The double-bond system of the acrylonitrile moiety is significantly non-planar and displays one very wide angle C—C(CN)=C.
Keywords: benzothiazol, acrylonitrile, crystal structure
Abstract
In the title compound, C14H14N2S3, the double-bond system of the acrylonitrile moiety is significantly non-planar, with absolute cis torsion angles of 13.9 (2) and 15.1 (2)°. The ring system and the double bond system subtend an interplanar angle of 11.16 (4)°. The wide angle C—C(CN)=C of 129.40 (12)° may be associated with a balance between planarity and avoidance of a very short S⋯S contact.
Chemical context
Research into medicinal chemistry based on benzothiazoles has become a fast developing and progressively more active topic. The high degree of structural diversity has proved to be important in the search for new effective treatments (Ammazzalorso et al., 2020 ▸; Elgemeie, 1989 ▸). A large number of therapeutic agents based on benzothiazole systems have been synthesized and evaluated in terms of their pharmacological properties (Gill et al., 2015 ▸; Fathy et al., 1988 ▸). Much information about benzothiazoles has been reported in the scientific literature, describing their anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, neuroprotective, anticonvulsant and antiproliferative effects (Seenaiah et al., 2014 ▸). The molecular mechanisms responsible for this variety of pharmacological activity have not been completely established, and various biological pathways have been indicated as possible targets of this class of molecules (Keri et al., 2015 ▸). We are engaged in developing synthetic strategies for benzothaizole systems that show important biological activity as novel antimicrobial and antiviral agents (Azzam et al. 2017a ▸,b ▸, 2020a ▸,b ▸,c ▸, 2021 ▸; Elgemeie et al., 2000a ▸,b ▸; 2020 ▸).
As an extension of this research (Fathy & Elgemeie, 1988 ▸; Elgemeie & Elghandour, 1990 ▸), we report here a novel benzothiazole cyanoketene dithioacetal (2). Compound 2 was synthesized by the reaction of 2-cyanomethylbenzothiazole 1 with carbon disulfide in the presence of sodium ethoxide, followed by alkylation with ethyl iodide. The structure of 2 was originally based on its elemental analysis and spectroscopic data (see Experimental). In order to establish the structure of the compound unambiguously, the crystal structure was determined.
Structural commentary
The molecule of 2 is shown in Fig. 1 ▸. The heterocyclic system is coplanar to within an r.m.s. deviation of only 0.007 Å, and its dimensions are as expected (a selection of molecular dimensions are presented in Table 1 ▸). There is appreciable twisting of ca 14° about the double bond C8=C9 (see torsion angles in Table 1 ▸), so that the ‘plane’ of the atoms C2, C8, C9, C10, S2 and S3 displays an r.m.s. deviation of 0.14 Å; the two planes subtend an interplanar angle of 11.16 (4)°. The angle C2—C8=C9 (formally sp
2) is strikingly wide, at 129.40 (12)°; for comparison, the corresponding angles in the five structures mentioned below (with refcodes) range from 122–126°. One might speculate that this large angle and the deviation from planarity about the double bond represent aspects of a compromise between (i) achieving coplanarity of the heterocycle with the double-bond system and (ii) avoiding too short an S⋯S contact. The intramolecular S⋯S distances are S1⋯S3 = 3.1155 (5) and S2⋯S3 = 3.0496 (5) Å. The ethyl groups project to opposite sides of the molecule.

Figure 1.
The molecule of 2 in the crystal. Ellipsoids represent 50% probability levels.
