Abstract
The involvement of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection has been reported in multiple studies. Since it has been demonstrated that human intestinal epithelial cells support productive viral replication and that a substantial portion of infected individuals shed the virus in feces, the possibility of fecal–oral and fecal-respiratory modes of transmission have been proposed for SARS-CoV-2. In order to establish viral replication in the intestine, enteric viruses need to retain their infectivity in often low pH gastric fluids, and in intestinal fluids, which contain digestive enzymes and bile salts. In this study, we examined whether human coronaviruses OC43 (HCoV-OC43) can remain infectious in simulated GI fluids that models human fasting-state and fed-state, in the presence or absence of food. We demonstrated that except for fasting-state gastric fluid (pH 1.6), the virus can remain infectious in all other gastrointestinal fluids for 1 h. Furthermore, we demonstrated that presence of food could significantly improve viral survival in gastric fluids. Therefore, this study provides evidence that ingestion with food could protect the virus against inactivation by the GI fluids.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s12560-022-09520-5.
Keywords: Human coronavirus OC43, Gastrointestinal fluids, Survival, Infectivity assay
Introduction
Coronaviruses are enveloped viruses with a genome composed of a non‐segmented positive sense single-stranded RNA with a size of approximately 30 kb (Fehr & Perlman, 2015). Based on phylogenetic clustering, coronaviruses are divided into four genera: Alphacoronavirus, Betacoronavirus, Gammacoronavirus and Deltacoronavirus. Coronaviruses that infect humans (HCoVs), belong to the alpha and beta genera. Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)-CoV-2, which is responsible for the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, is a Betacoronavirus that causes mild to severe respiratory infections, as well as gastrointestinal symptoms (Cimolai, 2020; Kariyawasam et al., 2021). Human-to-human transmission of SARS-CoV-2 is mainly attributed to contaminated respiratory droplets and aerosols (Meyerowitz et al., 2021). Although gastrointestinal (GI) manifestations are reported in 11.4–61.1% of COVID-19 patients (Kariyawasam et al., 2021; Leal et al., 2021) and multiple lines of evidence suggest that the infectious viral particles are excreted in the feces of 41% of infected individuals (Britton et al., 2021; Shi et al., 2020), there is no conclusive evidence for fecal–oral or fecal-respiratory transmission.
It has been reported that the viral load in feces could reach to 107 RNA copies/g, even higher than that in nasopharyngeal swabs (Wolfel et al., 2020). The presence and persistence of such large amounts of viral RNA in feces cannot only be explained by ingestion of viral particles replicated in the respiratory system, but suggests potential replication of SARS-CoV-2 in the intestinal tract (Guo et al., 2021). Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), which is the main receptor for SARS-CoV-2 entry, is abundantly expressed in the lung and upper respiratory epithelia, as well as in the duodenum and small intestine, with lower levels in the stomach and large intestine (Hikmet et al., 2020). Although the mere expression of viral receptors in the GI system does not mean these cells are permissive to respiratory virus infection. The possibility of enteric propagation is further supported by the fact that human intestinal cells are highly permissive to infection with SARS-CoV- 2 (Lamers et al., 2020; Zhou et al., 2020). The ability to retain infectivity in the GI fluids is essential for a microbe to establish infection in the human intestinal tract, and it has been reported that SARS-CoV, SARS-CoV-2, middle-east respiratory syndrome (MERS), and HCoV-229E can tolerate fed-state gastric fluid and fasting-state intestinal fluid, but not fasting-state gastric fluids and fed-state intestinal fluids (Chak-Yiu Lee et al., 2020; Zhou et al., 2017).
