Abstract
Aims
The purpose of this study was to perform an assessment of circulating microRNAs (miRNAs) as promising biomarker for hepatitis C virus (HCV)-associated hepatocellular carcinoma (HCV-HCC) through a meta-analysis.
Methods
A comprehensive literatures search extended up to March 1, 2020 in PubMed, Cochrane library, Embase, Web of Science, Scopus and Ovid databases. The collected data were analyzed by random-effects model, the pooled sensitivity (SEN), specificity (SPE), positive and negative likelihood ratios (PLR and NLR), diagnostic odds ratio (DOR), and area under the curve (AUC) were used to explore the diagnostic performance of circulating miRNAs. Meta-regression and subgroup analysis were further carried out to explore the heterogeneity.
Results
A total of 16 articles including 3606 HCV-HCC patients and 3387 HCV patients without HCC were collected. The pooled estimates indicated miRNAs could distinguish HCC patients from chronic hepatitis C (CHC) and HCV-associated liver cirrhosis (HCV-LC), with a SEN of 0.83 (95% CI, 0.79–0.87), a SPE of 0.77 (95% CI, 0.71–0.82), a DOR of 17 (95% CI, 12–28), and an AUC of 0.87 (95% CI, 0.84–0.90). The combination of miRNAs and AFP showed a better diagnostic accuracy than each alone. Subgroup analysis demonstrated that diagnostic accuracy of miRNAs was better for plasma types, up-regulated miRNAs, and miRNA clusters. There was no evidence of publication bias in Deeks’ funnel plot.
Conclusions
Circulating miRNAs, especially for miRNA clusters, have a relatively high diagnostic value for HCV-HCC from CHC and HCV-LC.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s12879-022-07292-8.
Keywords: Hepatitis C virus, Hepatocellular carcinoma, microRNAs, Biomarkers
Background
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is one of the main risk factors for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) development. Approximately 399,000 people are estimated to die annually from HCV-associated liver cirrhosis (HCV-LC) and HCC [1]. The rate of progression from chronic hepatitis C (CHC) to HCC is variable and the cancerogenesis mechanism of HCV has yet completely known [2]. In addition, the only strategy to implement for HCV-HCC is still prevention despite advances in an era of all-oral direct-acting antivirals (DAAs) regimens [3]. However, detection of early HCC remains difficult due to technical challenge in non-invasive methods [4]. Therefore, new biomarkers with higher diagnostic accuracy are mandatory for early HCV-associated HCC (HCV-HCC).
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) could regulate gene expression and control cellular processes [5]. Numerous studies indicate that dysregulation of miRNAs expression lead to pathological processes of several types of cancer [6]. Recently, it has been increasingly recognized the meaningful properties of circulating miRNAs as the potential biomarkers for HCC [7]. Several HCV-HCC related miRNAs, such as miR-16, miR-122, miR-150, miR-182, miR-199a, miR-211, and miR-224, have been confirmed [8–11]. However, no consensus on diagnosis accuracy of circulating miRNAs for HCV-HCC has yet emerged. In the present study, a systematic review and meta-analysis was performed to evaluate the expression levels of circulating miRNAs of patients with HCV infections, in order to clarify the diagnostic accuracy of HCC from CHC and HCV-LC.
Methods
Search strategy and literatures selection
According to the guidelines of diagnostic meta-analysis, a systematic search of the literatures was performed by two investigators (WY and YCH) using the sources of Pubmed, Cochrane library, Embase, Web of Science, Scopus and Ovid from inception through the end of March 1, 2020. The retrieval terms included: "Liver Neoplasms" or "Hepatic Neoplasms" or “Liver Cancers” or "Carcinoma, Hepatocellular" or "Liver Cell Carcinoma" and "Hepatitis C" and "microRNAs" or "miRNA".
Literatures included according to the following information: (1) both HCC groups and control groups ware HCV-related; (2) the detection of the circulating miRNAs was related to HCV-HCC; (3) true positive (TP), true negative (TN), false positive (FP), and false negative (FN) of the miRNAs were reported or could be calculated. On the other hand, the exclusion criteria were shown as following: (1) meta-analysis, case reports, reviews or letters; (2) repetitive research; (3) the obtained miRNAs were not from blood; (4) insufficient data were not available for the diagnosis value.
Data collection and quality assessment
The final set of the included studies was assessed by two investigators (YSC and ST). The final judgment originated from any disagreements were made by a third investigator (YCH). The data of included studies were extracted including the name of first author, publication year, ethnicity, the type and alteration of circulating miRNAs, sample source, normalization controls, alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), numbers of HCC, CHC and HCV-LC, and numbers of TP, TN, FP, FN observations.
The quality of included studies was assessed using Quality Diagnostic Accuracy Studies-2 (QUADAS-2) criteria by two independent authors (WY and JJZ) [12]. The disagreement was settled by a third reviewer (YCH).
Data synthesis and analysis
All the statistical analysis was conducted by STATA version 14 (STATA Corp, College Station, TX, USA). The pooled sensitivity (SEN), specificity (SPE), positive and negative likelihood ratios (PLR and NLR), diagnostic odds ratio (DOR), summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) curve and area under the curve (AUC) were calculated for circulating miRNAs using bivariate random-effects regression model. In addition, potential sources of heterogeneity were explored using threshold effect analysis and regression analysis. Then subgroup analysis was further analyzed based on varied factors. Moreover, differences between the overall accuracy (OA) of miRNAs, AFP or the combination of miRNAs and AFP in discriminating HCV-HCC patients from controls were analyzed using SPSS Statistics 20 (IBM, China). Publication bias were assessed by Deeks’ funnel plot. P-value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Included studies
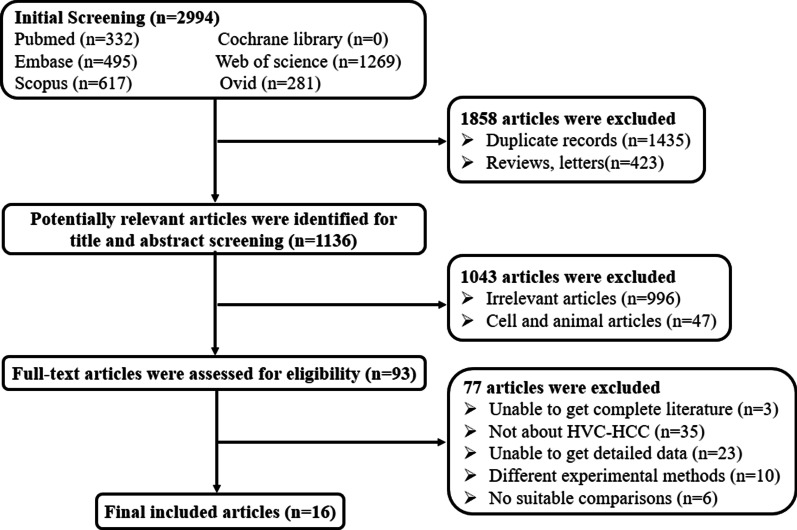
The process of studies selection was shown in Fig. 1. A total of 2994 articles were identified from initial literatures search, including 332 in Pubmed, 495 in Embase, 1269 in Web of Science, and 617 in Scopus and 281 in Ovid. After preliminary selection, 1858 articles were removed due to duplicate records and unfit literary forms. Finally, 16 articles were included according to inclusion and exclusion criteria [9–11, 13–25].
