Abstract
Background
Curative resection for colorectal cancer and their synchronous liver metastases are increasingly performed. However, it is still unclear whether the operative order affects the surgical outcome in laparoscopic simultaneous resection of primary and liver metastatic lesions.
Patients and Methods
A total of 27 patients underwent laparoscopic simultaneous resection of primary colorectal cancer and liver metastases at Kumamoto University Hospital. They were divided into two groups based on the order of resection: Colon-first (n=11) and liver-first (n=16) groups. The surgical outcomes between the two groups were retrospectively compared.
Results
There was no significant difference in the perioperative surgical outcomes between the two groups except for operative blood loss, which was significantly less in the liver-first group [164 (range=5-820) versus 560 (range=95-2,016) ml, respectively] (p=0.0299).
Conclusion
In the simultaneous resection of primary and liver metastatic lesions, the operative order does not affect the short-term surgical outcomes except for operative blood loss.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer, CRC, colorectal liver metastasis, CRLM, synchronous liver metastasis, SLM, colon-first approach, liver-first approach
Colorectal cancer is one of the most common types of cancer. Colorectal liver metastases (CRLMs) are present in 60% of patients with colorectal cancer and 15-20% of patients present CRLM at the time of diagnosis (1,2). The opportunity to treat synchronous liver metastases (SLMs) is increasing because of the development of improved diagnostic imaging, surgical techniques, and chemotherapy. The presence of SLM is an independent prognostic factor for recurrence and death (3-5). If a SLM is initially unresectable, effective chemo- and targeted therapy may facilitate conversion hepatectomy, resulting in an excellent prognosis (6,7).
Both simultaneous resection and staged resection of primary and liver metastases in patients with SLM are associated with similar perioperative and oncological outcomes (8). When SLMs are initially non-resectable, chemotherapy is administered first. If they are initially resectable, surgical resection of both primary and metastatic lesions is most effective. Simultaneous resection of primary cancer and liver metastases is increasing because of the advantage of a single operation. Simultaneous resection was considered to increase postoperative complications but recently it was reported that its associated postoperative complications rates were significantly lower (9) or did not differ (10), and the length of hospital stay was also significantly shorter (11).
In the simultaneous resection of primary and metastatic lesions, it is still unclear whether the operative order (colon-first or liver-first approach) affects the surgical outcome. Simultaneous laparoscopic resection of primary tumor and liver metastases is said to be technically feasible and safe (12). Laparoscopic surgery was reported to be associated with significantly fewer postoperative complications and was cost-effective compared with open surgery (13,14). Here, we investigated the clinical impact of the operative order (colon-first or liver-first) on short-term surgical outcomes, especially in patients with a laparoscopic approach for both primary and liver metastatic lesions.
Patients and Methods
Patients and study design. This was a retrospective study of prospectively collected data at Kumamoto University Hospital. Between January 2008 and January 2020, a total of 27 patients underwent simultaneous resection of SLM. The patients were divided into two groups based on the operative order: Colon-first and liver-first groups. Clinicopathological features, operative results, and postoperative complications were compared between the two groups. The use of clinical data was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Kumamoto University Hospital (approval number: 1047) and was carried out in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Clinicopathological features and operative methods. The following data were collected from medical charts: Age, sex, body mass index, American Society of Anesthetists-physical status, primary tumor site (right/left/rectal), primary tumor diameter, number of metastatic liver lesions, number of involved hepatic segments and whether unilobar or bilobar, largest diameter of liver metastases, presence or absence of preoperative chemotherapy, and chemotherapy regimen. The primary tumor site was categorized as the right colon (from the cecum to the transverse colon), the left colon (from the splenic flexure to the sigmoid colon), or rectal colon. The operative order was at the surgeon’s discretion.
Statistical analysis. This study’s endpoint was the short-term perioperative results. Clavien–Dindo classification was used to evaluate postoperative complications. All of the statistical analyses were performed with JMP statistical software version 10 (SAS Institute, Inc, Cary, NC, USA). Categorical variables were analyzed using a chi-square test (case number ≥5) or Fisher’s exact test (case number <5), and continuous variables were analyzed by Student’s t-test or Mann–Whitney test. A p-value of less than 0.05 was considered to be significant. Operating room stay time was defined as the time between entry to and exit from the operatiing room.
