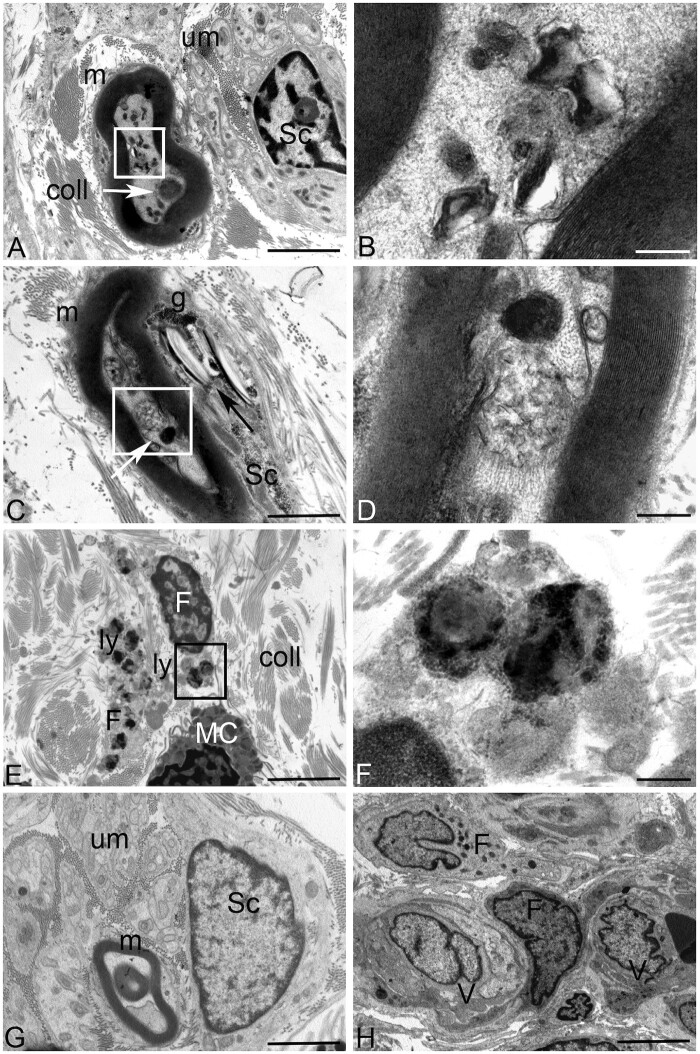
Figure 5.
Ultrastructural analysis of the skin biopsy from DHDDS Patient 1 (A–D) compared to control (G and H). (A) No ultrastructural alterations are visible in the unmyelinated nerve fibres in the stroma (um). Deposits of osmyophilic materials are observed in myelinated (m) nerve fibres (white arrow) along with numerous vacuoles containing lamellated membrane structures resembling phospholipids (white square). Stromal collagens (coll) structure was conventional. Sc = Schwann cell. (B) Higher magnification of the area included in the white square of A: Single membrane-surrounded vacuoles containing lamellated membrane structures resembling phospholipids are visible in the axon of myelinated fibres. (C) Deposits of osmyophilic materials are observed in myelinated (m) nerve fibres (white arrow) along with vacuoles containing membranous structures of probable lipid origin. Cholesterol/lipid-like deposits (black arrow) associated with glycogen (g) are visible in the cytoplasm of Schwann cells (Sc). (D) Higher magnification of the area included in the white square of B: deposits of osmyophilic materials and a single-membrane-surrounded vacuole containing membranous structures of probable lipid origin are visible. (E) Stromal fibroblasts (F) containing large secondary lysosomes (ly) are visible in the stroma. coll = collagen; MC = mast cell. (F) Higher magnification of the area included in the black square of E. Large secondary lysosomes filled with different electron-density substances are visible in the cytoplasm of stromal fibroblasts. (G) No ultrastructural alterations are visible in the unmyelinated (um), myelinated (m) nerve fibres or Schwann cells (Sc) in a not pathological skin biopsy. (H) No ultrastructural alterations are visible in the stromal fibroblasts (F) or in vessels (V) in a not pathological skin biopsy. Scale bars = 2 µm (A, C, E, G and H) and 200 nm (B, D and F).