Fig. 1.
Flowchart of literatures selection in this meta-analysis
Among 16 articles, we extracted 39 studies including 3607 HCV-HCC patients and 3387 HCV infected patients as control population. The characteristics of included studies were shown in Table 1. Quantitative real-time reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) was used to measure the expression of miRNAs from 34 serum specimens and 5 plasma specimens. Among 39 studies, 4 studies assessed multiple miRNAs for HCV-HCC diagnosis, and the other 35 studies were focused on single miRNA. The conduct of patient selection introduced unclear risk in 8 articles during quality assessment [10, 13–17, 19, 24] (Additional file 1: Fig. S1).
Table 1.
Characteristics of studies included in this meta-analysis
| First author | Year | Region | MicroRNAs | Regulation mode | Specimen | Internal reference types in qRT-PCR | Sample size | Diagnostic power | Ref. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case | Number | Control | Number | SEN (%) | SPE (%) | AUC | ||||||||
| El-Garem H | 2014 | Egypt | miR-211 | Downregulated | Serum | SNORD68 | HCC | 30 | LC + HC | 60 | 87 | 40 | 0.655 | [9] |
| El-Abd NE | 2015 | Egypt | miR-16 | Downregulated | Serum | RNU48 | HCC | 40 | CHC | 40 | 57.5 | 70 | 0.638 | [10] |
| Motawi TK | 2015 | Egypt | miR-19a | Downregulated | Serum | SNORD68 | HCC | 112 | LC | 50 | 85.7 | 75 | 0.816 | [13] |
| Motawi TK | 2015 | Egypt | miR-296 | Upregulated | Serum | SNORD68 | HCC | 112 | LC | 50 | 76.9 | 56.5 | 0.666 | [13] |
| Motawi TK | 2015 | Egypt | miR-195 | Downregulated | Serum | SNORD68 | HCC | 112 | LC | 50 | 66.7 | 70.8 | 0.665 | [13] |
| Motawi TK | 2015 | Egypt | miR-192 | Upregulated | Serum | SNORD68 | HCC | 112 | LC | 50 | 78.6 | 62.5 | 0.730 | [13] |
| Motawi TK | 2015 | Egypt | miR-34a | Upregulated | Serum | SNORD68 | HCC | 112 | LC | 50 | 51.9 | 82.6 | 0.663 | [13] |
| Motawi TK | 2015 | Egypt | miR-146a | Upregulated | Serum | SNORD68 | HCC | 112 | LC | 50 | 96.4 | 73.9 | 0.880 | [13] |
| Amr KS | 2017 | Egypt | miR-122 | Downregulated | Plasma | RUN6B | HCC | 40 | CHC | 40 | 87.5 | 97.5 | NA | [11] |
| Amr KS | 2017 | Egypt | miR-244 | Upregulated | Plasma | RUN6B | HCC | 40 | CHC | 40 | 87.5 | 97 | NA | [11] |
| Shaker O | 2017 | Egypt | miR-101-1 | Downregulated | Serum | SNORD68 | HCC | 37 | LC + HC | 78 | 73 | 71 | 0.763 | [14] |
| Shaker O | 2017 | Egypt | miR-221 | Upregulated | Serum | SNORD68 | HCC | 37 | LC + HC | 78 | 56.8 | 73.9 | 0.673 | [14] |
| Elemeery MN | 2017 | Egypt | miR-214-5P | Downregulated | Serum | SNORD68 | HCC | 224 | CHC | 250 | 92.2 | 75.5 | 0.842 | [15] |
| Elemeery MN | 2017 | Egypt | miR-494 | Upregulated | Serum | SNORD68 | HCC | 224 | CHC | 250 | 77 | 56 | 0.631 | [15] |
| Elemeery MN | 2017 | Egypt | miR-138b | Downregulated | Serum | SNORD68 | HCC | 224 | CHC | 250 | 68.2 | 58.2 | 0.642 | [15] |
| Elemeery MN | 2017 | Egypt | miR-125b | Downregulated | Serum | SNORD68 | HCC | 224 | CHC | 250 | 92.6 | 55.4 | 0.769 | [15] |
| Elemeery MN | 2017 | Egypt | miR-1269 | Upregulated | Serum | SNORD68 | HCC | 224 | CHC | 250 | 78.6 | 59.8 | 0.691 | [15] |
| Elemeery MN | 2017 | Egypt | miR-145 | Downregulated | Serum | SNORD68 | HCC | 224 | CHC | 250 | 81.5 | 51.5 | 0.624 | [15] |
| Elemeery MN | 2017 | Egypt | miR-375 | Downregulated | Serum | SNORD68 | HCC | 224 | CHC | 250 | 96.4 | 69.3 | 0.811 | [15] |
| Elemeery MN | 2017 | Egypt | miRNA clusters(4) | NA | Serum | SNORD68 | HCC | 224 | Fibrosis | 150 | 96,7 | 94.3 | 0.945 | [15] |
