Abstract
Background:
Glyphosate is the most commonly used herbicide in the world and is purported to have a variety of health effects, including endocrine disruption and an elevated risk of several types of cancer. Blood DNA methylation has been shown to be associated with many other environmental exposures, but to our knowledge, no studies to date have examined the association between blood DNA methylation and glyphosate exposure.
Objective:
We conducted an epigenome-wide association study to identify DNA methylation loci associated with urinary glyphosate and its metabolite aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA) levels. Secondary goals were to determine the association of epigenetic age acceleration with glyphosate and AMPA and develop blood DNA methylation indices to predict urinary glyphosate and AMPA levels.
Methods:
For 392 postmenopausal women, white blood cell DNA methylation was measured using the Illumina Infinium MethylationEPIC BeadChip array. Glyphosate and AMPA were measured in two urine samples per participant using liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Methylation differences at the probe and regional level associated with glyphosate and AMPA levels were assessed using a resampling-based approach. Probes and regions that had an false discovery rate in of 1,000 subsamples of the study population were considered differentially methylated. Differentially methylated sites from the probe-specific analysis were combined into a methylation index. Epigenetic age acceleration from three epigenetic clocks and an epigenetic measure of pace of aging were examined for associations with glyphosate and AMPA.
Results:
We identified 24 CpG sites whose methylation level was associated with urinary glyphosate concentration and two associated with AMPA. Four regions, within the promoters of the MSH4, KCNA6, ABAT, and NDUFAF2/ERCC8 genes, were associated with glyphosate levels, along with an association between ESR1 promoter hypomethylation and AMPA. The methylation index accurately predicted glyphosate levels in an internal validation cohort. AMPA, but not glyphosate, was associated with greater epigenetic age acceleration.
Discussion:
Glyphosate and AMPA exposure were associated with DNA methylation differences that could promote the development of cancer and other diseases. Further studies are warranted to replicate our results, determine the functional impact of glyphosate- and AMPA-associated differential DNA methylation, and further explore whether DNA methylation could serve as a biomarker of glyphosate exposure. https://doi.org/10.1289/EHP10174
Introduction
Glyphosate is the most used pesticide in the world,1 used in both agricultural (for weed control and preharvest desiccation) and nonagricultural settings.1,2,3 Studies have detected glyphosate in the air, soil, drinking water, and food.4 Use of glyphosate-based herbicides has increased dramatically since their introduction,1 largely due to the growing use of genetically modified glyphosate-resistant crops starting in the late 1990s.5 Glyphosate and/or its primary metabolite, aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA), are frequently detected in the food supply at different levels,6,7,8,9,10 and recent studies in the United States have detected glyphosate in the urine of 70%–90% of participants.11,12,13,14
Concerns have been raised about the safety of glyphosate exposure in humans, and the topic remains controversial. In 2015 the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) classified glyphosate as a probable human carcinogen.15 This classification was supported by a meta-analysis that suggested an elevated risk of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma associated with glyphosate exposure,16 although another large cohort study did not find a relationship between glyphosate and cancer risk.17 Epidemiological studies have also found associations with other health problems, including shortened gestational length,14 birth defects,18 endocrine disruption,12 and thyroid dysfunction.19 Animal and in vitro studies have shown associations with endocrine disruption,20,21 fatty liver disease,22 breast cancer cell proliferation,23 changes to the microbiome,24,25,26,27 and increased risk of antibiotic resistance in bacteria.28 Although limited data exists about potential adverse effects of AMPA, some studies suggest that AMPA may have effects similar to those of glyphosate.29,30,31 One recent study found elevated breast cancer risk among women with high urinary AMPA.32
Epigenetic markers, such as DNA methylation, may be a powerful tool for understanding the potential effects of glyphosate exposure in humans. White blood cell (WBC) DNA methylation has been associated with environmental exposures,33,34 including endocrine-disrupting compounds,35,36 other pesticides,37 and air pollution.38,39,40 In addition, DNA methylation indices combining information from multiple sites have been developed as biomarkers of some exposures, including smoking41,42 and alcohol consumption.43 Some smoking-associated DNA methylation markers have also been shown to be associated with risk for lung44 and bladder45 cancers.
Recent in vitro29,46 and animal47,48 evidence (reviewed in reference49) suggests that glyphosate and AMPA may influence DNA methylation, including in ways that could promote the development of breast cancer.50 However, the association of glyphosate and AMPA with DNA methylation differences in humans has been rarely studied. One recent study of pesticide applicators identified a single CpG site (cg06950346) at which methylation was associated with history of self-reported glyphosate use.51 To our knowledge, no studies to date have examined direct glyphosate and AMPA measurement in association with blood DNA methylation.
Another recent avenue of research is the development of “epigenetic clocks” that purport to measure biological age using DNA methylation at a selection of CpG sites.52,53,54 Epigenetic age acceleration (biological age greater than chronological age) or a faster molecular pace of aging55 have been associated with a host of adverse outcomes, including all-cause mortality,56,57,58 risk for breast cancer,59 B-cell lymphoma,60 which have been associated with glyphosate16 and AMPA32 in epidemiological studies. Epigenetic age acceleration has also been associated with other environmental exposures,61,62,63,64 but to our knowledge, the association between epigenetic age acceleration and glyphosate and AMPA measurements has not been previously explored.
We conducted an epigenome-wide association study to identify DNA methylation loci associated with urinary glyphosate and AMPA levels. Secondary goals were to determine the association of epigenetic age acceleration with glyphosate and AMPA and develop blood DNA methylation indices to predict urinary glyphosate and AMPA levels.
Methods
Study Population
The study population consisted of postmenopausal women residing in southern California between the ages of 45 and 66 y (). All participants provided informed consent to participate, and the study was approved by the University of California, Irvine institutional review board, HS #2016-3,127. Recruitment, questionnaires, and specimen collection were described in detail previously.65 Briefly, women were recruited from 2017 to 2019 via two recruitment arms: targeted mailings to members of the Athena Breast Health Network (a cohort of women receiving screening mammograms at University of California, Irvine health facilities), and untargeted recruitment from the broader community via flyers, social media, events, and word of mouth. The study was designed to identify epigenetic markers for factors potentially related to breast cancer risk; thus, women with a personal history of breast cancer or mastectomy were excluded from the study.
Biospecimen Collection and Processing
Specimens were collected and processed as previously described.65 Briefly, participants self-collected first-morning urine samples on 2 d within a 10-d period not known to them in advance to capture their typical behaviors and exposures. Urine samples were stored in a freezer () until they could be transported to the laboratory. At an appointment attempted to be scheduled within 10 d of the second urine sample collection (median 1 d, range 0–24 d), a certified phlebotomist collected peripheral blood in three glass Vacutainer blood collection tubes: one containing ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), one containing acid citrate dextrose (ACD), and one with no anticoagulants. DNA was extracted from the buffy coat (from EDTA and ACD tubes, pooled) within 6 h of collection using the QIAamp DNA Blood Maxi Kit (Cat. No. 51,194, QIAGEN) and stored at for later analysis.
Urinary glyphosate and AMPA were measured using liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) at the Collaborative Center for Translational Mass Spectrometry (CCTMS) (Tgen) using a Vanquish UHPLC coupled to TSQ Altis triple quadrupole mass spectrometer (Thermo Scientific) as previously described.12 Briefly, glyphosate and AMPA assay validation was performed in a commercially available urine pool from LeeBio Solutions prior to analysis. The calibration curves for glyphosate and AMPA were prepared over a linear range of (coefficient of determination ) by spiking variable concentrations of glyphosate and AMPA and their respective isotopically labeled internal standards, and (Sigma-Aldrich) at a fixed concentration of . Data acquisition and processing were performed using Xcalibur 4.1.50 and QuanBrowser, 4.1.50 (Thermo Scientific). Both assays were linear (coefficient of determination ) over a range (Figure S1). The limits of detection (LOD) for glyphosate and AMPA were 0.014 and , and the limits of quantitation (LOQ) were 0.041 and , respectively (Table S1). Creatinine was measured using the DetectX urinary creatinine detection kit (Arbor Assays, K002-H5) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The data were tested for batch effects using the Kruskal-Wallis test, and batch correction was performed for glyphosate values using the removeBatchEffects function in limma.66 Four samples with implausibly low creatinine () were excluded from subsequent analysis. Measurements were averaged for the two urine samples for each analyte after replacing values with .67
Genomic DNA was bisulfite converted using the Zymo EZ DNA methylation kit (Zymo Research), and then DNA methylation at over 850,000 CpG sites was measured using the Illumina Infinium MethylationEPIC BeadChip (Illumina) at the University of Southern California Molecular Genomics Core. Laboratory staff were blinded to glyphosate and AMPA measurements. Methylation data preprocessing was performed according to recommended steps,68 including probe filtering, normalization, and batch correction. All data analysis was performed in R, (version 3.6.2; R Development Core Team). Probes with a detection were considered missing, and other low-quality probes were removed as follows: missing in at least 20% of samples (); had SNPs with global minor allele frequency within 5 base pairs of the target sequence or mapping problems with the probe sequence ();69 hybridized to multiple locations ();70 or located on the X or Y chromosome (). All samples passed quality control, including efficiency of bisulfite conversion, verification of reported sex and identity, and having failed probes (maximum value: 0.13%), and were included in the final data analysis. Values were normalized with noob normalization as implemented in the minfi package (version 1.32.0)71 for background correction and dye bias adjustment followed by beta mixture quantile normalization (BMIQ) to correct for type II probe bias.72 Except where noted, filtering and normalization was completed using the ChAMP package (version 2.12.4).73 Finally, DNA methylation measurements were corrected for batch and position on chip using ComBat74 as implemented in sva version 3.30.1.75 We used a reference-based method76 to estimate the proportions of six WBC types in our samples, which did not significantly differ with glyphosate or AMPA tertile (Table S2). We used the methylation M value (the base 2 logarithm of the ratio of methylated to unmethylated intensities) for all analyses; in some cases, we also reported values (percent methylation) for ease of interpretation.77
Covariates
Relevant covariates, including age, self-reported race/ethnicity, height, weight, smoking status (current, former, or never smoker), alcohol consumption, organic eating habits, physical activity, and recent herbicide use, were collected via questionnaires. Race and ethnicity were self-reported in response to two questions: “What is your racial background?” (response choices: “Black or African American,” “White,” “Asian,” “American Indian or Alaska Native,” “Native Hawaiian or other Pacific Islander,” “Some other race,” “Do not know,” or “Prefer not to answer”) and “Are you of Hispanic, Latino, or Spanish origin or ancestry?” (yes/no; “yes” responses were prompted to further self-identify as “Mexican, Mexican American, or Chicano,” “Puerto Rican,” “Cuban,” and/or “Other Hispanic, Latino, or Spanish origin”). Responses to these questions were pooled into a combined race/ethnicity measure with categories non-Hispanic White, non-Hispanic Asian, non-Hispanic Black, Hispanic, or Other. All those who answered “yes” to the Hispanic/Latino/Spanish origin question were placed into the Hispanic category, regardless of response to the race question. Multiple selections were allowed; individuals who selected more than one race () were placed into the “Other” category. Those who answered “American Indian or Alaska Native,” “Native Hawaiian or other Pacific Islander,” or “Some other race” were placed into the “Other” category due to small numbers in the study cohort (total including ). Race/ethnicity was included in the analysis due to known associations with DNA methylation.78,79,80
Self-reported height and weight were used to calculate body mass index (BMI) by dividing the weight in kilograms by the height in meters squared. Organic eating habits were self-reported as “seldom or never,” “sometimes,” or “often or always.”81 Physical activity was reported as typical frequency and duration of moderate and vigorous physical activity. These responses were converted to minutes per week of moderate exercise, with each minute of vigorous exercise equivalent to 2 min of moderate exercise.82 Diet quality was estimated by using up to three unannounced ASA24 24-h dietary recalls,83 completed during the 10 d prior to blood collection, to calculate the Healthy Eating Index-2015 (HEI) averaged across all recalls. The HEI is scored on a 0–100 scale, with higher values indicating greater adherence to the Dietary Guidelines for Americans.84 Some participants were asked whether they had used herbicides at home or work within the past 7 d. This question was added to the questionnaire partway through study recruitment, so data on recent herbicide use is missing for 37% () of participants.
Statistical Analyses
Variability and correlation of urinary glyphosate and AMPA levels between and within samples were characterized with the intraclass correlation (ICC) and Pearson’s correlation, respectively. The association between all covariates and the natural logarithm of glyphosate and AMPA concentration (adjusted for urinary creatinine) was assessed using linear regression. In all linear regression analyses, two-sided were considered statistically significant. In the DNA methylation analyses, missing data for covariates (from individuals) were substituted with the median (numeric variables) or mode (categorical variables).
