Abstract
Scrub typhus is a bacterial zoonotic acute febrile illness (AFI) caused by the obligate intracellular bacterium Orientia tsutsugamushi, which is an antigenically diverse strain frequently observed in the tropical region of Southeast Asian countries. The recent investigation was conducted to delineate the genotype identification of Orientia tsutsugamushi predominating in the eastern zone of India such as Odisha to decipher its strain type, and evaluate its diversity as well as evolutionary pattern based on the nucleotide analysis of the immune dominant 56 KDa gene. During this study, we have investigated 100 clinical samples (2014–2018), out of which 28 were positive for scrub typhus followed by its molecular characterization and phylogenetic analysis utilizing 56 KDa partial genes. Population genetic parameters showed the presence of 287 polymorphic sites within the analyzed 56 KDa gene. The gene diversity (Hd) and sequence diversity (π) was estimated 0.638 and 0.280, respectively. Selection pressure analysis (θ = dN/dS) having the value 0.222 suggests that the gene lied under purifying selection. The present study suggested a high rate of genetic diversity within the isolates. This research study sheds light on the hereditary and evolutionary relationships of Orientia strains found in the eastern Indian population. Understanding regional genetic variation is critical for vaccine development and sero-diagnostics methods. A significant level of genetic variability was observed during this study. This information has a way to understand more about antigen diversity that leads to develop an effective vaccine candidate for this pathogen.
Keyword: Scrub typhus, Orientia tsutsugamushi, Vector-borne disease, Genetic diversity, Phylogenetic tree
Introduction
Scrub typhus is a vector-borne zoonotic bacterial infection caused by bacteria, Orientia tsutsugamushi (OT). It is a Gram-negative obligate intracellular parasite that belongs to genus Orientia, family Rickettsiaceae with significant genetic differences in peptidoglycan and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) compared with Rickettsia genus (Hayashi 1920; Ogata 1931; Tamura et al. 1995). The pathogen has worldwide distribution and promotes acute febrile illness (AFI) (Khan et al. 2017). The disease manifested by high temperature for 14 days lacks other clinical symptoms. Latter the infection leads to lymphadenopathy, rash, interstitial pneumonitis, meningitis, and myocarditis, and causes serious problems in vital organs like the lungs, liver, kidneys, and central nervous system (Jeung et al. 2016). Therefore, this disease is clinically indistinguishable from infection-causing acute fever, such as malaria, dengue, other rickettsioses, and leptospirosis (Kundavaram et al. 2013; Acestor et al. 2012). The mortality rate differed and can be reached up to 50% (Hu et al. 2015). OT is introduced into humans through trombiculid mites bite, those belonging to the genus Leptotrombidium. People who share the geographical regions with these vectors are at high risk of infection (Wardrop et al. 2013). Vectors usually prefer temperate and rainfall climates for their proliferation and spread.
The genome size of the bacterium varies from 1.93 to 2.47 Mb with a low GC content of 30–31%. The genome consists of 2086–2709 genes; those were enriched with repeat, which contributes 37.1% of the total genome (Batty et al. 2018). Recently, observed that OT interferes with a5b1 integrin-mediated signaling pathway to seize the replication of HeLa cells (Cho et al. 2010). Some reports suggested that during phagocytosis by L929 cells, OT exits the phagosome and goes into the cytoplasm (Chu et al. 2006). OT also regulates the clathrin-mediated endocytosis signaling pathway to infect endothelial and fibroblast cell lines. This leads to affect the organ like the lungs, liver, kidneys, and central nervous system (Jeung et al. 2016). For strain identification and genotype demarcation, the groES and groEL genes, the membrane proteins 47 kDa, and 56 kDa genes were extensively used worldwide due to their high diversity (Arai et al. 2013; Jiang et al. 2013; Lu et al. 2010). Due to the high immunogenic response in human and animal models, the 56 kDa and 47 kDa genes are used for vaccines. However, 120 antigenically different strains have been described which are further classified as Karp, Gilliam, and Kato (Kelly et al. 2002; Varghese et al. 2015). The antigenic diversity acts as an obstacle to develop an effective vaccine candidate. The sequence of a highly diverse immune dominant gene such as 56KDa, unique to OT, has become an important tool for strain demarcation (Blacksell et al. 2008).
