•− production by hyperoxia remains unclear. Because UCP2 decreases O2•− generation by partial uncoupling due to proton conductance to the matrix without coupling (7, 8), we speculated that hyperoxia may modulate UCP2 expression. As shown in Figures 1A and 1B, we observed a time-dependent hyperoxia-induced decrease in UCP2 mRNA expression in mouse lung alveolar epithelial cells (MLE-12 cells). In addition, the expression of UCP2 protein was also decreased in a time-dependent manner (Figures 1C and 1D). However, the expression of Tom40, another mitochondrial protein, did not change, indicating a specific effect of hyperoxia on UCP2 expression. Loss of UCP2 expression was correlated with increased O2•− generation in a time-dependent manner, as determined by using electron paramagnetic resonance spectrometry (Figures 1E and 1F). To further understand the role of UCP2 in hyperoxia-mediated O2•− generation, we downregulated UCP2 by using siRNA and determined O2•− generation in normoxia or hyperoxia. As shown in Figures 1G and 1H, O2•− was significantly increased in UCP2-depleted cells in normoxia; however, cells depleted of UCP2 and exposed to hyperoxia had significantly increased amount of O2•− compared with cells depleted of UCP2 in normoxia, establishing that loss of UCP2 caused increased O2•− generation in the lung cells during normoxia and potentiated O2•− generation during hyperoxia. In addition, depletion of UCP2 caused a significant increase in the apoptosis of lung cells in normoxia that was potentiated in hyperoxia (Figure 1I; see Figure E1 in the data supplement).
Figure 1.
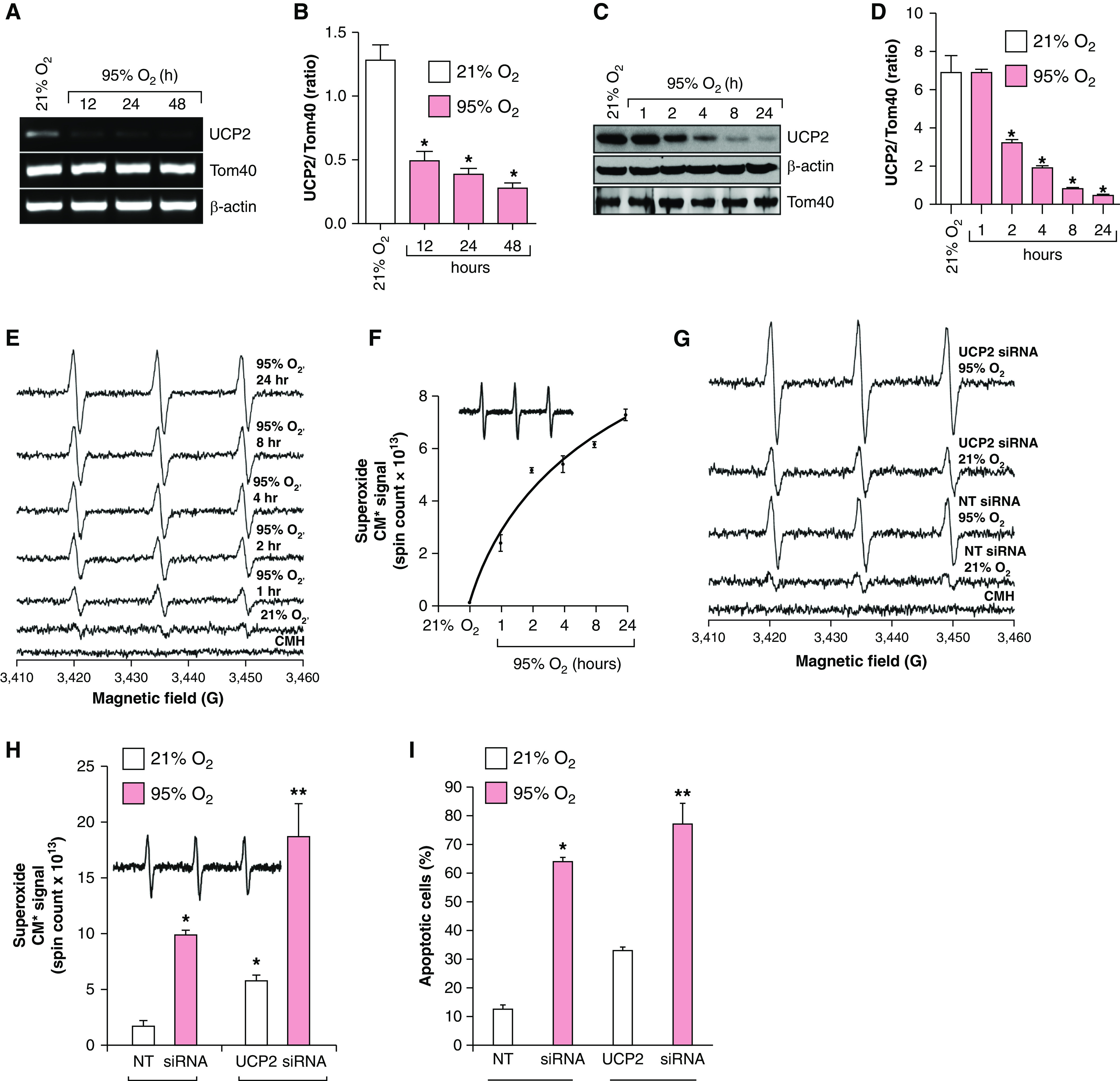
Hyperoxia decreases UCP2 (uncoupling protein 2) expression, and loss of UCP2 increases superoxide anion (O2•−) generation and apoptosis in lung cells. (A) MLE-12 cells (n = 3) were exposed to 21% or 95% O2 for the indicated time, and total RNA was isolated and analyzed for UCP2 and Tom40 (mitochondrial protein control) expression and normalized for β-actin. (B) Densitometry of A. *P < 0.05, hyperoxia versus normoxia (ANOVA). (C) Extracts from MLE-12 cells (n = 3) were exposed to normoxia or hyperoxia and analyzed for UCP2 expression through Western blotting using its specific antibody. (D) Densitometry of C. *P < 0.05, hyperoxia versus normoxia (ANOVA). (E) MLE-12 cells (n = 3) were exposed to 21% O2 or 95% O2 for the indicated periods, and O2•− generation was determined through electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) by using 1-hydroxy-3-methoxycarbonyl-2,2,5,5-tetramethylpyrrolidine hydrochloride (CMH) as described in the Methods. (F) Superoxide production (CM*, nitroxide radical) over time in hyperoxia (spin counts over time). (G) MLE-12 cells (n = 3) were transfected with 100-nM nontargeted (NT) siRNA or UCP2 siRNA and exposed to 21% O2 or 95% O2 for 24 hours. The O2•− level was determined by using EPR. (H) Total spin counts from G are plotted as a bar graph. *P < 0.01, 95% O2 + NT siRNA versus 21% O2 + NT siRNA; and **P < 0.01, 95% O2 + UCP2 siRNA versus 21% O2 + UCP2 siRNA. (I) MLE-12 cells (n = 3) were transfected with 100-nM NT siRNA or UCP2 siRNA and exposed to 21% or 95% O2 for 24 hours, and apoptosis was determined by using an annexin V binding assay. *P < 0.05, 21% O2 + NT siRNA versus 95% O2 + NT siRNA; and **P < 0.05, 21% O2 + UCP2 siRNA versus 95% O2 + UCP2 siRNA.
Trx Is Required to Maintain Baseline UCP2 Expression in Normoxia, Rescues the Loss of UCP2, and Decreases Lung-Cell Apoptosis in Hyperoxia
We have previously demonstrated that increased amount of Trx protect against hyperoxic lung injury in mice (4); however, the mechanism remains unclear. We hypothesized that Trx-mediated rescue of UCP2 loss might account for the protection afforded by Trx. We treated MLE-12 cells with rhTrx and exposed these cells to normoxia or hyperoxia, as rhTrx is known to be internalized into cells and exerts its biological actions (13, 15, 17). Treatment of cells with rhTrx rescued the loss of UCP2 mRNA (Figures 2A and 2B) and protein (Figures 2C and 2D) expression during hyperoxia in MLE-12 cells. To further understand the role of Trx in UCP2 expression in normoxia, we downregulated Trx in MLE-12 cells and evaluated its effect on UCP2 expression. Intriguingly, as shown in Figures 2E and 2F, UCP2 expression was acutely decreased in Trx-depleted cells during normoxia, indicating that cellular Trx is required for the baseline expression of UCP2 in normoxia. In addition, UCP2 expression was decreased in hyperoxia; however, Trx-depleted cells exposed to hyperoxia showed complete loss of UCP2. As shown in Figures 2G and 2H, the hyperoxia-mediated increase in O2•− was significantly decreased in rhTrx-treated cells. In addition, as shown in Figures 2I and 2J, rhTrx treatment significantly decreased lung-cell apoptosis in hyperoxia. These data demonstrate that a hyperoxia-mediated decrease in UCP2 is a major contributor to O2•− generation, leading to increased apoptosis. Trx is not a direct O2•− scavenger (18); however, it could indirectly decrease O2•− by restoring UCP2 expression in hyperoxia. Our data also suggest that Trx is required for basal UCP2 expression, which could reduce the ROS load during normal mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation at ambient oxygen tension.