Coronaviruses are enveloped, and as such, are expected to be susceptible to gastric acid and bile, therefore theoretically, it is unlikely that these viruses retain their infectivity and reach the lower GI tract to be excreted in the feces (Hirose et al., 2017). On the other hand, many of the mammal and avian‐associated coronaviruses are well known to cause gastroenteritis in their host species, including poultry, swine, bovine, equine, canine, and feline hosts (Cimolai et al., 2020; Pusterla et al., 2018; Wang, et al., 2019). Furthermore, evidence of the presence of SARS-CoV has been found in the intestinal mucosal epithelium and lymphoid tissue of human fatal cases (Gu et al., 2005; Shi et al., 2005). Notably, SARS-CoV-2 antigen has been detected in duodenum of infected golden hamster model (Sia et al., 2020). These observations suggest that at least some coronaviruses are resistant to gastrointestinal fluids and enzymes.
Given the limited access to biosafety level 3 (BSL-3) containment facilities required to safely handle SARS-CoV-2, scientists have turned to surrogate viruses that enable studies of viral replication as well as survival and inactivation at biosafety level 2 (BSL-2). This approach has expanded the current knowledge regarding the molecular and applied aspects of highly pathogenic coronaviruses.
The aim of this study is to examine the potential protective effect of food against HCoV inactivation by gastrointestinal fluids, using HCoV-OC43 as a surrogate for more pathogenic coronaviruses. In a previous study, we demonstrated that HCoV-229E and HCoV-OC43 survive significantly longer on cucumbers than apples and tomatoes (96 h vs 16 h) when stored at 22 °C (Blondin-Brosseau et al., 2021). As an extension of the previous study, we investigated the potential for HCoV to remain infectious following ingestion, in the presence or absence of cucumber slices.
Materials and Methods
Cell line and Virus
Human lung fibroblast cells, MRC-5 (ATCC# CCL-171), and human coronavirus OC43 (HCoV-OC43; ATCC# VR-1558) were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) (Cedarlane, Canada). Cells were grown and maintained at 37 °C and 5% CO2 in culture media composed of Eagle’s minimal essential medium, supplemented with 0.22% (w/v) sodium bicarbonate, 500 µg/mL penicillin/streptomycin), 1% Glutamax-1, 1% non-essential amino acids, 1% amphotericin B and 10% (v/v) fetal bovine serum (FBS) (ThermoFisher Scientific Inc, Canada). MEM maintenance media was used for dilution media of experimental samples, with the same composition as growth media but with 2% FBS.
Quantification of HCoV-OC43 Using Median Tissue Culture Infectious Dose (TCID50) Assay
Quantification of infectious HCoV-OC43 was conducted as described previously (Dallner et al., 2021). Briefly, MRC-5 cells were grown for 2 to 3 days and were seeded in 96 well plates at a cell concentration of 5 × 104 cells/100 µL well, up to 24 h in advance of the assay, in order to reach 90% confluence. Maintenance media was used to dilute gastric fluid treated, intestinal fluid treated, or maintenance media control samples. Cell monolayers were washed once with 1 × PBS (pH 7.35) and 100 µL of each dilution was used for quantification of tissue culture infectious dose, measured in quadruplicate for each sample. HCoV-OC43 stock was used as the positive control, diluted in maintenance media. Uninoculated maintenance media was the negative control. MRC-5 plates were then incubated at 33 °C for 5 days. Samples were removed from the 96 well plate, discarded, and stained with 0.1% crystal violet. Cells were observed under the microscope and the cytopathic effect for each sample was recorded. TCID50/mL was calculated using the Reed-Muench method (Reed & Muench, 1938). TCID50 values were converted to PFU by multiplying by 0.7, which is a constant value obtained based upon Poisson distribution (ATCC, 2021). The percentage viral recovery of HCoV-OC43 from 2 g cucumbers was determined by this equation:
Sample Preparation and HCoV-OC43 Treatment with Simulated Gastrointestinal Fluids
English cucumbers (PLU code 4593, Ontario, Canada) were purchased from a local grocery store in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. Simulated gastric and intestinal fluids were prepared according to manufacturer’s instructions (Biorelevant, London, UK). Simulated gastric fluids were supplemented with 0.1 mg/mL pepsin (Millipore Sigma, Canada). The surface of intact cucumbers were disinfected with 70% ethanol, dried, and chopped into 2 g amounts. Each 2 g sample of cucumber was inoculated, in triplicate, with 100 µL of 106 TCID50/mL HCoV-OC43, applied as drops to provide an even cover of the cucumber surface, then left at room temperature for 10 min to dry. Each sample was then mixed with 5 mL of fed-state gastric fluid, (FEDGAS pH 6, pH 4.5, or pH 3), fasting-state gastric fluid (FaSSGF, pH 1.6), fed-state intestinal fluid (FeSSIF pH 5), or fasting-state intestinal fluid (FaSSIF pH 6.5). Instead of gastric or intestinal fluid, maintenance media was added to inoculated cucumber samples as a control and to calculate viral recovery. Samples were then incubated at 37 °C for 0, 10 or 60 min with rocking at 320 rpm. At the end of incubation, the gastric or intestinal fluid was neutralized to pH 7 using 2.5 M sodium hydroxide, and then processed immediately for viral quantification.