The disease has a worldwide distribution including Japan, China, Korea, Philippines, Australia, Chile, India, Pakistan, Taiwan, and Afghanistan (Xu et al. 2017; Kuo et al. 2012). Reinfections were common due to the diversity of strains (Smadel et al. 1949). Scrub typhus has recently been observed in India and is now thought to be a major cause of severe febrile sickness. Limited information is available throughout India concerning its strain types (Mahajan et al. 2006; Varghese et al. 2015). Although a few reports suggested the endemicity of this disease within the Northeast region such as Assam and Meghalaya having Karp-like strains and Gilliam-like strains, respectively (Khan et al. 2017; Varghese et al. 2015). Still, continuous surveillance is required to get a clear picture to reveal the prevalence of genotype circulating within India. Thus, in the present investigation, the sequence information of the immunological dominant 56 KDa gene was utilized to define the strains of OT circulating in Odisha, a state of eastern India, and deciphered its genotype followed by estimation of genetic diversity and evolutionary trend.
Material and methods
Clinical sample collection from outbreak areas
Blood samples were collected from suspected humans from 28 outbreaks that occurred in different locations of Odisha during the years 2014–2018. The primary symptoms of infection comprised of headache, altered mental changes, vomiting, unconsciousness, nausea. These clinical samples were kept in an Eppendorf tube treated with aseptic phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) having pH 7.2, treated with antimicrobial reagents, and kept at − 20 °C for further processes.
DNA isolation
DNA from human blood was obtained utilizing the HipurA DNA blood kit (Himedia, India). One hundred μl of blood samples were processed to eliminate DNA according to the manufacturer’s protocol. DNA was extracted utilizing 100 μl of the elution buffer provided by the kit followed by its transfer into a 0.6 ml cryovial and stored at − 20 °C for future use (Fig. 1).
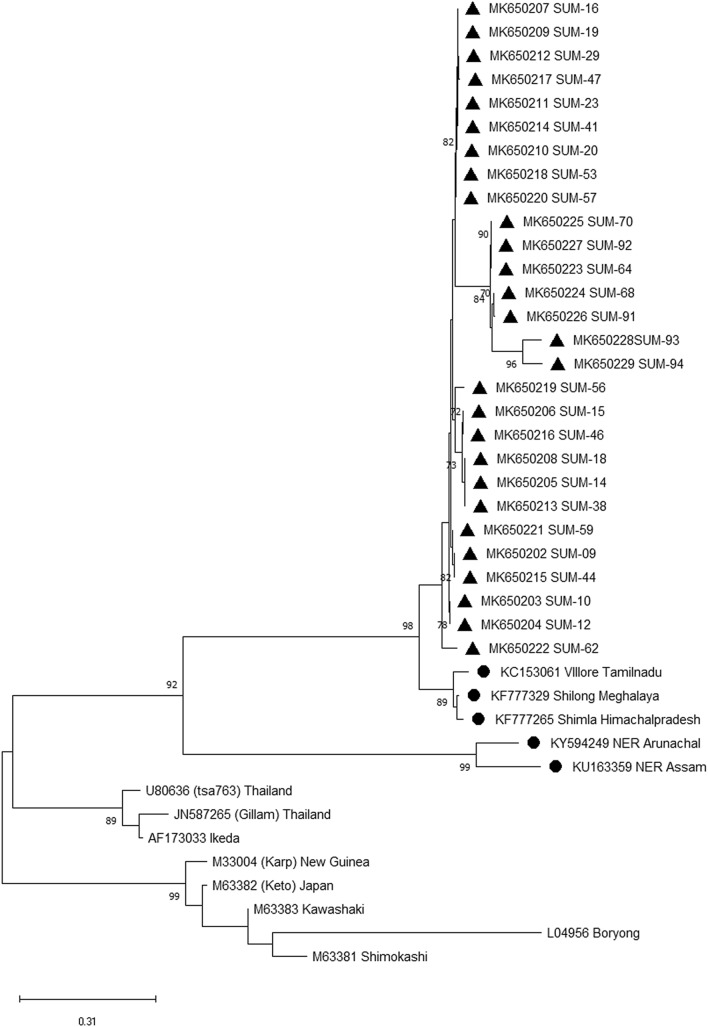
Fig. 1.