DNA Methylation Analysis
We calculated epigenetic age for each sample according to three epigenetic clocks: Hannum,52 Horvath,53 and Levine,54 and one epigenetic measure of pace of aging, DunedinPoAm.55 The Hannum and Horvath clocks are designed to correlate with chronological age, whereas the Levine clock also incorporates phenotypic measures, including mortality and physical functioning. DunedinPoAm is intended to capture the current rate of change of biological age. Epigenetic age was calculated from the model coefficients provided by each author using normalized methylation beta values. Values for missing probes ( for Hannum, for Horvath, for Levine, for DunedinPoAm) were imputed using k-nearest neighbors imputation. DunedinPoAm was calculated using code provided by its developers.55 Epigenetic age acceleration (residuals from a model regressing chronological age on epigenetic age from each clock) and epigenetic pace of aging from DunedinPoAm was examined for association with glyphosate and AMPA, first in univariate linear regression models adjusted for urinary creatinine concentration and then adjusted for age, race/ethnicity, BMI, smoking status, alcohol consumption, organic eating, and HEI, in addition to batch and position on chip. A third model also included estimated WBC type proportions predicted according to Houseman’s method.76 These covariates were selected based on known relationships with either DNA methylation, glyphosate/AMPA, or both; creatinine was included to account for differences in urine concentration.
For probe- and region-specific analyses, the study samples were divided into training () and validation () sets stratified by glyphosate tertile. Demographic and dietary variables were compared for the training and validation sets (Table S3). All variables except smoking were not significantly associated with the randomly assigned set; there was a larger proportion of former smokers in the validation set (). Because all the former smokers in the validation set reported cessation prior to blood sample collection, we proceeded with the planned analysis. Using the training set, we identified differentially methylated probes (DMPs) and differentially methylated regions (DMRs) according to a resampling-based method.85
We selected a random subsample consisting of 90% of the training set (). Using this subsample, we identified candidate DMPs using limma (version 3.44.3),66 to fit linear models and candidate DMRs using DMRcate (version 2.0.7),86 with a kernel bandwidth of 1,000 base pairs and scaling factor of 2. Each model was adjusted for the same variables as in the final epigenetic aging model. Models without adjustment for dietary variables (organic eating and HEI) did not show substantially different results (Pearson’s for test statistics from the two versions of the model for both analytes), nor did models that used creatinine-standardized glyphosate and AMPA concentrations instead of including creatinine as a covariate in the model (Pearson’s for glyphosate and 0.985 for AMPA). A false discovery rate (FDR) q-value of was considered statistically significant. This process was repeated in a series of 1,000 subsamples of 90% of the training set and sampling distributions for all summary statistics constructed. Probes and regions that were selected as candidate DMPs or DMRs in of subsamples were considered differentially methylated and carried forward for further analysis. This approach results in a more stable list of DMPs and DMRs, because DNA methylation microarray results are known to be sensitive to small differences in the study cohort.87,88,89,90 The median FDR q-value was used to rank the relative significance of DMPs. For DMRs, overlapping regions were combined, and then significance was ranked after combining median q-values for the probes within the region using Stouffer’s method. A traditional epigenome-wide association analysis with the entire training set74 was also done to determine whether findings were robust to changes in the analysis approach.
DMPs and DMRs were annotated using the Illumina manifest (version B4) to identify associated genes and genomic context. Probes were also mapped to ChromHMM data from ENCODE91 to determine predicted chromatin state; data from the GM12878 lymphoblastic cell line was used because it is the tissue most similar to leukocytes. Chromatin states were pooled into six categories as follows: promoter (active, weak, or poised promoters), enhancer (strong or weak enhancers), transcribed (transcriptional transition, transcriptional elongation, or weak transcribed), polycomb-repressed, inactive (heterochromatin and repetitive regions), and insulators. DMPs were examined for enrichment of certain locations relative to CpG islands or chromatin states, in comparison with the background of all probes included on the array, using Fisher’s exact test. We used the “gometh” function from the missMethyl package (version 1.16.0)92 to examine enrichment of Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathways and gene ontology terms in genes associated with DMPs and assessed enrichment of pathways using Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) software (version 62089861; release Date: 17 February 2021). Terms or pathways with and at least three genes associated with DMPs were considered enriched.
We developed methylation indices to predict urinary glyphosate and AMPA levels using blood DNA methylation at the glyphosate- and AMPA-associated DMPs. Methylation () values for each DMP were passed to an elastic net () regression model with 10-fold cross-validation repeated 100 times to estimate lambda (the penalty coefficient) and regression coefficients for each site. The final lambda was selected as the largest lambda within one standard error of the minimum prediction error. This approach was implemented using the glmnet package (version 2.0-18).93 The performance of the methylation indices were assessed by calculating the Pearson correlation between predicted and actual glyphosate and AMPA concentration in the 60 validation samples. The indices’ relationship with glyphosate and AMPA tertile was also tested using analysis of variance (ANOVA), and the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) was computed to characterize the discriminatory accuracy for the highest vs. lowest tertile.
Results
Glyphosate and AMPA Concentrations
A total of 96% of study participants had detectable () glyphosate, and 82% had detectable AMPA in at least one urine sample. Table 1 describes glyphosate and AMPA concentrations stratified by various demographic, dietary, and lifestyle factors. The median glyphosate concentration (averaged between two urine samples for each participant) was (range ), and the median AMPA concentration was (range ). Both glyphosate and AMPA concentrations were strongly right-skewed and thus transformed with the natural logarithm for all further analyses (Figure S2). Between-sample agreement was moderate for both glyphosate () and AMPA (), as was the within-sample correlation between glyphosate and AMPA measurements (Pearson’s , ) (Figure S3).
Table 1.
Median urinary glyphosate and AMPA concentrations, averaged for two samples collected between 2017 and 2019 from 392 postmenopausal California women, stratified by cohort characteristics.
| (%) | Glyphosate | AMPA | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ng/mL median (IQR) |
creatinine median (IQR) |
-Value | ng/mL median (IQR) |
creatinine median (IQR) |
-Value | ||
| Overall | 392 | 0.12 (0.06, 0.22) | 0.20 (0.11, 0.38) | NA | 0.06 (0.02, 0.12) | 0.10 (0.04, 0.22) | NA |
| Race/ethnicity | |||||||
| Asian | 43 (11.1) | 0.11 (0.07, 0.23) | 0.19 (0.09, 0.34) | 0.30 | 0.08 (0.02, 0.14) | 0.13 (0.03, 0.24) | 0.50 |
| Hispanic | 69 (17.9) | 0.12 (0.07, 0.21) | 0.20 (0.11, 0.37) | 0.90 | 0.06 (0.02, 0.11) | 0.08 (0.04, 0.17) | 0.41 |
| Other | 20 (5.2) | 0.07 (0.04, 0.13) | 0.11 (0.06, 0.24) | 0.004 | 0.02 (0.01, 0.05) | 0.04 (0.02, 0.07) | 0.005 |
| White | 254 (65.8) | 0.12 (0.06, 0.24) | 0.21 (0.12, 0.42) | Ref | 0.05 (0.02, 0.12) | 0.10 (0.04, 0.22) | Ref |
| Missing | 6 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Age (y) | |||||||
| 45–49 | 27 (6.9) | 0.18 (0.09, 0.24) | 0.23 (0.11, 0.33) | 0.72 | 0.11 (0.05, 0.19) | 0.12 (0.05, 0.29) | 0.12 |
| 50–54 | 85 (21.7) | 0.14 (0.06, 0.19) | 0.18 (0.12, 0.33) | 0.07 (0.02, 0.11) | 0.09 (0.04, 0.17) | ||
| 55–59 | 155 (39.5) | 0.11 (0.06, 0.21) | 0.18 (0.10, 0.33) | 0.05 (0.02, 0.12) | 0.08 (0.03, 0.22) | ||
| 60–66 | 125 (31.9) | 0.11 (0.06, 0.29) | 0.23 (0.11, 0.56) | 0.05 (0.01, 0.12) | 0.10 (0.04, 0.22) | ||
| Missing | 0 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| BMI () | |||||||
| 188 (48.0) | 0.12 (0.06, 0.24) | 0.21 (0.10, 0.44) | 0.78 | 0.06 (0.02, 0.12) | 0.10 (0.04, 0.21) | 0.63 | |
| 25–29.9 | 116 (29.6) | 0.12 (0.06, 0.22) | 0.20 (0.12, 0.33) | 0.05 (0.02, 0.12) | 0.09 (0.04, 0.20) | ||
| 88 (22.4) | 0.13 (0.07, 0.19) | 0.19 (0.12, 0.31) | 0.06 (0.01, 0.13) | 0.09 (0.04, 0.22) | |||
| Missing | 0 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Smoking status | |||||||
| Never | 285 (72.9) | 0.12 (0.06, 0.22) | 0.22 (0.11, 0.38) | Ref | 0.06 (0.02, 0.13) | 0.11 (0.04, 0.22) | Ref |
| Former | 89 (22.8) | 0.10 (0.05, 0.22) | 0.17 (0.10, 0.38) | 0.52 | 0.04 (0.01, 0.09) | 0.07 (0.03, 0.15) | 0.04 |
| Current | 17 (4.3) | 0.11 (0.05, 0.21) | 0.17 (0.09, 0.33) | 0.60 | 0.05 (0.02, 0.14) | 0.09 (0.03, 0.26) | 0.59 |
| Missing | 1 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Alcohol (drinks/wk) | |||||||
| None | 107 (27.4) | 0.12 (0.06, 0.22) | 0.22 (0.11, 0.48) | Ref | 0.05 (0.02, 0.11) | 0.08 (0.04, 0.22) | Ref |
| 1 or fewer | 161 (41.2) | 0.12 (0.05, 0.24) | 0.19 (0.09, 0.37) | 0.14 | 0.06 (0.01, 0.12) | 0.08 (0.03, 0.18) | 0.49 |
| 2–6 | 72 (18.4) | 0.14 (0.07, 0.19) | 0.23 (0.14, 0.41) | 0.92 | 0.06 (0.03, 0.12) | 0.13 (0.04, 0.24) | 0.64 |
| 7 or more | 51 (13.0) | 0.10 (0.05, 0.21) | 0.16 (0.12, 0.25) | 0.17 | 0.07 (0.03, 0.15) | 0.12 (0.06, 0.21) | 0.16 |
| Missing | 1 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Organic eating | |||||||
| Seldom/Never | 124 (31.7) | 0.14 (0.07, 0.23) | 0.21 (0.13, 0.38) | Ref | 0.07 (0.03, 0.13) | 0.12 (0.05, 0.23) | Ref |
| Sometimes | 114 (29.2) | 0.12 (0.05, 0.24) | 0.19 (0.11, 0.38) | 0.47 | 0.06 (0.02, 0.13) | 0.10 (0.04, 0.25) | 0.44 |
| Often/Always | 153 (39.1) | 0.10 (0.06, 0.20) | 0.19 (0.09, 0.38) | 0.05 | 0.04 (0.01, 0.11) | 0.07 (0.03, 0.18) | 0.01 |
| Missing | 1 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| HEI | |||||||
| Quartile 1 | 93 (25.1) | 0.13 (0.07, 0.22) | 0.22 (0.13, 0.37) | 0.99 | 0.07 (0.02, 0.12) | 0.12 (0.05, 0.22) | 0.03 |
| Quartile 2 | 93 (25.1) | 0.10 (0.05, 0.19) | 0.19 (0.09, 0.35) | 0.07 (0.02, 0.13) | 0.13 (0.04, 0.26) | ||
| Quartile 3 | 92 (24.8) | 0.11 (0.06, 0.22) | 0.17 (0.10, 0.41) | 0.05 (0.02, 0.12) | 0.08 (0.04, 0.16) | ||
| Quartile 4 | 93 (25.1) | 0.12 (0.06, 0.25) | 0.24 (0.11, 0.54) | 0.04 (, 0.12) | 0.06 (0.03, 0.21) | ||
| Missing | 21 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Physical activity | |||||||
| min/wk | 153 (40.7) | 0.10 (0.05, 0.24) | 0.19 (0.09, 0.38) | 0.03 | 0.05 (0.01, 0.11) | 0.08 (0.04, 0.19) | 0.08 |
| min/wk | 223 (59.3) | 0.13 (0.07, 0.22) | 0.22 (0.12, 0.41) | 0.06 (0.02, 0.13) | 0.11 (0.04, 0.23) | ||
| Missing | 16 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Herbicide use (past week) | |||||||
| Yes | 21 (8.5) | 0.14 (0.08, 0.20) | 0.22 (0.11, 0.44) | 0.61 | 0.04 (, 0.11) | 0.11 (0.04, 0.16) | 0.39 |
| No | 227 (91.5) | 0.12 (0.06, 0.24) | 0.21 (0.11, 0.38) | 0.06 (0.02, 0.12) | 0.10 (0.03, 0.20) | ||
| Missing | 144 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
Note: -Values are from linear regression with the natural logarithm of glyphosate or AMPA as outcome, adjusted for urinary creatinine. LOD: for glyphosate and for AMPA. Values of glyphosate or AMPA were substituted with . Age, BMI, and HEI were evaluated as continuous variables; results were comparable when evaluated as categorical variables. —, no data; AMPA, aminomethylphosphonic acid; BMI, body mass index; HEI, Healthy Eating Index; LOD, limit of detection; min, minutes; NA, not applicable; Ref, reference.