HCoV-OC43 Treatment with Simulated Gastrointestinal Fluids Without Food
Simulated gastric and intestinal fluids were prepared as described above. In triplicate, 100uL of 106 TCID50/mL HCoV-OC43 was added directly to each type of gastric or intestinal fluid and incubated at 37 °C for 0, 10 or 60 min with rocking at 320 rpm. The gastric or intestinal fluid was neutralized to pH 7 using 2.5 M sodium hydroxide and samples were processed immediately.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism v9.0 (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA) (2-way ANOVA multiple comparisons) was used to determine significant differences between treatments. Student t-test was used to determine the statistical significance of the difference between treatments in the presence or absence of cucumber.
Results and Discussion
In order to determine whether HCoV-OC43 can survive in gastrointestinal fluid, 7 × 104 PFU/mL (1 × 105 TCID50/mL) of the virus, in the presence or absence of food (cucumber slices), were exposed to fasting (pH 1.6) and fed-state gastric fluids (pH 3, 4.5, and 6), supplemented with pepsin, as well as fasting- and fed-state intestinal fluids, pH 6.5 and 5, respectively, for 0 to 60 min. The extraction efficiency of HCoV-OC43 from cucumber slices in the presence of maintenance media was 11.1%. The detection limit (LOD) for HCoV-OC43 on cucumbers was previously determined by our group to be 32 PFU (Dallner et al., 2021).
Figure 1a demonstrates the log reduction compared with the media control following treatments in the absence of food and Fig. 1b demonstrates the log reduction in viral infectivity in the presence of food. As shown in Fig. 1a, and b, HCoV-OC43 infectivity was rapidly lost after 10 min of treatment with the fasting-state gastric fluid (FaSSGF, pH 1.6). The presence of food did not lead to recovery of any infectious virus after treatment with (FaSSGF, pH 1.6) for 10 and 60 min (Fig. 1b, and Supplementary Table 1). We compared this to fed-state gastric fluids (FEDGAS) at different stages of stomach emptying (early: pH 6, mid: pH 4.5, and late: pH 3), as well as fed-state intestinal fluid (FeSSIF, pH 5) and fasting-state intestinal fluid (FaSSIF, pH 6.5). The results showed that HCoV-OC43 remain infectious for 60 min in all other types of fed-state gastric fluids and both intestinal fluids. However, the infectivity was reduced in fluids modeling the mid and late stages of stomach emptying (FEDGAS pH 4.5 and pH 3, respectively) compared to FEDGAS pH 6.5, possibly due to the higher acidic conditions. Importantly, the presence of food significantly improved the viral survival in FEDGAS pH 6.5, 4.5 and pH 3 (Supplementary Table 1). However, the presence of food did not lead to a significant difference in viral survival in the presence of fed-state or fasting-state intestinal fluids (Supplementary Table 1). In general, HCoV-OC43 retained the most infectivity at the fasting-state intestinal fluids, followed by the early stage fed-state gastric fluid (pH 6).
