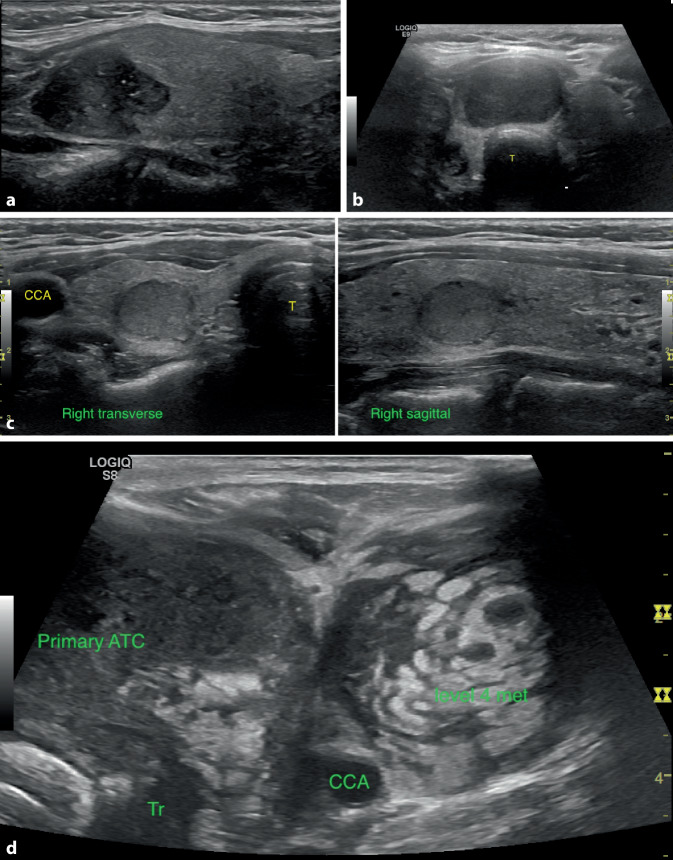
Fig. 3.
a Papillary Thyroid carcinoma. Solid, hypoechoic lesion with microcalcifications or PEF and lobulated margins (right sagittal view). b Follicular neoplasms are typically solid, and can be hyperechoic, isoechoic, or hypoechoic like this follicular carcinoma (midline transverse view of isthmus nodule; T trachea). c Medullary thyroid carcinoma appears solid and hypoechoic but cannot be distinguished from other neoplasms on ultrasound alone (right transverse and sagittal views, CCA common carotid artery; T trachea). d Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma is typically large, hypoechoic and heterogeneous, infiltrating, and associated with lymph node metastases (left transverse view; ATC anaplastic thyroid carcinoma, Tr trachea, CCA common carotid artery, level 4 met = lymph node metastasis in left lateral neck)