Figure 2.
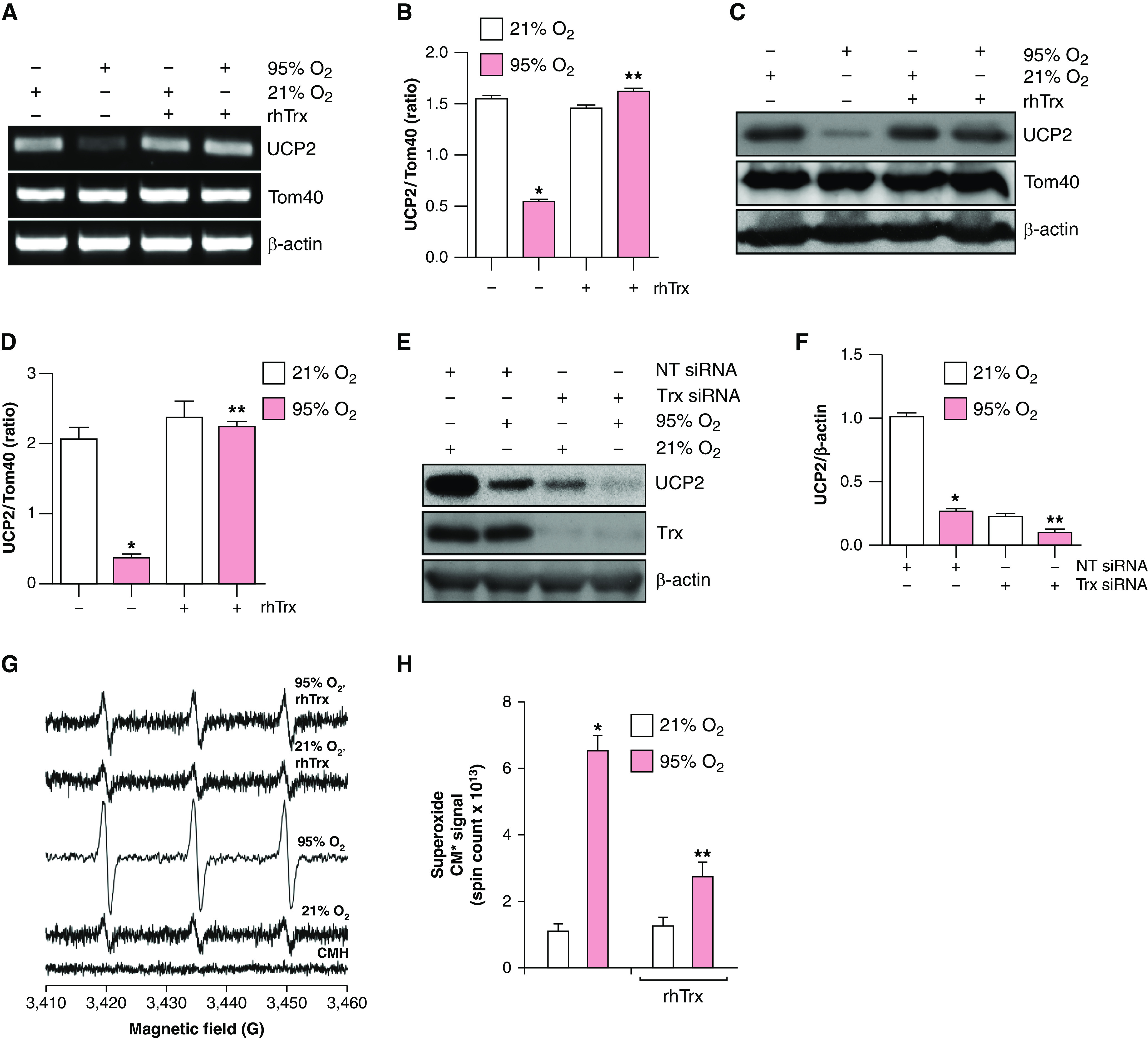
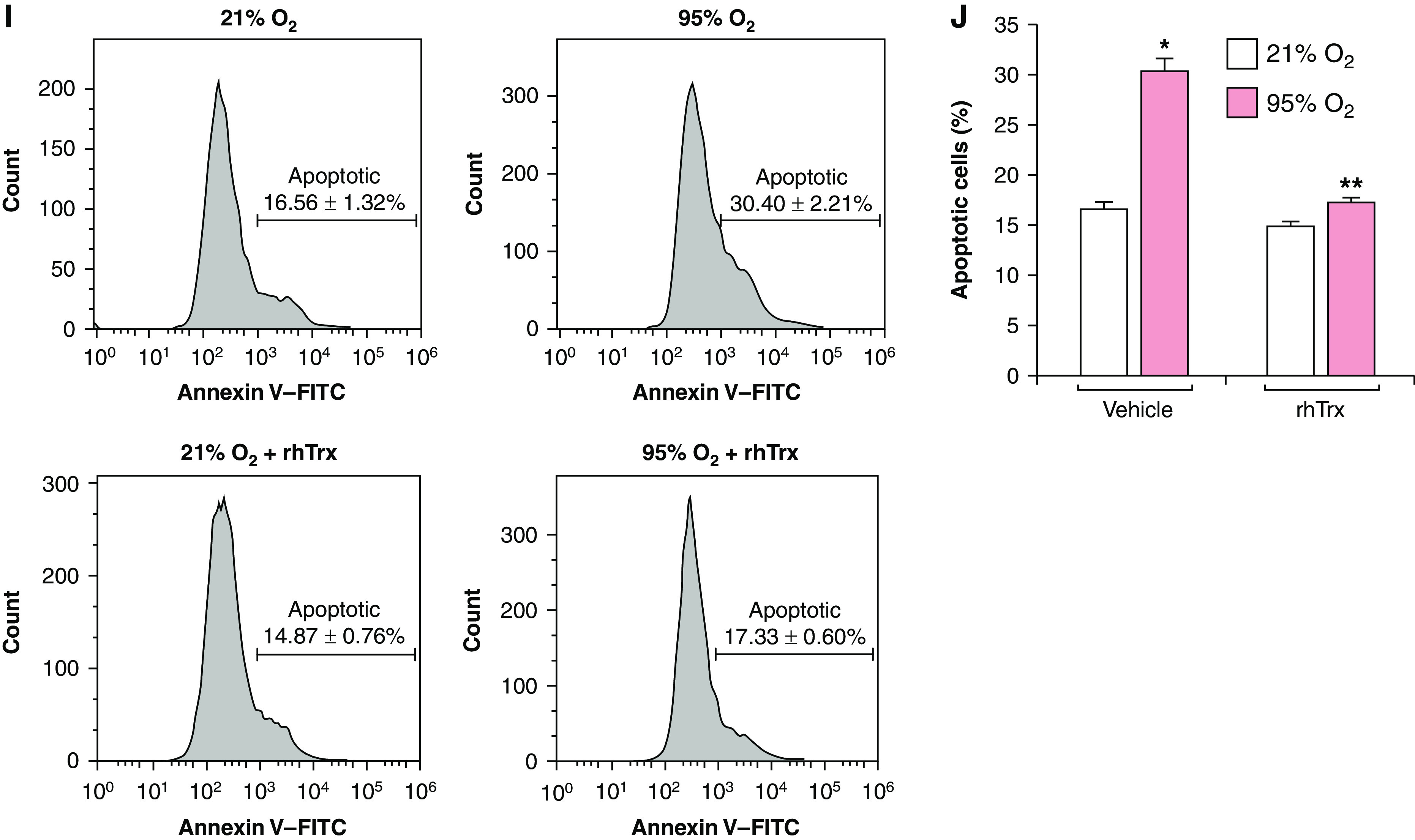
rhTrx (recombinant human thioredoxin) rescues loss of UCP2 expression in hyperoxia, and depletion of endogenous Trx decreases UCP2 expression in normoxia. (A) MLE-12 cells (n = 3) were pretreated with rhTrx (2 μg/ml) and exposed to 21% O2 or 95% O2 for 24 hours. RNA was isolated and mRNA was analyzed by using RT-PCR analysis to determine UCP2 and Tom40 expression. (B) Densitometry of A. *P < 0.05, 21% O2 versus 95% O2; and **P < 0.05, 95% O2 + no treatment versus 95% O2 + rhTrx. (C) MLE-12 cells (n = 3) were pretreated with rhTrx (2 μg/ml) and exposed to 21% O2 or 95% O2 for 24 hours. Total protein was isolated and analyzed for UCP2, Tom40, and β-actin expression by using Western blotting. (D) Densitometry of C. *P < 0.05, 21% O2 versus 95% O2; and **P < 0.05, 95% O2 + no treatment versus 95% O2 + rhTrx. (E) MLE-12 cells were transfected with 100-nM NT siRNA or Trx siRNA and exposed to 21% O2 or 95% O2 for 24 hours, and protein was analyzed for UCP2 expression. (F) Densitometry of E. *P < 0.05, 95% O2 versus 21% O2 + NT siRNA; and **P < 0.05, 95% O2 + Trx siRNA versus 95% O2 + NT siRNA. (G) MLE-12 cells were pretreated with or without rhTrx (2 μg/ml) and exposed to 21% O2 or 95% O2 for 24 hours, and O2•− generation was analyzed by using EPR and CMH as described in the Methods. (H) Total spin counts. *P < 0.05, 21% O2 versus 95% O2; and **P < 0.05, 95% O2 versus 95% O2 + rhTrx. (I) MLE-12 cells were exposed to 21% or 95% O2 with or without rhTrx (2 μg/ml) for 24 hours, and apoptosis was analyzed by using annexin V–FITC labeling. (J) Percentage of apoptosis. *P < 0.01, 95% O2 versus 21% O2; and **P < 0.05, 95% O2 versus 95% O2 + rhTrx.