Fig. 1.
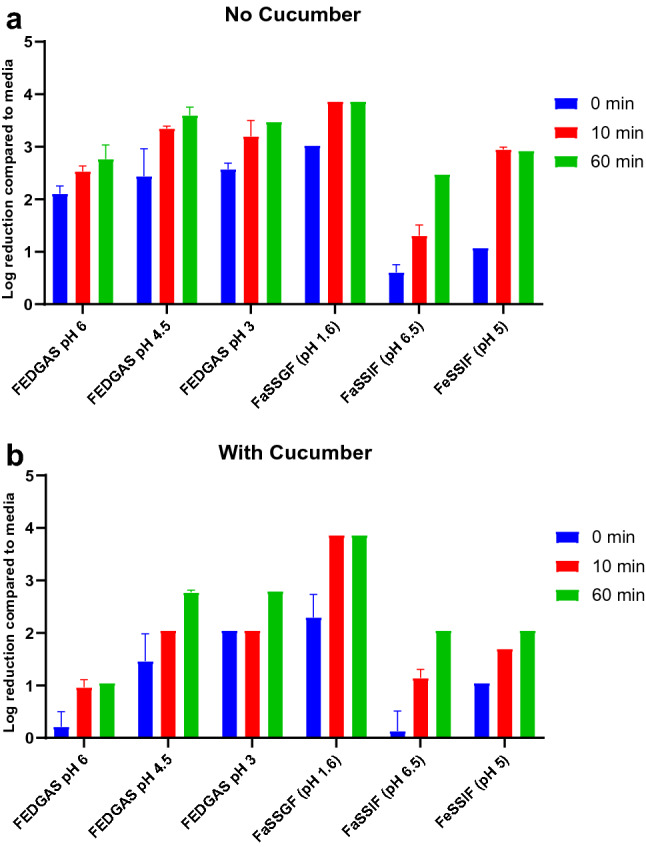
In vitro stability of HCoV-OC43 in simulated human gastrointestinal fluids a in the absence of food b on two grams of cucumber slices. HCoV-OC43 inoculum (105 TCID50) was added directly to each type of gastric or intestinal fluid and incubated at 37 °C for 0, 10 or 60 min. FaSSIF: fasting-state simulated intestinal fluid. FeSSIF: fed-state simulated intestinal fluid. FEDGAS: fed-state gastric fluid. FaSSGF: fasting-state gastric fluid. Data are presented as log reduction in viral infectivity compared to the media treatment. Data obtained from three independent experiments. Error bars are standard deviations
Treatment with FaSSGF (pH 1.6) rapidly inactivated the virus, at T0 the infectious viral titer was reduced by more than 2 log and longer treatment times of 10 and 60 min completely inactivated the virus (< LOD, i.e. 3.8 log reduction in infectivity). This finding is in accordance with previous studies that have reported complete inactivation of HCoVs in fasting-state gastric fluids (Chak-Yiu Lee et al., 2020; Zhou et al., 2017). Consistent with previous reports, treatment with each of the GI fluids at 10 and 60 min significantly reduced viral infectivity compared to the treatment with maintenance media. Furthermore, there was a significant decrease in viral infectivity following treatment with FeSSIF, compared to FaSSIF at T0. Potentially, this was due to the deleterious effect of bile on the viral membrane. However, in contrast to previous studies (Chak-Yiu Lee et al., 2020; Zhou et al., 2017), treatment with FeSSIF in the presence or absence of cucumber, did not lead to complete inactivation of HCoV-OC43 (Fig. 1a, and b). Nonetheless, in the absence of food, there is approximately 3 logs reduction in viral infectivity at 10 and 60 min treatment with FeSSIF (Supplementary Table 1).