Table 1. Selected geometric parameters (Å, °).
| S1—C7A | 1.7371 (13) | C3A—C7A | 1.4057 (17) |
| S1—C2 | 1.7519 (13) | C9—S3 | 1.7489 (13) |
| C2—N3 | 1.3078 (16) | C9—S2 | 1.7526 (13) |
| N3—C3A | 1.3813 (16) | ||
| C7A—S1—C2 | 88.97 (6) | C9—C8—C2 | 129.40 (12) |
| N3—C2—S1 | 115.52 (9) | C10—C8—C2 | 111.90 (10) |
| C2—N3—C3A | 110.98 (11) | C8—C9—S3 | 121.13 (10) |
| N3—C3A—C7A | 115.03 (11) | C8—C9—S2 | 117.68 (10) |
| C3A—C7A—S1 | 109.49 (9) | S3—C9—S2 | 121.14 (7) |
| C9—C8—C10 | 118.69 (11) | ||
| C2—C8—C9—S3 | 13.90 (19) | C2—C8—C9—S2 | −163.46 (10) |
| C10—C8—C9—S2 | 15.10 (16) | C8—C9—S2—C11 | −146.43 (10) |
Supramolecular features
The molecular packing is fairly featureless; a general view is given in Fig. 2 ▸ and some borderline possible ‘weak’ hydrogen bonds are listed in Table 2 ▸. The main feature is the loose association of pairs of molecules across inversion centres, whereby the heterocyclic systems face each other; however, there is a considerable offset. The centroids of the five-membered rings lie 3.72 Å apart, and the shortest contact is C7A⋯C7A′ (operator 1 − x, 1 − y, 1 − z) 3.741 (2) Å. The sulfur atom S1 lies 3.61 Å from the centroid of the six-membered ring in the facing molecule; such potential S⋯π interactions have been discussed by e.g. Ringer et al. (2007 ▸) and Silva et al. (2018 ▸).
Figure 2.
Crystal packing of 2 viewed parallel to the a axis (hydrogen atoms omitted for clarity). The loose association of the heterocyclic systems across inversion centres can be recognized in the central horizontal rows of rings.
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C7—H7⋯S2i | 0.95 | 3.02 | 3.6083 (13) | 122 |
| C12—H12B⋯S1ii | 0.98 | 3.03 | 3.9677 (15) | 161 |
| C13—H13A⋯N3i | 0.99 | 2.68 | 3.5746 (17) | 151 |
| C14—H14A⋯S1iii | 0.98 | 2.91 | 3.7648 (15) | 146 |
| C14—H14B⋯N3iv | 0.98 | 2.63 | 3.5277 (18) | 152 |
Symmetry codes: (i)
 ; (ii)
; (ii)
 ; (iii)
; (iii)
 ; (iv)
; (iv)
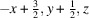 .
.
Database survey
Searches of the Cambridge Structural Database (Groom et al., 2016 ▸) were performed using ConQuest Version 2021.3.0. A search for the moiety benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl joined to C(CN)=C gave 27 hits, but none in which any further atom at the double bond was sulfur. A search for the group C—C(CN)=C(S—C)2, with the first carbon atom three-coordinate, both sulfur atoms two-coordinate and not involving cyclicity, gave only five hits. The refcodes, references and absolute cis torsion angles NC—C=C—S were as follows: CIYDIY, Kumar et al. (2008 ▸), 9.9°; MTBCEY, Abrahamsson et al. (1974 ▸), 15.4°; VAPJAA, Azzam et al. (2017c ▸), 7.3°; VELSIP, Peng et al. (2006 ▸), 3.6°; ZEDJEX, Osaka et al. (1994 ▸), 10.5°.
