Abstract
Background and aims
FoMO has been considered a predisposing factor toward excessive internet use, and a great deal of literature has investigated the link between FoMO and internet use. However, there is still a lack of cohesion in the literature.
Methods
The current study have been conducted and reported in accordance with Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA).
Results
In the current systematic review and meta-analysis of 86 effect-sizes, representative of 55,134 participants (Mean age = 22.07, SD = 6.15, females = 58.37%), we found that the strength of the trait FoMO- internet use association significantly varies from r = 0.11 to r = 0.63. In some populations, FoMO appears to increase with age and it is reverse in other populations. Facebook use was unrelated to FoMO in some populations, and higher FoMO was linked with stopping Instagram use for some individuals. The FoMO- internet use association was independent of their severity, as the interaction was not significant, and this association was neither linear nor curvilinear. The FoMO-internet use association does not appear to be associated with depressive, anxiety, and stress symptoms or level of life satisfaction. The COVID-19 pandemic was the only significant moderator of the FoMO-internet use association, strengthening this relationship.
Discussion and Conclusions
FoMO demonstrates a considerable role in internet use; however, there is no evidence of interaction or bi-directional association between the mentioned. Overall, we still don’t know what factors contribute to individuals exhibiting distinct patterns in the FoMO-internet use association.
Keywords: fear of missing out (FoMO), internet use, smartphone use, social media use
Introduction
The proliferation of technology has enabled almost half of the world’s population to access the internet through smartphones (Statista.com, 2021; We are Social, 2018). It has significantly reduced distance and isolation and made the world community resemble a global village. However, these vast benefits also have some costs, such as overuse or excessive use by some people, which has led researchers to study this behavior (Griffiths, 1996; Young, 1996). This trend has led to taxonomical problems, such as using different but similar terms, including internet addiction (Young, 1997), smartphone addiction (Kwon et al., 2013), or social media addiction (Andreassen, Torsheim, Brunborg, & Pallesen, 2012).
Montag et al. (2019) recently debated that the mentioned terminologies present a diagnostic challenge in the study of internet use disorders, as the self-report inventories that address the constructs mentioned earlier overlap in terms of what they measure. Accordingly, the authors suggest that it is plausible that all mentioned terms above are unified, accessible through the internet, and people use smartphones as access vehicles. With this in mind, authors have coined the term ’mobile internet use’ and accessing the internet with something other than non-mobile internet use.
This proposed taxonomy seems fair to codify internet (over-) use (Browne, May, Colucci, & Rumpf, 2021; Elhai, Yang, & Levine, 2021; Moretta, Chen, & Potenza, 2020; Rumpf, Browne, Brandt, & Rehbein, 2021; Wu, Lin, & Lin, 2021). Although this dichotomization (predominantly mobile or non-mobile use) has faced some critiques, as the means of access to the internet may not matter (Griffiths, 2021) and is not clinically useful, potentially resulting in diagnostic inflation (Starcevic et al., 2021). However, Montag et al. (2019) point out that predisposing factors, specific usage motives, and cognitive and affective factors matter more than the particular devices used.
The last global estimated prevalence of excessive internet use (from 1996 to 2012) across seven world regions was approximately 6% of the surveyed populations (Cheng & Li, 2014). Given the high prevalence, excessive internet use is a global concern that needs to be addressed given that it has been linked to health threats such as texting while driving, which can result in accidents (Cazzulino, Burke, Muller, Arbogast, & Upperman, 2014); as well as multiple psychopathologies, including anxiety, depression and suicidal ideation (Demirci, Akgönül, & Akpinar, 2015; Elhai, Dvorak, Levine, & Hall, 2017; Ryu, Choi, Seo, & Nam, 2004), increased procrastination (Li, Griffiths, Mei, & Niu, 2020), disrupted sleep (Rod, Dissing, Clark, Gerds, & Lund, 2018), stress, and loneliness (Karsay, Schmuck, Matthes, & Stevic, 2019), social anxiety (Weinstein et al., 2015), substance use disorder, attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, and hostility (Ko, Yen, Yen, Chen, & Chen, 2012). Internet use can also lead to phubbing behavior or snubbing others via smartphone, thus impairing the person’s relationship bonds (Al-Saggaf & O’Donnell, 2019). Some people may also experience ’nomophobia’ (no mobile phone phobia), which is described as the fear that results from being separated from one’s smartphone (King et al., 2014). Furthermore, excessive internet use may result in multiple neuroanatomical and neurochemical changes, such as cortical diminishing of different brain components and changed dopaminergic reward circuitry (Tripathi, 2017).
