Abstract
The Wnt1-Cre transgenic mouse line is widely used to express the Cre recombinase in neural crest lineages, but it overexpresses Wnt1 itself, which can cause undesired phenotypes. To address this, we and others previously developed a Wnt1-Cre2 line based on the same regulatory elements as Wnt1-Cre but without ectopic Wnt1 expression. However, while Wnt1-Cre2 exhibits normal activity when transmitted from female mice, it exhibits unexpected activity in the male germline. The Wnt1-Cre2 transgene was previously mapped to the E2f1 locus. Several genes in this genomic region exhibit significant expression in spermatogonia or spermatocytes, suggesting that local regulatory elements may be driving ectopic transgene expression. The Wnt1-Cre2 line can therefore be used both as a neural crest specific and a general deleter, and care should be taken when setting up genetic crosses.
Keywords: Wnt1-Cre, Wnt1-Cre2, mouse genetics, germline
Introduction
Wnt1-Cre is a transgenic Cre line used extensively to drive recombination in the dorsal neural tube and neural crest (Danielian et al., 1998; Jiang et al., 2000). However, the original Wnt1-Cre line resulted not only in Cre expression but also ectopic expression of Wnt1 itself (Lewis et al., 2013). Ectopic expression of Wnt1 caused several unintended consequences, including alterations in neural tube patterning and overgrowth of the midbrain. To circumvent this, we previously generated a second Wnt1-Cre transgenic line, Wnt1-Cre2, using the same regulatory elements as the original line but without the possibility of ectopic Wnt1 expression (Lewis et al., 2013). Crosses to reporter lines indicated an identical expression pattern as the original Wnt1-Cre but Wnt1 itself was expressed at normal levels.
We subsequently received reports and sometimes observed ourselves evidence of germline recombination using Wnt1-Cre2. We therefore set up a series of crosses to determine the penetrance of this phenotype and whether it was due to activity in the male germline, female germline, or sporadic activity in the epiblast itself, any of which might result in complete recombination of a conditional allele in the subsequent generation. We found that Wnt1-Cre2 is highly expressed in the male germline, but not in the female germline or epiblast. We confirmed that Wnt1-Cre2 drives reporter expression in spermatogonia of adult male mice. Further, we identify several genes near the Wnt1-Cre2 transgene insertion site that are highly expressed in the male germline. Their regulatory elements likely contribute to the ectopic germline expression of Wnt1-Cre2.
We caution researchers using this line to take the possibility of germline recombination into account when setting up crosses and always utilize genotyping primers that can detect wild type, conditional, and recombined (Δ) alleles to best manage their colony and accurately genotype embryos.
Results and Discussion
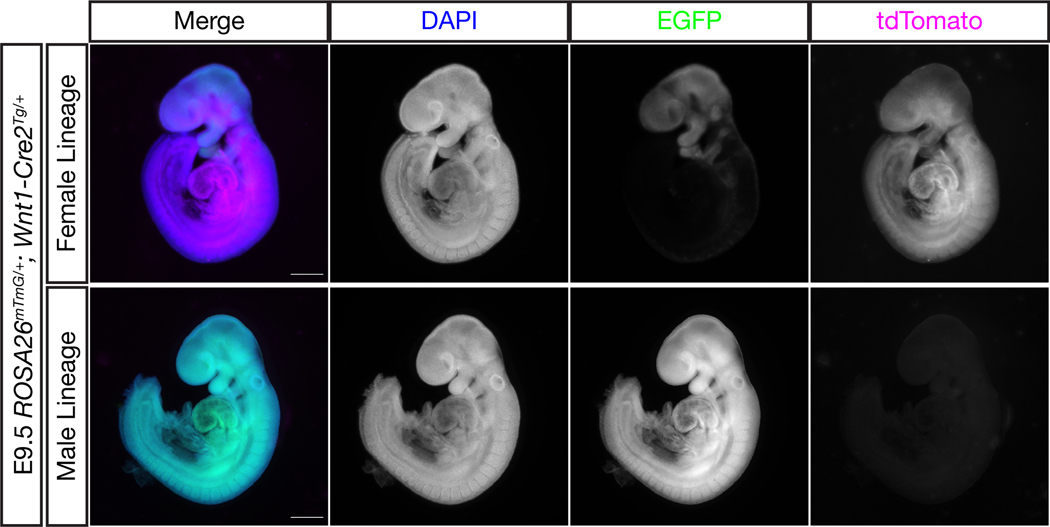