Synthesis and crystallization
A mixture of sodium ethoxide (0.08 mol) and 2-cyanomethylbenzothiazole (0.04 mol) in absolute ethanol (100 ml) was refluxed for 20 min. After cooling, carbon disulfide (0.04 mol) was added gradually and then the solution was warmed for 20 min. Ethyl iodide (0.08 mol) was then added, and the reaction mixture was stirred overnight at room temperature. The solution was poured onto ice–water and the solid product thus formed was filtered off. The product was purified by dissolving it in hot petroleum ether, filtering, and allowing the solution to cool. The solid that formed was recrystallized from DMF to give pale-yellow crystals, m.p. = 366–368 K, yield 72%; IR (KBr, cm−1): υ 3056 (ArCH), 2924 (CH3), 2213 (CN), 1502 (C=N); 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6 ): δ 1.27–1.34 (m, 6H, 2 SCH2CH3), 3.16–3.23 (m, 4H, 2 SCH2CH3), 7.50–7.57 (m, 2H, benzothiazole H), 8.04–8.15 (m, 2H, benzothiazole H); analysis, calculated for C14H14N2S3 (306.47): C% 54.87; H% 4.60; N% 9.14; S% 31.39; found: C% 54.85, H% 4.58; N% 9.16; MS m/z (%): 306 (M +, 15%), 276 (100%), 273 (57%), 248 (26%), 217 (76%), 204 (26%), 146 (20%).
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 3 ▸. The methyl groups were refined as idealized rigid groups allowed to rotate but not tip, with C—H = 0.98 Å and H—C—H = 109.5°. Other hydrogen atoms were included using a riding model starting from calculated positions (C—Haromatic = 0.95, C—Hmethylene = 0.99 Å). The U(H) values were fixed at 1.5 or 1.2 times the equivalent U iso value of the parent carbon atoms for methyl and non-methyl hydrogen atoms, respectively.
Table 3. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C14H14N2S3 |
| M r | 306.45 |
| Crystal system, space group | Orthorhombic, P b c a |
| Temperature (K) | 100 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 10.0771 (3), 16.0292 (5), 17.8768 (6) |
| V (Å3) | 2887.58 (16) |
| Z | 8 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.50 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.4 × 0.4 × 0.15 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur, Eos |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2014 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.954, 1.000 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 58593, 4475, 3679 |
| R int | 0.053 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.729 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.032, 0.077, 1.05 |
| No. of reflections | 4475 |
| No. of parameters | 174 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.40, −0.33 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022002572/ex2055sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022002572/ex2055Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022002572/ex2055Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 2156777
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge support by the Open Access Publication Funds of the Technical University of Braunschweig.