Women who reported “often or always” eating organic food had lower glyphosate [median (interquartile range, IQR) 0.10 (0.06, 0.20) ng/mL compared with 0.14 (0.07, 0.23) ng/mL for “seldom or never,” ] and AMPA [median (IQR) 0.04 (0.01, 0.11) ng/mL compared with 0.07 (0.03, 0.13) ng/mL for “seldom or never,” ]. Lower diet quality was associated with elevated AMPA [median (IQR) 0.07 (0.02, 0.12) ng/mL for highest quartile of diet quality vs. 0.04 (, 0.12) ng/mL for lowest quartile, ], but not glyphosate (). Those who met the Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans ( of moderate-intensity exercise per week) had lower glyphosate [median (IQR) 0.10 (0.05, 0.24) ng/mL for those meeting guidelines vs. 0.13 (0.07, 0.22) for those not meeting, ]. Former smokers had marginally lower AMPA concentrations in comparison with never smokers [median (IQR) 0.04 (0.01, 0.09) ng/mL vs. 0.06 (0.02, 0.13) ng/mL, ]. Women in the “Other” race/ethnicity category had lower concentrations of both glyphosate [median (IQR) 0.07 (0.04, 0.13) vs. 0.12 (0.06, 0.24) ng/mL, ] and AMPA [median (IQR) 0.02 (0.01, 0.05) vs. 0.05 (0.02, 0.12) ng/mL, ] in comparison with White women, although there were only 20 women in the “Other” category. None of the other variables examined (age, BMI, alcohol consumption, or herbicide use) were associated with urinary glyphosate or AMPA.
DNA Methylation Analysis
Each of the three epigenetic clocks (Hannum, Horvath, and Levine) was well-correlated with chronologic age (Pearson’s , 0.64, and 0.54, respectively), although the Hannum and Levine clocks were poorly calibrated in this sample (Figure S4). Glyphosate was not significantly associated with differences in epigenetic age acceleration according to any of the epigenetic clocks (Table 2). AMPA was associated with increased epigenetic age acceleration according to the Hannum clock [adjusted coefficient 0.36 y; 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.03, 0.70, ]. AMPA was also associated with increased epigenetic age acceleration according to the Horvath clock in the adjusted model (adjusted coefficient 0.41; 95% CI: 0.02, 0.80, ) but not the univariate model (); the opposite was true for the Levine clock (univariate coefficient 0.61; 95% CI: 0.04, 1.18, ; adjusted ). Epigenetic pace of aging according to DunedinPoAm was not significantly associated with glyphosate or AMPA concentration (Table 2).
Table 2.
Association of epigenetic age acceleration from three epigenetic clocks with urinary glyphosate and AMPA concentration in 392 postmenopausal California women.
| Glyphosate | AMPA | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient (95% CI) | -Value | Adjusted | Coefficient (95% CI) | -Value | Adjusted | |
| Univariate | ||||||
| Hannum | 0.08 (, 0.44) | 0.64 | 0.0058 | 0.35 (0.03, 0.67) | 0.03 | 0.017 |
| Horvath | ( , 0.21) | 0.39 | 0.21 ( , 0.56) | 0.24 | ||
| Levine | 0.34 (, 0.97) | 0.30 | 0.61 (0.04, 1.18) | 0.04 | 0.0061 | |
| DunedinPoAm | 0.08 (, 0.17) | 0.11 | 0.016 | 0.04 (, 0.13) | 0.36 | 0.011 |
| Adjusted, no WBC types | ||||||
| Hannum | (, 0.16) | 0.24 | 0.056 | 0.43 (0.07, 0.80) | 0.02 | 0.056 |
| Horvath | (, 0.07) | 0.10 | 0.037 | 0.40 (0.001, 0.79) | 0.0499 | 0.037 |
| Levine | 0.02 (, 0.72) | 0.97 | 0.047 | 0.49 (, 1.14) | 0.14 | 0.047 |
| DunedinPoAm | 0.08 (, 0.18) | 0.09 | 0.25 | 0.02 (, 0.11) | 0.64 | 0.25 |
| Adjusted, with WBC types | ||||||
| Hannum | (, 0.15) | 0.24 | 0.22 | 0.36 (0.03, 0.70) | 0.04 | 0.22 |
| Horvath | (, 0.10) | 0.13 | 0.075 | 0.41 (0.02, 0.80) | 0.04 | 0.075 |
| Levine | 0.03 (, 0.66) | 0.93 | 0.26 | 0.30 (, 0.88) | 0.32 | 0.26 |
| DunedinPoAm | 0.07 (, 0.16) | 0.11 | 0.39 | 0.01 (, 0.09) | 0.85 | 0.39 |
Note: Coefficients are from linear regression with epigenetic age acceleration (years) from the Hannum, Horvath, and Levine epigenetic clocks or DunedinPoAm (z-score) as the dependent variable and the natural logarithm of glyphosate or AMPA concentration as the independent variable, adjusted for urinary creatinine. The adjusted model is additionally adjusted for age, race/ethnicity, body mass index, smoking status, alcohol consumption, self-reported organic eating habits, diet quality (Healthy Eating Index), batch, and position on chip. The adjusted model with WBC types is additionally adjusted for WBC type proportions estimated via Houseman’s method. Glyphosate and AMPA concentrations are averaged for two urine samples collected within approximately 10 d of each other. Missing data for covariates (from individuals) were substituted with the median (numeric variables) or mode (categorical variables). AMPA, aminomethylphosphonic acid; CI, confidence interval; WBC, white blood cell.
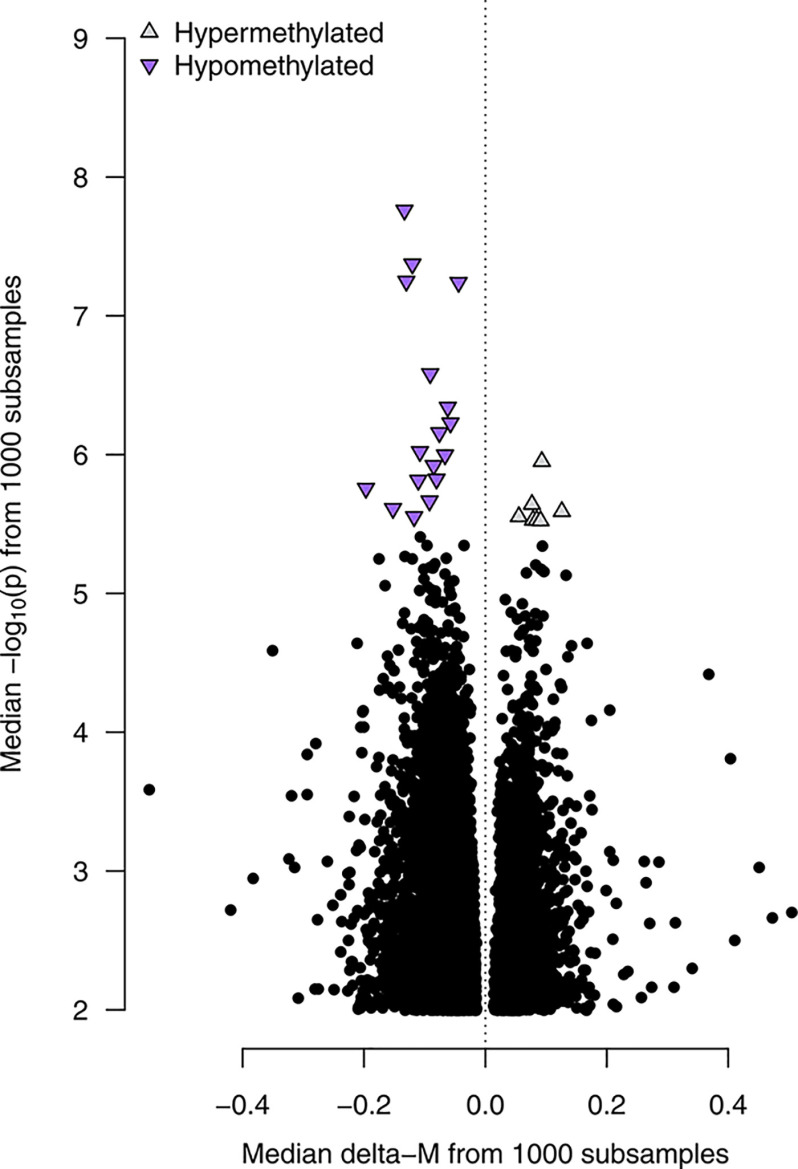
Twenty-four probes associated with urinary glyphosate concentration and two with urinary AMPA were identified in of subsamples and considered differentially methylated (Table 3). Seventeen of the 24 probes (71%) were hypomethylated with higher glyphosate (Figure 1), whereas both AMPA-associated probes were hypermethylated (Table 3). Glyphosate-associated probes with the smallest median -values were located within the PEX26, SF3B2, and CHMP1A genes. The largest methylation difference between glyphosate tertiles were observed in probes within the VMO1, KCP, and QARS1 genes. Our findings were robust to changes in the analysis approach: All glyphosate- and AMPA-associated DMPs were statistically significant (FDR ) using a traditional epigenome-wide association analysis with the entire training set, except for one AMPA-associated DMP (cg23261070, ).
Table 3.
Differentially methylated probes (DMPs) associated with urinary glyphosate and AMPA concentration in 332 postmenopausal California women.
