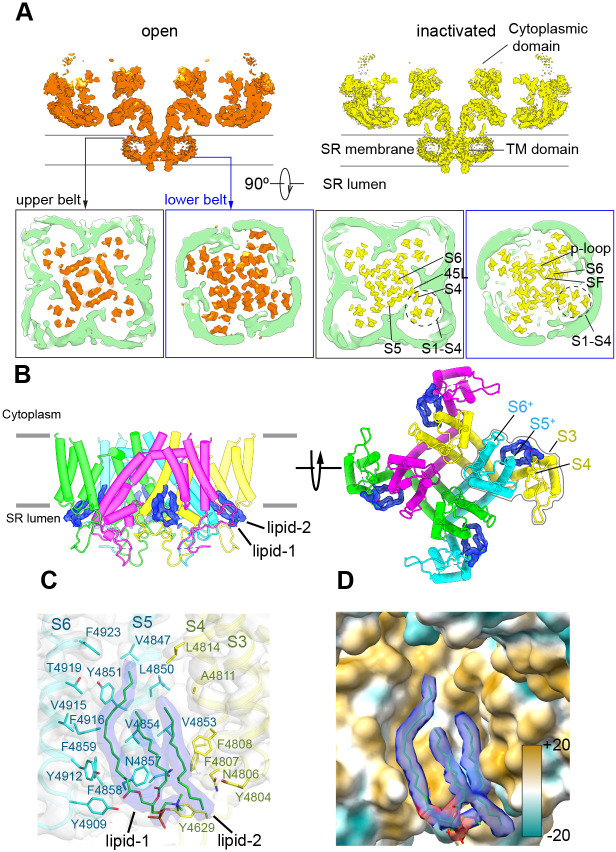
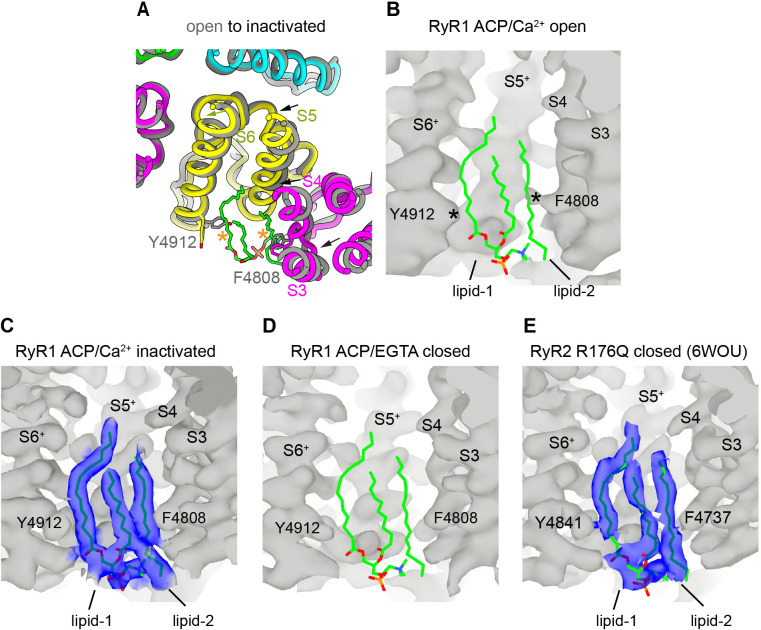
Figure 5. The nanodisc environment and visualization of lipids in a crevice of the transmembrane domain (TMD).
(A) Top: central slice of the side view of the RyR1-ACP/Ca2+A open and RyR1-ACP/Ca2+A-inactivated cryogenic electron microscopy cryo-EM maps highlighting the density corresponding to the upper and lower nanodisc belts. Bottom: corresponding views seen from the cytoplasmic direction. For clarity, the nanodisc density (green) was extracted and low-pass filtered to 7 Å resolution. The top belt of the nanodisc expands slightly to accommodate the conformational change; see also Figure 5—video 1. (B) Side and luminal views of the TMD of RyR1-ACP/Ca2+A inactivated with putative lipid densities shown in blue. (C) Lipid-binding pocket of RyR1-ACP/Ca2+A inactivated lined by lipophilic amino acids from S3 and S4 of the voltage sensor-like domain (S1–S4; yellow) and core helices S5 and S6 (cyan) from two different protomers. Amino acids within 5 Å from the lipids are shown (sticks) with their corresponding side chain densities. Densities corresponding to the lipids contoured at 8σ (in blue) are modeled as a PC (16:0-11:0) for lipid 1 and a 16C acyl chain for lipid 2. (D) Molecular lipophilicity potential of the surface lining the crevice, ranging from hydrophilic (cyan) to hydrophobic (golden). The hydrophobic tails of the lipids are shown in blue, and the negative electrostatic surface potential of the polar lipid head is shown in red.