To determine the extent of germline activity in the Wnt1-Cre2 transgenic line, we first crossed Wnt1-Cre2Tg/+ mice to ROSA26mTmG/mTmG mice, generating G1 Wnt1-Cre2Tg/+; ROSA26mTmG/+ double heterozygous mice of both sexes. ROSA26mTmG mice constitutively express membrane targeted tdTomato but switch to expressing membrane targeted EGFP in cells (and their progeny) where Cre is expressed (Muzumdar et al. 2007). These G1 mice were then crossed to wild type mice and the resulting G2 embryos were subject to genotyping and characterization by fluorescence microscopy. We found that 100% of embryos that inherited the ROSA26mTmG and Wnt1-Cre2 alleles together through the female lineage displayed the expected pattern of recombination, i.e. completely tdTomato positive in Cre-negative embryos (n=15) and a GFP-positive neural crest lineage in Cre-positive embryos (n=14) (Figure 1, top). On the other hand, 100% of embryos that inherited the ROSA26mTmG allele from a sire also positive for Wnt1-Cre2 showed recombination throughout the embryo (100% GFP-positive), whether they inherited the Wnt1-Cre2 allele (n=28) or not (n=25), indicative of significant CRE activity in the male germline (Figure 1, bottom). Genotyping results are summarized in Table 1.
Figure 1.
Wnt1-Cre2 is active in the male germline
Male or female ROSA26mTmG/+; Wnt1-Cre2Tg/+ mice were crossed to wild type mice and the resulting embryos were analyzed for their recombination patterns. Here, embryos with identical genotypes show either an expected pattern of recombination in the neural crest or complete recombination throughout the embryo depending on whether the genes were inherited through the female or male lineage, respectively. Scale bars represent 500 μm.
Table 1.
Genotyping results and recombination patterns for Wnt1-Cre2 reporter crosses
| ♂ROSA26mTmG/+; Wnt1-Cre2Tg/+ × ♀Wild Type n=6 Sires | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genotype | Expected Pattern | Germline Pattern | Total Embryos | # Expected Pattern (%) | # Germline Pattern (%) |
|
ROSA26+/+; Wnt1-Cre2+/+ |
Not Fluorescent | Not Fluorescent | 34 | 34 (100) | N/A |
|
ROSA26+/+; Wnt1-Cre2Tg/+ |
Not Fluorescent | Not Fluorescent | 29 | 29 (100) | N/A |
|
ROSA26mTmG/+; Wnt1-Cre2+/+ |
All tdTomato+ | All EGFP+ | 25 | 0 (0) | 25 (100) |
|
ROSA26mTmG/+; Wnt1-Cre2Tg/+ |
EGFP+ Neural Crest | All EGFP+ | 28 | 0 (0) | 28 (100) |
| ♂Wild Type x ♀ROSA26mTmG/+; Wnt1-Cre2Tg/+ n=6 Dams | |||||
| Genotype | Expected Pattern | Germline Pattern | Total Embryos | # Expected Pattern (%) | # Germline Pattern (%) |
|
ROSA26+/+; Wnt1-Cre2+/+ |
Not Fluorescent | Not Fluorescent | 18 | 18 (100) | N/A |
|
ROSA26+/+; Wnt1-Cre2Tg/+ |
Not Fluorescent | Not Fluorescent | 13 | 13 (100) | N/A |
|
ROSA26mTmG/+; Wnt1-Cre2+/+ |
All tdTomato+ | All EGFP+ | 15 | 15 (100) | 0 (0) |
|
ROSA26mTmG/+; Wnt1-Cre2Tg/+ |
EGFP+ Neural Crest | All EGFP+ | 14 | 14 (100) | 0 (0) |
When Wnt1-Cre2 and a floxed reporter coexist in the male line, 100% germline recombination is observed in ROSA26mTmG/+ offspring, even whenWnt1-Cre2 is not coinherited (25/25 Cre− embryos and 28/28 Cre+ embryos), indicating germline activity for this strain. However, germline activity is not observed when the genes are inherited through the female lineage.