Phylogenetic analysis utilizing 56-kDa partial gene. Phylogenetic relationships of Orientia tsutsugamushi detected in human patients with scrub typhus in eastern Indian population. Relationships were determined based on the partial 56-kDa type-specific antigen gene by the minimum-evolution method with the Kimura 2-parameter distance model. Bootstrap values > 50% are shown at the branches. Location and GenBank accession numbers are indicated for each sequence. A solid triangle indicates sequences determined in this study
PCR amplification
Nested PCR was obtained following the method used by Furuya et al. 1993 with some modifications (Furuya et al. 1993). PCR primer F1-5′-TCA AGC TTA TTG CTA GTG CAA TGT CTG C-3′; R1-5′-AGG GAT CCC TGC TGC TGT GCT TGC TGC G-3′ and F2-5′-GAT CAA GCT TCC TCA GCC TAC TAT AAT GCC-3′; R2-5′-CTA GGG ATC CCG ACA GAT GCA CTA TTA GGC-3′ for the nested PCR to get the 56-kDa amplicons (Lee et al. 2011). The PCR master mix (25 μl) was composed of 5 pmol of each primer, 2 mM dNTPs in 1 × buffer supplemented with 2.5 U Taq polymerase according to the supplier's recommendations (NEB). The PCR reaction conditions were as follows: initial denaturation at 95 °C for 5 min, followed by 35 cycles of denaturation at 95 °C for 50 s, annealing at 55 °C for 60 s, extension at 72 °C for 90 s, and a final extension at 72 °C for 7 min. The PCR amplified products (10 μl) were stacked into a 1% agarose gel. Furthermore, these amplicons were gel-purified utilizing a QIAquick Gel Extraction Kit (QIAGEN) and sequenced commercially.
Construction of phylogenetic tree and evaluation of population genetics parameters
The nucleotide sequences of the 56-kDa gene were verified and aligned by the Bioedit software version 7.0.5.3 to get a consensus sequence. MEGA 7 was utilized to construct a phylogenetic tree through the minimum-evolution method with a bootstrap value of 1000 replicates (Saitou and Nei 1987). The polymorphic sites, haplotype diversity (Hd), nucleotide diversity (π), selection pressure (dn/ds), and Tajima D of the population were calculated using DnaSP version 5.10.01 (Librado and Rozas 2009).
Results
Phylogenetic analysis
Primers targeting the 56 KDa gene amplified in 28 clinical samples having fragments size 464 bp. The respective sequences were submitted to the GenBank to get the accession number MK650201-MK650229 (Table 1). A phylogenetic tree was constructed utilizing the sequence submitted during this study along with all 13 available sequences retrieved from GenBank. The nucleic acid and amino acid sequence of the present isolates revealed 99.0–100% and 98.2–100% similarities, respectively. The phylogenetic tree consists of five groups, from which group I and group II mostly have Indian isolates. All isolates of the present study exhibited in one group having a close relation with Meghalaya isolate.
Table 1.
Details of Orientia tsutsugamushi infected children and the location of the samples collected in this study
| Sr no. | Disease | Host species | Geographic area of distribution | Coordinates | Year of outbreak | Accession no. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Scrub typhus | Human | Nayagarh | 20.1231° N, 85.1038° E | 2014 | MK650202 |
| 2 | Scrub typhus | Human | Puri | 19.8135° N, 85.8312° E | 2014 | MK650203 |
| 3 | Scrub typhus | Human | Khurda | 20.1301° N, 85.4788° E | 2014 | MK650204 |
| 4 | Scrub typhus | Human | Nayagarh | 20.1231° N, 85.1038° E | 2015 | MK650205 |
| 5 | Scrub typhus | Human | Khurda | 20.1301° N, 85.4788° E | 2015 | MK650206 |
| 6 | Scrub typhus | Human | Nayagarh | 20.1231° N, 85.1038° E | 2015 | MK650207 |
| 7 | Scrub typhus | Human | Mayurbhanj | 21.5140° N, 86.5325° E | 2015 | MK650208 |
| 8 | Scrub typhus | Human | Khurda | 20.1301°N, 85.4788° E | 2015 | MK650209 |
| 9 | Scrub typhus | Human | Dhenkanal | 20.6505° N, 85.5981° E | 2015 | MK650210 |
| 10 | Scrub typhus | Human | Khurda | 20.1301° N, 85.4788° E | 2016 | MK650211 |
| 11 | Scrub typhus | Human | Nayagarh | 20.1231° N, 85.1038° E | 2016 | MK650212 |
| 12 | Scrub typhus | Human | Koraput | 18.8135° N, 82.7123° E | 2016 | MK650213 |
| 13 | Scrub typhus | Human | Nayagarh | 20.1231° N, 85.1038° E | 2016 | MK650214 |
| 14 | Scrub typhus | Human | Khurda | 20.1301° N, 85.4788° E | 2016 | MK650215 |