| Probe | Freq. | Median -value | Median FDR -value | Methylation () difference per unit glyphosate/AMPA | Chr. | Position (hg19) | Gene(s) | Gene summary | Location within gene(s) | CpG Island | Predicted chromatin state |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glyphosate | |||||||||||
| cg13499896 | 1,000 | 0.006 | 22 | 18,571,657 | PEX26 | Probably required for protein import into peroxisomes. | 3’UTR | Open Sea | Strong enhancer | ||
| cg24576174 | 1,000 | 0.010 | 11 | 65,828,083 | SF3B2 | Involved in pre-mRNA splicing as a component of the splicing factor SF3B complex. | Body | Open Sea | Transcription elongation | ||
| cg00355690 | 996 | 0.011 | 16 | 89,722,417 | CHMP1A | Involved in multivesicular body sorting of proteins to the interiors of lysosome. Involved in cytokinesis. May also be involved in chromosome condensation. May play a role in stable cell cycle progression and in PcG gene silencing. | Body | N. Shore | Weak enhancer | ||
| cg26833395 | 1,000 | 0.012 | 20 | 30,102,102 | HM13 | Plays a key role in generating signal sequence-derived human lymphocyte antigen-E epitopes that are recognized by the immune system. | Promoter | Island | Weak promoter | ||
| cg06993862 | 987 | 0.023 | 3 | 49,141,001 | QARS1 | Plays a critical role in brain development. | Body | N. Shore | Strong enhancer | ||
| cg13310154 | 978 | 0.029 | 17 | 55,910,843 | — | — | Intergenic | Open Sea | Insulator | ||
| cg16601151 | 959 | 0.031 | 16 | 19,079,341 | COQ7 | Involved in ubiquinone biosynthesis. Involved in lifespan determination in a ubiquinone-independent manner. | Body | Island | Active promoter | ||
| cg26787244 | 965 | 0.034 | 11 | 644,011 | — | — | Intergenic | Island | Weak transcribed | ||
| cg07261978 | 950 | 0.038 | 8 | 82,043,566 | — | — | Intergenic | Open Sea | Weak enhancer | ||
| cg19029576 | 954 | 0.040 | 9 | 140,330,686 | ENTPD8 | Plays a central role in concentration of extracellular nucleotides. | Body | Island | Weak transcribed | ||
| cg25629796 | 971 | 0.041 | 0.35 | 17 | 11,940,467 | MAP2K4 | Member of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) family, which is involved in a wide variety of cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, transcription regulation, and development. | Body | Open Sea | Weak transcribed | |
| cg01430385 | 954 | 0.042 | 10 | 1,033,349 | GTPBP4 | Involved in the biogenesis of the 60S ribosomal subunit. | Promoter | N. Shore | Active promoter | ||
| cg02519806 | 948 | 0.045 | 4 | 119,810,036 | SYNPO2 | Has an actin-binding and actin-bundling activity. Involved in regulation of cell migration; may be a tumor suppressor. | Promoter | Open Sea | Poised promoter | ||
| cg04915788 | 959 | 0.044 | 12 | 25,156,888 | — | — | Intergenic | Open Sea | Weak enhancer | ||
| cg13170005 | 957 | 0.048 | 17 | 4,690,632 | VMO1 | Unknown function, homolog of a gene that encodes component of the outer membrane of the vitelline layer of the egg in chickens. | Promoter | N. Shore | Repressed | ||
| cg26483235 | 938 | 0.050 | 8 | 62,870,065 | — | — | Intergenic | Open Sea | Heterochromatin | ||
| cg07318309 | 913 | 0.051 | 0.19 | 5 | 156,537,633 | HAVCR2 | Cell surface receptor implicated in modulating innate and adaptive immune responses | Promoter | Open Sea | Weak enhancer | |
| cg07509511 | 913 | 0.051 | 2 | 65,297,852 | CEP68 | Involved in maintenance of centrosome cohesion | Body | Open Sea | Transcription elongation | ||
| cg11062848 | 913 | 0.052 | 2.08 | 6 | 13,616,537 | NOL7 | Maintains nucleolar structure and cell growth rates; also functions as a tumor suppressor and regulator of angiogenesis. Expression regulated by the RB tumor suppressor gene. | Body | S. Shore | Active promoter | |
| cg18722557 | 917 | 0.054 | 0.23 | 10 | 123,734,694 | NSMCE4A | Component of a complex involved in DNA double-strand breaks by homologous recombination. Required for telomere maintenance via recombination in ALT (alternative lengthening of telomeres) cell lines. | Promoter | Island | Active promoter | |
| cg20531550 | 923 | 0.054 | 7 | 128,550,902 | KCP | Enhances bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling in a paracrine manner. | Promoter | Island | Weak transcribed | ||
| cg05730283 | 933 | 0.055 | 0.42 | 2 | 62,422,808 | B3GNT2 | Probably constitutes the main polylactosamine synthase | Promoter | Island | Active promoter | |
| cg20540608 | 901 | 0.053 | 1.53 | 5 | 60,241,003 | NDUFAF2; ERCC8 | NDUFAF2: Acts as a molecular chaperone for mitochondrial complex I assembly. ERCC8: Plays a role in DNA single-strand and double-strand breaks (DSSBs) repair; involved in repair of DSSBs by nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ) | Promoter | Island | Active promoter | |
| cg25597976 | 929 | 0.055 | 1.05 | 8 | 74,750,772 | UBE2W | Promotes the ubiquitination of Fanconi anemia complementation group proteins and may be important in the repair of DNA damage | Body | Open Sea | Weak enhancer | |
| AMPA | |||||||||||
| cg22171277 | 938 | 0.038 | 0.32 | 2 | 70,363,119 | — | — | Intergenic | Open Sea | Strong enhancer | |
| cg23261070 | 946 | 0.041 | 0.13 | 17 | 6,918,037 | C17orf49 | Component of chromatin complexes such as the MLL1/MLL and NURF complexes | Promoter | Island | Active promoter | |
Note: Linear models adjusted for urinary creatinine, age, race/ethnicity, BMI, smoking status, alcohol consumption, self-reported organic eating habits, diet quality (HEI), estimated WBC type proportions, batch, and position on chip, were fitted for all probes on the Illumina HumanMethylationEPIC array which remained after quality filtering. Results were pooled from 1,000 random subsamples of the training set (individuals per subsample). Probes that were statistically significant with FDR in 90% or more subsamples were considered differentially methylated. Missing data for covariates (from individuals in the training set) were substituted with the median (numeric variables) or mode (categorical variables). Chromatin state is predicted by ChromHMM from ENCODE data for the GM12878 cell line. Gene summaries are condensed from the RefSeq and UniProt gene summaries and provide a broad overview of the known function(s) of the gene product. —, no data; AMPA, aminomethylphosphonic acid; BMI, body mass index; Chr, Chromosome; FDR, false discovery rate; Freq., number of iterations in which DMP was identified as significant; HEI, Healthy Eating Index; WBC, white blood cell.
Figure 1.
Results from probe-level differential methylation analysis for urinary glyphosate in 332 postmenopausal California women. The volcano plot shows delta-M (difference in methylation M value for a 1-unit increase in the natural log of glyphosate) on the horizontal axis and on the vertical axis. Linear models adjusted for urinary creatinine, age, race/ethnicity, BMI, smoking status, alcohol consumption, self-reported organic eating habits, diet quality (Healthy Eating Index), estimated WBC type proportions, batch, and position on chip, were fitted for all probes on the Illumina HumanMethylationEPIC array, which remained after quality filtering. Results were pooled from 1,000 random subsamples of the training set ( individuals per subsample). Probes that were statistically significant with FDR in 90% or more subsamples are marked as hypermethylated or hypomethylated. Note: BMI, body mass index; FDR, false discovery rate; WBC, white blood cell.
Biological and functional analyses were performed on only glyphosate-associated probes because there were only two AMPA-associated probes (Figure 2). In comparison with all other probes on the array, a greater proportion of glyphosate-associated DMPs were located within CpG islands (33.3% vs. 19.2%), although this difference was not statistically significant (Fisher ). Glyphosate-associated DMPs were significantly enriched for enhancer regions (29.2% vs. 12.6%, Fisher ) and depleted for inactive/heterochromatin regions (4.2% vs. 36.8%, Fisher ). Three gene ontology terms were enriched in the 20 annotated genes containing glyphosate-associated probes: DNA metabolic process (biological process), intracellular organelle part (cellular component), and organelle part (cellular component), all with . No KEGG or IPA pathways were enriched in glyphosate-associated genes.
Figure 2.
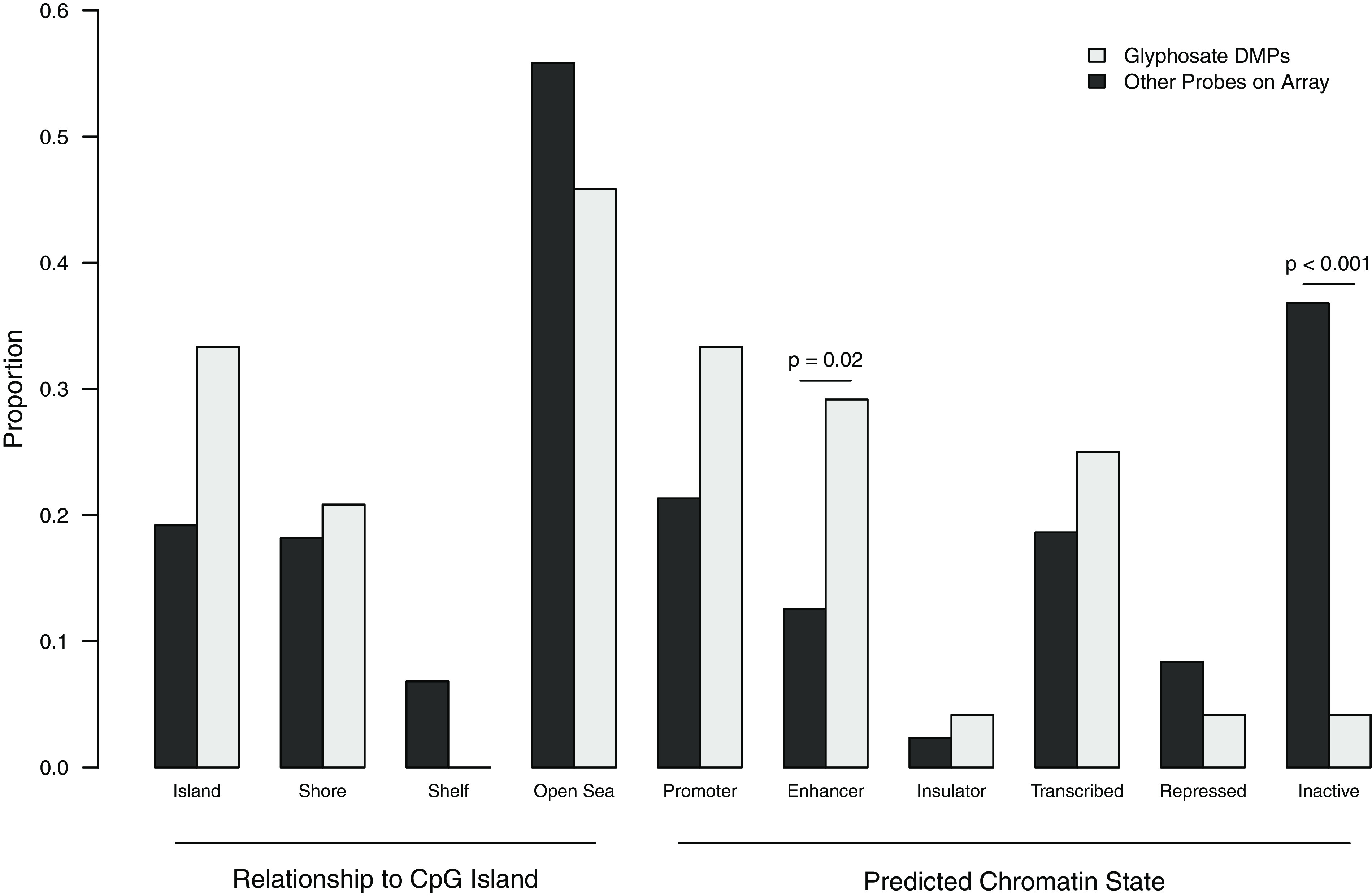
Enrichment analysis for genomic context of glyphosate-associated differentially methylated probes (DMPs) identified in 332 postmenopausal California women. The proportions of glyphosate-associated DMPs compared to other probes on the array in each genomic context were compared with Fisher’s exact test; significant () -values are labeled.
Four regions for glyphosate and none for AMPA were significant in of subsamples and considered differentially methylated (Table 4). Three regions were significantly associated with AMPA at a relaxed threshold of of subsamples and are also included in Table 4. The glyphosate-associated regions were all located within gene promoters. Three were hypomethylated with greater glyphosate (MSH4, KCNA6, and ABAT), and the other was hypermethylated (NDUFAF2/ERCC8). The top AMPA-associated regions were all hypomethylated. Two were located within gene bodies (RNF39, TRIM31) and one within a gene promoter (ESR1).
Table 4.
Differentially methylated regions (DMRs) associated with urinary glyphosate and AMPA concentration in 332 postmenopausal California women.
| Chr. | Region start (hg19) | Region end (hg19) | Width (bases) | Number of CpGs in region | Freq. | Combined FDR q-value | Average methylation () difference per unit glyphosate/AMPA for probes in region | Gene(s) | Gene summary | Location within gene(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glyphosate | ||||||||||
| 1 | 76,262,302 | 76,262,984 | 682 | 9 | 979 | 0.023 | MSH4 | Member of the DNA mismatch repair mutS family. Meiosis-specific protein that is required for reciprocal recombination and proper segregation of homologous chromosomes at meiosis I | Promoter | |
| 5 | 60,240,926 | 60,241,324 | 398 | 5 | 918 | 0.074 | 0.58 | NDUFAF2; ERCC8 | NDUFAF2: Acts as a molecular chaperone for mitochondrial complex I assembly. ERCC8: Plays a role in DNA single-strand and double-strand breaks (DSSBs) repair; involved in repair of DSSBs by nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ) | Promoter |
| 12 | 4,918,169 | 4,919,230 | 1061 | 10 | 976 | 0.011 | KCNA6 | Voltage-gated potassium channel that mediates transmembrane potassium transport in excitable membranes | Promoter | |
| 16 | 8,806,359 | 8,806,756 | 397 | 9 | 925 | 0.034 | ABAT | Responsible for catabolism of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), an important, mostly inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system, into succinic semialdehyde | Promoter | |
| AMPA | ||||||||||
| 6 | 30,039,380 | 30,039,524 | 144 | 8 | 606 | 0.42 | RNF39 | Lies within the major histocompatibility complex class I region on chromosome 6. Rat studies suggest that this gene encodes a protein that plays a role in an early phase of synaptic plasticity. | Body | |
| 6 | 30,071,496 | 30,071,612 | 116 | 5 | 636 | 0.025 | TRIM31 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase. Shows altered expression in certain tumors and may be a negative regulator of cell growth. | Body | |
| 6 | 152,126,736 | 152,126,938 | 202 | 5 | 616 | 0.030 | ESR1 | Estrogen receptor and ligand-activated transcription factor. Regulates the transcription of many estrogen-inducible genes that play a role in growth, metabolism, sexual development, gestation, and other reproductive functions and is expressed in many non-reproductive tissues. The receptor encoded by this gene plays a key role in breast cancer, endometrial cancer, and osteoporosis. | Promoter | |
Note: Linear models adjusted for urinary creatinine, age, race/ethnicity, BMI, smoking status, alcohol consumption, self-reported organic eating habits, diet quality (HEI), estimated WBC type proportions, batch, and position on chip, were fitted for all probes on the Illumina HumanMethylationEPIC array which remained after quality filtering. Results were pooled from 1,000 random subsamples of the training set ( individuals per subsample). Regions that were statistically significant with FDR in 90% or more subsamples were considered differentially methylated. Overlapping regions were combined, and FDR q-values were combined for all CpGs in region by Stouffer’s method. Missing data for covariates (from individuals in the training set) were substituted with the median (numeric variables) or mode (categorical variables). Gene summaries are condensed from the RefSeq and UniProt gene summaries and provide a broad overview of the known function(s) of the gene product. AMPA, aminomethylphosphonic acid; BMI, body mass index; Chr. Chromosome; FDR, false discovery rate; Freq., number of iterations out of 1,000 in which DMR was identified as significant; HEI, Healthy Eating Index; WBC, white blood cell.