The compensatory internet use theory (CIUT; Kardefelt-Winther, 2014) conceptualizes internet use as a substitute for something that is needed but not available. As a result, stressful life events will increase the probability of (for example) internet browsing to alleviate negative emotions. From this perspective, internet use is a response to stressful life experiences; namely, it emerges through the perseveration of engagement in technology as a coping strategy to regulate cognitive-affective states. For example, if a person needs social stimulation, using a social media app might help to compensate for real social connection needs. However, although it can initially mitigate negative feelings, the social media app can trigger more negative feelings concomitantly to the ’real world’ issue remaining unaddressed. “Theoretically” it might also lead to more fear of missing out (FoMO)-related thoughts as others may be perceived to be having better moments than oneself.
One of the most well-known phenomena in the internet use context is FoMO (Alt, 2015; Blackwell, Leaman, Tramposch, Osborne, & Liss, 2017; Elhai, Gallinari, Rozgonjuk, & Yang, 2020; Elhai, Levine, Dvorak, & Hall, 2016; Gil, Chamarro, & Oberst, 2015; Kuss & Griffiths, 2017; O’Connell, 2020; Przybylski, Murayama, DeHaan, & Gladwell, 2013; Van-Den-Eijnden, Doornwaard, & Ter Bogt, 2017; Wang, Wang, Yang, et al., 2019; Wolniewicz, Tiamiyu, Weeks, & Elhai, 2018). The FoMO from a rewarding experience that others are experiencing and a constant, pervasive tendency to live connected with others through social networks have been proposed as the two key components of FoMO (Przybylski et al., 2013). Some researchers have proposed the counter-concept of JoMO, the ’joy of missing out’ (Brinkmann, 2019; Crook, 2014), as relief from FoMO-risen anxiety (Przybylski et al., 2013). The link between internet use (Griffiths, 1998) and FoMO is not always detrimental, as FoMO may positively affect well-being if using social media to promote social interaction (Roberts & David, 2020). However, FoMO, and its related negative affectivity, underlies psychopathology and addictive behaviors, which may predispose to excessive internet use, predominantly triggered via FoMO (Alt, 2015; Blackwell et al., 2017; Elhai et al., 2016; Elhai et al., 2020; Gil et al., 2015; Kuss & Griffiths, 2017; O’Connell, 2020; Przybylski et al., 2013; Van-Den-Eijnden et al., 2017; Wang, Wang, Yang, et al., 2019; Wolniewicz et al., 2018). The reverse is also the case, as internet use can increase FoMO levels (Fernandez, Kuss, & Griffiths, 2020), however, its trajectory is unclear, and drawing a firm conclusion on the bi-directionality necessitates more research (Elahi et al., 2021).
The aim of the current study
The Interaction of Person-Affect-Cognition-Execution (I-PACE; Brand, Young, Laier, Wolfling, & Potenza, 2016, 2019) model conceptualizes any addictive behavior “as a consequence of the interactions between predisposing variables, affective and cognitive responses to specific stimuli, and executive functions, such as inhibitory control and decision-making.” Furthermore, “the associations between cue-reactivity/craving and diminished inhibitory control contribute to habitual behaviors” (Brand et al., 2019, p. 2). Considering the I-PACE model, as a cognitive bias and a stable personality trait, FoMO could be considered a predisposing variable and personality trait (Wegman et al., 2017), which by affecting the person’s perception of internal or external stimuli (Brand et al., 2016), underpins the association of personal factors such as dysphoric mood with internet use (Baker, Krieger, & LeRoy, 2016; Dempsey, O’Brien, Tiamiyu, & Elhai, 2019; Wang, Wang, Yang, et al., 2019; Wolniewicz, Rozgonjuk, & Elhai, 2020). Given the trait-like nature of FoMO (Wegman et al., 2017), the current study concentrates on trait-FoMO in association with internet use.