Our results are in accordance with the observations made in a study from COVID-19 patients undergoing gastrointestinal endoscopy, in which SARS-CoV-2 RNA was detected and quantified in the gastric fluid and intestinal fluids obtained (Miyake et al., 2021). This indirectly indicates that the virus was able to endure gastrointestinal fluids.
While fecal-respiratory and fecal–oral modes of transmission have been demonstrated for some respiratory viruses including Hantavirus and Nipah virus (O'Brien et al., 2020; Witkowski et al., 2017), these modes of transmission remain controversial for SARS-CoV-2 (Britton et al., 2021). To date, only a few reports have indicated the possibility of fecal-respiratory transmission of SARS-CoV-2 (Meyerowitz et al., 2021). For example, one study demonstrated that exposure to a ruptured sewage pipe might have led to an outbreak of COVID-19 in a passenger ship (Colson et al., 2021) where travelers and crewmembers were infected with the same virus without being in direct contact with each other (Dergham et al., 2021; Guo et al., 2021). In the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, it is still unclear how gastrointestinal virus replication might affect the clinical outcome of infection and the transmission dynamics in the population. Further studies are required to determine whether SARS-CoV-2 shed in fecal matter can transmit COVID-19 between susceptible hosts. Addressing this knowledge gap will allow for understanding the potential role of fecal–oral and fecal-respiratory routes in COVID-19 transmission, which in turn will aid in the implementation of effective disease control measures.
Altogether, this study demonstrates that coronaviruses could be remain infectious in human GI fluid if ingested, and therefore, it is possible that infection could begin in the intestine. Nevertheless, it seems that the proportion of the virus that remains infectious in stool is not remarkable (Cuicchi et al., 2021).
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Acknowledgements
This study is financially supported by the Bureau of Microbial Hazards, Health Canada. The authors would like to thank Dr. Alex Gill and Dr. John Austin for thorough review of the manuscript.
Funding
A-base Health Canada.
Data Availability
The information is provided in the article. Further details can be provided upon request.
Declarations
Conflict of interest
None to be declared.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- ATCC. Is it possible to determine from the TCID[50] how many plaque forming units to expect?. Retrieved from https://www.atcc.org/support/technical-support/faqs/converting-tcid-50-to-plaque-forming-units-pfu.
- Blondin-Brosseau M, Harlow J, Doctor T, Nasheri N. Examining the persistence of human Coronavirus 229E on fresh produce. Food Microbiology. 2021;98:103780. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2021.103780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britton GJ, Chen-Liaw A, Cossarini F, Livanos AE, Spindler MP, Plitt T, Eggers J, Mogno I, Gonzalez-Reiche AS, Siu S, Tankelevich M, Grinspan LT, Dixon RE, Jha D, van de Guchte A, Khan Z, Martinez-Delgado G, Amanat F, Hoagland DA, tenOever BR, Dubinsky MC, Merad M, van Bakel H, Krammer F, Bongers G, Mehandru S, Faith JJ. Limited intestinal inflammation despite diarrhea, fecal viral RNA and SARS-CoV-2-specific IgA in patients with acute COVID-19. Science and Reports. 2021;11:13308. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-92740-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chak-Yiu Lee A, Zhang AJ, Fuk-Woo Chan J, Li C, Fan Z, Liu F, Chen Y, Liang R, Sridhar S, Cai JP, Kwok-Man Poon V, Chung-Sing Chan C, Kai-Wang To K, Yuan S, Zhou J, Chu H, Yuen KY. Oral SARS-CoV-2 inoculation establishes subclinical respiratory infection with virus shedding in golden Syrian hamsters. Cell Reports Medicine. 2020;1:100121. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2020.100121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cimolai N. Features of enteric disease from human coronaviruses: Implications for COVID-19. Journal of Medical Virology. 