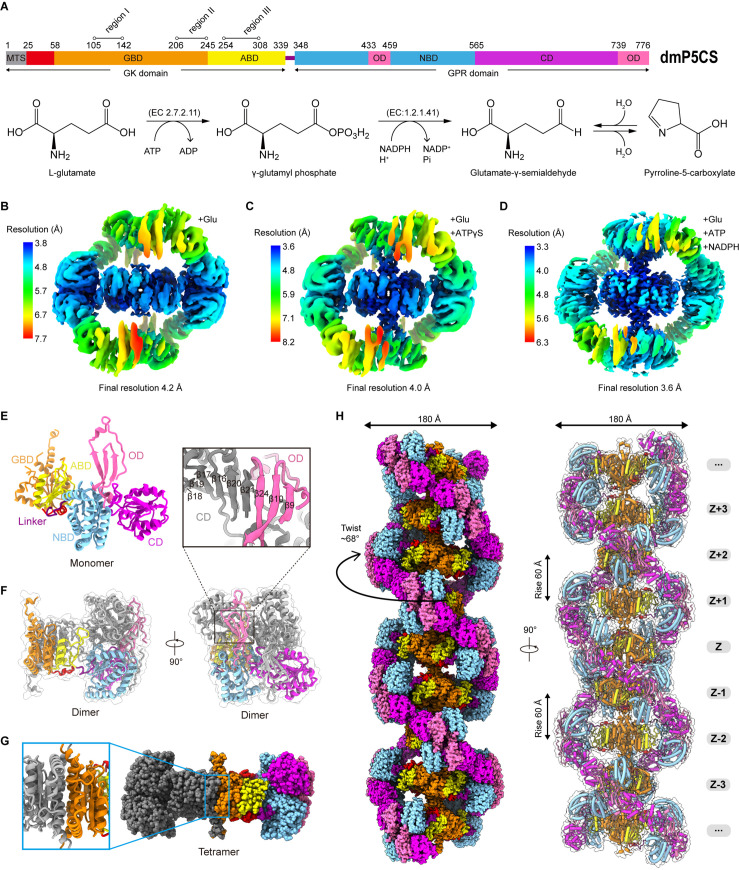
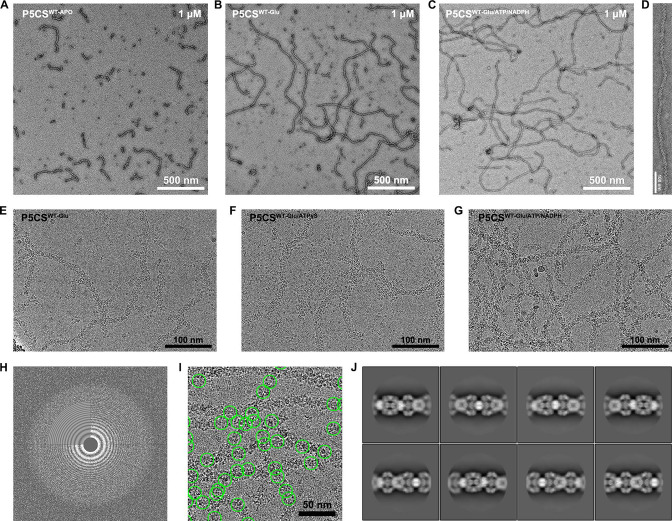
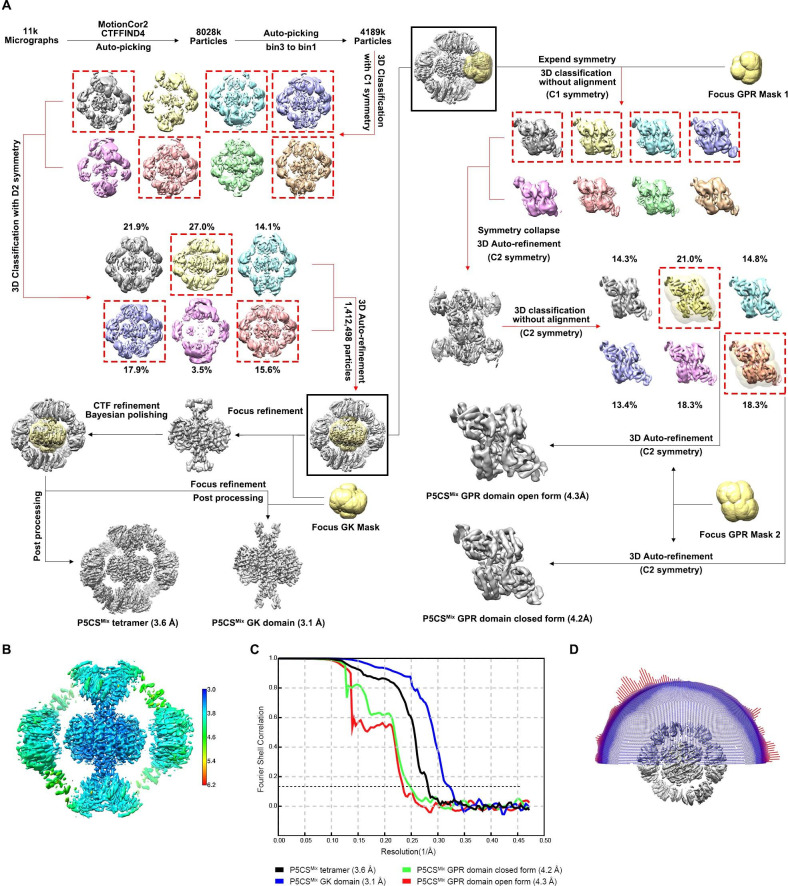
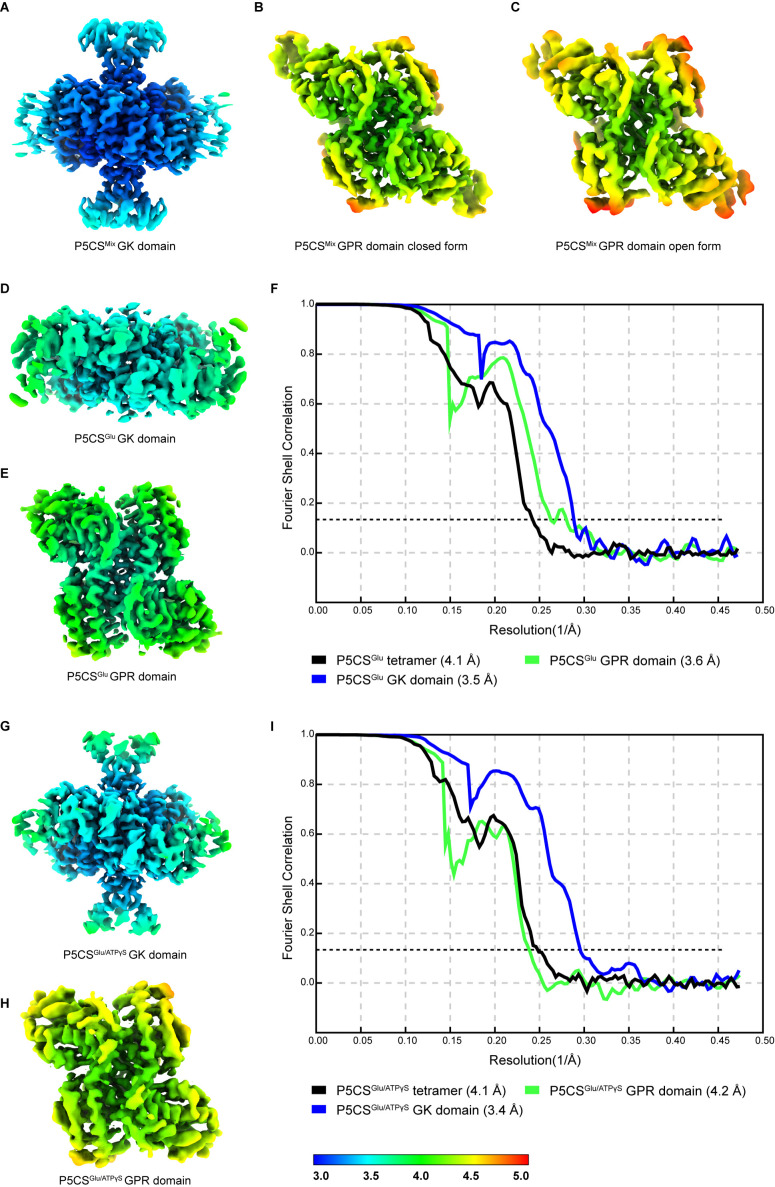
Figure 1. Bifunctional enzyme properties and cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) analysis of P5CS filaments.
(A) Domain organization of Drosophila melanogaster P5CS, which consists of two domains, N-terminal glutamate kinase (GK) domain and C-terminal γ-glutamyl phosphate reductase (GPR) domain. Putative mitochondrial targeting sequence (MTS) is labeled in gray; the glutamate-binding domain (GBD) and the ATP-binding domain (ABD) of the GK domain are respectively shown in orange and yellow; the NADPH-binding domain (NBD), the catalytic domain (CD), and the oligomerization domain (OD) of the GPR domain are shown in cyan, purple, and pink, respectively. Bifunctional P5CS enzyme catalytic reaction and residue numbers for domain boundaries are shown. (B–D) Single-particle analysis for 3D reconstruction of P5CS filaments, three cryo-EM maps of P5CSGlu filament, P5CSGlu/ATPγS filament, and P5CSMix filament are colored by local resolution estimations. (E) The structures of the P5CS monomer and color codes for P5CS models are indicated. (F) The P5CS dimer. Two monomers (gray or color coded by domain) interact via GPR domain hairpins contact. (G) The P5CS tetramer (sphere representation) is formed via GK domain interaction (cartoon representation) between two P5CS dimers (gray or color coded by domain). (H) The sphere and cartoon representation of P5CS filaments. P5CS filaments are modeled by the cryo-EM map. The rotated view is shown in the right panel; its rise, twist, and width are indicated.