| Elemeery MN | 2017 | Egypt | miRNA clusters(4) | NA | Serum | SNORD68 | HCC | 224 | Fibrosis | 100 | 98.7 | 98.3 | 0.990 | [15] |
| Shaheen NMH | 2018 | Egypt | miR-182 | Downregulated | Serum | Cel-miR-39 | HCC | 40 | CHC | 20 | 72.5 | 65 | 0.675 | [16] |
| Shaheen NMH | 2018 | Egypt | miR-150 | Downregulated | Serum | Cel-miR-39 | HCC | 40 | CHC | 20 | 67.5 | 70 | 0.704 | [16] |
| Rashad NM | 2018 | Egypt | miR-27a | Upregulated | Serum | SNORD68 | HCC | 51 | LC | 39 | 96.7 | 71.7 | 0.897 | [17] |
| Rashad NM | 2018 | Egypt | miR-18b | Upregulated | Serum | SNORD68 | HCC | 51 | LC | 39 | 75.6 | 46.7 | 0.732 | [17] |
| Rashad NM | 2018 | Egypt | miRNA clusters(2) | Upregulated | Serum | SNORD68 | HCC | 51 | LC | 39 | 91.1 | 71.7 | 0.821 | [17] |
| El-Hamouly MS | 2019 | Egypt | miR-301 | Upregulated | Plasma | U6 | HCC | 42 | CHC | 48 | 78.6 | 89.6 | 0.890 | [18] |
| Ali LH | 2019 | Egypt | miR-215 | Upregulated | Serum | SNORD68 | HCC | 60 | LC | 60 | 97.1 | 91 | 0.997 | [19] |
| Shehab-Eldeen S | 2019 | Egypt | miR-122 | Downregulated | Plasma | U6 | HCC | 20 | CHC | 20 | 95 | 81 | 0.930 | [20] |
| Shehab-Eldeen S | 2019 | Egypt | miR-224 | Upregulated | Plasma | U6 | HCC | 20 | CHC | 20 | 85 | 79 | 0.770 | [20] |
| Sun Q | 2019 | China | miR-331-3p | Upregulated | Serum | Cel-miR-39 | HCC | 40 | CHC | 106 | 62.5 | 74.5 | 0.748 | [21] |
| Sun Q | 2019 | China | miR-23b-3p | Downregulated | Serum | Cel-miR-39 | HCC | 40 | CHC | 106 | 85.8 | 65 | 0.806 | [21] |
| Sun Q | 2019 | China | miR-331-3p | Upregulated | Serum | Cel-miR-39 | HCC | 40 | LC | 47 | 75 | 85.1 | 0.832 | [21] |
| Sun Q | 2019 | China | miR-23b-3p | Downregulated | Serum | Cel-miR-39 | HCC | 40 | LC | 47 | 85.1 | 65 | 0.796 | [21] |
| Oura K | 2019 | Japan | miR-125a-5p | Upregulated | Serum | Cel-miR-39 | HCC | 20 | LC + CHC | 20 | 80 | 100 | 0.980 | [22] |
| Weis A | 2019 | Australia | miRNA clusters(3) | NA | Serum | SNORD68 | HCC | 20 | CHC | 20 | 80 | 95 | 0.940 | [23] |
| Fatma A | 2019 | Egypt | miR-19a | Upregulated | Serum | SNORD68 | HCC | 40 | LC + CHC | 40 | 60 | 67.5 | 0.616 | [24] |
| Fatma A | 2019 | Egypt | miR-223 | Downregulated | Serum | SNORD68 | HCC | 40 | LC + CHC | 40 | 60 | 95 | 0.816 | [24] |
| Aly DM | 2020 | Egypt | miR-let-7a-1 | Downregulated | Serum | SNORD68 | HCC | 40 | LC | 20 | 70 | 82.5 | 0.740 | [25] |
qRT-PCR quantitative real-time reverse transcription PCR, HCC hepatocellular carcinoma, LC liver cirrhosis, CHC chronic hepatitis C, SEN sensitivity, SPE specificity, AUC area under the curve, Ref., references
Accurate diagnosis of miRNAs compared with AFP in HCV-HCC patients
The threshold effect was evaluated before data combination. The correlation coefficient was 0.33 (P = 0.11), indicating no significant threshold effect in the present study.
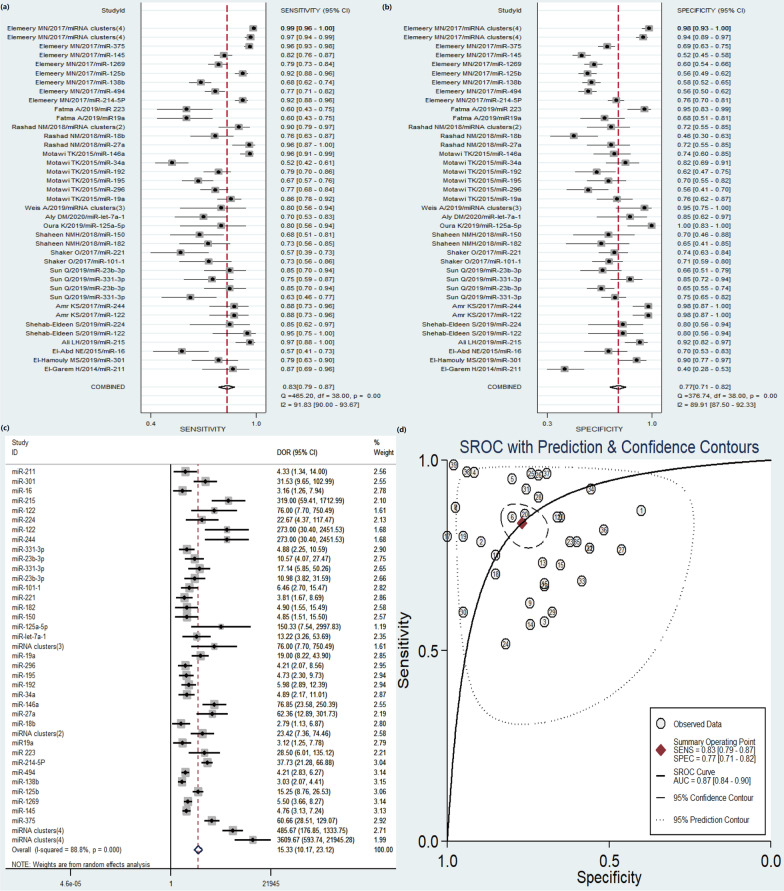
Significant heterogeneity was observed among 39 studies (I-squared = 91.83% for SEN, I-squared = 89.91% for SPE, I-squared = 88.8% for DOR, respectively), therefore, random-effects model was selected for the overall analysis. Forest plots of SEN, SPE and DOR results were shown in Fig. 2a–c. The overall pooled results were summarized as following: SEN 0.83 (95% CI, 0.79–0.87), SPE 0.77 (95% CI, 0.71–0.82), PLR 3.6 (95% CI, 2.8–4.7), NLR 0.21 (95% CI, 0.16–0.29), and DOR 17 (95% CI, 12–28) (Additional file 1: Table S1). The AUC value was 0.87 (95% CI, 0.84–0.90) in the overall SROC curve (Fig. 2d). The above results manifested the diagnostic accuracy of circulating miRNAs for HCC is relatively high.