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C14H14N2S3 | Dx = 1.410 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 306.45 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Orthorhombic, Pbca | Cell parameters from 10579 reflections |
| a = 10.0771 (3) Å | θ = 2.6–30.3° |
| b = 16.0292 (5) Å | µ = 0.50 mm−1 |
| c = 17.8768 (6) Å | T = 100 K |
| V = 2887.58 (16) Å3 | Tablet, pale yellow |
| Z = 8 | 0.4 × 0.4 × 0.15 mm |
| F(000) = 1280 |
Data collection
| Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur, Eos diffractometer | 4475 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Enhance (Mo) X-ray Source | 3679 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.053 |
| Detector resolution: 16.1419 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 31.2°, θmin = 2.3° |
| ω–scan | h = −14→14 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlisPro; Agilent, 2014) | k = −23→22 |
| Tmin = 0.954, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −25→25 |
| 58593 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.032 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.077 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.05 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0318P)2 + 1.3474P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 4475 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.002 |
| 174 parameters | Δρmax = 0.40 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.32 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.48621 (3) | 0.63526 (2) | 0.48864 (2) | 0.01440 (8) | |
| C2 | 0.64877 (12) | 0.62079 (7) | 0.52085 (7) | 0.0129 (2) | |
| N3 | 0.72242 (10) | 0.57082 (6) | 0.48059 (6) | 0.0141 (2) | |
| C3A | 0.65225 (12) | 0.54010 (7) | 0.42020 (7) | 0.0135 (2) | |
| C4 | 0.70382 (14) | 0.48489 (8) | 0.36681 (7) | 0.0169 (2) | |
| H4 | 0.793137 | 0.466208 | 0.369750 | 0.020* | |
| C5 | 0.62153 (14) | 0.45833 (8) | 0.30983 (7) | 0.0194 (3) | |
| H5 | 0.654822 | 0.420983 | 0.273082 | 0.023* | |
| C6 | 0.48945 (14) | 0.48568 (8) | 0.30536 (7) | 0.0198 (3) | |
| H6 | 0.435044 | 0.466538 | 0.265499 | 0.024* | |
| C7 | 0.43675 (14) | 0.53990 (8) | 0.35774 (7) | 0.0179 (3) | |
| H7 | 0.347076 | 0.557869 | 0.354695 | 0.022* | |
| C7A | 0.51995 (12) | 0.56737 (7) | 0.41532 (7) | 0.0141 (2) | |
| C8 | 0.70646 (12) | 0.65707 (7) | 0.58882 (7) | 0.0135 (2) | |
| C9 | 0.66224 (12) | 0.72227 (7) | 0.63140 (7) | 0.0137 (2) | |
| C10 | 0.82871 (13) | 0.61618 (8) | 0.60980 (7) | 0.0147 (2) | |
| N1 | 0.92273 (12) | 0.58066 (7) | 0.62713 (6) | 0.0200 (2) | |
| S2 | 0.77453 (3) | 0.76792 (2) | 0.69408 (2) | 0.01682 (8) | |
| C11 | 0.67428 (14) | 0.80013 (8) | 0.77350 (7) | 0.0190 (3) | |
| H11A | 0.723828 | 0.842357 | 0.802710 | 0.023* | |
| H11B | 0.591943 | 0.826694 | 0.754915 | 0.023* | |
| C12 | 0.63786 (15) | 0.72831 (9) | 0.82435 (8) | 0.0224 (3) | |
| H12A | 0.584732 | 0.687626 | 0.796466 | 0.034* | |
| H12B | 0.586321 | 0.749299 | 0.866859 | 0.034* | |
| H12C | 0.718942 | 0.701444 | 0.842693 | 0.034* | |
| S3 | 0.50142 (3) | 0.76155 (2) | 0.62083 (2) | 0.01684 (8) | |
| C13 | 0.53315 (14) | 0.87150 (8) | 0.60082 (8) | 0.0192 (3) | |
