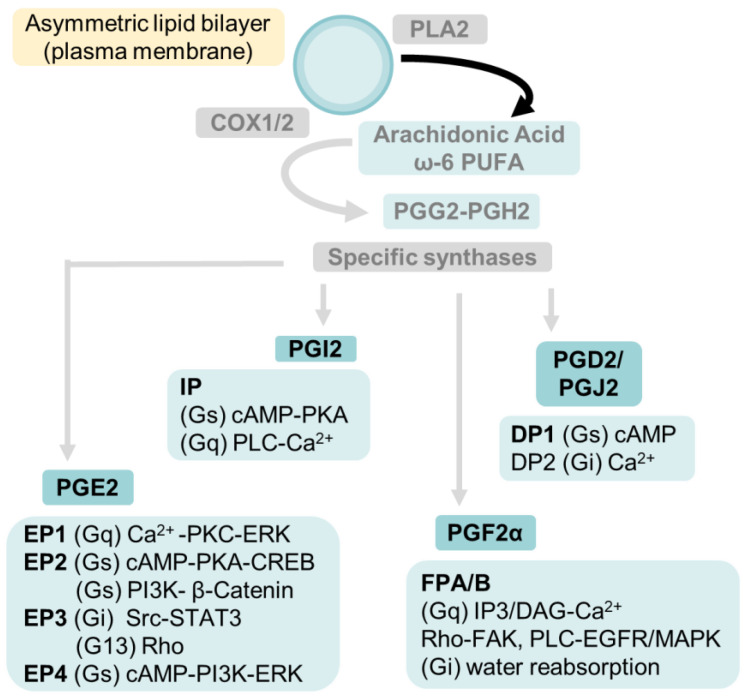
Figure 2.
Key steps in the synthesis of prostaglandins from membrane phospholipid derived arachidonic acid. Phospholipase A2 activity releases free ω-6 PUFA arachidonic acid (ARA) from phospholipids in the asymmetric plasma membrane. COX1/2 converts free ARA into PGG2/PGH2 utilized by specific synthases to form prostanoids—prostaglandins E2, I2, J2, D2, F2α and thromboxane A2 (shown separately). Each of these bioactive metabolites binds to specific G-protein-coupled receptors for signaling. Receptors, specific G proteins (in parentheses) and activated the signaling pathways in a separate box under each prostaglandin. PGI2, an active metabolite, exists transiently and is metabolized to 6-keto-PGF1α (not shown here).