Fig. 2.
Forest plots of pooled sensitivity (SEN), specificity (SPE), diagnostic odds ratio (DOR), and summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) curve of circulating miRNAs for diagnosis of HCV-HCC among 39 studies. a SEN; b SPE; c DOR; d SROC curve
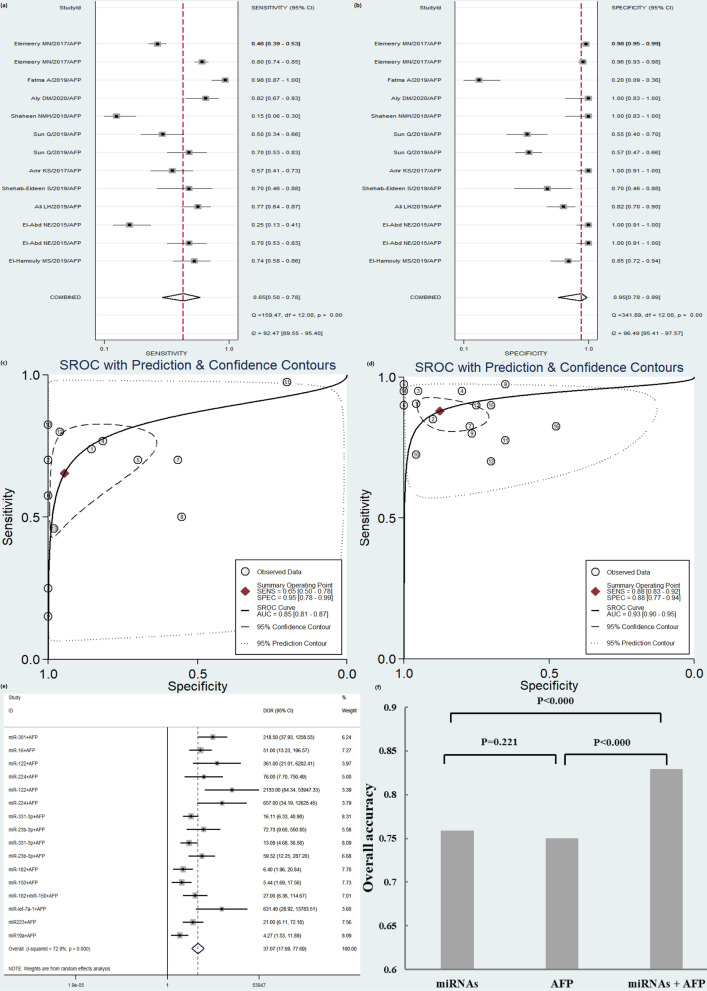
Thirteen studies determined the accuracy of AFP diagnosis, and 16 studies determined the combination of miRNAs and AFP for HCV-HCC patients. miRNAs combined with AFP showed a higher accuracy than AFP alone with SEN of 0.88 versus 0.65, SPE of 0.88 versus 0.95, PLR of 7.1 versus 12.0, NLR of 0.14 versus 0.37, DOR of 51 versus 33, and AUC of 0.93 versus 0.85, respectively (Fig. 3a–c and Additional file 1: Table S1). The OA value analysis indicated that the combination of miRNAs and AFP had a significantly higher accuracy for HCV-HCC than AFP or miRNAs alone (P < 0.000). Although the DOR of AFP is higher than miRNAs alone (33 versus 17), there was no significant difference existed in the diagnostic accuracy of the OA value between the two methods (Fig. 3d–f).
Fig. 3.
Diagnostic accuracy of AFP for HCV-HCC diagnosis compared with circulating miRNAs combined with AFP. a sensitivity (SEN) of AFP; b specificity (SPE) of AFP; c SROC of AFP; d summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) curve of miRNAs combined with AFP; e diagnostic odds ratio (DOR) of circulating miRNAs combined with AFP; f overall accuracy (OA) value
Meta-regression analysis to exploring Sources of Heterogeneity
Meta-regression analysis was used to explore sources of heterogeneity. Region, specimen types, regulation mode, internal reference types, miRNAs profiling, sample size, control groups were internal considered as parameters (Table 2). It can be seen from the results that the specimen types (P = 0.03), regulation mode (P = 0.01), miRNAs profiling (P < 0.01) had statistical significance. However, the parameter region (P = 0.07), internal reference types (P = 0.09), sample size (P = 0.12) and control groups (P = 0.14) were not statistically significant (P > 0.05).
Table 2.
The meta-regression analysis of variable parameters
| Parameters | Sensitivity | Specificity | Joint model | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| estimate (95% CI) | Coef | Z | P >|z| | estimate (95% CI) | Coef | Z | P >|z| | I-squared (95% CI) | LRTChi | P value | |
| Region | 0.75 (0.45–0.92) | 1.09 | − 0.77 | 0.44 | 0.92 (0.74–0.98) | 2.43 | 1.66 | 0.10 | 61.57 (13.37–100.00) | 5.2 | 0.07 |
| Specimen types | 0.88 (0.71–0.96) | 2.00 | 0.77 | 0.51 | 0.93 (0.82–0.97) | 2.57 | 2.47 | 0.01 | 72.39 (38.81–100.00) | 7.24 | 0.03 |
| Regulation mode | 0.88 (0.81–0.93) | 2.02 | 1.17 | 0.24 | 0.87 (0.79–0.92) | 1.90 | 2.21 | 0.03 | 77.68 (51.46–100.00) | 8.96 | 0.01 |
| Internal reference types | 0.78 (0.63–0.89) | 1.28 | − 0.77 | 0.44 | 0.85 (0.74–0.92) | 1.77 | 1.35 | 0.18 | 59.09 (7.72–100.00) | 4.89 | 0.09 |
| miRNAs profiling | 0.96 (0.89–0.98) | 3.11 | 2.70 | 0.01 | 0.94 (0.84–0.98) | 2.70 | 2.73 | 0.01 | 85.14 (69.07–100.00) | 13.46 | < 0.01 |
| Sample size | 0.88 (0.78–0.93) | 1.95 | 0.90 | 0.37 | 0.69 (0.53–0.81) | 0.80 | − 1.33 | 0.26 | 52.19 (0.00–100.00) | 4.18 | 0.12 |
| Control groups | 0.86 (0.79–0.91) | 1.78 | 0.54 | 0.59 | 0.82 (0.75–0.88) | 1.54 | 1.25 | 0.21 | 49.72 (0.00–100.00) | 3.98 | 0.14 |
miRNAs microRNAs, 95% CI 95% confidence intervals, Coef. coefficient
Subgroup analyses
Subgroup analyses were performed based on region, specimen types, regulation mode, internal reference types, miRNAs profiling, sample size, source of control. Majority of the research populations were Egypt (33 studies contained 3407 HCV-HCC patients and 3041 controls) with the pooled SEN of 0.84 (95% CI 0.79–0.89), SPE of 0.76 (95% CI 0.69–0.82), PLR of 3.5 (95% CI 2.6–4.6), NLR of 0.21 (95% CI 0.15–0.30), DOR 17 (95% CI 9–30) of and AUC of 0.87 (95% CI 0.84–0.90). The difference among subgroup analysis based on internal reference types, miRNAs profiling, and sample size was minimal (Table 3).