Trx Induces PGC1α Phosphorylation and Nuclear Translocation in Hyperoxia
Because loss of UCP2 expression is rescued by Trx in hyperoxia, we speculated that Trx may induce PGC1α expression and its translocation to the nucleus in hyperoxia. As shown in Figures 3A and 3B, PCG1α expression was significantly increased in hyperoxia by rhTrx, as compared with normoxia or hyperoxia alone. Furthermore, PGC1α phosphorylation was increased in hyperoxia in rhTrx-treated cells (Figures 3C and 3D). We also evaluated whether Trx would promote PGC1α translocation to the nucleus. As shown in Figures 3E and 3F, rhTrx significantly induced PGC1α translocation to the nucleus in normoxia, which was further increased in hyperoxia. Collectively, these data demonstrate that Trx promotes PGC1α expression and its translocation to the nucleus in normoxia, with a further increase being shown in hyperoxia. To better delineate the specific role of Trx in PGC1α translocation, we downregulated endogenous Trx by using an siRNA approach and evaluated the level of PGC1α in the nuclear extracts. As shown in Figures 3G and 3H, depletion of endogenous Trx abrogated PGC1α nuclear translocation in normoxia and in hyperoxia, indicating a crucial role of endogenous Trx in nuclear transport of PGC1α.
Figure 3.
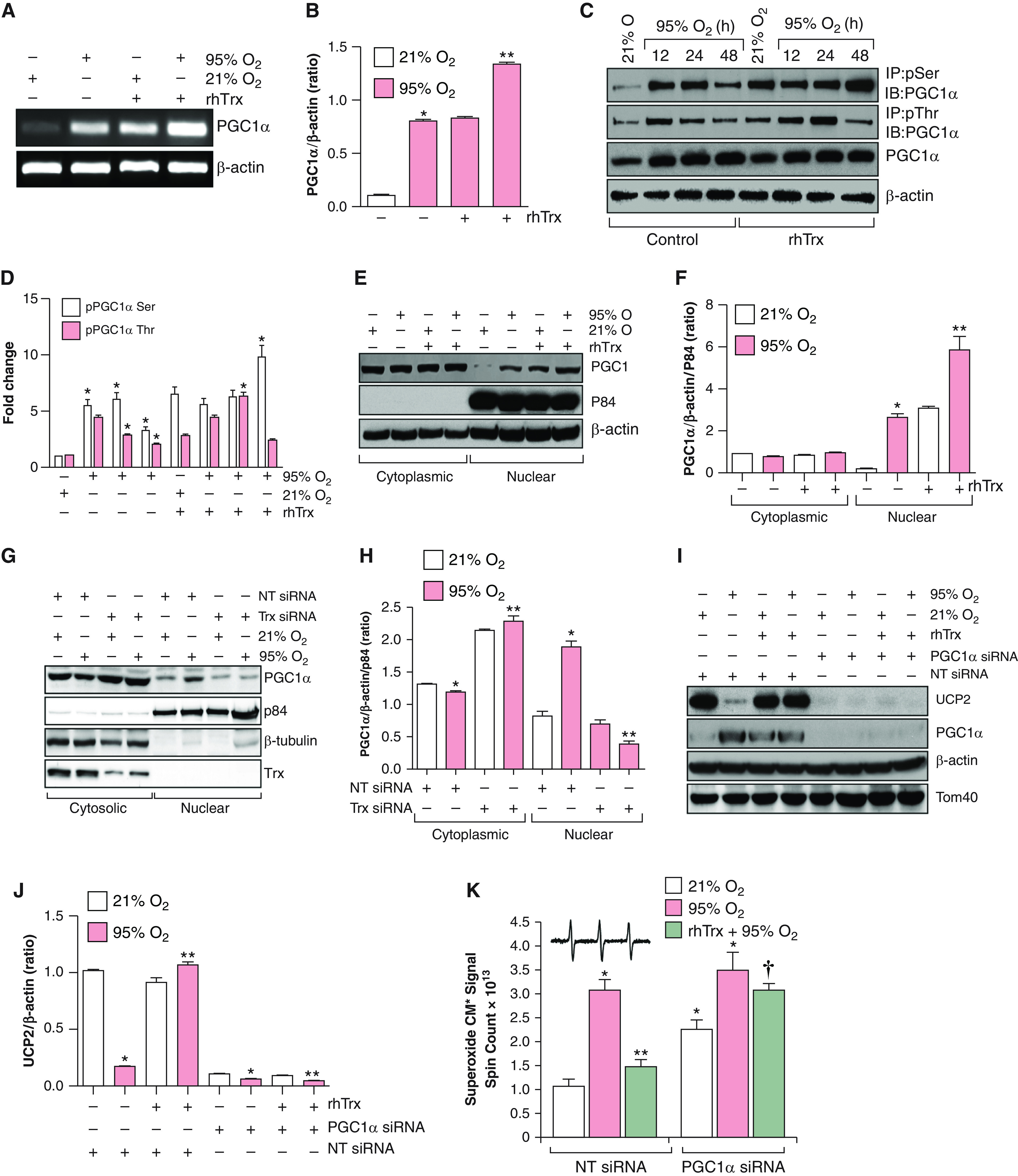
Trx induces UCP2 expression by regulating PGC1α (PPARγ [peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor γ] coactivator 1α) nuclear transport. (A) MLE-12 cells (n = 3) were exposed to 21% or 95% O2 for the indicated periods, and RNA was isolated and mRNA was analyzed for PGC1α expression by using RT-PCR analysis. (B) Densitometry of A. *P < 0.05, 95% O2 versus 21% O2; and **P < 0.05, 95% O2 + rhTrx versus 95% O2 without rhTrx (ANOVA). (C) MLE-12 cells were pretreated with or without rhTrx (2 μg/ml) and exposed to 21% or 95% O2 for the indicated periods, cell lysates were prepared and immunoprecipitated with phosphorylated serine (pSer)/phosphorylated threonine (pThr) antibodies, and the immunocomplexes were analyzed by using Western blotting for PGC1α phosphorylation. (D) Densitometry of C. *P < 0.05, 95% O2 versus 21% O2; and *P < 0.05, 95% + rhTrx versus 21% O2 + rhTrx. (E) Nuclear and cytosolic extracts from MLE-12 cells pretreated with or without rhTrx (2 μg/ml) and exposed to normoxia or hyperoxia for 24 hours were analyzed for PGC1α levels through Western blotting using their specific antibodies; p84 was used as nuclear protein control, and β-actin was used as a cytosolic protein control. (F) Densitometry of E. *P < 0.05, 95% O2 versus 21% O2 + nuclear extract; and **P < 0.05, 95% O2 versus 95% O2 + nuclear extract + rhTrx. (G) MLE-12 cells were transfected with 100-nM NT or Trx siRNA and were exposed to 21% or 95% O2 for 16 hours. Nuclear and cytoplasmic extracts were analyzed for PGC1α expression. Readers may view the uncut gels for G in the data supplement. (H) Densitometry of G. *P < 0.05, 95% O2 + NT siRNA versus 21% O2 + NT siRNA; and **P < 0.05, Trx siRNA + 95% O2 versus Trx siRNA + 21% O2. (I) MLE-12 cells were transfected with 100-nM NT siRNA or PGC1α siRNA, pretreated with rhTrx (2 μg/ml), and exposed to 21% or 95% O2 for 24 hours and were analyzed for UCP2 expression. (J) The same lysate was used for analysis to determine PGC1α, Tom40, and β-actin expression. *P < 0.05, NT siRNA + 95% O2 versus NT siRNA + 21% O2; and **P < 0.05, NT siRNA + 21% O2 versus NT siRNA + 95% O2. (K) MLE-12 cells were transfected with 100-nM NT siRNA or PGC1α siRNA, pretreated with rhTrx (2 μg/ml), and exposed to 21% O2 or 95% O2 for 24 hours, and superoxide generation was determined through EPR using CMH. Total spin counts are shown. *P < 0.01, PGC1α siRNA + 21% O2 versus NT siRNA + 21% O2; **P < 0.01, PGC1α siRNA + rhTrx + 95% O2 versus NT siRNA + 95% O2; and †P < 0.05, versus NT siRNA + rhTrx + hyperoxia (95% O2).