Methylation Index
All 24 DMPs were selected by the elastic net for inclusion in the final glyphosate methylation index (Table S4). The index was significantly correlated with urinary glyphosate in the training (Pearson’s ; 95% CI: 0.55, 0.68, ; Figure 3A) and validation (; 95% CI: 0.10, 0.55, ; Figure 3B) sets. In the validation set, the methylation index was significantly associated with glyphosate tertile [median (IQR) ( to ) for lowest tertile vs. ( to ) for highest tertile, ANOVA ; Figure 3C] and showed excellent discrimination between the top and bottom tertiles of urinary glyphosate (, 95% CI: 0.57, 0.90; Figure 3D). A modified index trained using only probes included on the HumanMethylation450 BeadChip (the previous version of the Illumina methylation array), which selected 14 probes in the final model, achieved similar performance (Figure S5). The AMPA index was not significantly correlated with urinary AMPA in either the training or validation set (Figure S6).
Figure 3.
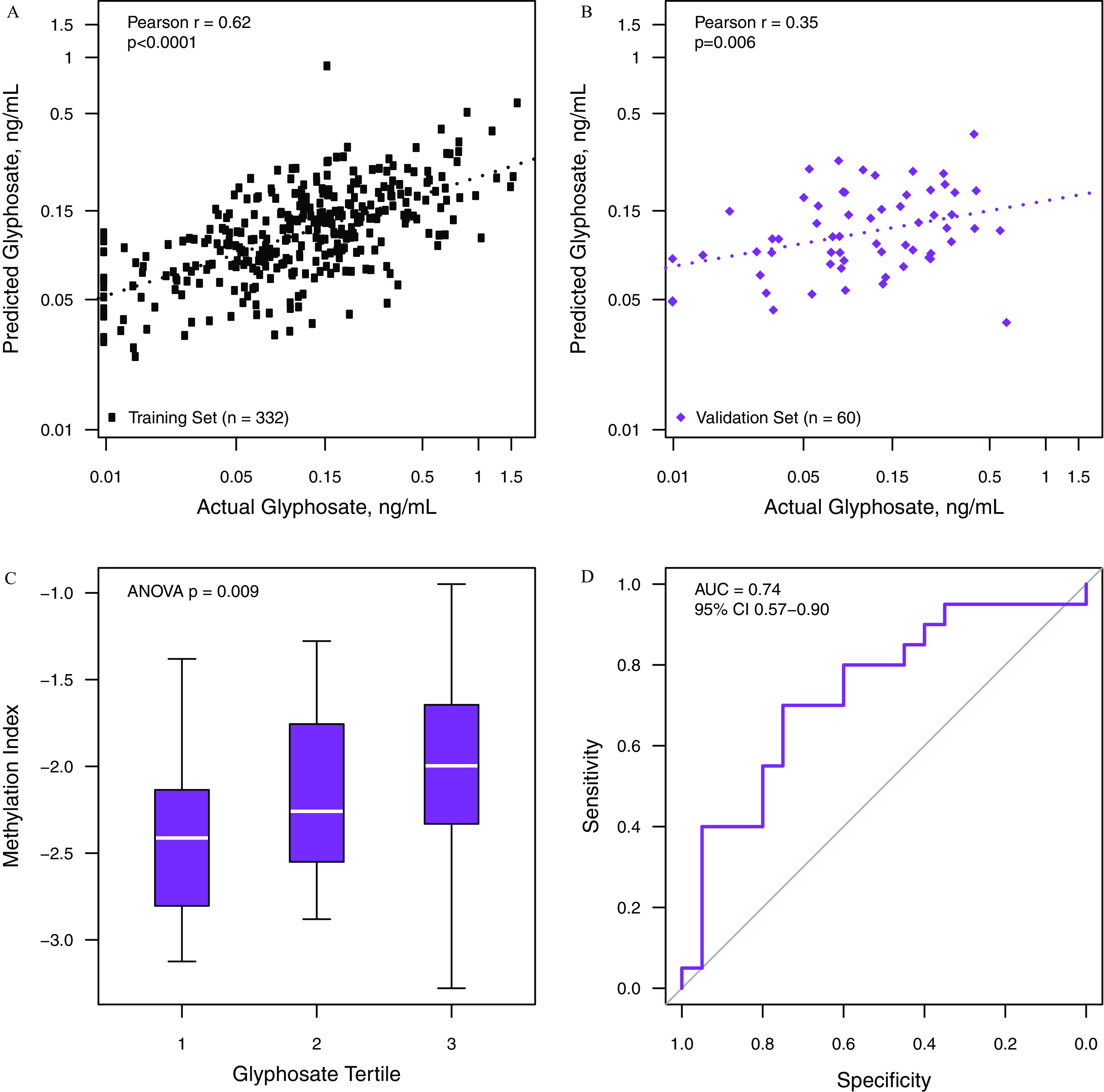
Performance of methylation index using 24 CpG sites to predict the natural logarithm of urinary glyphosate concentration in the training set (A) and the validation set (B, C). Panel C shows the methylation index was significantly associated with glyphosate tertile [median (IQR) ( to for lowest tertile vs. ( to ) for highest tertile, ANOVA ] in the validation set. Panel D shows the classification performance of the methylation index in the validation set for classifying the highest vs. the lowest tertile of urinary glyphosate. The index was developed using elastic net regression on methylation values of differentially methylated probes associated with glyphosate in the training set, a population of 332 postmenopausal California women. Note: ANOVA, analysis of variance; IQR, interquartile range.
Discussion
To our knowledge, this is the first study examining associations between urinary glyphosate and AMPA levels and DNA methylation. Higher AMPA, but not glyphosate, was associated with greater epigenetic age acceleration, a phenomenon which has previously been linked to the risk of all-cause mortality56,57,58 and cancer.59,60,94 We identified 24 CpG sites whose methylation was associated with glyphosate and two associated with AMPA. Four regions were associated with glyphosate, within the promoters of MSH4, KCNA6, ABAT, and NDUFAF2/ERCC8, and we found an association between ESR1 promoter hypomethylation and elevated AMPA. Finally, using 24 CpG sites, we developed a methylation index that was significantly associated with glyphosate concentration in an internal validation set. The AMPA index was not significantly associated with urinary AMPA in either set, likely due to the use of only two DMPs for prediction.
The significant and replicable differential DNA methylation associated with urinary glyphosate and AMPA informs the hypothesis that these compounds may have biological effects in humans, but the mechanisms by which glyphosate and AMPA could impact human health remain unclear. Although humans and other animals do not possess the shikimate pathway inhibited by glyphosate,95,96,97 conversion of glyphosate to AMPA has been observed in multiple types of bacteria.98 Previous studies have shown glyphosate-induced microbiome changes in honeybees,99,100 birds,101 and rats.24,25,26,27 Because the microbiome can have significant and wide-ranging impacts on human health,102 it is possible that glyphosate and/or AMPA could influence various aspects of human health via perturbations of the microbiome, changes that could be reflected in differential peripheral blood DNA methylation.103,104
In our study, AMPA was associated with epigenetic age acceleration, which has been previously associated with other environmental exposures61,62,63,64 and risk of many diseases, including breast cancer,59 B-cell lymphoma,60 lung cancer,96 obesity and metabolic syndrome,105,106,107 and all-cause mortality.56,57,58 The fact that this relationship was present only for AMPA supports the hypothesis that glyphosate and AMPA have distinct effects on the human body. This association was present for all epigenetic clocks considered (Hannum, Horvath, and Levine), although adjustment for age, race/ethnicity, BMI, smoking status, alcohol consumption, self-reported organic eating habits, and diet quality attenuated the relationship for the Levine clock, which incorporates phenotypic information and thus may be more influenced by these covariates. However, we observed no statistically significant relationship between epigenetic pace of aging and glyphosate or AMPA concentrations. Pace of aging aims to measure a distinct biological phenomenon in comparison with epigenetic age acceleration (rate of change of biological age vs. differences between chronological and biological age).
Furthermore, the genes whose methylation was associated with glyphosate and AMPA included those involved in various biological pathways related to cancer. SF3B2 is involved in RNA splicing and DNA repair108 and associated with various types of cancer.109,110,111 A germline mutation in the mismatch repair gene MSH4112 was described in a family with a high incidence of nervous system tumors.113 ERCC8 is also involved in DNA repair via transcription-coupled nucleotide excision repair and double-strand break repair.114,115,116 Hypomethylation at TRIM31, which has been shown to promote progression in a variety of tumor types,117,118,119 was associated with AMPA. The AMPA-associated hypomethylation at the ESR1 promoter is fascinating, given the potential link between AMPA and breast cancer risk23,32 and the potential for glyphosate-induced endocrine disruption.20 Perturbed expression of the ESR1 product in response to glyphosate exposure has been observed in in vitro studies of breast cancer cells.23 Rat studies have also demonstrated altered expression accompanying changes in promoter methylation.48,120 However, it should be noted that the relationship between AMPA and ESR1 promoter hypomethylation was only present after relaxing the original threshold for significance.
To our knowledge, this is also the largest report of urinary glyphosate and AMPA levels in the nonagricultural setting in the United States, complementing previous studies in the general population in other countries121,122,123 and in limited settings in the United States.11,12,124,125 The majority of women () had detectable glyphosate and AMPA in at least one urine sample, highlighting the near-ubiquitous exposure to these compounds, although the small convenience sample may not be representative of the general population. The levels observed among participants in our study (median of for glyphosate and for AMPA) were slightly lower than those previously reported, likely due to differences in the study population and detection assays. Our LC-MS/MS assay had a considerably higher analytic sensitivity (LOD/LOQ for glyphosate and for AMPA) than most assays previously described.126,127
This study used the most recent methylation array chip and best practices for methylation array data filtering, normalization, and analysis alongside a resampling-based approach intended to improve the stability and reproducibility of the results.88,89,90,91 We previously demonstrated that this method is capable of identifying differentially methylated sites associated with smoking with a minimal number of false positives in comparison with a traditional epigenome-wide association approach.86
However, the lack of an external validation cohort is a limitation of the study. To our knowledge, no other studies have measured both urinary glyphosate and AMPA and DNA methylation, so an external data set is not currently available. The successful performance of the methylation index for glyphosate concentration in the internal validation set suggests that the glyphosate-associated differential methylation may be replicated in other cohorts with a similar participant profile. Our study cohort consisted of postmenopausal women age 45–66 y, so results may not be generalizable to other populations or those residing outside California. The power of these analyses may be limited by the relatively low exposure levels in this population. A further limitation of our study is the lack of gene expression data. Without this, we cannot state whether the differential DNA methylation identified in our study translates to differences in gene expression that could confer functional impacts in the body, nor can we infer the temporal relationship between DNA methylation differences and glyphosate exposure, given the cross-sectional nature of the study. Finally, although we did not observe a relationship between recent herbicide use and glyphosate and AMPA concentrations, those data were missing for 37% of participants, which should be considered another limitation of the study.
DNA methylation is highly dependent on tissue type.128 Given the ambiguity of glyphosate’s impact on health and the systemic nature of exposure, blood likely represents the best available tissue at this time, especially considering its availability for epidemiological study. A major concern regarding the use of blood in epigenome-wide association studies is its heterogeneous cell composition, which may be impacted by disease states or exposure to pro-inflammatory compounds.129 However, we saw no evidence of differences in WBC composition by glyphosate or AMPA levels (Table S2), and all analyses were adjusted for these proportions.