To test the possibility that a paternally-inherited Wnt1-Cre2 allele could act in trans and recombine a female-inherited flox allele, either through residual CRE protein associated with the male pronucleus or activation of the gene during early embryogenesis, we also analyzed several embryos resulting from male Wnt1-Cre2Tg/+ mice crossed to female ROSA26mTmG/mTmG mice. The resulting embryos all showed the expected fluorescence pattern for their genotype, ruling out this possibility (data not shown).
To confirm that CRE activity is already present in adult male mice, we examined the testes of three adult male G1 Wnt1-Cre2Tg/+; ROSA26mTmG/+ mice. All three showed extensive GFP signal in the seminiferous tubules, with particularly high expression in the maturing spermatocytes (Figure 2). As a control, we also examined two adult male G1 Wnt1-CreTg/+; ROSA26mTmG/+ mice, which did not show GFP signal in this tissue (Figure 2, bottom). Somatic tissue remained unrecombined (red) in both lines, indicating CRE activity specifically in the germline of male Wnt1-Cre2 mice.
Figure 2.
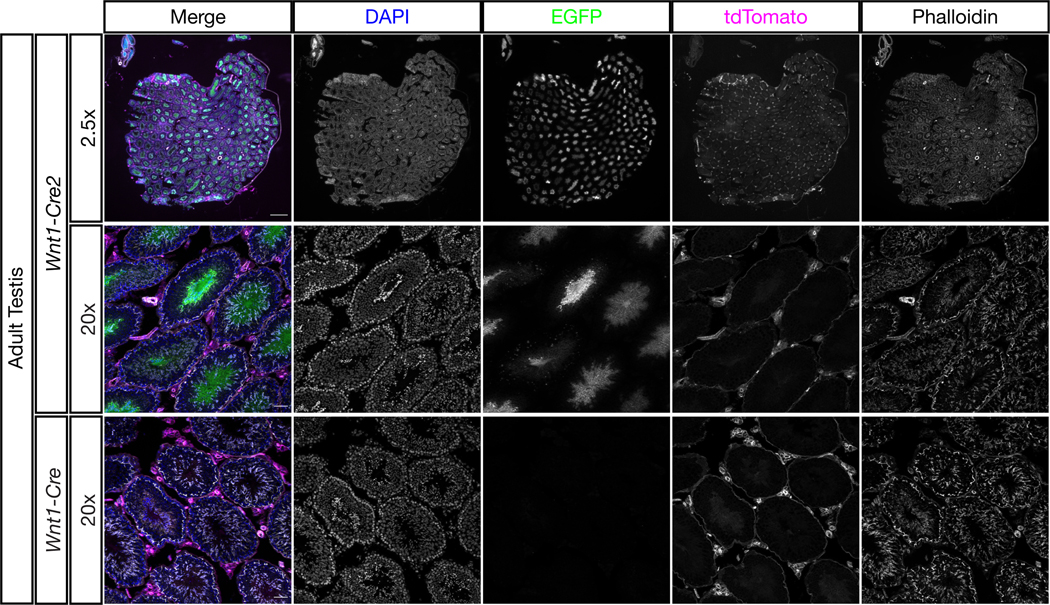
Wnt1-Cre2 activity is detectable in adult male germ cells
Testes from adult male ROSA26mTmG/+; Wnt1-Cre2Tg/+ and ROSA26mTmG/+; Wnt1-CreTg/+ mice were sectioned and stained with DAPI and phalloidin. EGFP signal indicating CRE activity was found extensively within the seminiferous tubules of Wnt1-Cre2 but not Wnt1-Cre mice. Somatic tissue outside the tubules remained negative for EGFP and positive for tdTomato, indicating that Wnt1-Cre2 is active in the adult male germline but not somatic tissue within the testis. At 2.5x scale bars represent 500 μm. At 20x scale bars represent 50 μm.