We also determined whether rhTrx would induce UCP2 expression without PGC1α mediation. We found that depletion of PGC1α by siRNA abolished UCP2 expression even in the presence of rhTrx, indicating that PGC1α is critically required for UCP2 induction by rhTrx (Figures 3I and 3J). Although the level of PGC1α was comparable in cells exposed to hyperoxia, normoxia plus rhTrx, or hyperoxia plus rhTrx, the expression of UCP2 was significantly decreased only in hyperoxia-exposed cells, indicating that additional factors may play a role in PGC1α-mediated UCP2 expression. Because expression of UCP2 modulates the O2•− generation in hyperoxia, we determined O2•− amounts in hyperoxia in PGC1α-depleted cells. Hyperoxia significantly increased O2•− generation in nontargeted (NT) siRNA–transfected cells, but PGC1α depletion potentiated O2•− generation in normoxic cells (Figure 3K). In addition, PGC1α-depleted cells treated with rhTrx and exposed to hyperoxia had a significant increase in O2•− compared with NT siRNA–treated cells with or without rhTrx treatment (Figures 3K and E2), demonstrating that PGC1α is required for the UCP2-dependent decrease of O2•− in hyperoxia to occur.
Trx-mediated Activation of MKK4 and p38 MAPK Induces PGC1α and UCP2 Expression
Because PGC1α phosphorylation and translocation to the nucleus were increased in hyperoxia in the presence of rhTrx, we reasoned that rhTrx might activate a kinase that phosphorylates PGC1α in hyperoxia. p38 MAPK (p38) activation increases the expression of PGC1α (19). Therefore, we determined whether rhTrx treatment would activate p38 MAPK in hyperoxia, resulting in phosphorylation of PGC1α. p38 MAPK was activated within 1 hour of exposure to hyperoxia, as detected by its phosphorylation in MLE-12 cells, but the expression began to decline in a time-dependent manner, with complete loss of activation being demonstrated at 24 hours of exposure to hyperoxia (Figures 4A and 4B). In addition, Erk1/2 was phosphorylated and activated in a sustained manner that peaked at 24 hours, but as shown in Figures 4C and 4D, there was no effect of rhTrx in the activation. Likewise, maximal activation of JNK was also noted at 24 hours (Figures 4A and 4B), but rhTrx had no effect in hyperoxia-mediated JNK activation. However, rhTrx treatment increased p38 MAPK phosphorylation in hyperoxia in contrast to JNK or ERK (Figure 4C and 4D). Therefore, we determined whether SB203580, a specific inhibitor of p38 MAPK, would inhibit UCP2 expression and PGC1α phosphorylation. We found that p38 inhibition by SB203580 significantly attenuated the hyperoxia-mediated increase in PGC1α phosphorylation and UCP2 expression (Figures 4E and 4F). However, rhTrx treatment had no effect on UCP2 expression or PGC1α phosphorylation in the presence of SB202580 in normoxia or hyperoxia, indicating that p38 MAPK activation is required for UCP2 expression via PGC1α phosphorylation (Figures 4E and 4G). Because SB203580 is a chemical inhibitor of p38MAPK activity, we used a genetic approach to downregulate p38 by using RNA interference (siRNA) and evaluated its effect on UCP2 and PGC1α expression. As shown in Figure E3A, the expression of p38 was significantly decreased in MLE-12 cells treated with siRNA and exposed to normoxia or hyperoxia (Figures E3A and E3B). The expression of PGC1α was significantly decreased in p38-downregulated MLE-12 cells exposed to hyperoxia or normoxia, indicating that p38MAPK is required for PGC1α expression. In addition, the expression of UCP2 was also significantly decreased in p38MAPK-depleted cells exposed to normoxia or hyperoxia (Figures E3A and E3D). A study has reported that phosphorylation of Ser-570 in PGC1α by angiotensin II–mediated AKT causes PGC1α protein degradation (20). Therefore, we evaluated whether hyperoxia-mediated PGC1a–Ser570 phosphorylation could result in decreased expression of PGC1α. As shown in Figures E3A and E3E, the level of Ser-570 remined unchanged in hyperoxia or normoxia with or without p38MAPK downregulation. These data indicate that PGC1α–Ser-570 phosphorylation does not modulate PGC1α expression in hyperoxia. Previously, we reported the activation of MKK4 by Trx in lung endothelial cells (15). Therefore, we evaluated the activation of MKK4 in hyperoxia in the presence or absence of rhTrx. Hyperoxia induced MKK4 phosphorylation maximally after 1 hour, which was decreased in a time-dependent manner with further exposure to hyperoxia (Figures 4H and 4I). We also found that hyperoxia-induced MKK4 phosphorylation was potentiated by rhTrx (Figures 4J and 4K). In addition, rhTrx induced MKK4 phosphorylation in normoxia (Figures 4J and 4K). Depletion of MKK4 by siRNA significantly inhibited PGC1α expression and nuclear translocation (Figures 4L and 4M), as well as PGC1α phosphorylation (Figures 4N and 4O). MKK4 is known to activate p38 MAPK (21–23). Therefore, if p38 MAPK is activated by MKK4 and this activation is required for UCP2 expression in hyperoxia, then depletion of MKK4 would result in p38 MAPK inactivation and would abrogate UCP2 expression. On the basis of this reasoning, we depleted MKK4 by using siRNA and evaluated PGC1α phosphorylation and UCP2 expression. As shown in Figures 4P and 4Q, depletion of MKK4 decreased p38 phosphorylation and UCP2 expression (Figures 4P and 4Q). This finding is in agreement with our data presented in Figures 4E and 4F, confirming the results with treatment of cells with SB203580. Collectively, our data demonstrate that activation of MKK4–p38 signaling by Trx induces PGC1α-dependent UCP2 expression.
Figure 4.