In humans, glyphosate and AMPA have short half-lives of approximately 5–10 h,130,131 which makes accurate assessment of long-term exposure challenging. Our choice to use two spot urine samples from a 10-d period was intended to balance the need for a more complete picture of typical exposure with feasibility. The moderate between-sample ICCs of 0.53 for glyphosate and 0.34 for AMPA in our study participants highlight the pitfalls of relying on a single urine sample and suggest that more samples per individual may be needed to provide a better estimate of long-term exposure. However, because the dates of spot urine samples were not known in advance to the study participants, the glyphosate and AMPA measurements should reflect their usual habits.
This study identified differential DNA methylation associated with the herbicide glyphosate and its metabolite AMPA and developed a methylation index that accurately predicted urinary glyphosate concentration and tertile in an internal validation sample. Glyphosate- and AMPA-associated methylation occurred near genes associated with cancer (SF3B2,109,110,111 MSH4,113 and TRIM31117,118,119) and endocrine disruption (ESR1132), and AMPA was associated with greater epigenetic age acceleration. These results suggest that exposure to these common chemicals affects the epigenome, informing the hypothesis that glyphosate and/or AMPA exposure might elevate the risk for disease, including cancer. Further studies are warranted to replicate our results, determine the functional impact of glyphosate- and AMPA-associated differential DNA methylation, and explore whether DNA methylation could serve as a biomarker of long-term glyphosate exposure.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank our patient advocates (V. Lee, D. Heditsian, and S. Brain) as well as our undergraduate students (K. Yang, D. Thampy, A., D. Forman, M. Elyasian, and A. Kim) for supporting this study. We also thank our study participants and the Athena Breast Health Network for support of this study.
This work was supported by funds from the California Breast Cancer Research Grants Program Office of the University of California, Grant Number 22UB-2311. Support of the Athena Breast Health Network was provided by the Safeway Foundation, University of California Office of the President (UCOP), and Salesforce. This reported research includes work performed in the mass spectrometry core supported by the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health (NIH) under grant number P30CA033572. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the NIH.
Author contributions: Conceptualization: R.M.L., D.G., A.O.O., A.Z., T.M.N.K., H.L.P.; Data curation: R.M.L., W.H., H.L.P.; Formal analysis: R.M.L., W.H., K.V.P., M.M., V.D.D., A.Z., P.P., T.M.N.K.; Funding acquisition: D.G., A.O.O., A.Z., P.P., T.M.N.K., H.L.P.; Investigation: R.M.L., W.H., K.V.P., M.M., V.D.D., A.A., I.M., P.P., T.M.N.K., H.L.P.; Methodology: R.M.L., W.H., K.V.P., M.M., V.D.D., D.G., I.M., A.O.O., A.Z., P.P., T.M.N.K., H.L.P.; Project administration: R.M.L., A.A., I.M., P.P., H.L.P.; Resources: P.P., H.L.P.; Software: R.M.L., W.H., T.M.N.K.; Supervision: P.P., H.L.P.; Visualization: R.M.L.; Writing, original draft: R.M.L., H.L.P.; Writing, review and editing: all authors.
Data availability: All laboratory and clinical data used in this study are available from the authors on reasonable request. Data are not publicly available to protect participant privacy.
References
- 1.Benbrook CM. 2016. Trends in glyphosate herbicide use in the United States and globally. Environ Sci Eur 28(1):3, PMID: , 10.1186/s12302-016-0070-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Duke SO. 2020. Glyphosate: uses other than in glyphosate-resistant crops, mode of action, degradation in plants, and effects on non-target plants and agricultural microbes. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 255:1–65. PMID: , 10.1007/398_2020_53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Duke SO. 2018. The history and current status of glyphosate. Pest Manag Sci 74(5):1027–1034, PMID: , 10.1002/ps.4652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Myers JP, Antoniou MN, Blumberg B, et al. . 2016. Concerns over use of glyphosate-based herbicides and risks associated with exposures: a consensus statement. Environ Health 15:19, PMID: , 10.1186/s12940-016-0117-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Duke SO, Scheffler BE, Dayan FE, Dyer WE. 2002. Genetic engineering crops for improved weed management traits. ACS Symp Ser 829:52–66. 10.1021/bk-2002-0829.ch006. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kolakowski B, Miller L, Murray A, Leclair A, Bietlot H, van de Riet J. 2020. Analysis of glyphosate residues in foods from Canadian retail markets between 2015 and 2017. J Agric Food Chem 68(18):5201–5211, PMID: , 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b07819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.United States Department of Agriculture. 2013. Pesticide Data Program Annual Summary Reports, 2011 Summary. https://www.ams.usda.gov/sites/default/files/media/2011 PDP Annual Summary.pdf [accessed 10 August 2021].
- 8.Zoller O, Rhyn P, Rupp H, Zarn JA, Geiser C. 2018. Glyphosate residues in Swiss market foods: monitoring and risk evaluation. Food Addit Contam Part B Surveill 11(2):83–91, PMID: , 10.1080/19393210.2017.1419509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Medina-Pastor P, Triacchini G. 2020. The 2018 European union report on pesticide residues in food. EFSA J 18(4):1–103, PMID: , 10.2903/J.EFSA.2020.6057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 2017. Pesticide Residue Monitoring 2017 Report and Data. https://www.fda.gov/food/pesticides/pesticide-residue-monitoring-2017-report-and-data [accessed 10 August 2021].
- 11.Mills PJ, Kania-Korwel I, Fagan J, McEvoy LK, Laughlin GA, Barrett-Connor E. 2017. Excretion of the herbicide glyphosate in older adults between 1993 and 2016. J Am Med Assoc 318(16):1610–1611, PMID: , 10.1001/jama.2017.11726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lesseur C, Pirrotte P, Pathak KV, Manservisi F, Mandrioli D, Belpoggi F, et al. . 2021. Maternal urinary levels of glyphosate during pregnancy and anogenital distance in newborns in a US multicenter pregnancy cohort. Environ Pollut 280:117002, PMID: , 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Schütze A, Morales-Agudelo P, Vidal M, Calafat AM, Ospina M. 2021. Quantification of glyphosate and other organophosphorus compounds in human urine via ion chromatography isotope dilution tandem mass spectrometry. Chemosphere 274:129427, PMID: , 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Parvez S, Gerona RR, Proctor C, Friesen M, Ashby JL, Reiter JL, et al. . 2018. Glyphosate exposure in pregnancy and shortened gestational length: a prospective Indiana birth cohort study. Environ Health 17(1):23, PMID: , 10.1186/s12940-018-0367-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Guyton KZ, Loomis D, Grosse Y, El Ghissassi F, Benbrahim-Tallaa L, Guha N, et al. . 2015. Carcinogenicity of tetrachlorvinphos, parathion, malathion, diazinon, and glyphosate. Lancet Oncol 16(5):490–491, PMID: , 10.1016/S1470-2045(15)70134-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Zhang L, Rana I, Shaffer RM, Taioli E, Sheppard L. 2019. Exposure to glyphosate-based herbicides and risk for non-Hodgkin lymphoma: a meta-analysis and supporting evidence. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res 781:186–206, PMID: , 10.1016/j.mrrev.2019.02.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Andreotti G, Koutros S, Hofmann JN, Sandler DP, Lubin JH, Lynch CF, et al. . 2018. Glyphosate use and cancer incidence in the Agricultural Health Study. J Natl Cancer Inst 110(5):509–516, PMID: , 10.1093/jnci/djx233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Rappazzo KM, Warren JL, Davalos AD, Meyer RE, Sanders AP, Brownstein NC, et al. . 2019. Maternal residential exposure to specific agricultural pesticide active ingredients and birth defects in a 2003–2005 North Carolina birth cohort. Birth Defects Res 111(6):312–323, PMID: , 10.1002/bdr2.1448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Piccoli C, Cremonese C, Koifman RJ, Koifman S, Freire C. 2016. Pesticide exposure and thyroid function in an agricultural population in Brazil. Environ Res 151:389–398, PMID: , 10.1016/j.envres.2016.08.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Muñoz JP, Bleak TC, Calaf GM. 2021. Glyphosate and the key characteristics of an endocrine disruptor: a review. Chemosphere 270:128619, PMID: , 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ingaramo P, Alarcón R, Muñoz-de-Toro M, Luque EH. 2020. Are glyphosate and glyphosate-based herbicides endocrine disruptors that alter female fertility? Mol Cell Endocrinol 518:110934, PMID: , 10.1016/j.mce.2020.110934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Mesnage R, Renney G, Séralini GE, Ward M, Antoniou MN. 2017. Multiomics reveal non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats following chronic exposure to an ultra-low dose of Roundup herbicide. Sci Rep 7(1):, PMID: , 10.1038/srep39328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Thongprakaisang S, Thiantanawat A, Rangkadilok N, Suriyo T, Satayavivad J. 2013. Glyphosate induces human breast cancer cells growth via estrogen receptors. Food Chem Toxicol 59:129–136, PMID: , 10.1016/j.fct.2013.05.057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Mao Q, Manservisi F, Panzacchi S, et al. . 2018. The Ramazzini Institute 13-week pilot study on glyphosate and Roundup administered at human-equivalent dose to Sprague Dawley rats: effects on the microbiome. Environ Heal 17(1):50, PMID: , 10.1186/s12940-018-0394-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Dechartres J, Pawluski JL, Gueguen M‐M, Jablaoui A, Maguin E, Rhimi M, et al. . 2019. Glyphosate and glyphosate-based herbicide exposure during the peripartum period affects maternal brain plasticity, maternal behaviour and microbiome. J Neuroendocrinol 31(9):e12731, PMID: , 10.1111/jne.12731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Tang Q, Tang J, Ren X, Li C. 2020. Glyphosate exposure induces inflammatory responses in the small intestine and alters gut microbial composition in rats. Environ Pollut 261:114129, PMID: , 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Mesnage R, Teixeira M, Mandrioli D, Falcioni L, Ducarmon QR, Zwittink RD, et al. . 2021. Use of shotgun metagenomics and metabolomics to evaluate the impact of glyphosate or Roundup MON 52276 on the gut microbiota and serum metabolome of Sprague-Dawley rats. Environ Health Perspect 129(1):017005–017015, PMID: , 10.1289/EHP6990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kurenbach B, Marjoshi D, Amábile-Cuevas CF, Ferguson GC, Godsoe W, Gibson P, et al. . 2015. Sublethal exposure to commercial formulations of the herbicides dicamba, 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid, and glyphosate cause changes in antibiotic susceptibility in Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium. mBio 6(2):e00009–e00015, PMID: , 10.1128/mBio.00009-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Woźniak E, Reszka E, Jabłońska E, Michałowicz J, Huras B, Bukowska B. 2021. Glyphosate and AMPA induce alterations in expression of genes involved in chromatin architecture in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (in vitro). Int J Mol Sci 22(6):2966, PMID: , 10.3390/ijms22062966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Martinez A, Al-Ahmad AJ. 2019. Effects of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid on an isogeneic model of the human blood-brain barrier. Toxicol Lett 304:39–49, PMID: , 10.1016/j.toxlet.2018.12.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Cheron M, Brischoux F. 2020. Aminomethylphosphonic acid alters amphibian embryonic development at environmental concentrations. Environ Res 190:109944, PMID: , 10.1016/j.envres.2020.109944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Franke AA, Li X, Shvetsov YB, Lai JF. 2021. Pilot study on the urinary excretion of the glyphosate metabolite aminomethylphosphonic acid and breast cancer risk: the Multiethnic Cohort study. Environ Pollut 277:116848, PMID: , 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Martin EM, Fry RC. 2018. Environmental influences on the epigenome: exposure- associated DNA methylation in human populations. Annu Rev Public Health 39(1):309–333, PMID: , 10.1146/annurev-publhealth-040617-014629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Park HL. 2020. Epigenetic biomarkers for environmental exposures and personalized breast cancer prevention. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(4):1181, PMID: , 10.3390/ijerph17041181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lu X, Fraszczyk E, van der Meer TP, van Faassen M, Bloks VW, Kema IP, et al. . 2020. An epigenome-wide association study identifies multiple DNA methylation markers of exposure to endocrine disruptors. Environ Int 144:106016, PMID: , 10.1016/j.envint.2020.106016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Curtis SW, Cobb DO, Kilaru V, Terrell ML, Kennedy EM, Marder ME, et al. . 2019. Exposure to polybrominated biphenyl (PBB) associates with genome-wide DNA methylation differences in peripheral blood. Epigenetics 14(1):52–66, PMID: , 10.1080/15592294.2019.1565590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Furlong MA, Paul KC, Yan Q, Chuang Y-H, Cockburn MG, Bronstein JM, et al. . 2020. An epigenome-wide association study of ambient pyrethroid pesticide exposures in California’s Central Valley. Int J Hyg Environ Health 229:113569, PMID: , 10.1016/j.ijheh.2020.113569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Lee MK, Xu C-J, Carnes MU, Nichols CE, Ward JM, Kwon SO, et al. . 2019. Genome-wide DNA methylation and long-term ambient air pollution exposure in Korean adults. Clin Epigenet 11(1):37, PMID: , 10.1186/s13148-019-0635-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Gondalia R, Baldassari A, Holliday KM, Justice AE, Méndez-Giráldez R, Stewart JD. et al. 2019. Methylome-wide association study provides evidence of particulate matter air pollution-associated DNA methylation. Environ Int 132:104723, PMID: , 10.1016/j.envint.2019.03.071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Sayols-Baixeras S, Fernández-Sanlés A, Prats-Uribe A, Subirana I, Plusquin M, Künzli N, Marrugat J, et al. . 2019. Association between long-term air pollution exposure and DNA methylation: the REGICOR study. Environ Res 176:108550, PMID: , 10.1016/j.envres.2019.108550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Shenker NS, Ueland PM, Polidoro S, van Veldhoven K, Ricceri F, Brown R, et al. . 