Table 3.
Summary diagnostic power based on subgroup analyses
| Subgroup | Number of studies | Number of HCC | Number of controls | SEN (95% CI) | I-squared (%) | SPE (95% CI) | I-squared (%) | PLR (95% CI) | NLR (95% CI) | DOR (95% CI) | AUC (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Region | |||||||||||
| Africa | 33 | 3407 | 3041 | 0.84 (0.79–0.89) | 92.93 | 0.76 (0.69–0.82) | 90.56 | 3.5 (2.6–4.6) | 0.21 (0.15–0.30) | 17 (9–30) | 0.87 (0.84–0.90) |
| Asia | 5 | 180 | 326 | 0.77 (0.68–0.85) | 49.68 | 0.78 (0.63–0.88) | 75.02 | 3.5 (2.0–5.9) | 0.29 (0.20–0.42) | 12 (6–26) | 0.84 (0.80–0.87) |
| Specimen types | |||||||||||
| Serum | 34 | 3445 | 3219 | 0.83 (0.77–0.87) | 92.28 | 0.74 (0.68–0.79) | 88.95 | 3.2 (2.5–4.1) | 0.23 (0.17–0.32) | 14 (8–23) | 0.85 (0.82–0.88) |
| Plasm | 5 | 162 | 168 | 0.86 (0.79–0.90) | 0 | 0.91 (0.83–0.96) | 62.13 | 10.0 (4.7–21.2) | 0.16 (0.11–0.23) | 64 (25–164) | 0.87 (0.84–0.90) |
| Regulation mode | |||||||||||
| Upregulated | 18 | 1388 | 1276 | 0.81 (0.74–0.87) | 89.46 | 0.77 (0.68–0.83) | 87.71 | 3.5 (2.5–4.9) | 0.25 (0.17–0.36) | 14 (7–27) | 0.86 (0.82–0.89) |
| Downregulated | 18 | 1751 | 1841 | 0.82 (0.75–0.87) | 89.88 | 0.71 (0.63–0.78) | 84.56 | 2.8 (2.2–3.6) | 0.25 (0.18,0.35) | 11 (7–18) | 0.83 (0.80–0.86) |
| Internal reference types | |||||||||||
| SNORD 68 | 26 | 3145 | 2813 | 0.85 (0.79–0.90) | 93.97 | 0.74 (0.66–0.80) | 91.15 | 3.2 (2.4–4.4) | 0.20 (0.13–0.31) | 16 (8–31) | 0.86 (0.83–0.89) |
| non-SNORD 68 | 13 | 462 | 574 | 0.79 (0.72–0.84) | 62.26 | 0.83 (0.74–0.90) | 78.75 | 4.6 (2.8–7.6) | 0.26 (0.19–0.35) | 18 (8–39) | 0.86 (0.83–0.89) |
| miRNAs profiling | |||||||||||
| Single miRNA | 35 | 3088 | 3078 | 0.77 (0.68–0.83) | 89.68 | 0.74 (0.68–0.79) | 85.88 | 3.1 (2.5–3.9) | 0.26 (0.20–0.33) | 12 (8–19) | 0.84 (0.81–0.87) |
| miRNA clusters | 4 | 519 | 309 | 0.95 (0.89–0.98) | 85.29 | 0.92 (0.79–0.97) | 88.77 | 11.8 (4.1–34.4) | 0.05 (0.02–0.13) | 237 (33–1687) | 0.98 (0.97–0.99) |
| Sample size | |||||||||||
| < 100 | 19 | 705 | 659 | 0.80 (0.74–0.85) | 70.29 | 0.82 (0.72–0.88) | 85.59 | 4.4 (2.8–6.8) | 0.25 (0.19–0.33) | 18 (9–33) | 0.87 (0.83–0.89) |
| > 100 | 20 | 2902 | 2728 | 0.86 (0.78–0.91) | 95.22 | 0.73 (0.65–0.80) | 92.11 | 3.2 (2.3–4.4) | 0.19 (0.12–0.32) | 16 (7–36) | 0.86 (0.82–0.89) |
| Control groups | |||||||||||
| CHC | 18 | 1950 | 2230 | 0.83 (0.77–0.88) | 90.65 | 0.74 (0.66–0.82) | 89.03 | 3.3 (2.3–4.5) | 0.23 (0.16–0.32) | 14 (8–26) | 0.86 (0.83–0.89) |
| LC | 13 | 1005 | 591 | 0.84 (0.75–0.90) | 90.52 | 0.73 (0.66–0.79) | 73.11 | 3.1 (2.4–4.2) | 0.22 (0.14–0.36) | 14 (7–28) | 0.84 (0.80–0.87) |
miRNAs microRNAs, 95% CI 95% confidence intervals, SEN sensitivity, SPE specificity, PLR positive likelihood ratios, NLR negative likelihood ratios, DOR diagnostic odds ratio, AUC area under the curve, HCC hepatocellular carcinoma, LC liver cirrhosis, CHC chronic hepatitis C
The types of specimens could influence the diagnostic accuracy. miRNAs from plasma showed higher quality of detection than that from serum. The corresponding pooled SEN, SPE, PLR, NLR, DOR, and AUC were 0.86 versus 0.83, 0.91 versus 0.74, 10.0 versus 3.2, 0.16 versus 0.23, 64 versus 14, 0.87 versus 0.85, respectively. It is of note that the pooled SEN and DOR were significantly higher among multiple miRNAs subgroup compared with single miRNA (SEN 0.95 versus 0.81, DOR 237 versus 12), indicating significantly higher diagnostic accuracy of miRNA clusters for HCV-HCC.