| H13A | 0.447342 | 0.900815 | 0.594773 | 0.023* | |
| H13B | 0.579883 | 0.896822 | 0.643920 | 0.023* | |
| C14 | 0.61552 (15) | 0.88404 (9) | 0.53106 (8) | 0.0242 (3) | |
| H14A | 0.701489 | 0.856282 | 0.537151 | 0.036* | |
| H14B | 0.629538 | 0.943837 | 0.522807 | 0.036* | |
| H14C | 0.568927 | 0.860130 | 0.487976 | 0.036* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.01247 (14) | 0.01380 (15) | 0.01694 (15) | 0.00051 (11) | 0.00032 (11) | −0.00103 (11) |
| C2 | 0.0125 (5) | 0.0120 (5) | 0.0143 (5) | −0.0005 (4) | 0.0015 (4) | 0.0019 (4) |
| N3 | 0.0150 (5) | 0.0129 (5) | 0.0143 (5) | −0.0007 (4) | 0.0011 (4) | −0.0009 (4) |
| C3A | 0.0158 (6) | 0.0119 (5) | 0.0129 (5) | −0.0019 (4) | 0.0006 (4) | 0.0020 (4) |
| C4 | 0.0197 (6) | 0.0152 (6) | 0.0158 (6) | 0.0014 (5) | 0.0009 (5) | −0.0003 (5) |
| C5 | 0.0268 (7) | 0.0158 (6) | 0.0157 (6) | 0.0009 (5) | −0.0002 (5) | −0.0016 (5) |
| C6 | 0.0261 (7) | 0.0171 (6) | 0.0163 (6) | −0.0023 (5) | −0.0067 (5) | −0.0011 (5) |
| C7 | 0.0184 (6) | 0.0153 (6) | 0.0200 (6) | −0.0014 (5) | −0.0039 (5) | 0.0021 (5) |
| C7A | 0.0173 (6) | 0.0106 (5) | 0.0144 (5) | −0.0013 (4) | 0.0003 (5) | 0.0012 (4) |
| C8 | 0.0131 (6) | 0.0127 (5) | 0.0145 (5) | −0.0018 (4) | 0.0018 (4) | 0.0008 (4) |
| C9 | 0.0134 (6) | 0.0127 (5) | 0.0150 (6) | −0.0017 (4) | 0.0024 (4) | 0.0010 (4) |
| C10 | 0.0182 (6) | 0.0137 (5) | 0.0122 (5) | −0.0011 (5) | 0.0010 (4) | −0.0028 (4) |
| N1 | 0.0218 (6) | 0.0205 (5) | 0.0177 (5) | 0.0028 (5) | −0.0026 (4) | −0.0029 (4) |
| S2 | 0.01627 (15) | 0.01690 (16) | 0.01730 (15) | −0.00122 (12) | 0.00140 (11) | −0.00523 (12) |
| C11 | 0.0250 (7) | 0.0161 (6) | 0.0159 (6) | 0.0035 (5) | 0.0025 (5) | −0.0049 (5) |
| C12 | 0.0231 (7) | 0.0208 (7) | 0.0232 (7) | 0.0015 (5) | 0.0051 (5) | 0.0012 (5) |
| S3 | 0.01226 (15) | 0.01522 (15) | 0.02304 (17) | 0.00007 (11) | 0.00338 (11) | −0.00326 (12) |
| C13 | 0.0198 (6) | 0.0139 (6) | 0.0240 (7) | 0.0024 (5) | −0.0015 (5) | −0.0002 (5) |
| C14 | 0.0270 (7) | 0.0238 (7) | 0.0218 (7) | −0.0025 (6) | −0.0011 (6) | 0.0031 (5) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S1—C7A | 1.7371 (13) | C9—S3 | 1.7489 (13) |
| S1—C2 | 1.7519 (13) | C9—S2 | 1.7526 (13) |
| C2—N3 | 1.3078 (16) | C10—N1 | 1.1480 (17) |
| C2—C8 | 1.4672 (17) | S2—C11 | 1.8174 (13) |
| N3—C3A | 1.3813 (16) | C11—C12 | 1.5121 (19) |
| C3A—C4 | 1.4015 (17) | C11—H11A | 0.9900 |
| C3A—C7A | 1.4057 (17) | C11—H11B | 0.9900 |
| C4—C5 | 1.3807 (18) | C12—H12A | 0.9800 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9500 | C12—H12B | 0.9800 |
| C5—C6 | 1.404 (2) | C12—H12C | 0.9800 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | S3—C13 | 1.8265 (14) |
| C6—C7 | 1.3835 (19) | C13—C14 | 1.512 (2) |
| C6—H6 | 0.9500 | C13—H13A | 0.9900 |
| C7—C7A | 1.3988 (18) | C13—H13B | 0.9900 |
| C7—H7 | 0.9500 | C14—H14A | 0.9800 |
| C8—C9 | 1.3675 (17) | C14—H14B | 0.9800 |
| C8—C10 | 1.4449 (18) | C14—H14C | 0.9800 |
| C7A—S1—C2 | 88.97 (6) | S3—C9—S2 | 121.14 (7) |
| N3—C2—C8 | 118.28 (11) | N1—C10—C8 | 177.05 (14) |
| N3—C2—S1 | 115.52 (9) | C9—S2—C11 | 105.02 (6) |
