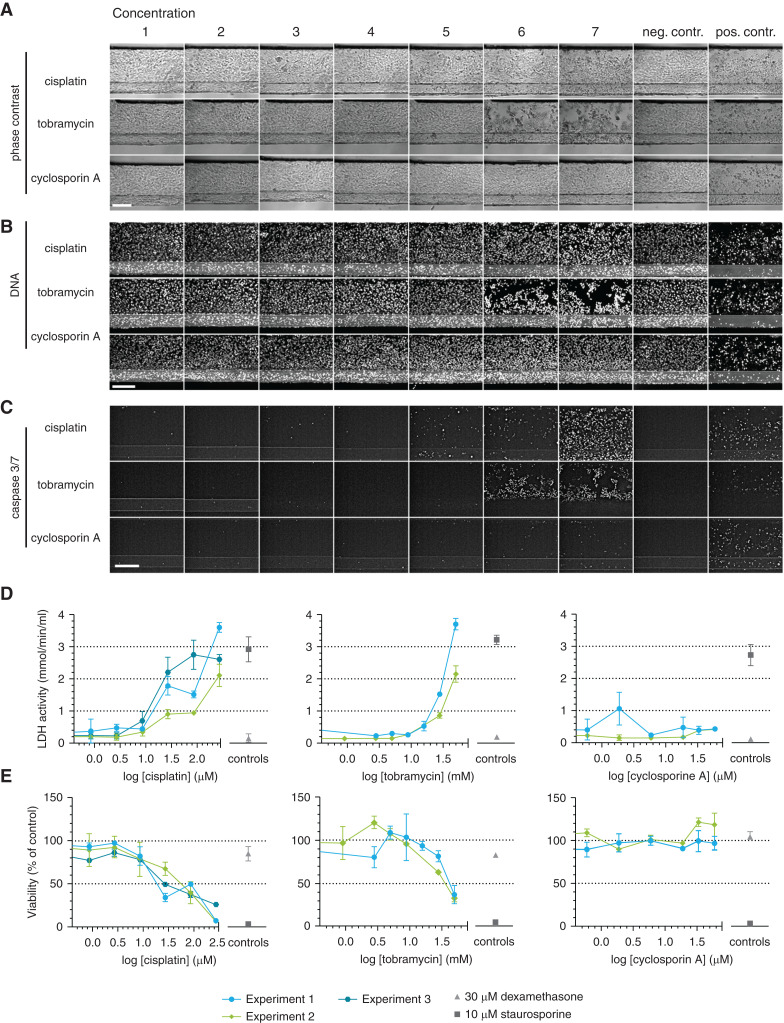
Figure 3.
A panel of assays shows susceptibility of the proximal tubule to AKI in response to nephrotoxic drugs. Cocultures were exposed to concentrations ranges of cisplatin, tobramycin, and cyclosporin A for 48 hours. (A–C) Phase-contrast imaging (A), DNA staining (B), and caspase-3/7 staining (C) showed cell damage after cisplatin and tobramycin exposure in a dose-dependent manner. Representative images. Scale bar, 200 µm. (D) Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release in the medium was measured and showed cell damage after cisplatin and tobramycin exposure in a dose-dependent manner. (E) Assessment of the viability relative to the corresponding vehicle control using a WST-8 assay showed a dose-dependent decrease in viability after cisplatin and tobramycin exposure. Dexamethasone (30 µM) was included as a negative control; staurosporine (10 µM) was included as a positive control. Error bars represent standard deviation. Experiments 1–3 are independent repeats of the experiment, n=2–4 chips per condition.