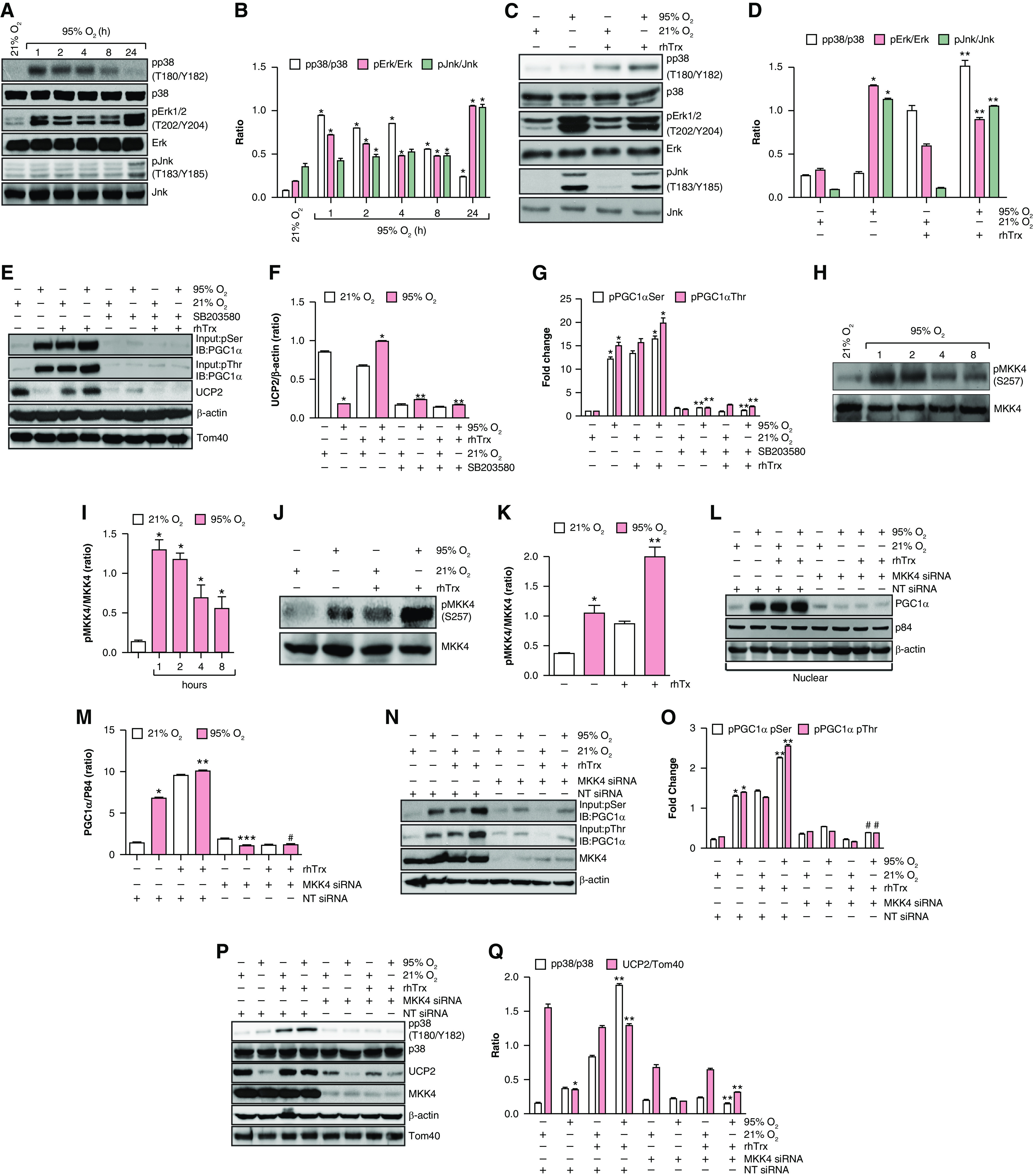
The hyperoxia-mediated increase in p38–MKK4 activation induces PGC1α and UCP2 expression. (A) MLE-12 cells were exposed to normoxia or hyperoxia, and cell lysates were analyzed for p-p38 (T180/Y182), Erk (T202/Y204), and Jnk (T183/Y185) phosphorylation through Western blotting using phosphospecific antibodies. (B) Densitometry of A. *P < 0.05, 95% O2 versus 21% O2 (ANOVA). (C) MLE-12 cells were pretreated with rhTrx (2 μg/ml) and exposed to 21% O2 or 95% O2 for 24 hours and were analyzed for p-p38 (T180/Y182), Erk (T202/Y204), and Jnk (T183/Y185) phosphorylation through Western blotting using phosphospecific antibodies. (D) Densitometry of C. *P < 0.05, 21% O2 versus 95% O2; and **P < 0.05, 95% O2 + rhTrx versus 21% O2 + rhTrx. (E) MLE-12 cells were pretreated with or without SB203580 (5 μM) or rhTrx (2 μg/ml) before being subjected to hyperoxia treatment for 24 hours. Cell lysates were prepared and immunoprecipitated with pSer/pThr antibodies, and the immunocomplexes were analyzed by using Western blotting for PGC1α, UCP2, Tom40, and β-actin. (F) Densitometry of E. *P < 0.05, 95% O2 versus 21% O2; and **P < 0.05, 21% O2 versus 95% O2 with or without Trx. (G) Densitometry of the expression of pPGC1α–Ser or pPGC1α–Thr in the experiment in E. *P < 0.05, 95% O2 versus 21% O2; **P < 0.05, 95% O2 + rhTrx versus 95% O2 + rhTrx + SB203580; and **P < 0.05, 95% O2 + SB203580 versus 95% O2. (H) Lysates of normoxia- or hyperoxia-treated MLE-12 cells were analyzed for MKK4 (S257) phosphorylation through Western blotting using phosphospecific antibodies. (I) Densitometry of H. *P < 0.05, 95% O2 versus 21% O2. (J) MLE-12 cells were pretreated with rhTrx (2 μg/ml) and exposed to 21% O2 or 95% O2 for 24 hours and were analyzed for MKK4 (S257) phosphorylation through Western blotting using phosphospecific antibodies. (K) Densitometry of K. *P < 0.05, 95% O2 versus 21% O2; and **P < 0.05, 21% O2 + rhTrx versus 95% O2 + rhTrx. (L) Cells were transfected with 100-nM NT or MKK4 siRNA, pretreated with rhTrx (2 μg/ml), and then treated with and without hyperoxia for 24 hours. Protein was analyzed for p-p38 (T180/Y182) phosphorylation and UCP2 expression by using specific antibodies. (M) Densitometry of L. *P < 0.05, 95% O2 + NT siRNA versus 21% O2 + NT siRNA; **P < 0.05, 95% O2 + rhTrx + NT siRNA versus 95% O2 + rhTrx; ***P < 0.05, 95% O2 + NT siRNA versus 95% O2 + MKK4 siRNA; and #P < 0.05, 95% O2 + rhTrx + NT siRNA versus 95% O2 + rhTrx + MKK4 siRNA. (N) All the conditions were same as in L, except that an equal amount of cell lysates was immunoprecipitated with pSer/pThr antibodies and that the immunocomplexes were analyzed by using Western blotting for PGC1α phosphorylation. (O) Densitometry of N. *P < 0.05, 21% O2 + NT siRNA versus 95% O2 + NT siRNA; **P < 0.05, 95% O2 versus 95% O2 + rhTrx; and #P < 0.05, 95% O2 + rhTrx versus 95% O2 + rhTrx + MKK4 siRNA. (P) MLE-12 cells were transfected with 100-nM NT siRNA or MKK4 siRNA, pretreated with rhTrx (2 μg/ml), and exposed to 21% O2 or 95% O2 for 24 hours, and total cell extracts were analyzed for PGC1α expression. (Q) Densitometry of P. *P < 0.05, 95% O2 + NT siRNA versus 21% O2 + NT siRNA; and **P < 0.005, 95% O2 + rhTrx + MKK4 siRNA versus 95% O2 + rhTrx + NT siRNA.
Hyperoxia-induced O2•− Generation in UCP2-Knockout Mice Is Decreased by Chemical Uncouplers
Because UCP2 regulates mitochondrial O2•− by limiting uncoupling, we speculated that a significant increase in O2•− generation would occur in the lungs of UCP2-knockout (KO) mice exposed to hyperoxia. As shown in Figures 5A and 5B, UCP2-KO mice showed an increase in O2•− during normoxia as well as during hyperoxia compared with WT mice. However, this increase was only 30% higher for O2•− generation in UCP2-KO mice compared with WT mice. Because WT mice showed almost complete loss of UCP2 after 48 hours of exposure to hyperoxia, UCP2−/− and WT mice generated increased amounts of O2•− in hyperoxia, with UCP2-KO mice producing significantly higher amounts of O2•− than WT mice. If uncoupling is the key mechanism of attenuation of ROS in hyperoxia in UCP2-KO or WT mice, then chemical uncouplers should decrease ROS generation in the lungs in hyperoxia. In Figures 5C–5E, we show that the chemical uncouplers BAM15 and niclosamide ethanolamine significantly decreased O2•− in the lungs of WT or UCP2-KO mice exposed to hyperoxia (Figure 5E), indicating that uncoupling by UCP2 can play a significant role in decreasing O2•− in mammalian lungs.
Figure 5.