| C8—C2—S1 | 126.18 (9) | C12—C11—S2 | 112.85 (9) |
| C2—N3—C3A | 110.98 (11) | C12—C11—H11A | 109.0 |
| N3—C3A—C4 | 124.58 (12) | S2—C11—H11A | 109.0 |
| N3—C3A—C7A | 115.03 (11) | C12—C11—H11B | 109.0 |
| C4—C3A—C7A | 120.38 (12) | S2—C11—H11B | 109.0 |
| C5—C4—C3A | 118.32 (12) | H11A—C11—H11B | 107.8 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.8 | C11—C12—H12A | 109.5 |
| C3A—C4—H4 | 120.8 | C11—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 121.01 (12) | H12A—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.5 | C11—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.5 | H12A—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 121.44 (12) | H12B—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—H6 | 119.3 | C9—S3—C13 | 101.91 (6) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.3 | C14—C13—S3 | 112.70 (10) |
| C6—C7—C7A | 117.76 (12) | C14—C13—H13A | 109.1 |
| C6—C7—H7 | 121.1 | S3—C13—H13A | 109.1 |
| C7A—C7—H7 | 121.1 | C14—C13—H13B | 109.1 |
| C7—C7A—C3A | 121.08 (12) | S3—C13—H13B | 109.1 |
| C7—C7A—S1 | 129.43 (10) | H13A—C13—H13B | 107.8 |
| C3A—C7A—S1 | 109.49 (9) | C13—C14—H14A | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—C10 | 118.69 (11) | C13—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—C2 | 129.40 (12) | H14A—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C10—C8—C2 | 111.90 (10) | C13—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C8—C9—S3 | 121.13 (10) | H14A—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C8—C9—S2 | 117.68 (10) | H14B—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C7A—S1—C2—N3 | 0.65 (10) | C2—S1—C7A—C7 | 178.99 (13) |
| C7A—S1—C2—C8 | −177.35 (11) | C2—S1—C7A—C3A | −0.97 (9) |
| C8—C2—N3—C3A | 178.07 (10) | N3—C2—C8—C9 | 165.41 (12) |
| S1—C2—N3—C3A | −0.10 (13) | S1—C2—C8—C9 | −16.64 (19) |
| C2—N3—C3A—C4 | −179.85 (12) | N3—C2—C8—C10 | −13.23 (16) |
| C2—N3—C3A—C7A | −0.71 (15) | S1—C2—C8—C10 | 164.72 (9) |
| N3—C3A—C4—C5 | 179.09 (12) | C10—C8—C9—S3 | −167.54 (9) |
| C7A—C3A—C4—C5 | −0.01 (18) | C2—C8—C9—S3 | 13.90 (19) |
| C3A—C4—C5—C6 | −0.11 (19) | C10—C8—C9—S2 | 15.10 (16) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −0.2 (2) | C2—C8—C9—S2 | −163.46 (10) |
| C5—C6—C7—C7A | 0.5 (2) | C8—C9—S2—C11 | −146.43 (10) |
| C6—C7—C7A—C3A | −0.63 (19) | S3—C9—S2—C11 | 36.21 (9) |
| C6—C7—C7A—S1 | 179.41 (10) | C9—S2—C11—C12 | 77.62 (11) |
| N3—C3A—C7A—C7 | −178.79 (11) | C8—C9—S3—C13 | −123.70 (11) |
| C4—C3A—C7A—C7 | 0.39 (18) | S2—C9—S3—C13 | 53.57 (9) |
| N3—C3A—C7A—S1 | 1.17 (13) | C9—S3—C13—C14 | 59.99 (11) |
| C4—C3A—C7A—S1 | −179.64 (10) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C7—H7···S2i | 0.95 | 3.02 | 3.6083 (13) | 122 |
| C12—H12B···S1ii | 0.98 | 3.03 | 3.9677 (15) | 161 |
| C13—H13A···N3i | 0.99 | 2.68 | 3.5746 (17) | 151 |
| C14—H14A···S1iii | 0.98 | 2.91 | 3.7648 (15) | 146 |
| C14—H14B···N3iv | 0.98 | 2.63 | 3.5277 (18) | 152 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x−1/2, −y+3/2, −z+1; (ii) x, −y+3/2, z+1/2; (iii) x+1/2, −y+3/2, −z+1; (iv) −x+3/2, y+1/2, z.