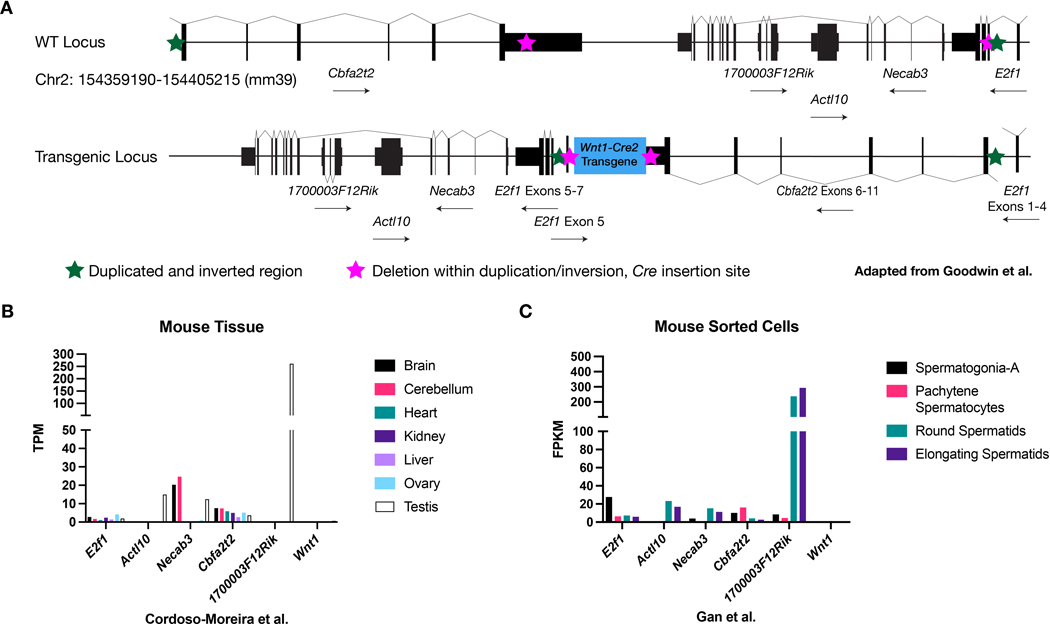
Because the original Wnt1-Cre transgene did not exhibit germline recombination, we suspected that regulatory elements near the Wnt1-Cre2 insertion site were responsible for this behavior. Wnt1-Cre2 has been previously mapped to the E2f1 locus and the nature of the insertion extensively characterized (Goodwin et al., 2019). The insertion resulted in a complicated rearrangement in which a genomic segment was duplicated and inverted (Figure 3A, green stars) and a smaller section within the duplication was deleted (Figure 3A, magenta stars). 1–3 copies of the Wnt1-Cre2 cassette inserted at this deletion site. The final Wnt1-Cre2 allele likely disrupts the E2f1 gene (Figure 3A, bottom).
Figure 3.
The Wnt1-Cre2 transgene inserted among genes expressed in the male germline
(A) Wnt1-Cre2 inserted at the E2f1 locus in a complicated rearrangement involving a large duplication and inversion (green stars) enclosing a smaller deletion (magenta stars) where 1–3 copies of the transgene itself inserted. The Wnt1-Cre2 transgenic locus is depicted at bottom. This panel is based on Figure 3 from Goodwin et al. (B) Several genes near the insertion site are expressed or enriched in the testis relative to other organs. (C) E2f1 expression is enriched in spermatogonia and nearby Actl10 and 170000F12Rik are enriched in spermatids.
In addition to E2f1, the genes Necab3, Actl10, 1700003F12Rik, and Cbfa2t2 are near the Wnt1-Cre2 insertion site. We first assessed the literature to determine whether any of the genes are implicated in testis biology in the mouse. Indeed, E2f1 knockout mice display testicular atrophy, among other phenotypes (Field et al., 1996; Yamasaki et al., 1996) and Cbfa2t2 mutants have defective male and female germline development (Tu et al., 2016). However, Actl10 and 1700003F12Rik mutant mice have not been linked to germline biology and Necab3 mice have not been studied (Dickinson et al., 2016). We also examined published expression datasets to assess if these genes are enriched in testis or have significant expression in the spermatogonial lineage (Cardoso-Moreira et al., 2019; Gan et al., 2013). Actl10 and 1700003F12Rik were both enriched in testis at the tissue level (Figure 3B). In sorted cells, E2f1 and Cbfa2t2 showed moderate expression in spermatogonia. Necab3 and Actl10 were moderately expressed and 1700003F12Rik highly expressed in spermatids (Figure 3C). Endogenous Wnt1 was not expressed in these tissues or cells (Figure 3B–C). Altogether, these results indicate that Wnt1-Cre2 integrated into a region of the genome harboring several genes important for male germline development and/or with significant expression in that lineage. While we cannot link Wnt1-Cre2 male germline activity to a particular regulatory element, it seems likely that one or more elements from nearby genes drive ectopic Cre expression in the male germline. Alternatively, sequence within the transgene may support germline expression but only in certain permissive chromatin environments or the insertion itself may have generated a novel binding site for a testis-enriched transcription factor.