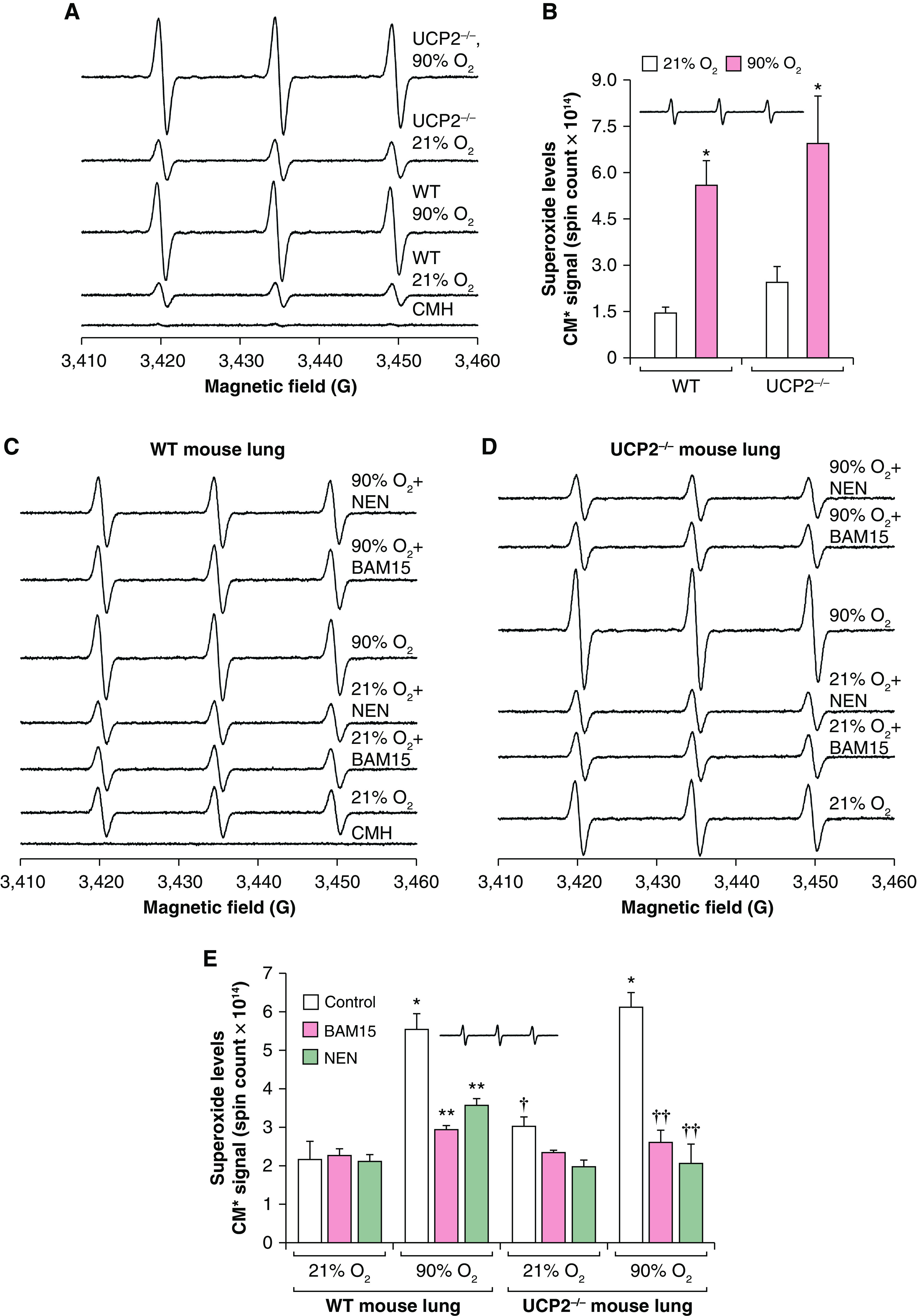
Chemical uncouplers decrease superoxide generation in hyperoxia in the lungs of wild-type (WT) and UCP2-knockout mice: (A) WT and UCP2−/− mice were exposed to 21% O2 or 90% O2 for 48 hours, and O2•− was measured through EPR using a CMH spin probe. (B) O2•− levels (absolute spin counts) are plotted in a bar graph. WT or UCP2−/− mice were exposed to normoxia or hyperoxia. *P < 0.05, versus WT mice exposed to 90% O2, versus WT mice exposed to 21% O2, and versus UCP2−/− mice exposed to 21% O2 (ANOVA, n = 3). (C) WT mice treated with 1.5-μM N5,N6-bis(2-fluorophenyl)[1,2,5]oxadiazolo[3,4-b]pyrazine-5,6-diamine (BAM15) or 1-μM niclosamide ethanolamine (NEN) for 30 minutes and exposed to normoxia or 90% O2 for 48 hours, which was followed by superoxide detection. The CMH EPR spectra are shown for WT mice. (D) UCP2−/− mice were treated with 1.5-μM BAM15 or 1-μM NEN for 30 minutes and exposed to normoxia or 90% O2 for 48 hours. Superoxide generation in the lungs was determined through EPR using a CMH spin probe as described in the Methods. EPR spectra were simulated with nitroxide radical signals. (E) Absolute spin counts were obtained by using Xenon nano version 1.2 software, and the mean ± SEM was plotted in a bar graph. *P < 0.01, 90% O2–exposed WT mice versus normoxia (21% O2)–exposed WT mice; **P < 0.01, BAM15- or NEN-treated mice in 90% O2 versus WT in hyperoxia (90% O2); †P < 0.05, WT mice treated with BAM15 or NEN and exposed to 21% O2 versus WT mice in 21% O2; and ††P < 0.01, UCP2−/− mice in normoxia versus UCP2−/− mice treated with BAM15 and NEN and exposed to hyperoxia (90% O2).
Trx Protects against Hyperoxia-mediated Lung Injury via Rescue of UCP2 Expression
We next evaluated whether restoration of UCP2 expression in hyperoxia would prevent lung injury in vivo. We determined the levels of PGC1α and UCP2 expression in the lungs of WT or Trx-Tg mice exposed to normoxia or hyperoxia. PGC1α phosphorylation was increased after 48-hour exposure of mice to hyperoxia (Figures 6A and 6B). However, UCP2 expression was decreased at 48 hours in hyperoxia. In contrast, UCP2 expression did not decrease in the lungs of Trx-Tg mice exposed to hyperoxia for 48 hours, indicating that Trx facilitated the expression of UCP2 in hyperoxia. In addition, the expression and phosphorylation of PGC1α was increased in the lungs of Trx-Tg mice compared with WT mice in normoxia (Figures 6A and 6B). We further evaluated the lung histopathology in WT, UCP2−/−, and Trx-Tg mice exposed to hyperoxia to assess relative lung injury in these mice. As shown in Figure 6C, WT and UCP2−/− mice had significant lung injury in hyperoxia in contrast to Trx-Tg mice, which did not demonstrate histopathological markers of lung injury in hyperoxia, demonstrating that loss of UCP2 is an important regulator of hyperoxic lung injury in mice.
Figure 6.
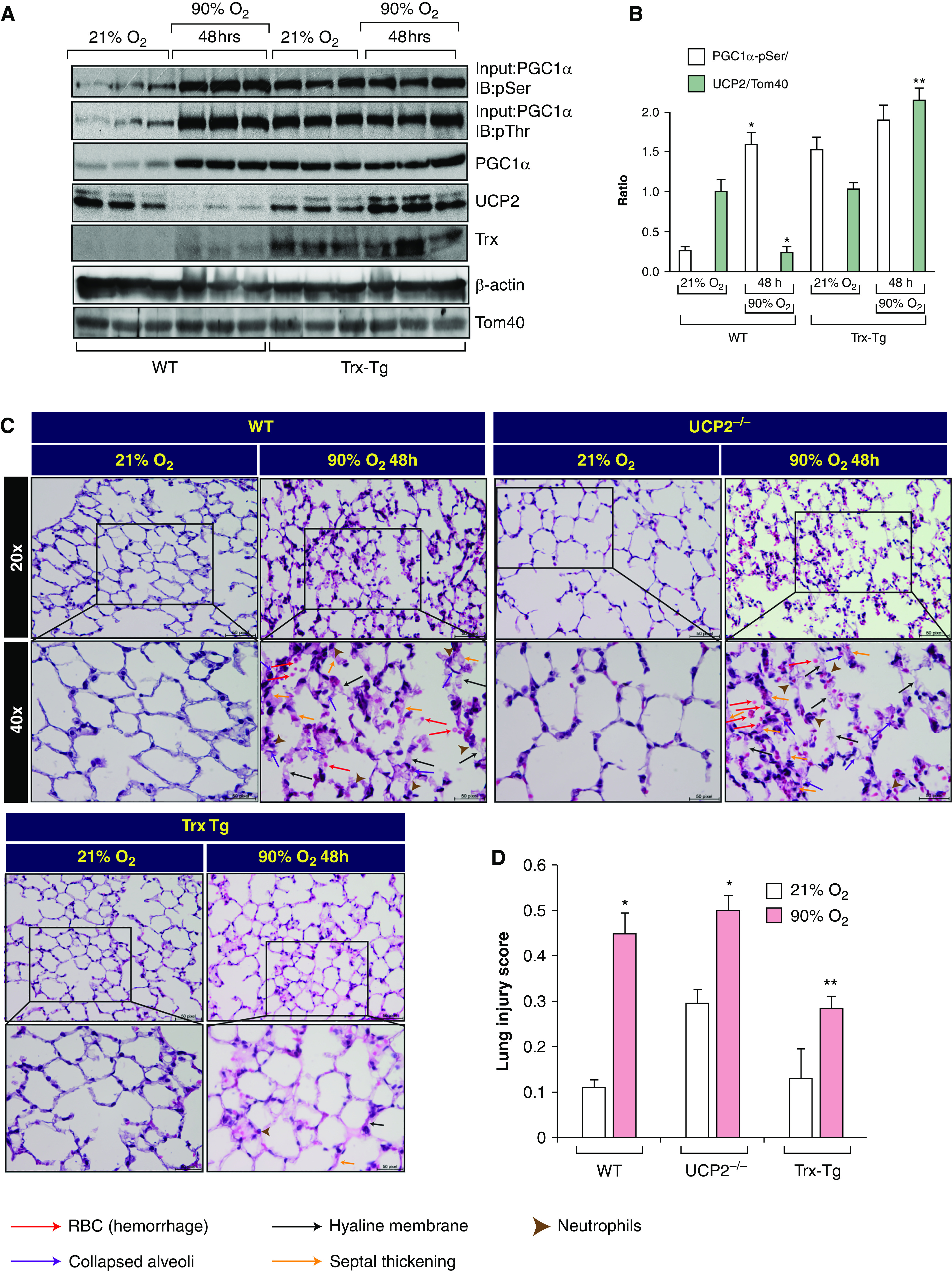
Trx protects against hyperoxia-mediated lung injury via rescue of UCP2 expression. (A) C57BL/6J (WT) and transgenic, hTrx overexpression–bearing (Trx-Tg) mice (12–14 wk; n = 3 for each strain) were exposed to either 21% O2 or 90% O2 for 48 hours. After exposure, mice were killed, lungs were dissected out, and lysed lung protein was analyzed for PGC1α, UCP2, Tom40, and β-actin expression. Scale bars, 50 µm. (B) Densitometry of ratio of PGC1α/β-actin and UCP2/Tom40. *P < 0.05, WT mice in normoxia versus WT mice in hyperoxia; and **P < 0.05, WT mice versus Trx-Tg mice in hyperoxia. (C) C57BL/6J mice, UCP2−/− mice, and Trx-Tg mice (12–14 wk; n = 3) were exposed to either 21% or 90% oxygen. Lung sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Stained lung sections were imaged by using a Zeiss AxioVert A1 microscope equipped with an AxioCam ICc5 color camera. (D) Lung injury was scored on the basis of neutrophil infiltration, hyaline membrane deposition, proteinaceous debris in the alveoli, and alveolar septal thickening (33). *P < 0.01, WT mice or UCP2−/− mice in normoxia versus hyperoxia; and **P < 0.01, Trx-Tg mice exposed to hyperoxia versus WT or UCP2−/− in hyperoxia. RBC = red blood cells.