| 15 | Scrub typhus | Human | Nayagarh | 20.1231° N, 85.1038° E | 2016 | MK650216 |
| 16 | Scrub typhus | Human | Khandagiri | 20.1301° N, 85.4788° E | 2017 | MK650217 |
| 17 | Scrub typhus | Human | Cuttack | 20.4625° N, 85.8830° E | 2017 | MK650218 |
| 18 | Scrub typhus | Human | Khurda | 20.1301° N, 85.4788° E | 2017 | MK650219 |
| 19 | Scrub typhus | Human | Khurda | 20.1301° N, 85.4788° E | 2017 | MK650220 |
| 20 | Scrub typhus | Human | Nayagarh | 20.1231° N, 85.1038°E | 2018 | MK650221 |
| 21 | Scrub typhus | Human | Puri | 19.8135° N, 85.8312° E | 2018 | MK650222 |
| 22 | Scrub typhus | Human | Khurda | 20.1301° N, 85.4788° E | 2018 | MK650223 |
| 23 | Scrub typhus | Human | Ganjam | 19.5860° N, 84.6897° E | 2018 | MK650224 |
| 24 | Scrub typhus | Human | Ganjam | 19.5860° N, 84.6897° E | 2018 | MK650225 |
| 25 | Scrub typhus | Human | Khurda | 20.1301°N, 85.4788° E | 2018 | MK650226 |
| 26 | Scrub typhus | Human | Puri | 19.8135° N, 85.8312° E | 2018 | MK650227 |
| 27 | Scrub typhus | Human | Nayagarh | 20.1231° N, 85.1038° E | 2018 | MK650228 |
| 28 | Scrub typhus | Human | Khurda | 20.1301° N, 85.4788° E | 2018 | MK650229 |
Population genetic analysis
Population genetic parameters showed the presence of 287 polymorphic sites within the analyzed gene. The Haplotype diversity (Hd) and nucleotide diversity (π) were observed 0.638 and 0.280, respectively. Selection pressure analysis (θ = dN/dS) having the value 0.222 suggests that the gene lied under purifying selection. This selection of virulence genes could enhance the mutation rate, which induces a strong host immune response. Tajima's D test otherwise known as the neutrality test of this gene resulted in a value of − 1.14586. The negative value revealed that, this pathogen might adapt to evolutionary expansion.
Discussion
Scrub typhus is commonly referred to as an acute febrile illness observed in the rural part of South Asia. The disease is manifested by the presence of fever, myalgia, chills, headache, fatigue, loss of appetite, and gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, cough, diarrhea, and skin rash. Other symptoms include obstetric complications in pregnant women which lead to poor pregnancy outcomes. Demographic data confirmed that it can be contracted by all age groups and farmers were the most affected profession. The causative agent of this infection is Orientia tsutsugamushi, which infects endothelial cells macrophages, monocytes, dendritic cells, or cardiac myocytes which leads to a variety of complications in the liver and kidneys (Paris et al. 2015).
In the present study, the common symptoms of positive patients had fever, headache, myalgia, conjunctivitis, and rash. A few patients also suffered from cough, vomiting, nausea, abdominal pain, lymphadenopathy, hepatomegaly, conjunctivitis, rash, and splenomegaly. The phylogenetic analysis indicates the presence of five groups and the current isolates belong to the Kato genotype. However, several studies in India suggested the presence of Kato genotype, and have sequence similarity with OT isolates from Korea, Taiwan, Vietnam, and Cambodia (Fournier et al. 2008; Duong et al. 2013). In India, the disease has been frequently reported from southern, northern, and northeast regions of the country (Varghese et al. 2015; Khan et al. 2017). The partial sequences of 56 KDa gene revealed the prevalence of Kato strains in South India; Karp-like strains in North India; Gilliam and Karp strain in North-eastern (NE) India (Varghese et al. 2015; Khan et al. 2017). The NE region acts as a gateway for trade exchange between India and South Asian countries. That might be responsible for the introduction of the new strain into the mainland of India. The present study suggested a high rate of genetic diversity within the isolates. The previous study suggested the presence of an elevated rate of recombination, genome duplication, and horizontal gene transfer to maintain the genetic diversity of OT isolates in Thailand (Fournier et al. 2008), Cambodia (Duong et al. 2013), and China (Long et al. 2020). These recombination events are usually responsible for substantial genetic polymorphism (Yang et al. 2012), and variable antigenicity (James et al. 2016). Along with that cause, geographical expansion of scrub typhus may lead to an increase the diversity.