Results
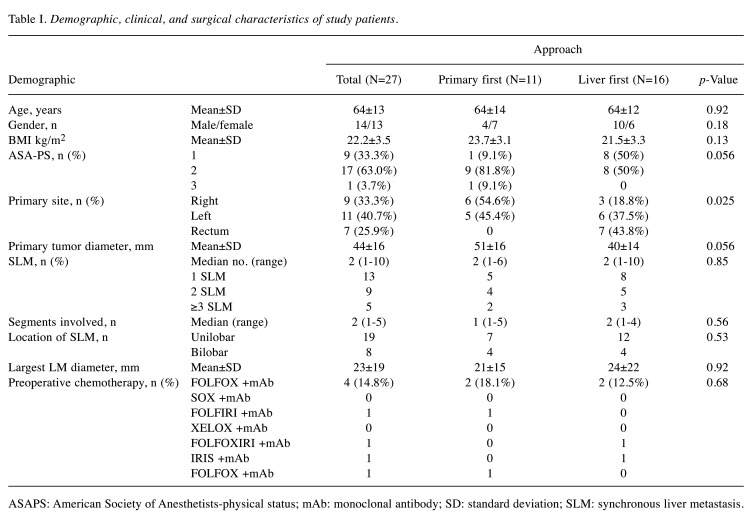
The baseline characteristics are summarized in Table I. In this cohort, a colon-first procedure was performed for 11 patients, and liver-first for 16 patients. There were no differences in demographics, but American Society of Anesthetists physical status in the colon-first group was marginally higher than that of the liver-first group (p=0.056). The site of primary colorectal cancer was right/left/rectum in 9/11/7, respectively, and in the liver-first group, there was a significantly higher frequency of rectal cancer than that in the colon-first group (p=0.025). The mean primary tumor diameter was 44±16 mm. Thirteen patients had one SLM, six patients had two SLMs, and eight patients had three or more. The median number of involved hepatic segments was two. SLM was unilobar in 19 patients (70.4%), and the other patients was bilobar (n=8, 29.6%). The mean largest diameter of liver metastases was 23±19 mm. Four patients (14.8%) were treated with preoperative chemotherapy, and the regimens are shown in Table I.
Table I. Demographic, clinical, and surgical characteristics of study patients.
ASAPS: American Society of Anesthetists-physical status; mAb: monoclonal antibody; SD: standard deviation; SLM: synchronous liver metastasis.
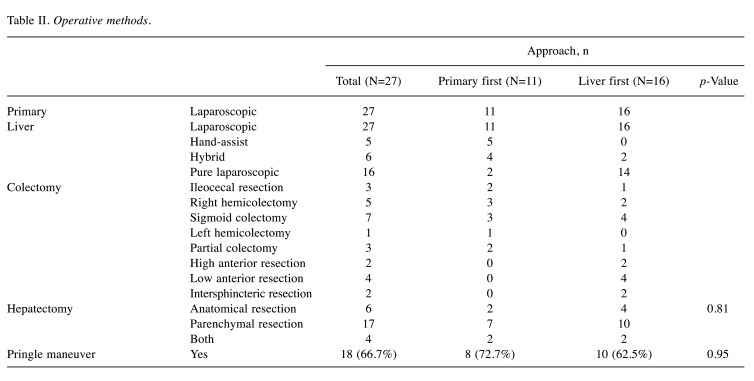
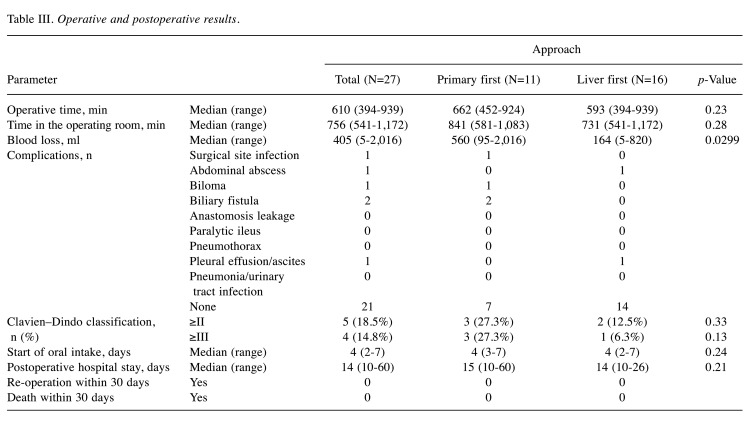
The operative methods for primary lesions is shown in Table II. In the liver-first group, pure laparoscopic surgery was performed more often. During hepatectomy, the Pringle maneuver was performed in 18 patients (66.7%). The median amount of blood loss in the liver-first group was smaller than that in the colon-first group [164 (range=5-820) versus 560 (range=95-2,016) ml, p=0.0299] (Table III). On the other hand, there was no significant difference in median operative time, or the operating room stay time between the two groups. Postoperative complications occurred in six patients; however, there was no significant difference in complications of Clavien–Dindo grade of II and III or higher (Table III). There was also no significant difference time to starting a meal after surgery and postoperative hospital stay. There was no patient with re-operation or death within 30 days after surgery.