2020;92:1834. doi: 10.1002/jmv.26066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colson P, Levasseur A, Gautret P, Fenollar F, Thuan Hoang V, Delerce J, Bitam I, Saile R, Maaloum M, Padane A, Bedotto M, Brechard L, Bossi V, Ben Khedher M, Chaudet H, Million M, Tissot-Dupont H, Lagier JC, Mboup S, Fournier PE, Raoult D. Introduction into the Marseille geographical area of a mild SARS-CoV-2 variant originating from sub-Saharan Africa: an investigational study. Travel Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2021;40:101980. doi: 10.1016/j.tmaid.2021.101980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuicchi D, Lazzarotto T, Poggioli G. Fecal-oral transmission of SARS-CoV-2: Review of laboratory-confirmed virus in gastrointestinal system. International Journal of Colorectal Disease. 2021;36:437–444. doi: 10.1007/s00384-020-03785-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallner M, Harlow J, Nasheri N. Human coronaviruses do not transfer efficiently between surfaces in the absence of organic materials. Viruses. 2021;13:1352. doi: 10.3390/v13071352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dergham J, Delerce J, Bedotto M, La Scola B, Moal V. Isolation of viable SARS-CoV-2 virus from feces of an immunocompromised patient suggesting a possible fecal mode of transmission. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021 doi: 10.3390/jcm10122696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehr AR, Perlman S. Coronaviruses: An overview of their replication and pathogenesis. Methods in Molecular Biology. 2015;1282:1–23. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2438-7_1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu J, Gong E, Zhang B, Zheng J, Gao Z, Zhong Y, Zou W, Zhan J, Wang S, Xie Z, Zhuang H, Wu B, Zhong H, Shao H, Fang W, Gao D, Pei F, Li X, He Z, Xu D, Shi X, Anderson VM, Leong AS. Multiple organ infection and the pathogenesis of SARS. Journal of Experimental Medicine. 2005;202:415–424. doi: 10.1084/jem.20050828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo M, Tao W, Flavell RA, Zhu S. Potential intestinal infection and faecal-oral transmission of SARS-CoV-2. Nature Reviews. Gastroenterology & Hepatology. 2021;18:269–283. doi: 10.1038/s41575-021-00416-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hikmet F, Mear L, Edvinsson A, Micke P, Uhlen M, Lindskog C. The protein expression profile of ACE2 in human tissues. Molecular System Biology. 2020;16:e9610. doi: 10.15252/msb.20209610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirose R, Nakaya T, Naito Y, Daidoji T, Watanabe Y, Yasuda H, Konishi H, Itoh Y. Mechanism of human influenza virus rna persistence and virion survival in feces: Mucus protects virions from acid and digestive juices. Journal of Infectious Diseases. 2017;216:105–109. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jix224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kariyawasam JC, Jayarajah U, Riza R, Abeysuriya V, Seneviratne SL. Gastrointestinal manifestations in COVID-19. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene. 2021;115:1362–1388. doi: 10.1093/trstmh/trab042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamers MM, Beumer J, van der Vaart J, Knoops K, Puschhof J, Breugem TI, Ravelli RBG, Paul van Schayck J, Mykytyn AZ, Duimel HQ, van Donselaar E, Riesebosch S, Kuijpers HJH, Schippers D, van de Wetering WJ, de Graaf M, Koopmans M, Cuppen E, Peters PJ, Haagmans BL, Clevers H. SARS-CoV-2 productively infects human gut enterocytes. Science. 2020;369:50–54. doi: 10.1126/science.abc1669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leal T, Costa E, Arroja B, Goncalves R, Alves J. Gastrointestinal manifestations of COVID-19: Results from a European centre. European Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 2021;33:691–694. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000002152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyerowitz EA, Richterman A, Gandhi RT, Sax PE. Transmission of SARS-CoV-2: A review of viral, host, and environmental factors. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2021;174:69–79. doi: 10.7326/M20-5008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake S, Ashikari K, Kato S, Takatsu T, Kuwashima H, Kaneko H, Nagai K, Watari I, Sato T, Yamaoka Y, Yamamoto T, Ryo A, Maeda S, Nakajima A, Higurashi T. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 prevalence in saliva and gastric and intestinal fluid in patients undergoing gastrointestinal endoscopy in coronavirus disease 2019 endemic areas: Prospective cross-sectional study in Japan. Digestive Endoscopy. 2021;10:1111. doi: 10.1111/den.13945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien B, Goodridge L, Ronholm J, Nasheri N. Exploring the potential of foodborne transmission of respiratory viruses. Food Microbiology. 2020;6:103709. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2020.103709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pusterla N, Vin R, Leutenegger CM, Mittel LD, Divers TJ. Enteric coronavirus infection in adult horses. The Veterinary Journal. 2018;231:13–18. doi: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2017.11.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed L, Muench H. A simple method of estimating fifty per cent endpoints. The American Journal of Hygiene. 1938;27:493–497. [Google Scholar]
- Shi J, Sun J, Hu Y. Enteric involvement of SARS-CoV-2: Implications for the COVID-19 management, transmission, and infection control. Virulence. 2020;11:941–944. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2020.1794410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi X, Gong E, Gao D, Zhang B, Zheng J, Gao Z, Zhong Y, Zou W, Wu B, Fang W, Liao S, Wang S, Xie Z, Lu M, Hou L, Zhong H, Shao H, Li N, Liu C, Pei F, Yang J, Wang Y, Han Z, Shi X, Zhang Q, You J, Zhu X, Gu J. Severe acute respiratory syndrome associated coronavirus is detected in intestinal tissues of fatal cases. American Journal of Gastroenterology. 2005;100:169–176. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2005.40377.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sia SF, Yan LM, Chin AWH, Fung K, Choy KT, Wong AYL, Kaewpreedee P, Perera RAPM, Poon LLM, Nicholls JM, Peiris M, Yen HL. Pathogenesis and transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in golden hamsters. Nature. 2020;583:834–838. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2342-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Q, Vlasova AN, Kenney SP, Saif LJ. Emerging and re-emerging coronaviruses in pigs. Current Opinion in Virology. 2019;34:39–49. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2018.12.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkowski PT, Perley CC, Brocato RL, Hooper JW, Jurgensen C, Schulzke JD, Kruger DH, Bucker R. Gastrointestinal tract as entry route for hantavirus infection. Frontiers in Microbiology. 2017;8:1721. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfel R, Corman VM, Guggemos W, Seilmaier M, Zange S, Muller MA, Niemeyer D, Jones TC, Vollmar P, Rothe C, Hoelscher M, Bleicker T, Brunink S, Schneider J, Ehmann R, Zwirglmaier K, Drosten C, Wendtner C. Virological assessment of hospitalized patients with COVID-2019. Nature. 2020;581:465–469. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2196-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou J, Li C, Liu X, Chiu MC, Zhao X, Wang D, Wei Y, Lee A, Zhang AJ, Chu H, Cai JP, Yip CC, Chan IH, Wong KK, Tsang OT, Chan KH, Chan JF, To KK, Chen H, Yuen KY. Infection of bat and human intestinal organoids by SARS-CoV-2. Nature Medicine. 2020;26:1077. doi: 10.1038/s41591-020-0912-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou J, Li C, Zhao G, Chu H, Wang D, Yan HH, Poon VK, Wen L, Wong BH, Zhao X, Chiu MC, Yang D, Wang Y, Au-Yeung RKH, Chan IH, Sun S, Chan JF, To KK, Memish ZA, Corman VM, Drosten C, Hung IF, Zhou Y, Leung SY, Yuen KY. Human intestinal tract serves as an alternative infection route for Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. Science Advances. 2017;3:4966. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aao4966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The information is provided in the article. Further details can be provided upon request.