The pattern of Wnt1-Cre2 recombinase activity was also examined by Jackson Labs using the ROSA26LacZ reporter allele (Mouse Genome Informatics, informatics.jax.org). They also report recombination in spermatogonia, but the observed activity is more sporadic than we find in our crosses. It is possible that the degree of germline recombination varies by mouse strain, age, or the specific conditional allele. With this in mind, although we did not detect female germline recombination in our crosses, we cannot rule out that this would ever occur with a low frequency that might vary by gene or mouse strain.
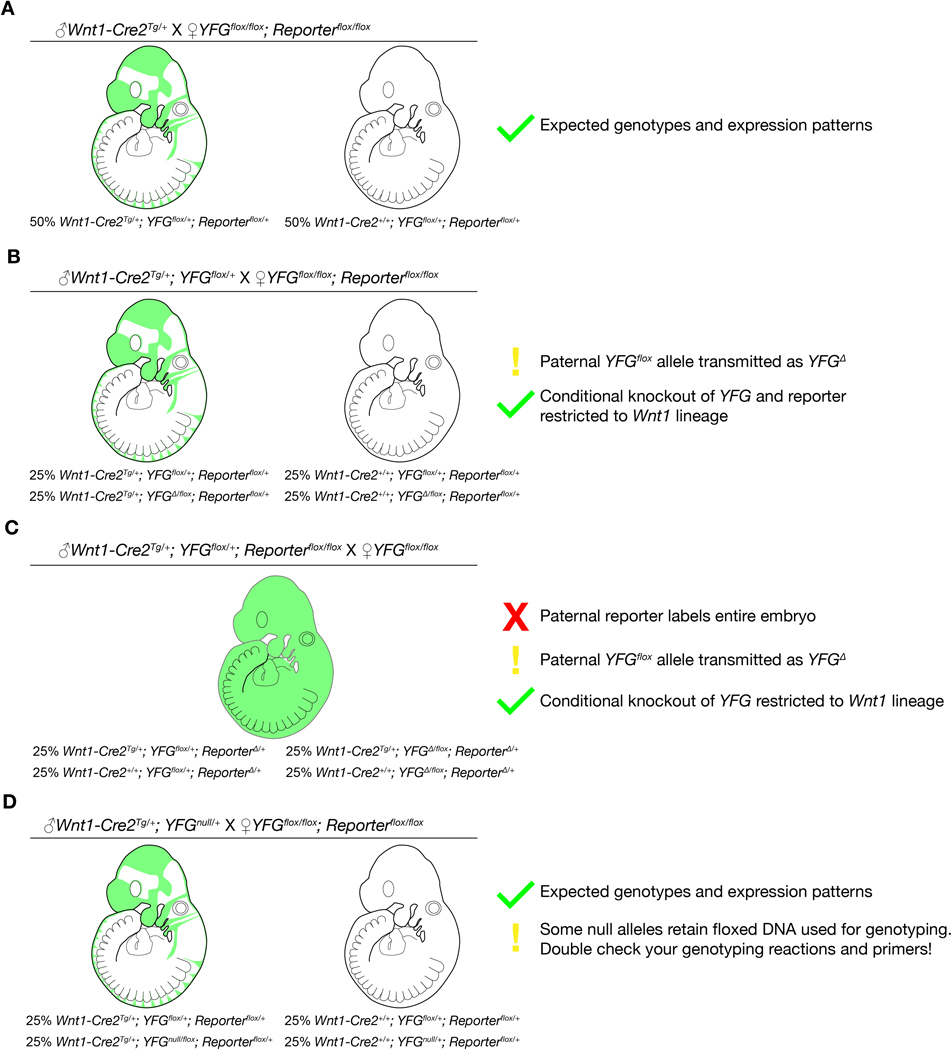
Male germline activity may have important implications for researchers using the Wnt1-Cre2 line. Because many breeding schemes involve a Cre-positive sire crossed to homozygous reporter dams, the reporter will behave as expected and germline activity will go undetected. If the male also carries a conditional flox allele, this will be inherited as a recombined (Δ) allele (Figure 4B–C). Additionally, some null alleles retain a floxed selection marker, such as NeoR, used for genotyping. If genotyping primers are not designed in a way to detect wild type, flox, and Δ alleles, then Δ allele could go undetected in a colony. Importantly, in the common breeding scheme where a Cre/+; flox/+ sire is crossed to a flox/flox dam, conditional knockout remains in the intended tissue only (Figure 4B). Cre-negative tissue, however, is Δ/flox, not flox/flox, so this could be an issue if the conditional gene has phenotypes in the heterozygous state. This could alternatively be advantageous if researchers are interested in studying timepoints shortly after Cre induction, as the need to only recombine a single floxed allele may lead to faster depletion of gene product and yield earlier or stronger phenotypes. Recommendations for future use of Wnt1-Cre2 (or any Cre with undesired male germline activity) are summarized in Figure 4.
Figure 4.
Advice for coinheritance of Wnt1-Cre2 and other alleles from the male lineage.
Depicted are four breeding schemes involving a conditional allele of Your Favorite Gene (YFG), a floxed reporter, and a paternal allele of Wnt1-Cre2. The cross and genotype ratios of the offspring are listed, and reporter activity is depicted in E9.5 embryos. (A) When no floxed allele is inherited from the sire, results are as expected. (B) When a floxed allele of YFG is present with Wnt1-Cre2 in the sire, it will transmit as a recombined (Δ) allele. This can complicate interpretation of results if heterozygous animals exhibit phenotypes. (C) Similarly, a reporter present in the sire will be fully recombined and be expressed ubiquitously in the next generation. (D) Coinheritance of Cre and a null allele will not affect results. Of note, many genotyping assays for conditional and null alleles rely on floxed sequences and are not able to detect a recombined (Δ) allele. This can lead to mis-genotyping of embryos and breeders, so primers that detect wild type, flox, and Δ alleles should always be used.