The higher genetic diversity hinders to development of an effective universal vaccine (Ni et al. 2005). Continuous emergence and re-emergence of this disease indicate its pandemicity (Ranjan and Prakash 2018). However, changes in human behavior, unplanned urbanization, and deforestation lead to the displacement of vectors as well rodents from one place to another (Yang et al. 2014; Park et al. 2015); that may introduce the pathogen in a new geographical area and spread the disease. The available vaccine of scrub typhus vaccine utilized the 56 KDa immune dominant protein, which provides homologous protection, but is unable to produce heterologous immunity (Chattopadhyay and Richards 2007). Our study might be helpful to develop an effective vaccine or antiviral drugs for disease eradication. During genetic recombination, the nonessential genes may be eliminated, or host genes may be inserted to generate new strains in the population. Some recent transcriptomic analysis revealed that the bacterial genotype plays a major role in the differential expression of immune regulatory genes (Mika-Gospodorz et al. 2020; Salje 2021). Therefore, one can assume that the introduction new genotype mimics the host factor and regulate the virulence of the respective pathogen. Due to the absence of enough genomic resources as well as complete genome sequence from India, it is impossible to decipher more about this pathogen biology. Therefore, our next objective would be revealing the complete genome information of the respective strain from India followed by the development of an appropriate vaccine for preventive interventions of this disease.
Conclusion
The present investigation suggests the surveillance followed by a molecular approach to decipher genetic heterogeneity exhibited within Orientia strains found in the eastern Indian population. A significant level of genetic variability was observed during this study. This information has a way to understand more about antigen diversity that leads to developing an effective vaccine candidate for this pathogen.
Acknowledgements
The authors are very much thankful to Medical Research Laboratory of Siksha “O” Anusandhan (deemed to be) University for providing laboratory facility.
Author contributions
SKS designed the Research, editing, and writing throughout the manuscript. BPS, SP, and RS analyzed the results of the research study, and wrote and edited the manuscript. All authors corrected the manuscript for the final draft.
Funding
This work was funded by Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) with Grant No. 5/3/8/51/ITR-F/2020.
Availability of data and materials
The partial nucleotide sequences of the 56-kDa gene of the present study can be obtained from the GenBank repository (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank) with the accession number MK650202-MK650229, respectively.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publication
Not applicable.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- Acestor N, Cooksey R, Newton PN, Menard D, Guerin PJ, Nakagawa J, Christophel E, Gonzalez IJ, Bell D. Mapping the etiology of non-malarial febrile illness in Southeast Asia through a systematic review—terra incognita impairing treatment policies. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(9):e44269. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai S, Tabara K, Yamamoto N, Fujita H, Itagaki A, Kon M, Satoh H, Araki K, Tanaka-Taya K, Takada N, Yoshikawa Y. Molecular phylogenetic analysis of Orientia tsutsugamushi based on the groES and groEL genes. Vector-Borne and Zoonotic Dis. 2013;13(11):825–829. doi: 10.1089/vbz.2012.1155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batty EM, Chaemchuen S, Blacksell S, Richards AL, Paris D, Bowden R, Chan C, Lachumanan R, Day N, Donnelly P, Chen S. Long-read whole genome sequencing and comparative analysis of six strains of the human pathogen Orientia tsutsugamushi. PLoS Neg Trop Dis. 2018;12(6):e0006566. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blacksell SD, Luksameetanasan R, Kalambaheti T, Aukkanit N, Paris DH, McGready R, Nosten F, Peacock SJ, Day NP. Genetic typing of the 56-kDa type-specific antigen gene of contemporary Orientia tsutsugamushi isolates causing human scrub typhus at two sites in north-eastern and western Thailand. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2008;52(3):335–342. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.2007.00375.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S, Richards AL. Scrub typhus vaccines: past history and recent developments. Hum Vaccin. 2007;3(3):73–80. doi: 10.4161/hv.3.3.4009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho BA, Cho NH, Seong SY, Choi MS, Kim IS. Intracellular invasion by Orientia tsutsugamushi is mediated by integrin signaling and actin cytoskeleton rearrangements. Infect Immun. 