2013. DNA methylation as a long-term biomarker of exposure to tobacco smoke. Epidemiology 24(5):712–716, PMID: , 10.1097/EDE.0b013e31829d5cb3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Teschendorff AE, Yang Z, Wong A, Pipinikas CP, Jiao Y, Jones A, et al. . 2015. Correlation of smoking-associated DNA methylation changes in buccal cells with DNA methylation changes in epithelial cancer. JAMA Oncol 1(4):476–485, PMID: , 10.1001/jamaoncol.2015.1053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Liu C, Marioni RE, Hedman ÅK, Pfeiffer L, Tsai P-C, Reynolds LM, et al. . 2018. A DNA methylation biomarker of alcohol consumption. Mol Psychiatry 23(2):422–433, PMID: , 10.1038/mp.2016.192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Zhang Y, Elgizouli M, Schöttker B, Holleczek B, Nieters A, Brenner H. 2016. Smoking-associated DNA methylation markers predict lung cancer incidence. Clin Epigenetics 8(1):127, PMID: , 10.1186/s13148-016-0292-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Jordahl KM, Phipps AI, Randolph TW, Tindle HA, Liu S, Tinker LF, et al. . 2019. Differential DNA methylation in blood as a mediator of the association between cigarette smoking and bladder cancer risk among postmenopausal women. Epigenetics 14(11):1065–1073, PMID: , 10.1080/15592294.2019.1631112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Woźniak E, Reszka E, Jabłońska E, Balcerczyk A, Broncel M, Bukowska B. 2020. Glyphosate affects methylation in the promoter regions of selected tumor suppressors as well as expression of major cell cycle and apoptosis drivers in PBMCs (in vitro study). Toxicol In Vitro 63:104736, PMID: , 10.1016/j.tiv.2019.104736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Ben Maamar M, Beck D, Nilsson EE, Kubsad D, Skinner MK. 2021. Epigenome-wide association study for glyphosate induced transgenerational sperm DNA methylation and histone retention epigenetic biomarkers for disease. Epigenetics 16(10):1150–1167, PMID: , 10.1080/15592294.2020.1853319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Gomez AL, Altamirano GA, Leturia J, Bosquiazzo VL, Muñoz-de-Toro M, Kass L. 2019. Male mammary gland development and methylation status of estrogen receptor alpha in Wistar rats are modified by the developmental exposure to a glyphosate-based herbicide. Mol Cell Endocrinol 481:14–25, PMID: , 10.1016/j.mce.2018.11.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Rossetti MF, Canesini G, Lorenz V, Milesi MM, Varayoud J, Ramos JG. 2021. Epigenetic changes associated with exposure to glyphosate-based herbicides in mammals. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 12:671991, PMID: , 10.3389/FENDO.2021.671991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Duforestel M, Nadaradjane A, Bougras-Cartron G, Briand J, Olivier C, Frenel J-S, et al. . 2019. Glyphosate primes mammary cells for tumorigenesis by reprogramming the epigenome in a TET3-dependent manner. Front Genet 10:885, PMID: , 10.3389/fgene.2019.00885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Hoang TT, Qi C, Paul KC, Lee M, White JD, Richards M, et al. . 2021. Epigenome-wide DNA methylation and pesticide use in the Agricultural Lung Health Study. Environ Health Perspect 129(9):097008, PMID: , 10.1289/EHP8928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Hannum G, Guinney J, Zhao L, Zhang L, Hughes G, Sadda S, et al. . 2013. Genome-wide methylation profiles reveal quantitative views of human aging rates. Mol Cell 49(2):359–367, PMID: , 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.10.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Horvath S. 2013. DNA methylation age of human tissues and cell types. Genome Biol 14(10):R115, PMID: , 10.1186/gb-2013-14-10-r115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Levine ME, Lu AT, Quach A, Chen BH, Assimes TL, Bandinelli S, et al. . 2018. An epigenetic biomarker of aging for lifespan and healthspan. Aging (Albany NY) 10(4):573–591, PMID: , 10.18632/aging.101414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Belsky DW, Caspi A, Arseneault L, Baccarelli A, Corcoran DL, Gao X, et al. . 2020. Quantification of the pace of biological aging in humans through a blood test, the DunedinPoAm DNA methylation algorithm. Elife 9:e54870, PMID: , 10.7554/eLife.54870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Perna L, Zhang Y, Mons U, Holleczek B, Saum KU, Brenner H. 2016. Epigenetic age acceleration predicts cancer, cardiovascular, and all-cause mortality in a German case cohort. Clin Epigenet 8(1):1–7, PMID: , 10.1186/s13148-016-0228-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Marioni RE, Shah S, McRae AF, Chen BH, Colicino E, Harris SE, et al. . 2015. DNA methylation age of blood predicts all-cause mortality in later life. Genome Biol 16(1):1–12, PMID: , 10.1186/s13059-015-0584-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Chen BH, Marioni RE, Colicino E, Peters MJ, Ward-Caviness CK, Tsai P-C, et al. . 2016. DNA methylation-based measures of biological age: meta-analysis predicting time to death. Aging (Albany NY) 8(9):1844–1865, PMID: , 10.18632/aging.101020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Kresovich JK, Xu Z, O’Brien KM, Weinberg CR, Sandler DP, Taylor JA. 2019. Methylation-based biological age and breast cancer risk. J Natl Cancer Inst 111(10):1051–1058, PMID: , 10.1093/jnci/djz020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Dugué PA, Bassett JK, Joo JE, Jung CH, Ming Wong E, Moreno-Betancur M, et al. . 2018. DNA methylation-based biological aging and cancer risk and survival: pooled analysis of seven prospective studies. Int J Cancer 142(8):1611–1619, PMID: , 10.1002/ijc.31189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Curtis SW, Cobb DO, Kilaru V, Terrell ML, Marder ME, Barr DB, et al. . 2019. Environmental exposure to polybrominated biphenyl (PBB) associates with an increased rate of biological aging. Aging (Albany NY) 11(15):5498–5517, PMID: , 10.18632/aging.102134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Gensous N, Garagnani P, Santoro A, Giuliani C, Ostan R, Fabbri C, et al. . 2020. One-year Mediterranean diet promotes epigenetic rejuvenation with country- and sex-specific effects: a pilot study from the NU-AGE project. GeroScience 42(2):687–701, PMID: , 10.1007/s11357-019-00149-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Lind PM, Salihovic S, Lind L. 2018. High plasma organochlorine pesticide levels are related to increased biological age as calculated by DNA methylation analysis. Environ Int 113:109–113, PMID: , 10.1016/j.envint.2018.01.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.White AJ, Kresovich JK, Keller JP, Xu Z, Kaufman JD, Weinberg CR, et al. . 2019. Air pollution, particulate matter composition and methylation-based biologic age. Environ Int 132:105071, PMID: , 10.1016/j.envint.2019.105071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Lucia RM, Huang WL, Alvarez A, Thampy D, Elyasian M, Hidajat A, et al. . 2020. Rationale, study design, and cohort characteristics for the Markers for Environmental Exposures (MEE) Study. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(5):1774, PMID: , 10.3390/ijerph17051774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW, Shi W, et al. . 2015. Limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res 43(7):e47, PMID: , 10.1093/nar/gkv007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Hornung RW, Reed LD. 1990. Estimation of average concentration in the presence of nondetectable values. Appl Occup Environ Hyg 5(1):46–51, 10.1080/1047322X.1990.10389587. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Dedeurwaerder S, Defrance M, Bizet M, Calonne E, Bontempi G, Fuks F. 2014. A comprehensive overview of Infinium HumanMethylation450 data processing. Brief Bioinform 15(6):929–941, PMID: , 10.1093/bib/bbt054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Zhou W, Laird PW, Shen H. 2017. Comprehensive characterization, annotation and innovative use of Infinium DNA methylation BeadChip probes. Nucleic Acids Res 45(4):e22, PMID: , 10.1093/nar/gkw967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Nordlund J, Bäcklin CL, Wahlberg P, Busche S, Berglund EC, Eloranta M-L, et al. . 2013. Genome-wide signatures of differential DNA methylation in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Genome Biol 14(9):r105, PMID: , 10.1186/gb-2013-14-9-r105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Fortin J-P, Triche TJ, Hansen KD. 2017. Preprocessing, normalization and integration of the Illumina HumanMethylationEPIC array with minfi. Bioinformatics 33(4):558–560, PMID: , 10.1093/bioinformatics/btw691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Teschendorff AE, Marabita F, Lechner M, Bartlett T, Tegner J, Gomez-Cabrero D, et al. . 2013. A beta-mixture quantile normalization method for correcting probe design bias in Illumina Infinium 450 k DNA methylation data. Bioinformatics 29(2):189–196, PMID: , 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Tian Y, Morris TJ, Webster AP, Yang Z, Beck S, Feber A, et al. . 2017. ChAMP: updated methylation analysis pipeline for Illumina BeadChips. Bioinformatics 33(24):3982–3984, PMID: , 10.1093/bioinformatics/btx513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Johnson WE, Li C, Rabinovic A. 2007. Adjusting batch effects in microarray expression data using empirical bayes methods. Biostatistics 8(1):118–127, PMID: , 10.1093/biostatistics/kxj037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Leek JT, Johnson WE, Parker HS, Jaffe AE, Storey JD. 2012. The sva package for removing batch effects and other unwanted variation in high-throughput experiments. Bioinformatics 28(6):882–883, PMID: , 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Houseman EA, Accomando WP, Koestler DC, Christensen BC, Marsit CJ, Nelson HH, et al. . 2012. DNA methylation arrays as surrogate measures of cell mixture distribution. BMC Bioinformatics 13(1):86, PMID: , 10.1186/1471-2105-13-86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Du P, Zhang X, Huang C-C, Jafari N, Kibbe WA, Hou L, et al. . 2010. Comparison of Beta-value and M-value methods for quantifying methylation levels by microarray analysis. BMC Bioinformatics 11(1):587, PMID: , 10.1186/1471-2105-11-587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Carja O, MacIsaac JL, Mah SM, Henn BM, Kobor MS, Feldman MW, et al. . 2017. Worldwide patterns of human epigenetic variation. Nat Ecol Evol 1(10):1577–1583, PMID: , 10.1038/s41559-017-0299-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Galanter JM, Gignoux CR, Oh SS, Torgerson D, Pino-Yanes M, Thakur N, et al. . 2017. Differential methylation between ethnic sub-groups reflects the effect of genetic ancestry and environmental exposures. Elife 6:e20532, PMID: , 10.7554/eLife.20532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Song M-A, Seffernick AE, Archer KJ, Mori KM, Park S-Y, Chang L, et al. . 2021. Race/ethnicity-associated blood DNA methylation differences between Japanese and European American women: an exploratory study. Clin Epigenet 13(1):1–13, PMID: , 10.1186/s13148-021-01171-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Curl CL, Beresford SAA, Fenske RA, Fitzpatrick AL, Lu C, Nettleton JA, et al. . 2015. Estimating pesticide exposure from dietary intake and organic food choices: the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA). Environ Health Perspect 123(5):475–483, PMID: , 10.1289/ehp.1408197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Piercy KL, Troiano RP, Ballard RM, Carlson SA, Fulton JE, Galuska DA, et al. . 2018. The physical activity guidelines for Americans. J Am Med Assoc 320(19):2020–2028, PMID: , 10.1001/jama.2018.14854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Subar AF, Kirkpatrick SI, Mittl B, Zimmerman TP, Thompson FE, Bingley C, et al. . 2012. The Automated Self-Administered 24-hour dietary recall (ASA24): a resource for researchers, clinicians, and educators from the National Cancer Institute. J Acad Nutr Diet 112(8):1134–1137, PMID: , 10.1016/j.jand.2012.04.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Krebs-Smith SM, Pannucci TE, Subar AF, Kirkpatrick SI, Lerman JL, Tooze JA, et al. . 2018. Update of the Healthy Eating Index: HEI-2015. J Acad Nutr Diet 118(9):1591–1602, PMID: , 10.1016/j.jand.2018.05.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Lucia RM, Huang W-L, Alvarez A, Masunaka I, Ziogas A, Goodman D, et al. . 2021. Association of mammographic density with blood DNA methylation. Epigenetics 1–16. PMID: 34116608, 10.1080/15592294.2021.1928994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Peters TJ, Buckley MJ, Statham AL, Pidsley R, Samaras K, Lord RV, et al. . 2015. De novo identification of differentially methylated regions in the human genome. Epigenetics Chromatin 8:6, PMID: , 10.1186/1756-8935-8-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.He Z, Yu W. 2010. Stable feature selection for biomarker discovery. Comput Biol Chem 34(4):215–225, PMID: , 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2010.07.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Michiels S, Koscielny S, Hill C. 2005. Prediction of cancer outcome with microarrays: a multiple random validation strategy. Lancet 365(9458):488–492, PMID: , 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)17866-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Ein-Dor L, Zuk O, Domany E. 2006. Thousands of samples are needed to generate a robust gene list for predicting outcome in cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(15):5923–5928, PMID: , 10.1073/pnas.0601231103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Qiu X, Xiao Y, Gordon A, Yakovlev A. 2006. Assessing stability of gene selection in microarray data analysis. BMC Bioinformatics 7:50, PMID: , 10.1186/1471-2105-7-50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Ernst J, Kellis M. 2017. Chromatin-state discovery and genome annotation with ChromHMM. Nat Protoc 12(12):2478–2492, PMID: , 10.1038/nprot.2017.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Phipson B, Maksimovic J, Oshlack A. 2016. MissMethyl: an R package for analyzing data from Illumina’s HumanMethylation450 platform. Bioinformatics 32(2):286–288, PMID: , 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Simon N, Friedman J, Hastie T, Tibshirani R. 2011. Regularization paths for Cox’s proportional hazards model via coordinate descent. J Stat Softw 39(5):1–13, PMID: , 10.18637/jss.v039.i05. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Levine ME, Hosgood HD, Chen B, Absher D, Assimes T, Horvath S. 2015. DNA methylation age of blood predicts future onset of lung cancer in the Women’s Health Initiative. Aging (Albany NY) 7(9):690–700, PMID: , 10.18632/aging.100809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Haslam E. 1993. Shikimic Acid: Metabolism and Metabolites. https://books.google.com/books/about/Shikimic_Acid.html?id=Y3wvAQAAIAAJ [accessed 14 May 2021].