A potential benefit of the unintended germline activity is the ability to use the line not only for conditional recombination in the neural crest, but also as a general deleter to intentionally generate Δ alleles or remove floxed selection cassettes from newly generated mouse lines without the need to maintain a separate general deleter Cre line.
Transgenesis as a method for expression of exogenous genes such as Cre is widely used in the mouse, despite the many recognized drawbacks to this method. These include damage due to injection, toxicity caused by Cre expression, variable expression, methylation-induced silencing over time, and ectopic expression including in the male and female germlines (Clark et al., 2020; Song & Palmiter, 2018). Indeed, Wnt1-Cre2 joins several other transgenic Cre lines recently found to have ectopic male germline activity (de Lange et al., 2008; He et al., 2017; McLeod et al., 2020). The ease of transgenesis has historically been viewed as a large enough advantage to overcome the many drawbacks and justify use of the technique. However, given advances in knock-in technology such as using CRISPR-Cas and the identification of multiple safe-harbor loci in the mouse, it may now be preferable to generate Cre lines by knock-in to the endogenous locus or ectopically at a safe harbor site. On the other hand, unanticipated germline activity can also be found using knock-in Cre lines (Shi et al., 2016). Therefore, in addition to screening for a desired recombination pattern by crossing a Cre mouse with a reporter, a second generation cross using double heterozygous mice of both sexes crossed back to wild type is recommended, regardless of the method used to generate the Cre line (Song & Palmiter, 2018). Even when such crosses are reported, the expression pattern may change over successive generations due to a shift in genetic background or phenomena such as epigenetic silencing (Shimshek et al., 2002), so individual researchers should remain attentive to how Cre lines behave in their own colonies.
In summary, we report significant male germline activity using the Wnt1-Cre2 transgene. While we believe it retains its intended benefit over the original Wnt1-Cre due to the normal expression levels of Wnt1, researchers should adjust their breeding schemes or genotyping protocols accordingly.