There are 18 studies (2230 patients) of CHC and 13 studies of HCC-LC (591 patients) as controls. As shown in Table 3 and Additional file 1: Figs. S2, S3, the analysis based on source of control demonstrated the no significant difference of diagnostic accuracy between CHC and HCV-LC. However, among CHC group, miRNAs combined with AFP displayed a better diagnostic accuracy than miRNAs alone. The pooled results were displayed as following: SEN 0.89 (95% CI 0.83–0.93), SPE 0.88 (95% CI 0.76–0.95), PLR 7.7 (95% CI 3.5–17), NLR 0.12 (95% CI 0.07–0.20), DOR 63 (95% CI 20–203) and AUC 0.94 (95% CI 0.92–0.96).
Publication bias and clinical utility of index
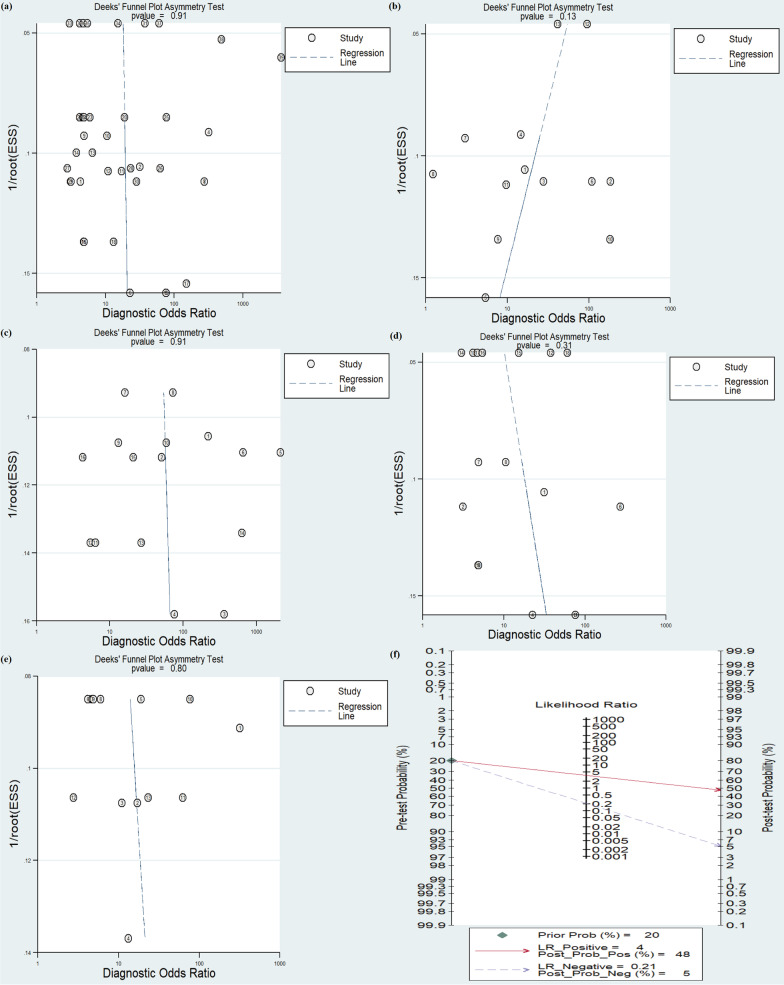
Deeks’ funnel plot asymmetry test was conducted to investigate the publication bias of included studies. The P value for overall circulating miRNAs was 0.43, indicating little possibility of publication bias in our meta-analysis. In addition, P value of publication bias for AFP, miRNAs combined with AFP, CHC and HCV-LC were 0.13, 0.91, 0.31, and 0.80, respectively (Fig. 4a–e).
Fig. 4.
The Deeks’ funnel plot and Fagan’s Nomogram of the diagnostic meta-analysis. a Deeks’ funnel plot of miRNAs; b Deeks’ funnel plot of AFP; c Deeks’ funnel plot of miRNAs combined with AFP; d Deeks’ funnel plot of miRNAs for CHC subgroup; e Deeks’ funnel plot of miRNAs for HCV-LC subgroup; f Fagan’s Nomogram
The post-test probabilities were assessed by Fagan’s Nomogram. When prior probability was 20%, post-test positive probability was 48% with PLR of 4 and negative probability was 5% with NLR of 0.21 (Fig. 4f).
Discussion
DAA shows effective against HCV, however, direct evidence on the effects of antiviral therapy on HCV-HCC remains limited. Furthermore, the development of non-invasive markers for screening of HCC presents a challenge during the last decades. Fortunately, accumulating evidence shows that aberrant miRNAs expression profiles have been associated with the development of HCC [6]. Previous study showed that miRNAs were correlated in hepatocarcinogenic effect of HCV [26]. However, different reports have the discrepancies due to samples, technical variations and analysis methods. Therefore, we conducted this meta-analysis to evaluate the clinical value of circulating miRNAs in diagnosis of HCV-HCC.
According to our results, circulating miRNAs showed high diagnostic accuracy for HCV-HCC detection, with SEN of 0.83 (95% CI, 0.79–0.87), SPE of 0.77 (95% CI, 0.71–0.82), and AUC of 0.87 (95% CI, 0.84–0.90). A significant improvement in the SEN was observed when circulating miRNAs combined with AFP than using alone (P < 0.000). Moreover, we have characterized the role of miRNA clusters as diagnostic and prognostic markers for distinction of HCV-HCC from CHC and HCV-LC subgroup.
Currently, available diagnostic or prognostic biomarkers have limited accuracy for HCC [27]. AFP is the most widely used for HCC, however, serum AFP levels are related to both HCC and benign liver diseases, such as hepatitis and cirrhosis [28, 29]. Precious studies have demonstrated that miRNAs could be served as high-precision detection of HCC biomarker [30]. In this present study, although the DOR of AFP is higher than miRNAs alone (33 versus 17), no statistical difference of OA value was observed. Similarly, He et al. found SEN and AUC-SROC of AFP for HCC were significantly less than miRNAs, while the DOR of AFP was higher than miRNAs [31]. The possible reasons for this are associated with the cut-off value of AFP, stage of HCC, and tumor size. Recent evidence indicated miRNAs had a better performance compared with AFP in detection of early-stage HCV-HCC from CHC and LC, such as miR-331-3p, miR-23b-3p, miR-19a, miR-223, miR-122, miR-199a, miR-16, miR-101–1 and miR-221 [10, 14, 21, 24]. In addition, the OA value of miRNAs combined with AFP had a significantly higher accuracy for HCV-HCC than AFP or miRNAs alone (P < 0.000). These findings together with previous results demonstrated circulating miRNAs could be used as putative diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for HCV-HCC.