Table II. Operative methods.
Table III. Operative and postoperative results.
Discussion
In this study, we elucidated the clinical impact of operative order on short-term surgical outcomes in laparoscopic simultaneous resection for SLM. Operative order did not affect the perioperative outcomes. Interestingly, the liver-first approach provided lower blood loss compared with the colon-first approach in laparoscopic simultaneous resection for SLM. There was no significant difference in the anastomotic leakage rates before and after liver resection in the present study.
The reason for less blood loss in the liver-first group may be due to the restricted volume control during hepatectomy. Low central venous pressure allows easy control of the hepatic veins before and during parenchymal transection (15). These restricted volumes in the liver-first group may have contributed to the reduced blood loss compared with the colon-first group. In addition, the technique and style of laparoscopic liver resection have advanced in the perst 12 years. Therefore, this might have affected the outcomes in the the liver-first group in which many pure laparoscopic surgeries were performed.
Although there was no significant difference, the operative time and the operative room stay time for the liver-first group were shorter than in the colon-first group in this study. Regarding these times, particularly in laparoscopic surgery, the positional difference of the patient’s body between primary resection and resection of metastatic lesions during surgery may have been relevant. At our hospital, laparoscopic hepatectomy requires various body positions, such as the semi-lateral decubitus position and right upper limb elevation, and use of the intercostal port for individual lesion sites, especially for the right lobe, posterior segment, and subphrenic lesions. The use of an intercostal port and proper management allows for a feasible approach and safe resection during laparoscopic hepatectomy (16). It takes time to adopt such positions without a familiar team, while laparoscopic colectomy requires a normal position such as a supine or lithotomy position. Therefore, performing the hepatectomy first shortens the time required for changing position, which leads to a reduction in the operative time and operating room stay. However, operative times for primary resection and metastatic resection were not measured in this study.
The Pringle maneuver is often performed to control liver inflow during hepatectomy (17,18), and for reducing blood loss during hepatectomy. However, during simultaneous resection, there are concerns that a lower volume may cause circulatory disorders in organs, and performing the Pringle maneuver may cause intestinal congestion and subsequent anastomotic leakage of the colorectum; however, in the present study, there was no difference in postoperative complication rates between the colon-first and liver-first groups.
This study has some limitations. Firstly, the operative time and blood loss were not evaluated during colectomy and hepatectomy separately. Secondly, the long-term outcome was unclear in the present study. With regard to simultaneous laparoscopic resection for CRLM, it has been reported that the long-term outcomes were similar to those of open surgery (19), whilst the perioperative outcomes were superior (20,21). Furthermore, it was reported that neither disease-free nor overall survival differed significantly between simultaneous and staged resection for CRLM (22). Finally, this study was a retrospective study. As there were significant differences in the number of liver metastases, the number of affected hepatic segments, and surgical procedures for resection, the number of cases were insufficient to compare two groups with similar backgrounds. It is also possible that the target period was long and the transition to laparoscopic hepatectomy affected the results. Therefore, a large cohort study or a randomized controlled trial is needed to clarify these issues.