Methods
Animal Husbandry
All animal experimentation was conducted according to protocols approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. Mice were kept in a dedicated animal vivarium with veterinarian support. They were housed on a 13hr-11hr light-dark cycle and had access to food and water ad libitum.
Mouse Models
The following previously described mouse lines were used: H2az2Tg(wnt1-cre)11Rth referred to as Wnt1-Cre (Danielian et al., 1998), E2f1Tg(Wnt1-cre)2Sor referred to as Wnt1-Cre2 (Lewis et al., 2013), Gt(ROSA)26Sortm4(ACTB-tdTomato,-EGFP)Luo referred to as R26RmTmG (Muzumdar et al., 2007). All mice were maintained on a 129S4 co-isogenic background until the final Wnt1-Cre2Tg/+; ROSA26mTmG/+ x wild type cross, where either 129S4 or C57Bl/6J wild type mice were used. In both cases, any germline recombination would have happened on a pure 129S4 background. Genotyping primers are available in Supplementary Table 1.
Whole-mount DAPI staining
Timed matings were set up and noon at the day of vaginal plug discovery was designated E0.5. Embryonic day E9.5 embryos were dissected in ice-cold PBS and subsequently fixed in 4% formaldehyde in PBS at 4º C for one hour, rinsed in PBS, and stained in 5 ug/ml DAPI in PBS overnight at 4º C on an orbital shaker. The next day embryos were rinsed in PBS and imaged using #1.5 coverglass-bottom dishes (Ibidi) on a Zeiss AxioObserver microscope with 2.5x objective. Z-stacks were projected using the wavelets function in Zeiss Zen software. Images were then identically thresholded using the FIJI implementation of ImageJ.
Testis sectioning
Adult male mice were euthanized by carbon dioxide inhalation followed by cervical dislocation. Testes were immediately dissected and fixed in 4% formaldehyde in PBS at 4º C for two hours. Following fixation, the tissue was rinsed in PBS, cryoprotected overnight in 30% sucrose, embedded in OCT, and frozen in a dry ice 100% ethanol bath. Cryosections were cut at 10 um thickness using a Leica cryostat. Slides were rinsed in PBS to remove OCT, briefly blocked with PBS supplemented with 1% bovine serum albumin, 5% calf serum, 0.1% Tween-20 and then stained with 5 ug/ml DAPI and 1:400 Phalloidin-Alexa647 in fresh blocking solution for thirty minutes at room temperature. Finally, sections were rinsed in PBS at room temperature, mounted in Slowfade Diamond under a #1.5 coverglass held in place with clear nail polish, and imaged on an inverted Zeiss AxioObserver microscope. Z-stacks were maximally projected and level adjustments made in the FIJI implementation of ImageJ.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements
We thank the members of the Soriano lab and Jeff Bush for helpful comments on the manuscript. C.J.D. was supported by F32 DE026678 from National Institutes of Health (NIH)/National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research (NIDCR). This work was supported by R01 DE022363 from NIH/NIDCR to P.S.
C.J.D. was supported by F32 DE026678 from National Institutes of Health (NIH)/National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research (NIDCR). This work was supported by R01 DE022363 from NIH/NIDCR to P.S.
Footnotes
Competing Interests Statement
The authors declare no competing financial or non-financial interests.
