Introduction
Follicular lymphoma is the most common of the indolent lymphomas and is the second most common subtype of lymphoma worldwide. Patients usually present with asymptomatic lymphadenopathy and advanced disease. Patients with asymptomatic and low burden disease are manage in a watch and wait approach and patient with high tumor and/or symptomatic disease are treated with immuno-chemotherapy.1,2 In the relapse setting Hodgkin and no Hodgkin lymphoma may respond to immunotherapy suggesting that the lymphocyte T activity can eliminate the lymphoma cells.3
There are few case reports about lymphoma remissions after bacterial or virus infections, including recently the COVID-19 infection, suggesting that the infection can trigger de immune system against the tumor cell.
Here, we show the case of a patient with advanced follicular lymphoma that presented spontaneously remission after a COVID-19 infection.
Case report
A 79-year-old woman was referred to hematologist with isolated skin lesion of 2 cm with biopsy showing cutaneous follicular lymphoma. Patient was treated with lesion resection and stayed in remission for 3 years when presented a localized relapse also treated with resection.
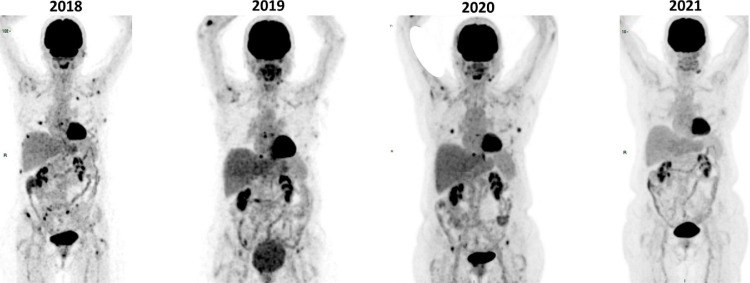
Three years later, in August 2018, patient was diagnosed with a solid breast lesion in the routine mammography. Core biopsy was diagnostic of breast follicular lymphoma. PET CT revealed avid stage IV disease (Figure 1) in breast and bone lesions without structure lesion. Patient denied to be submitted to a bone marrow biopsy. Patient was submitted to watch and wait approach since she was asymptomatic with low burden disease.
Figure 1.
PET CT revealed avid stage IV disease in breast and bone lesions in 2018, 2019 and 2020 and no uptake in 2021 even with no specific treatment for the lymphoma.
Patient was diagnosed COVID-19 positive in April 2020 with a positive serology. Nine months later she came to the hematologist to routine evaluation. PET CT revealed widespread resolution of the lesions with no lymphoma treatment.
Comments
The patient presented has an advanced follicular lymphoma and was in a watch and wait approach when got in remission without any treatment. This patient had a COVID infection and we believe that must exist relation between the infection and the remission since a spontaneous Hodgkin remissions was reported after a COVID 19 infection.4,5
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- 1.McNamara C, Montoto S, Eyre TA, Ardeshna K, Burton C, Illidge T, et al. The investigation and management of follicular lymphoma. Br J Haematol. 2020;191(3):363–381. doi: 10.1111/bjh.16872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Dada R. Diagnosis and management of follicular lymphoma: a comprehensive review. Eur J Haematol. 2019;103:152–163. doi: 10.1111/ejh.13271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Zinzani PL, Santoro A, Gritti G, Brice P, Barr PM, Kuruvilla J, et al. Nivolumab combined with brentuximab vedotin for relapsed/refractory primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma: efficacy and safety from the phase II CheckMate 436 study. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37(33):3081–3089. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.01492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Shallenor S, Tucker D. SARS-CoV-2-induced remission of Hodgkin lymphoma. Br J Haematol. 2021;192:415. doi: 10.1111/bjh.17116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Xu ML, Fedoriw Y. Lymphoma microenvironment and immunotherapy. Surg Pathol Clin. 2016;9(1):93–100. doi: 10.1016/j.path.2015.10.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]