Discussion
In the present investigation, we have shown that 1) hyperoxia-mediated loss of UCP2 expression is restored by Trx; 2) steady-state expression of UCP2 are maintained by Trx, as depletion of Trx results in loss of UCP2 expression in normoxia; 3) loss of UCP2 is a major mechanism of O2•− generation in hyperoxia in the lung; 4) Trx-mediated MKK4 phosphorylation is required to maintain steady-state expression of UCP2 in the lung in normoxia; 5) PGC1α phosphorylation by Trx-mediated MKK4–p38 MAPK induces its translocation to the nucleus and promotes UCP2 expression; and 6) UCP2−/− mice and WT mice exposed to hyperoxia show significant lung injury in contrast to Trx-Tg mice, demonstrating that loss of UCP2 in hyperoxia potentially very important mechanism of lung injury.
Although hyperoxia is known to cause ALI due to ROS, elimination of antioxidant enzymes in KO mouse models may not sensitize them to ALI (24–26). Likewise, high amounts of exogenous antioxidants often do not provide protection against the lung injury hyperoxia brings about (27). We have recently reported that mice overexpressing human Trx are resistant to hyperoxia-induced ALI; in contrast, mice deficient in endogenous Trx are sensitive to ALI due to hyperoxia (4). We have previously shown that hyperoxia induces the expression of Trx TrxR1 in the lungs of nonhuman primates (28). In addition, we have shown that overexpression of human Trx in mice (Trx-Tg mice) protects against Trx oxidation and prevents lung injury (4). However, the molecular mechanism(s) of Trx-mediated protection of lung injury remain(s) poorly understood. Our study provides a compelling mechanism by which loss of UCP2 in hyperoxia induces the generation of O2•− in the mitochondria. Consistent with these findings, chemical uncouplers were able to decrease production of ROS in the lungs of WT and UCP2−/− mice, establishing an important role of UCP2 in protection against lung injury. Because depletion of Trx promoted loss of UCP2 in normoxia, UCP2 is also critically required for normal lung function, as established by elimination of physiological ROS in mitochondrial respiration in normoxia. This could be an additional mechanism besides the presence of Sod2 in the mitochondria, together with other mitochondrial antioxidant enzymes.
UCP2 is the only UCP in the lung, whereas other organs may have UCP2 and UCP3 with overlapping functions (7). Therefore, lung UCP2 is uniquely important in the removal of the mitochondrial O2•− generated during oxidative phosphorylation. Because the lung is the only organ that experiences 21% oxygen in normal breathing, it is important to decrease the oxidative burden in the lung in a normal physiological state. In addition, in hyperoxia exposure, uncoupling by UCP2 is further important to decrease pathological ROS generation. UCP2 attenuates mitochondrial ROS production due to mild uncoupling with a limited increase in proton conductance, which lowers the protonmotive force (7). Surprisingly, depletion of Trx resulted in a severe decrease in UCP2 expression in normoxia, indicating a pivotal role of Trx in maintaining a steady-state level of UCP2 in cells. In addition, the lungs of Trx-Tg mice showed a significant level of PGC1α and phosphorylated PGC1α in normoxia, suggesting a baseline activating role of Trx in PGC1α phosphorylation. Therefore, it is likely that Trx regulates UCP2 basal expression due to redox signaling. We have previously reported that Trx activates MKK4 due to autophosphorylation of cysteine residues (15). Because MKK4 activates p38 MAPK, which phosphorylates PGC1α and facilitates its nuclear translocation, we believe that depletion of Trx in normoxia inactivates MKK4, resulting in inactivation of p38MAPK and the consequent cytosolic retention of PGC1α and decrease in UCP2 transcription. Therefore, a steady-state level of MKK4 phosphorylation by Trx is required to maintain the UCP2 level in normoxia. In addition, because p38 siRNA is specific to p38α, as per the manufacturer, and the antibody is reactive to p38α and p38β isoforms, as per the manufacturer, we believe that the p38MAPK α isotype is specifically involved in PGC1α phosphorylation. Furthermore, ERK and JNK are activated in hyperoxia, but they do not contribute to downstream signaling to activate PGC1α, as they remain unaltered in rhTrx treatment. Although we have shown loss of UCP2 expression in hyperoxia, the mechanism of this loss is not fully understood. In addition, the loss of expression of UCP2 in hyperoxia is due to transcription rather than RNA stability, as most of the genes that are downregulated or upregulated in hyperoxia are known to be regulated by transcription (29, 30). Because both mRNA and protein expression were severely decreased in hyperoxia, we speculate that oxidative stress in hyperoxia may inactivate MKK4–p38MAPK signaling due to oxidation of critical cysteines on MKK4 (15). PGC1α contains a negative regulatory domain—Thr261, Ser 265, and Thr298—which is known to bind to p160 myc binding protein as a repressor of PGC1α (31). Phosphorylation of these residues on PGC1α by p38 MAPK prevents p160 binding, resulting in translocation of PGC1α to the nucleus and its interaction with PPARγ and the transcription of genes. We have previously shown that the level of PPARγ was decreased in mice lacking redox-active Trx (mice deficient in endogenous Trx). However, mice overexpressing Trx (Trx-Tg mice) showed a significant increase in PPARγ during hyperoxia (4). Therefore, it is likely that Trx facilitates the interaction of PGC1α and PPARγ in a redox-dependent manner by increasing PPARγ expression and inducing the transcription of UCP2 in hyperoxia.
A previous study by others has demonstrated an early increase (1–8 h) of UCP2 in the lung in response to hyperoxia, but the UCP2 expression was decreased after 8 hours, with further decline being shown in 24 hours (32). Furthermore, in the same study, it was shown that in primary bone marrow–derived monocyte and macrophages and RAW164.7 macrophage cell lines, the UCP2 expression was slightly increased at 1 hour, which was followed by a decrease to the basal level at 4 hours. However, mRNA expression did not increase during this time course. Thus, the effect of this minor increase for a very short period of time is relatively small compared with the significant decrease in UCP2 expression and the consequent ROS generation in the lung reported in this study.
Hyperoxia-mediated lung injury is a major impediment to the clinical use of high concentrations of oxygen in respiratory disorders and in critical care units. Our present findings suggest that maintaining UCP2 expression in hyperoxia would decrease oxygen toxicity, which could better enable prolonged hyperoxic ventilation of patients with respiratory deficiency in situations such as the current coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic. Loss of UCP2 due to hyperoxia may cause overwhelming oxidative stress in the lung, which may not be controlled by antioxidants, as the source of O2•− generation would still exist in the lung. Because hyperoxia is also implicated in various lung diseases, understanding the functional state of UCP2 could advance our understanding of therapeutic interventions in lung diseases in which hyperoxia is implicated.