2010;78(5):1915–1923. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01316-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu H, Lee JH, Han SH, Kim SY, Cho NH, Kim IS, Choi MS. Exploitation of the endocytic pathway by Orientia tsutsugamushi in nonprofessional phagocytes. Infect Immun. 2006;74(7):4246–4253. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01620-05. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duong V, Mai TT, Blasdell K, Morvan C, Lay S, Anukool W, Wongprompitak P, Suputtamongkol Y, Laurent D, Richner B, Ra C. Molecular epidemiology of Orientia tsutsugamushi in Cambodia and Central Vietnam reveals a broad region-wide genetic diversity. Infect Genet Evol. 2013;15:35–42. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2011.01.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournier PE, Siritantikorn S, Rolain JM, Suputtamongkol Y, Hoontrakul S, Charoenwat S, Losuwanaluk K, Parola P, Raoult D. Detection of new genotypes of Orientia tsutsugamushi infecting humans in Thailand. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2008;14(2):168–173. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2007.01889.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuya YU, Yoshida YO, Katayama TA, Yamamoto SE, Kawamura A., Jr Serotype-specific amplification of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi DNA by nested polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1993;31(6):1637–1640. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.6.1637-1640.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi N. Etiology of tsutsugamushi disease. J Parasitol. 1920;7(2):53–68. doi: 10.2307/3270957. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Hu J, Tan Z, Ren D, Zhang X, He Y, Bao C, Liu D, Yi Q, Qian W, Yin J, Xu Z. Clinical characteristics and risk factors of an outbreak with scrub typhus in previously unrecognized areas, Jiangsu province, China 2013. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(5):e0125999. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James SL, Blacksell SD, Nawtaisong P, Tanganuchitcharnchai A, Smith DJ, et al. Antigenic relationships among human pathogenic Orientia tsutsugamushi isolates from Thailand. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016 doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeung YS, Kim CM, Yun NR, Kim SW, Han MA, Kim DM. Effect of latitude and seasonal variation on scrub typhus, South Korea, 2001–2013. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2016;94(1):22. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.15-0474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang J, Paris DH, Blacksell SD, Aukkanit N, Newton PN, Phetsouvanh R, Izzard L, Stenos J, Graves SR, Day NP, Richards AL. Diversity of the 47-kD HtrA nucleic acid and translated amino acid sequences from 17 recent human isolates of Orientia. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2013;13(6):367–375. doi: 10.1089/vbz.2012.1112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly DJ, Richards AL, Temenak J, Strickman D, Dasch GA. The past and present threat of rickettsial diseases to military medicine and international public health. Clin Inf Dis. 2002;34:S145–S169. doi: 10.1086/339908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan SA, Bora T, Laskar B, Khan AM, Dutta P. Scrub typhus leading to acute encephalitis syndrome, Assam India. Emerg Infect Dis. 2017;23(1):148. doi: 10.3201/eid2301.161038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kundavaram AP, Jonathan AJ, Nathaniel SD, Varghese GM. Eschar in scrub typhus: a valuable clue to the diagnosis. J Postgrad Med. 2013;59(3):177. doi: 10.4103/0022-3859.118033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo CC, Huang JL, Shu PY, Lee PL, Kelt DA, Wang HC. Cascading effect of economic globalization on human risks of scrub typhus and tick-borne rickettsial diseases. Ecol Appl. 2012;22(6):1803–1816. doi: 10.1890/12-0031.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee HI, Shim SK, Song BG, Choi EN, Hwang KJ, Park MY, Park C, Shin EH. Detection of Orientia tsutsugamushi, the causative agent of scrub typhus, in a novel mite species, Eushoengastia koreaensis in Korea. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2011;11(3):209–214. doi: 10.1089/vbz.2009.0180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Librado P, Rozas J. DnaSP v5: software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics. 2009;25(11):1451–1452. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long J, Wei Y, Tao X, He P, Xu J, Wu X, Yang Z. Representative genotyping, recombination and evolutionary dynamics analysis of TSA56 gene segment of Orientia tsutsugamushi. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020;10:383. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu HY, Tsai KH, Yu SK, Yang CH, Su CL, Hu HC, Wang HC, Huang JH, Shu PY. Phylogenetic analysis of 56-kDa type-specific antigen gene of Orientia tsutsugamushi isolates in Taiwan. The Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2010;83(3):658. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.2010.09-0608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahajan SK, Rolain JM, Kashyap R, Bakshi D, Sharma V, Prasher BS, Pal LS, Raoult D. Scrub typhus in Himalayas. Emerg Infect Dis. 2006;12(10):1590. doi: 10.3201/eid1210.051697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mika-Gospodorz B, Giengkam S, Westermann AJ, Wongsantichon J, Kion-Crosby W, Chuenklin S, Salje J. Dual RNA-seq of Orientia tsutsugamushi informs on host-pathogen interactions for this neglected intracellular human pathogen. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):1–14. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-17094-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ni YS, Chan TC, Chao CC, Richards AL, Dasch GA, et al. Protection against scrub typhus by a plasmid vaccine encoding the 56-KD outer membrane protein antigen gene. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2005;73:936–941. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.2005.73.936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata N. Aetiologie der Tsutsugamushi-krankheit: Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. Zbl Bakt (1 Abt) Org. 1931;122:249–253. [Google Scholar]
- Paris DH, Stephan F, Bulder I, Wouters D, Van der Poll T, Newton PN, Day NP, Zeerleder S. Increased nucleosomes and neutrophil activation link to disease progression in patients with scrub typhus but not murine typhus in Laos. PLoS Neg Trop Dis. 2015;9(8):e0003990. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park SW, Ha NY, Ryu B, Bang JH, Song H, et al. Urbanization of scrub typhus disease in South Korea. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015;9:e0003814. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranjan J, Prakash JAJ. Scrub typhus re-emergence in India: contributing factors and way forward. Med Hypotheses. 2018;115:61–64. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2018.03.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitou N, Nei M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol. 1987;4(4):406–425. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salje J. Cells within cells: Rickettsiales and the obligate intracellular bacterial lifestyle. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2021;19(6):375–390. doi: 10.1038/s41579-020-00507-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smadel JE, Woodward TE, Ley HL, Lewthwaite R. Chloramphenicol (chloromycetin) in the treatment of tsutsugamushi disease (scrub typhus) J Clin Investig. 1949;28(5):1196–1215. doi: 10.1172/jci102154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura A, Ohashi N, Urakami H, Miyamura S. Classification of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi in a new genus, Orientia gen. nov., as Orientia tsutsugamushi comb nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1995;45(3):589–591. doi: 10.1099/00207713-45-3-589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varghese GM, Janardhanan J, Mahajan SK, Tariang D, Trowbridge P, Prakash JA, Abraham OC. Molecular epidemiology and genetic diversity of Orientia tsutsugamushi from patients with scrub typhus in 3 regions of India. Emerg Infect Dis. 2015;21(1):64. doi: 10.3201/eid2101.140580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardrop NA, Kuo CC, Wang HC, Clements AC, Lee PF, Atkinson PM (2013) Bayesian spatial modeling and the significance of agricultural land use to scrub typhus infection in Taiwan. Geospatial Health 8(1):229–239. www.geospatialhealth.unina.it/articles/v8i1 [DOI] [PubMed]
- Xu G, Walker DH, Jupiter D, Melby PC, Arcari CM. A review of the global epidemiology of scrub typhus. PLoS Neg Trop Dis. 2017;11(11):e0006062. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang HH, Huang IT, Lin CH, Chen TY, Chen LK. New genotypes of Orientia tsutsugamushi isolated from humans in Eastern Taiwan. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e46997. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang LP, Liu J, Wang XJ, Ma W, Jia CX, et al. Effects of meteorological factors on scrub typhus in a temperate region of China. Epidemiol Infect. 2014;142:2217–2226. doi: 10.1017/S0950268813003208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The partial nucleotide sequences of the 56-kDa gene of the present study can be obtained from the GenBank repository (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank) with the accession number MK650202-MK650229, respectively.
Not applicable.