- 96.Kishore GM, Shah DM. 1988. Amino acid biosynthesis inhibitors as herbicides. Annu Rev Biochem 57:627–663, PMID: , 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.003211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Cerdeira AL, Duke SO. 2006. The current status and environmental impacts of glyphosate-resistant crops. J Environ Qual 35(5):1633–1658, PMID: , 10.2134/jeq2005.0378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Van Eerd LL, Hoagland RE, Zablotowicz RM, Hall JC. 2003. Pesticide metabolism in plants and microorganisms. Weed Sci 51(4):472–495. [Google Scholar]
- 99.Blot N, Veillat L, Rouzé R, Delatte H. 2019. Glyphosate, but not its metabolite AMPA, alters the honeybee gut microbiota. PLoS One 14(4):e0215466, PMID: , 10.1371/journal.pone.0215466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Motta EVS, Raymann K, Moran NA. 2018. Glyphosate perturbs the gut microbiota of honey bees. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115(41):10305–10310, PMID: , 10.1073/pnas.1803880115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Ruuskanen S, Rainio MJ, Gómez-Gallego C, Selenius O, Salminen S, Collado MC, et al. . 2020. Glyphosate-based herbicides influence antioxidants, reproductive hormones and gut microbiome but not reproduction: a long-term experiment in an avian model. Environ Pollut 266(Part 1):115108, PMID: , 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Lynch SV, Pedersen O. 2016. The human intestinal microbiome in health and disease. N Engl J Med 375(24):2369–2379, PMID: , 10.1056/NEJMra1600266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Xiao C, Fedirko V, Beitler J, Bai J, Peng G, Zhou C, et al. . 2021. The role of the gut microbiome in cancer-related fatigue: pilot study on epigenetic mechanisms. Support Care Cancer 29(6):3173–3182, PMID: , 10.1007/s00520-020-05820-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Sobhani I, Bergsten E, Couffin S, Amiot A, Nebbad B, Barau C, et al. . 2019. Colorectal cancer-associated microbiota contributes to oncogenic epigenetic signatures. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116(48):24285–24295, PMID: , 10.1073/pnas.1912129116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Quach A, Levine ME, Tanaka T, Lu AT, Chen BH, Ferrucci L, et al. . 2017. Epigenetic clock analysis of diet, exercise, education, and lifestyle factors. Aging (Albany NY) 9(2):419–446, PMID: , 10.18632/aging.101168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.McCartney DL, Hillary RF, Stevenson AJ, Ritchie SJ, Walker RM, Zhang Q, et al. . 2018. Epigenetic prediction of complex traits and death. Genome Biol 19(1):136, PMID: , 10.1186/s13059-018-1514-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Nannini DR, Joyce BT, Zheng Y, Gao T, Liu L, Yoon G, et al. . 2019. Epigenetic age acceleration and metabolic syndrome in the coronary artery risk development in young adults study. Clin Epigenet 11(1):160, PMID: , 10.1186/s13148-019-0767-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Prados-Carvajal R, López-Saavedra A, Cepeda-García C, Jimeno S, Huertas P. 2018. Multiple roles of the splicing complex SF3B in DNA end resection and homologous recombination. DNA Repair (Amst) 66-67:11–23, PMID: , 10.1016/j.dnarep.2018.04.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Kawamura N, Nimura K, Saga K, Ishibashi A, Kitamura K, Nagano H, et al. . 2019. SF3B2-mediated RNA splicing drives human prostate cancer progression. Cancer Res 79(20):5204–5217, PMID: , 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-3965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Xu W, Huang H, Yu L, Cao L. 2015. Meta-analysis of gene expression profiles indicates genes in spliceosome pathway are up-regulated in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Med Oncol 32(4):96, PMID: , 10.1007/s12032-014-0425-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Sugimoto T, Seki N, Shimizu S, Kikkawa N, Tsukada J, Shimada H, et al. . 2009. The galanin signaling cascade is a candidate pathway regulating oncogenesis in human squamous cell carcinoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 48(2):132–142, PMID: , 10.1002/gcc.20626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Her C, Zhao N, Wu X, Tompkins JD. 2007. MutS homologues hMSH4 and hMSH5: diverse functional implications in humans. Front Biosci 12(3):905–911, PMID: , 10.2741/2112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Kim Y-H, Ohta T, Oh JE, Le Calvez-Kelm F, McKay J, Voegele C, et al. . 2014. TP53, MSH4, and LATS1 germline mutations in a family with clustering of nervous system tumors. Am J Pathol 184(9):2374–2381, PMID: , 10.1016/j.ajpath.2014.05.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Moslehi R, Tsao HS, Zeinomar N, Stagnar C, Fitzpatrick S, Dzutsev A. 2020. Integrative genomic analysis implicates ERCC6 and its interaction with ERCC8 in susceptibility to breast cancer. Sci Rep 10(1):21276, PMID: , 10.1038/s41598-020-77037-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Wu Z, Zhu X, Yu Q, Xu Y, Wang Y. 2019. Multisystem analyses of two Cockayne syndrome associated proteins CSA and CSB reveal shared and unique functions. DNA Repair (Amst) 83:102696, PMID: , 10.1016/j.dnarep.2019.102696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Pascucci B, Fragale A, Marabitti V, Leuzzi G, Calcagnile AS, Parlanti E, et al. . 2018. CSA and CSB play a role in the response to DNA breaks. Oncotarget 9(14):11581–11591, PMID: , 10.18632/oncotarget.24342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Xiao Y, Deng T, Ming X, Xu J. 2020. TRIM31 promotes acute myeloid leukemia progression and sensitivity to daunorubicin through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Biosci Rep 40(4):BSR20194334, PMID: , 10.1042/BSR20194334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Shi G, Lv C, Yang Z, Qin T, Sun L, Pan P, et al. . 2019. TRIM31 promotes proliferation, invasion and migration of glioma cells through Akt signaling pathway. Neoplasma 66(5):727–735, PMID: , 10.4149/neo_2019_190106N21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Guo P, Ma X, Zhao W, Huai W, Li T, Qiu Y, et al. . 2018. TRIM31 is upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes disease progression by inducing ubiquitination of TSC1-TSC2 complex. Oncogene 37(4):478–488, PMID: , 10.1038/onc.2017.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Lorenz V, Milesi MM, Schimpf MG, Luque EH, Varayoud J. 2019. Epigenetic disruption of estrogen receptor alpha is induced by a glyphosate-based herbicide in the preimplantation uterus of rats. Mol Cell Endocrinol 480:133–141, PMID: , 10.1016/j.mce.2018.10.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Connolly A, Leahy M, Jones K, Kenny L, Coggins MA. 2018. Glyphosate in Irish adults - a pilot study in 2017. Environ Res 165:235–236, PMID: , 10.1016/j.envres.2018.04.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Conrad A, Schröter-Kermani C, Hoppe HW, Rüther M, Pieper S, Kolossa-Gehring M. 2017. Glyphosate in german adults – time trend (2001 to 2015) of human exposure to a widely used herbicide. Int J Hyg Environ Health 220(1):8–16, PMID: , 10.1016/j.ijheh.2016.09.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Soukup ST, Merz B, Bub A, Hoffmann I, Watzl B, Steinberg P, et al. . 2020. Glyphosate and AMPA levels in human urine samples and their correlation with food consumption: results of the cross-sectional KarMeN study in Germany. Arch Toxicol 94(5):1575–1584, PMID: , 10.1007/s00204-020-02704-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.McGuire MK, McGuire MA, Price WJ, Shafii B, Carrothers JM, Lackey KA, et al. . 2016. Glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid are not detectable in human milk. Am J Clin Nutr 103(5):1285–1290, PMID: , 10.3945/ajcn.115.126854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Curwin BD, Hein MJ, Sanderson WT, Striley C, Heederik D, Kromhout H, et al. . 2007. Urinary pesticide concentrations among children, mothers and fathers living in farm and non-farm households in Iowa. Ann Occup Hyg 51(1):53–65, PMID: , 10.1093/annhyg/mel062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Gillezeau C, van Gerwen M, Shaffer RM, Rana I, Zhang L, Sheppard L, et al. . 2019. The evidence of human exposure to glyphosate: a review. Environ Health 18(1):2, PMID: , 10.1186/s12940-018-0435-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Connolly A, Coggins MA, Koch HM. 2020. Human biomonitoring of glyphosate exposures: state-of-the-art and future research challenges. Toxics 8(3):60, PMID: , 10.3390/toxics8030060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Roadmap Epigenomics Consortium, Kundaje A, Meuleman W, Ernst J, Bilenky M, Yen A, et al. . 2015. Integrative analysis of 111 reference human epigenomes. Nature 518(7539):317–329, PMID: , 10.1038/nature14248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Michels KB, Binder AM, Dedeurwaerder S, Epstein CB, Greally JM, Gut I, et al. . 2013. Recommendations for the design and analysis of epigenome-wide association studies. Nat Methods 10(10):949–955, PMID: , 10.1038/nmeth.2632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Faniband MH, Norén E, Littorin M, Lindh CH. 2021. Human experimental exposure to glyphosate and biomonitoring of young Swedish adults. Int J Hyg Environ Health 231:113657, PMID: , 10.1016/j.ijheh.2020.113657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Connolly A, Jones K, Basinas I, Galea KS, Kenny L, McGowan P, et al. . 2019. Exploring the half-life of glyphosate in human urine samples. Int J Hyg Environ Health 222(2):205–210, PMID: , 10.1016/j.ijheh.2018.09.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Baker ME, Lathe R. 2018. The promiscuous estrogen receptor: evolution of physiological estrogens and response to phytochemicals and endocrine disruptors. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 184:29–37, PMID: , 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2018.07.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.