Conclusion
In the simultaneous resection of primary and liver metastatic lesions, the operative order does not affect the short-term surgical outcomes except for marginally increased operative blood loss in the colon-first approach.
Conflicts of Interest
The Authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Authors’ Contributions
TT described and designed the article. HH edited the article. HB supervised the editing of the article. The remaining co-authors collected the data and discussed the content of the article. All Authors read and approved the final article.
Acknowledgements
The Authors thank Dr Daniel Mrozek, president of the Medical English Service for editing a draft of this article.
References
- 1.Kemeny N. The management of resectable and unresectable liver metastases from colorectal cancer. Curr Opin Oncol. 2010;22(4):364–373. doi: 10.1097/CCO.0b013e32833a6c8a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Araujo RLC, Figueiredo MN, Sanctis MA, Romagnolo LGC, Linhares MM, Melani AGF, Marescaux J. Decision making process in simultaneous laparoscopic resection of colorectal cancer and liver metastases. Review of literature. Acta Cir Bras. 2020;35(3):e202000308. doi: 10.1590/s0102-865020200030000008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Creasy JM, Sadot E, Koerkamp BG, Chou JF, Gonen M, Kemeny NE, Saltz LB, Balachandran VP, Peter Kingham T, DeMatteo RP, Allen PJ, Jarnagin WR, D’Angelica MI. The impact of primary tumor location on long-term survival in patients undergoing hepatic resection for metastatic colon cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2018;25(2):431–438. doi: 10.1245/s10434-017-6264-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Tomlinson JS, Jarnagin WR, DeMatteo RP, Fong Y, Kornprat P, Gonen M, Kemeny N, Brennan MF, Blumgart LH, D’Angelica M. Actual 10-year survival after resection of colorectal liver metastases defines cure. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25(29):4575–4580. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.11.0833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Fong Y, Fortner J, Sun RL, Brennan MF, Blumgart LH. Clinical score for predicting recurrence after hepatic resection for metastatic colorectal cancer: analysis of 1001 consecutive cases. Ann Surg. 1999;230(3):309–18. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199909000-00004. discussion 318-21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Beppu T, Miyamoto Y, Sakamoto Y, Imai K, Nitta H, Hayashi H, Chikamoto A, Watanabe M, Ishiko T, Baba H. Chemotherapy and targeted therapy for patients with initially unresectable colorectal liver metastases, focusing on conversion hepatectomy and long-term survival. Ann Surg Oncol. 2014;21 Suppl 3:S405–S413. doi: 10.1245/s10434-014-3577-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hayashi H, Beppu T, Sakamoto Y, Miyamoto Y, Yokoyama N, Higashi T, Nitta H, Hashimoto D, Chikamoto A, Baba H. Prognostic value of Ki-67 expression in conversion therapy for colorectal liver-limited metastases. Am J Cancer Res. 2015;5(3):1225–1233. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Brouquet A, Mortenson MM, Vauthey JN, Rodriguez-Bigas MA, Overman MJ, Chang GJ, Kopetz S, Garrett C, Curley SA, Abdalla EK. Surgical strategies for synchronous colorectal liver metastases in 156 consecutive patients: classic, combined or reverse strategy. J Am Coll Surg. 2010;210(6):934–941. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2010.02.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chen J, Li Q, Wang C, Zhu H, Shi Y, Zhao G. Simultaneous vs. staged resection for synchronous colorectal liver metastases: a metaanalysis. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2011;26(2):191–199. doi: 10.1007/s00384-010-1018-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Boudjema K, Locher C, Sabbagh C, Ortega-Deballon P, Heyd B, Bachellier P, Métairie S, Paye F, Bourlier P, Adam R, Merdrignac A, Tual C, Le Pabic E, Sulpice L, Meunier B, Regimbeau JM, Bellissant E, METASYNC Study group Simultaneous versus delayed resection for initially resectable synchronous colorectal cancer liver metastases: a prospective, open-label, randomized, controlled trial. Ann Surg. 2021;273(1):49–56. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000003848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Silberhumer GR, Paty PB, Temple LK, Araujo RL, Denton B, Gonen M, Nash GM, Allen PJ, DeMatteo RP, Guillem J, Weiser MR, D’Angelica MI, Jarnagin WR, Wong DW, Fong Y. Simultaneous resection for rectal cancer with synchronous liver metastasis is a safe procedure. Am J Surg. 2015;209(6):935–942. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2014.09.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Miyamoto Y, Beppu T, Sakamoto Y, Imai K, Hayashi H, Nitta H, Ishiko T, Watanabe M, Baba H. Simultaneous laparoscopic resection of primary tumor and liver metastases for colorectal cancer: surgical technique and short-term outcome. Hepatogastroenterology. 2015;62(140):846–852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Fretland ÅA, Dagenborg VJ, Bjørnelv GMW, Kazaryan AM, Kristiansen R, Fagerland MW, Hausken J, Tønnessen TI, Abildgaard A, Barkhatov L, Yaqub S, Røsok BI, Bjørnbeth BA, Andersen MH, Flatmark K, Aas E, Edwin B. Laparoscopic versus open resection for colorectal liver metastases: The OSLO-COMET randomized controlled trial. Ann Surg. 2018;267(2):199–207. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000002353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hayashi H, Ozaki N, Ogawa K, Ikuta Y, Tanaka H, Ogata K, Doi K, Takamori H. Assessing the economic advantage of laparoscopic vs. open approaches for colorectal cancer by a propensity score matching analysis. Surg Today. 2018;48(4):439–448. doi: 10.1007/s00595-017-1606-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Melendez JA, Arslan V, Fischer ME, Wuest D, Jarnagin WR, Fong Y, Blumgart LH. Perioperative outcomes of major hepatic resections under low central venous pressure anesthesia: blood loss, blood transfusion, and the risk of postoperative renal dysfunction. J Am Coll Surg. 1998;187(6):620–625. doi: 10.1016/s1072-7515(98)00240-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hayashi H, Yamashita YI, Okabe H, Imai K, Higashi T, Yamamura K, Chikamoto A, Beppu T, Takamori H, Baba H. Varied application of intercostal trans-diaphragmatic ports for laparoscopic hepatectomy. PLoS One. 2020;15(6):e0234919. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0234919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Pringle JH. V. Notes on the arrest of hepatic hemorrhage due to trauma. Ann Surg. 1908;48(4):541–549. doi: 10.1097/00000658-190810000-00005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Weiss MJ, Ito H, Araujo RL, Zabor EC, Gonen M, D’Angelica MI, Allen PJ, DeMatteo RP, Fong Y, Blumgart LH, Jarnagin WR. Hepatic pedicle clamping during hepatic resection for colorectal liver metastases: no impact on survival or hepatic recurrence. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013;20(1):285–294. doi: 10.1245/s10434-012-2583-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Takasu C, Shimada M, Sato H, Miyatani T, Imura S, Morine Y, Ikemoto T, Kanamoto M, Kurita N, Eto S, Utsunomiya T. Benefits of simultaneous laparoscopic resection of primary colorectal cancer and liver metastases. Asian J Endosc Surg. 2014;7(1):31–37. doi: 10.1111/ases.12066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hu MG, Ou-yang CG, Zhao GD, Xu DB, Liu R. Outcomes of open versus laparoscopic procedure for synchronous radical resection of liver metastatic colorectal cancer: a comparative study. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2012;22(4):364–369. doi: 10.1097/SLE.0b013e31825af6b2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Tranchart H, Fuks D, Vigano L, Ferretti S, Paye F, Wakabayashi G, Ferrero A, Gayet B, Dagher I. Laparoscopic simultaneous resection of colorectal primary tumor and liver metastases: a propensity score matching analysis. Surg Endosc. 2016;30(5):1853–1862. doi: 10.1007/s00464-015-4467-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Silberhumer GR, Paty PB, Denton B, Guillem J, Gonen M, Araujo RLC, Nash GM, Temple LK, Allen PJ, DeMatteo RP, Weiser MR, Wong WD, Jarnagin WR, D’Angelica MI, Fong Y. Long-term oncologic outcomes for simultaneous resection of synchronous metastatic liver and primary colorectal cancer. Surgery. 2016;160(1):67–73. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2016.02.029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]