Footnotes
Supported by grant R01 HL130061 (K.C.D.) from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute of the National Institutes of Health and grant U54ES027698 (C.W.W.) from the Countermeasures against Chemical Threats Program, National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, National Institutes of Health. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of National Institutes of Health.
Author Contributions: K.C.D. conceived the project and designed experiments. S.R., V.K.-S., and S.K. designed and performed experiments and analyzed data. K.C.D. wrote and edited the manuscript. C.W.W. critically read and edited the manuscript.
This article has a data supplement, which is accessible from this issue’s table of contents at www.atsjournals.org.
Originally Published in Press as DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2021-0219OC on December 10, 2021
Author disclosures are available with the text of this article at www.atsjournals.org.
References
- 1. Freeman BA, Crapo JD. Hyperoxia increases oxygen radical production in rat lungs and lung mitochondria. J Biol Chem . 1981;256:10986–10992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Mellado-Artigas R, Ferreyro BL, Angriman F, Hernández-Sanz M, Arruti E, Torres A, et al. COVID-19 Spanish ICU Network High-flow nasal oxygen in patients with COVID-19-associated acute respiratory failure. Crit Care . 2021;25:58. doi: 10.1186/s13054-021-03469-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. McDonough G, Khaing P, Treacy T, McGrath C, Yoo EJ. The use of high-flow nasal oxygen in the ICU as a first-line therapy for acute hypoxemic respiratory failure secondary to coronavirus disease 2019. Crit Care Explor . 2020;2:e0257. doi: 10.1097/CCE.0000000000000257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Das KC. Thioredoxin-deficient mice, a novel phenotype sensitive to ambient air and hypersensitive to hyperoxia-induced lung injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol . 2015;308:L429–L442. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00285.2014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Das KC, Guo XL, White CW. Induction of thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase gene expression in lungs of newborn primates by oxygen. Am J Physiol . 1999;276:L530–L539. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1999.276.3.L530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Echtay KS, Roussel D, St-Pierre J, Jekabsons MB, Cadenas S, Stuart JA, et al. Superoxide activates mitochondrial uncoupling proteins. Nature . 2002;415:96–99. doi: 10.1038/415096a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Brand MD, Esteves TC. Physiological functions of the mitochondrial uncoupling proteins UCP2 and UCP3. Cell Metab . 2005;2:85–93. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2005.06.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Brand MD. Uncoupling to survive? The role of mitochondrial inefficiency in ageing. Exp Gerontol . 2000;35:811–820. doi: 10.1016/s0531-5565(00)00135-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Xiao H, Massaro D, Massaro GD, Clerch LB. Expression of lung uncoupling protein-2 mRNA is modulated developmentally and by caloric intake. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) . 2004;229:479–485. doi: 10.1177/153537020422900605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. St-Pierre J, Drori S, Uldry M, Silvaggi JM, Rhee J, Jäger S, et al. Suppression of reactive oxygen species and neurodegeneration by the PGC-1 transcriptional coactivators. Cell . 2006;127:397–408. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Wu Z, Puigserver P, Andersson U, Zhang C, Adelmant G, Mootha V, et al. Mechanisms controlling mitochondrial biogenesis and respiration through the thermogenic coactivator PGC-1. Cell . 1999;98:115–124. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80611-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Das KC. Hyperoxia decreases glycolytic capacity, glycolytic reserve and oxidative phosphorylation in MLE-12 cells and inhibits complex I and II function, but not complex IV in isolated mouse lung mitochondria. PLoS One . 2013;8:e73358. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Hilgers RH, Kundumani-Sridharan V, Subramani J, Chen LC, Cuello LG, Rusch NJ, et al. Thioredoxin reverses age-related hypertension by chronically improving vascular redox and restoring eNOS function. Sci Transl Med . 2017;9:eaaf6094. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aaf6094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Das KC, Wasnick JD. Biphasic response of checkpoint control proteins in hyperoxia: exposure to lower levels of oxygen induces genome maintenance genes in experimental baboon BPD. Mol Cell Biochem . 2014;395:187–198. doi: 10.1007/s11010-014-2124-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Kundumani-Sridharan V, Subramani J, Das KC. Thioredoxin activates MKK4-NFκB pathway in a redox-dependent manner to control manganese superoxide dismutase gene expression in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem . 2015;290:17505–17519. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.660365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Kundumani-Sridharan V, Subramani J, Raghavan S, Maiti GP, Owens C, Walker T, et al. Short-duration hyperoxia causes genotoxicity in mouse lungs: protection by volatile anesthetic isoflurane. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol . 2019;316:L903–L917. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00142.2018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Subramani J, Kundumani-Sridharan V, Das KC. Thioredoxin protects mitochondrial structure, function and biogenesis in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion via redox-dependent activation of AKT-CREB-PGC1α pathway in aged mice. Aging (Albany NY) . 2020;12:19809–19827. doi: 10.18632/aging.104071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Das KC, Das CK. Thioredoxin, a singlet oxygen quencher and hydroxyl radical scavenger: redox independent functions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun . 2000;277:443–447. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2000.3689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Akimoto T, Pohnert SC, Li P, Zhang M, Gumbs C, Rosenberg PB, et al. Exercise stimulates Pgc-1α transcription in skeletal muscle through activation of the p38 MAPK pathway. J Biol Chem . 2005;280:19587–19593. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M408862200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Xiong S, Salazar G, San Martin A, Ahmad M, Patrushev N, Hilenski L, et al. PGC-1α serine 570 phosphorylation and GCN5-mediated acetylation by angiotensin II drive catalase down-regulation and vascular hypertrophy. J Biol Chem . 2010;285:2474–2487. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.065235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Hickson JA, Huo D, Vander Griend DJ, Lin A, Rinker-Schaeffer CW, Yamada SD. The p38 kinases MKK4 and MKK6 suppress metastatic colonization in human ovarian carcinoma. Cancer Res . 2006;66:2264–2270. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-3676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Li W, Zhu J, Dou J, She H, Tao K, Xu H, et al. Phosphorylation of LAMP2A by p38 MAPK couples ER stress to chaperone-mediated autophagy. Nat Commun . 2017;8:1763. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-01609-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Zhang J, Min RWM, Le K, Zhou S, Aghajan M, Than TA, et al. The role of MAP2 kinases and p38 kinase in acute murine liver injury models. Cell Death Dis . 2017;8:e2903. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Ho YS. Transgenic and knockout models for studying the role of lung antioxidant enzymes in defense against hyperoxia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med . 2002;166:S51–S56. doi: 10.1164/rccm.2206017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Ho YS, Magnenat JL, Bronson RT, Cao J, Gargano M, Sugawara M, et al. Mice deficient in cellular glutathione peroxidase develop normally and show no increased sensitivity to hyperoxia. J Biol Chem . 1997;272:16644–16651. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.26.16644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Ho YS, Gargano M, Cao J, Bronson RT, Heimler I, Hutz RJ. Reduced fertility in female mice lacking copper-zinc superoxide dismutase. J Biol Chem . 1998;273:7765–7769. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.13.7765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Ho YS, Vincent R, Dey MS, Slot JW, Crapo JD. Transgenic models for the study of lung antioxidant defense: enhanced manganese-containing superoxide dismutase activity gives partial protection to B6C3 hybrid mice exposed to hyperoxia. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol . 1998;18:538–547. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.18.4.2959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Das KC, Guo XL, White CW. Hyperoxia induces thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase gene expression in lungs of premature baboons with respiratory distress and bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Chest . 1999;116:101S. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Lee PJ, Alam J, Sylvester SL, Inamdar N, Otterbein L, Choi AM. Regulation of heme oxygenase-1 expression in vivo and in vitro in hyperoxic lung injury. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol . 1996;14:556–568. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.14.6.8652184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. van Wijngaarden P, Brereton HM, Coster DJ, Williams KA. Stability of housekeeping gene expression in the rat retina during exposure to cyclic hyperoxia. Mol Vis . 2007;13:1508–1515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Fan M, Rhee J, St-Pierre J, Handschin C, Puigserver P, Lin J, et al. Suppression of mitochondrial respiration through recruitment of p160 myb binding protein to PGC-1α: modulation by p38 MAPK. Genes Dev . 2004;18:278–289. doi: 10.1101/gad.1152204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Steer JH, Mann TS, Lo SZ, Inglis JJ, Yap HS, Henry PJ, et al. Early induction of uncoupling protein-2 in pulmonary macrophages in hyperoxia-associated lung injury. Inhal Toxicol . 2013;25:544–552. doi: 10.3109/08958378.2013.810679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Matute-Bello G, Downey G, Moore BB, Groshong SD, Matthay MA, Slutsky AS, et al. Acute Lung Injury in Animals Study Group An official American Thoracic Society workshop report: features and measurements of experimental acute lung injury in animals. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol . 2011;44:725–738. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2009-0210ST. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