In the subgroup analyses, miRNAs from plasma had higher precision detection for HCV-HCC than that from serum. The DOR of plasm and serum miRNAs was 64 (95% CI 25–164) versus 14 (95% CI 8–23), and AUC was 0.87 (95% CI 0.84–0.90) versus 0.85 (95% CI 0.82–0.88), respectively. Previous studies reported that miRNAs concentration in plasma is higher than that in serum due to more proteins in plasma [32, 33]. However, the opposite results were also found in serum [31]. Therefore, further studies are needed to confirm application of specimen types in clinical practice. Interestingly, our study revealed differences in DOR (237 versus 12) when selecting miRNA clusters for HCV-HCC diagnosis. However, the miRNAs panel has not been definitely decided yet due to differentially expressed circulating miRNAs in HCV-HCC [13, 23]. All the above researches suggested that multiple miRNAs panel may be a promising prospect for application as a non-invasive method for HCV-HCC.
Although the results are promising, several limitations need to be addressed. First, some related studies, such as letters, editorials, case reports and conference proceedings, were not included. Second, most studies included in this meta-analysis were from Egypt, having an adverse effect on population selection bias. Third, different cut-off values were not extracted due to limited data, such as HCC characteristics and different baseline features of patients, which may result in a latent problem and high heterogeneity when interpreting the results. Fourthly, the data on special single type of miRNA were insufficient, restricting the clinical application. Therefore, the results of this study need more higher quality studies for confirmation in the future.
Conclusions
In conclusion, miRNAs could distinguish HCV-HCC from CHC and LC. Combined application of miRNAs and AFP was more effective. In addition, the diagnostic accuracy of miRNA clusters was significantly high in HCV-HCC patients. Therefore, the results of our study strongly suggested that there is a real possibility of using circulating miRNAs as potential non-invasive biomarker of HCV-HCC.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Table S1. Summary diagnostic accuracy of circulating miRNAs, AFP and miRNAs combined with AFP for HCV-HCC. Figure S1. The quality assessment of included articles using the QUADAS-2 criteria. Figure S2. Forest plots of pooled sensitivity (SEN), specificity (SPE), diagnostic odds ratio (DOR), and summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) curve of circulating miRNAs alone and combined with AFP for diagnosis of HCV-HCC among CHC patients. (a) SEN of miRNAs; (b) SPE of miRNAs; (c) DOR of miRNAs; (d) SROC curve of miRNAs; (e) SEN of miRNAs combined with AFP; (f) SPE of miRNAs combined with AFP; (g) DOR of miRNAs combined with AFP; (h) SROC curve of miRNAs combined with AFP. Figure S3. Forest plots of pooled sensitivity (SEN), specificity (SPE), diagnostic odds ratio (DOR), and summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) curve of circulating miRNAs alone for diagnosis of HCV-HCC among HCV-LC patients. (a) SEN of miRNAs; (b) SPE of miRNAs; (c) DOR of miRNAs; (d) SROC curve of miRNAs.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- miRNAs
Circulating microRNAs
- HCV
Hepatitis C virus
- HCV-HCC
HCV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma
- qRT-PCR
Quantitative real-time reverse transcription PCR
- HCC
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- LC
Liver cirrhosis
- CHC
Chronic hepatitis C
- SEN
Sensitivity
- SPE
Specificity
- AUC
Area under the curve
- PLR
Positive likelihood ratios
- NLR
Negative likelihood ratios
- SROC
Summary receiver operating characteristic
- 95% CI
95% Confidence intervals
- Coef.
Coefficient
- Ref.
References
- DOR
Diagnostic odds ratio
Authors' contributions
The work presented here was carried out in collaboration between all authors. WY and YQQ developed the concept and designed the study. YSC, ST and YCH carried out the literatures research and studies selection. YCH and ST co-worked on associated data collection. The qualities of included studies were carried out by WY, ZJJ and YCH. Data synthesis and analysis were carried out by WY, YCH and YSC. The manuscript was written by YCH and corrected by WY and YQQ. All authors discussed the results and implications and commented on the manuscript at all stages. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Department of Education of Zhejiang Province [Y202044501]. The funder had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish or preparation of the manuscript.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors have seen and approved the content and fulfil the journal’s requirements for authorship.
Competing interests
Not applicable.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Yunqing Qiu, Email: qiuyq@zju.edu.cn.
Wei Yu, Email: wyu@zju.edu.cn.