References
- Cardoso-Moreira M, Halbert J, Valloton D, Velten B, Chen C, Shao Y, Liechti A, Ascencao K, Rummel C, Ovchinnikova S, Mazin PV, Xenarios I, Harshman K, Mort M, Cooper DN, Sandi C, Soares MJ, Ferreira PG, Afonso S, … Kaessmann H. (2019). Gene expression across mammalian organ development. Nature, 571(7766), 505–509. 10.1038/s41586-019-1338-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark JF, Dinsmore CJ, & Soriano P. (2020). A most formidable arsenal: genetic technologies for building a better mouse. Genes Dev, 34(19–20), 1256–1286. 10.1101/gad.342089.120 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielian PS, Muccino D, Rowitch DH, Michael SK, & McMahon AP (1998). Modification of gene activity in mouse embryos in utero by a tamoxifen-inducible form of Cre recombinase. Curr Biol, 8(24), 1323–1326. 10.1016/s0960-9822(07)00562-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lange WJ, Halabi CM, Beyer AM, & Sigmund CD (2008). Germ line activation of the Tie2 and SMMHC promoters causes noncell-specific deletion of floxed alleles. Physiol Genomics, 35(1), 1–4. 10.1152/physiolgenomics.90284.2008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson ME, Flenniken AM, Ji X, Teboul L, Wong MD, White JK, Meehan TF, Weninger WJ, Westerberg H, Adissu H, Baker CN, Bower L, Brown JM, Caddle LB, Chiani F, Clary D, Cleak J, Daly MJ, Denegre JM, … Murray SA (2016). High-throughput discovery of novel developmental phenotypes. Nature, 537(7621), 508–514. 10.1038/nature19356 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field SJ, Tsai FY, Kuo F, Zubiaga AM, Kaelin WG Jr., Livingston DM, Orkin SH, & Greenberg ME (1996). E2F-1 functions in mice to promote apoptosis and suppress proliferation. Cell, 85(4), 549–561. 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81255-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gan H, Wen L, Liao S, Lin X, Ma T, Liu J, Song CX, Wang M, He C, Han C, & Tang F. (2013). Dynamics of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine during mouse spermatogenesis. Nat Commun, 4, 1995. 10.1038/ncomms2995 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin LO, Splinter E, Davis TL, Urban R, He H, Braun RE, Chesler EJ, Kumar V, van Min M, Ndukum J, Philip VM, Reinholdt LG, Svenson K, White JK, Sasner M, Lutz C, & Murray SA (2019). Large-scale discovery of mouse transgenic integration sites reveals frequent structural variation and insertional mutagenesis. Genome Res, 29(3), 494–505. 10.1101/gr.233866.117 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He Y, Sun X, Wang L, Mishina Y, Guan JL, & Liu F. (2017). Male germline recombination of a conditional allele by the widely used Dermo1-cre (Twist2-cre) transgene. Genesis, 55(9). 10.1002/dvg.23048 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang X, Rowitch DH, Soriano P, McMahon AP, & Sucov HM (2000). Fate of the mammalian cardiac neural crest. Development, 127(8), 1607–1616. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10725237 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis AE, Vasudevan HN, O’Neill AK, Soriano P, & Bush JO (2013). The widely used Wnt1-Cre transgene causes developmental phenotypes by ectopic activation of Wnt signaling. Dev Biol, 379(2), 229–234. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2013.04.026 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod VM, Cuic B, Chiam MDF, Lau CL, & Turner BJ (2020). Exploring germline recombination in Nestin-Cre transgenic mice using floxed androgen receptor. Genesis, 58(10–11), e23390. 10.1002/dvg.23390 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muzumdar MD, Tasic B, Miyamichi K, Li L, & Luo L. (2007). A global double-fluorescent Cre reporter mouse. Genesis, 45(9), 593–605. 10.1002/dvg.20335 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi J, Getun I, Torres B, & Petrie HT (2016). Foxn1[Cre] Expression in the Male Germline. PLoS One, 11(11), e0166967. 10.1371/journal.pone.0166967 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimshek DR, Kim J, Hubner MR, Spergel DJ, Buchholz F, Casanova E, Stewart AF, Seeburg PH, & Sprengel R. (2002). Codon-improved Cre recombinase (iCre) expression in the mouse. Genesis, 32(1), 19–26. 10.1002/gene.10023 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song AJ, & Palmiter RD (2018). Detecting and Avoiding Problems When Using the Cre-lox System. Trends Genet, 34(5), 333–340. 10.1016/j.tig.2017.12.008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tu S, Narendra V, Yamaji M, Vidal SE, Rojas LA, Wang X, Kim SY, Garcia BA, Tuschl T, Stadtfeld M, & Reinberg D. (2016). Co-repressor CBFA2T2 regulates pluripotency and germline development. Nature, 534(7607), 387–390. 10.1038/nature18004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki L, Jacks T, Bronson R, Goillot E, Harlow E, & Dyson NJ (1996). Tumor induction and tissue atrophy in mice lacking E2F-1. Cell, 85(4), 537–548. 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81254-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.