References
- Abrahamsson, S., Rehnberg, G., Liljefors, T. & Sandström, J. (1974). Acta Chem. Scand. 28b, 1109–1120.
- Agilent (2014). CrysAlis PRO. Agilent Technologies, Yarnton, England.
- Ammazzalorso, A., Carradori, S., Amoroso, R. & Fernández, I. F. (2020). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 207, 112762. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Azzam, R. A., Elboshi, H. A. & Elgemeie, G. H. (2020a). ACS Omega, 5, 30023–30036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Azzam, R. A., Elgemeie, G. H., Elsayed, R. E. & Jones, P. G. (2017a). Acta Cryst. E73, 1820–1822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Azzam, R. A., Elgemeie, G. H., Elsayed, R. E. & Jones, P. G. (2017b). Acta Cryst. E73, 1041–1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Azzam, R. A., Elgemeie, G. H., Ramadan, R. & Jones, P. G. (2017c). Acta Cryst. E73, 752–754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Azzam, R. A., Elgemeie, G. H., Seif, M. M. & Jones, P. G. (2021). Acta Cryst. E77, 891–894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Azzam, R. A., Elsayed, R. E. & Elgemeie, G. H. (2020b). ACS Omega, 5, 26182–26194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Azzam, R. A., Osman, R. R. & Elgemeie, G. H. (2020c). ACS Omega, 5, 1640–1655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Elgemeie, G. H. (1989). Chem. Ind. 19, 653–654.
- Elgemeie, G. H., Azzam, R. A. & Osman, R. R. (2020). Inorg. Chim. Acta, 502, 119302.
- Elgemeie, G. H. & Elghandour, A. H. (1990). Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon, 48, 281–284.
- Elgemeie, G. H., Shams, H. Z., Elkholy, Y. M. & Abbas, N. S. (2000a). Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon, 165, 265–272.
- Elgemeie, G. H., Shams, Z., Elkholy, M. & Abbas, N. S. (2000b). Heterocycl. Commun. 6, 363–268.
- Fathy, N. M. & Elgemeie, G. H. (1988). Sulfur Lett. 7, 189–193.
- Fathy, N. M., Motti, F. M. & Elgemeie, G. H. (1988). Arch. Pharm. Pharm. Med. Chem. 321, 509–512.
- Gill, R. K., Rawal, R. K. & Bariwal, J. (2015). Arch. Pharm. Chem. Life Sci. 348, 155–178. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Keri, R. S., Patil, M. R., Patil, S. A. & Budagumpi, S. (2015). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 89, 207–251. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S., Peruncheralathan, S., Ila, H. & Junjappa, H. (2008). Org. Lett. 10, 965–968. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Osaka, H., Ishida, T., Nogami, T., Yamazaki, R., Yasui, M., Iwasaki, F., Mizoguchi, A., Kubata, M., Uemiya, T. & Nishimura, A. (1994). Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn, 67, 918–923.
- Peng, T., Fu, Y., Yu, C.-Y., Wang, L.-B. & Huang, Z.-T. (2006). Acta Cryst. E62, o3382–o3383.
- Ringer, A. L., Senenko, A. & Sherrill, C. D. (2007). Protein Sci. 16, 2216–2223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Seenaiah, D., Reddy, P. R., Reddy, G. M., Padmaja, A., Padmavathi, V. & Siva krishna, N. (2014). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 77, 1–7. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Siemens (1994). XP. Siemens Analytical X-Ray Instruments Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Silva, R. F. N., Sacco, A. C. S., Caracelli, I., Zukerman-Schpector, J. & Tiekink, E. R. T. (2018). Z. Krist. Cryst. Mater. 233, 531–537.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022002572/ex2055sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022002572/ex2055Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022002572/ex2055Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 2156777
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