References
- 1.Rasche A, Sander AL, Corman VM, Drexler JF. Evolutionary biology of human hepatitis viruses. J Hepatol. 2019;70(3):501–520. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.11.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Petruzziello A. Epidemiology of hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) related hepatocellular carcinoma. Open Virol J. 2018;12:26–32. doi: 10.2174/1874357901812010026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61(2):69–90. doi: 10.3322/caac.20107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Yang JD. Detect or not to detect very early stage hepatocellular carcinoma? The western perspective. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2019;25(4):335–343. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2019.0010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Armand-Labit V, Pradines A. Circulating cell-free microRNAs as clinical cancer biomarkers. Biomol Concepts. 2017;8(2):61–81. doi: 10.1515/bmc-2017-0002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ali Syeda Z, Langden SSS, Munkhzul C, Lee M, Song SJ. Regulatory mechanism of microRNA expression in cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(5):E1723. doi: 10.3390/ijms21051723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Pezzuto F, Buonaguro L, Buonaguro FM, Tornesello ML. The Role of circulating free DNA and microRNA in non-invasive diagnosis of HBV- and HCV-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(4):E1007. doi: 10.3390/ijms19041007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Piluso A, Gragnani L, Fognani E, et al. Deregulation of microRNA expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with HCV-related malignancies. Hepatol Int. 2015;9(4):586–593. doi: 10.1007/s12072-015-9658-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.El-Garem H, Ammer A, Shehab H, et al. Circulating microRNA, miR-122 and miR-221 signature in Egyptian patients with chronic hepatitis C related hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Hepatol. 2014;6(11):818–824. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v6.i11.818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.El-Abd NE, Fawzy NA, El-Sheikh SM, Soliman ME. Circulating miRNA-122, miRNA-199a, and miRNA-16 as biomarkers for early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma in Egyptian patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Mol Diagn Ther. 2015;19(4):213–220. doi: 10.1007/s40291-015-0148-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Amr KS, ElmawgoudAtia HA, ElazeemElbnhawy RA, Ezzat WM. Early diagnostic evaluation of miR-122 and miR-224 as biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma. Genes Dis. 2017;4(4):215–221. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2017.10.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME, et al. QUADAS-2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann Intern Med. 2011;155(8):529–536. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-155-8-201110180-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Motawi TK, Shaker OG, El-Maraghy SA, Senousy MA. Serum microRNAs as potential biomarkers for early diagnosis of hepatitis C virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma in Egyptian patients. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(9):e0137706. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Shaker O, Alhelf M, Morcos G, Elsharkawy A. miRNA-101-1 and miRNA-221 expressions and their polymorphisms as biomarkers for early diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Infect Genet Evol. 2017;51:173–181. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2017.03.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Elemeery MN, Badr AN, Mohamed MA, Ghareeb DA. Validation of a serum microRNA panel as biomarkers for early diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma post-hepatitis C infection in Egyptian patients. World J Gastroenterol. 2017;23(21):3864–3875. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i21.3864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Shaheen NMH, Zayed N, Riad NM, et al. Role of circulating miR-182 and miR-150 as biomarkers for cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma post HCV infection in Egyptian patients. Virus Res. 2018;255:77–84. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2018.07.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Rashad NM, El-Shal AS, Shalaby SM, Mohamed SY. Serum miRNA-27a and miRNA-18b as potential predictive biomarkers of hepatitis C virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cell Biochem. 2018;447(1–2):125–136. doi: 10.1007/s11010-018-3298-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.El-Hamouly MS, Azzam AA, Ghanem SE, El-Bassal FI, Shebl N, Shehata AMF. Circulating microRNA-301 as a promising diagnostic biomarker of hepatitis C virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Biol Rep. 2019;46(6):5759–5765. doi: 10.1007/s11033-019-05009-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ali LH, Higazi AM, Moness HM, et al. Clinical significances and diagnostic utilities of both miR-215 and squamous cell carcinoma antigen-IgM versus alpha-fetoprotein in Egyptian patients with hepatitis C virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2019;12:51–66. doi: 10.2147/CEG.S179832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Shehab-Eldeen S, Nada A, Abou-Elela D, El-Naidany S, Arafat E, Omar T. Diagnostic performance of microRNA-122 and microRNA-224 in hepatitis C virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2019;20(8):2515–2522. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2019.20.8.2515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sun Q, Li J, Jin B, Wang T, Gu J. Evaluation of miR-331-3p and miR-23b-3p as serum biomarkers for hepatitis c virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma at early stage. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2020;44(1):21–28. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2019.03.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Oura K, Fujita K, Morishita A, et al. Serum microRNA-125a-5p as a potential biomarker of HCV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 2019;18(1):882–890. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Weis A, Marquart L, Calvopina DA, Genz B, Ramm GA, Skoien R. Serum microRNAs as biomarkers in hepatitis C: preliminary evidence of a microRNA panel for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(4):E864. doi: 10.3390/ijms20040864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Fatma A, Reham A, Mona M, et al. Study of serum microRNA19a and microRNA223 as potential biomarkers for early diagnosis of hepatitis C virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Gene Rep 2019;15.
- 25.Aly DM, Gohar NA, Abd El-Hady AA, Khairy M, Abdullatif MM. Serum microRNA let-7a-1/let-7d/let-7f and miRNA 143/145 gene expression profiles as potential biomarkers in HCV induced hepatocellular carcinoma. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2020;21(2):555–562. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2020.21.2.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Motawi TK, Shaker OG, El-Maraghy SA, Senousy MA. Serum interferon-related microRNAs as biomarkers to predict the response to interferon therapy in chronic hepatitis C genotype 4. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(3):e0120794. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ahn JC, Teng PC, Chen PJ, et al. Detection of circulating tumor cells and their implications as a novel biomarker for diagnosis, prognostication, and therapeutic monitoring in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2020 doi: 10.1002/hep.31165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Collier J, Sherman M. Screening for hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 1998;27(1):273–278. doi: 10.1002/hep.510270140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Oka H, Tamori A, Kuroki T, Kobayashi K, Yamamoto S. Prospective study of alpha-fetoprotein in cirrhotic patients monitored for development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 1994;19(1):61–66. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840190111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Mao D, Chen H, Tang Y, Li J, Cao Y, Zhao J. Application of isothermal nucleic acid signal amplification in the detection of hepatocellular carcinoma-associated microRNA. ChemPlusChem. 2019;84(1):8–17. doi: 10.1002/cplu.201800382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.He S, Hu XW, Wang D, Han LF, Zhang DC, Wei C. Accuracy of microRNAs for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2016;40(4):405–417. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2016.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Arroyo JD, Chevillet JR, Kroh EM, et al. Argonaute2 complexes carry a population of circulating microRNAs independent of vesicles in human plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(12):5003–5008. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1019055108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.McDonald JS, Milosevic D, Reddi HV, Grebe SK, Algeciras-Schimnich A. Analysis of circulating microRNA: preanalytical and analytical challenges. Clin Chem. 2011;57(6):833–840. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2010.157198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1: Table S1. Summary diagnostic accuracy of circulating miRNAs, AFP and miRNAs combined with AFP for HCV-HCC. Figure S1. The quality assessment of included articles using the QUADAS-2 criteria. Figure S2. Forest plots of pooled sensitivity (SEN), specificity (SPE), diagnostic odds ratio (DOR), and summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) curve of circulating miRNAs alone and combined with AFP for diagnosis of HCV-HCC among CHC patients. (a) SEN of miRNAs; (b) SPE of miRNAs; (c) DOR of miRNAs; (d) SROC curve of miRNAs; (e) SEN of miRNAs combined with AFP; (f) SPE of miRNAs combined with AFP; (g) DOR of miRNAs combined with AFP; (h) SROC curve of miRNAs combined with AFP. Figure S3. Forest plots of pooled sensitivity (SEN), specificity (SPE), diagnostic odds ratio (DOR), and summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) curve of circulating miRNAs alone for diagnosis of HCV-HCC among HCV-LC patients. (a) SEN of miRNAs; (b) SPE of miRNAs; (c) DOR of miRNAs; (d) SROC curve of miRNAs.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.