So far, four qualitative literature reviews (Elhai et al., 2020; Tandon, Dhir, Almugren, AlNemer, & Mäntymäki, 2021; Wang, 2021; Yuxiang, Xuanhui, & Xiaokang, 2017) and only two meta-analyses (Fioravanti et al., 2021; Yali, Sen, & Guoliang, 2021) have been published examining social media and FoMO. While they are important and timely, these meta-analyses have only examined social media, and it is necessary to consider internet use as a broader branch, as debated by Montag et al. (2019). Also, the authors did not directly consider the observed heterogeneity, which, when significant, should be considered in calculating the prediction interval, given that a meta-analysis should address how much effect-sizes vary across studies (Borenstein, Higgins, Hedges, & Rothstein, 2017; Borenstein, 2019). Therefore we decided to retain social media use (Instagram and Facebook) to contribute to the literature by addressing how effect sizes vary across studies, a critical point that previous meta-analyses overlooked.
To our knowledge, there is a necessity of cohesion in the literature adhering to the new taxonomy as mentioned before, to study smartphone-FoMO, Internet-FoMO, and social media-FoMO under the umbrella term of mobile-internet use, addressing the potential heterogeneity of studies. However, two important points should be noted. First, internet use disorder is yet to be confirmed as an official diagnosis. The included studies did not clarify if internet use was assessed in such a mammer as to identify disordered behavior. Second, the included studies did not report whether or not participants have used a mobile phone to access the internet. Consequently, in this study, we use the term “internet use” as indicating the behavior of using the internet. With this in mind, we remained adhered to the new taxonomy (Montag et al., 2019) by recognizing the overlapping between included variables under the term “internet use.”
Therefore, the current study sought to deliver a bigger picture of the current status of FoMO by undertaking a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis of this phenomenon in relationship with internet use. Accordingly, the first aim of the current study was to quantify the magnitude of the FoMO and internet use association and dissect it in terms of the specific content used, such as Instagram and Facebook. Secondly, since the first empirical psychological study published by Przybylski et al. (2013), extensive empirical research findings have supported that FoMO is associated with internet use and that the stronger the FoMO, the higher the internet use (Balta, Emirtekin, Kircaburun, and Griffiths 2020; Casale & Fioravanti, 2020; Cheng, Lau, Chan, & Luk, 2021; Cheng & Li, 2014; Elhai et al., 2018; Long et al., 2016; Moreno, Jelenchick, Cox, Young, & Christakis, 2011; Servidio, 2021; Sohn, Rees, Wildridge, Kalk, & Carter, 2019; Spada, 2014). Furthermore, although FoMO can increase internet use; the reverse might be possible as internet use can also increase FoMO levels (Fernandez et al., 2020). However, given that its trajectory is unclear, drawing a firm conclusion on the bi-directionality requires for more research (Elahi et al., 2021), making it worthwhile to investigate meta-analytically whether there is an interaction between levels of FoMO and internet use, as a significant interaction may shed some light on the possible bi-directionality.
Thirdly, considering the COVID-19 pandemic as an obvious burden for people worldwide, and given that internet use is a response to stressful life experiences according to the CIUT, it is worthy of examination to compare studies conducted before/after this crisis. This allows for assessing the possible adverse impact of the pandemic as a moderator on the FoMO- internet use association. Lastly, to explore the potential continuous and categorical moderators of the aforementioned.
Method
Study selection
Study selection methodology has been reported following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines (Moher et al., 2009).
Eligible studies included
The following inclusion criteria were applied to the literature search: (a) English-language articles published in peer-reviewed journals or thesis/dissertations; (b) articles related to trait- FoMO (Przybylski et al., 2013; Wegmann, Oberst, Stodt, & Brand, 2017); (c) articles related to INTERNET USE; (e) research using a case-control design/prospective cohort studies/experimental studies/large population-based cross-sectional studies; and (f) research reporting Pearson’s or Spearman’s r correlation coefficients of the variables of interest, or any data that could be converted to r, such as Cohen’s d/f, T-value, or Fisher’s Z. Studies on participants with a diagnosis of neurological and/or neurocognitive organic impairment, or co-occurring psychiatric disorders were excluded (Hamonniere & Varescon, 2018), as well as studies on cognitive processes not specifically referring to trait-FoMO (Przybylski et al., 2013; Wegmann et al., 2017).
Information sources and search
PsycINFO, PubMed, Scopus, and ProQuest were systematically searched from inception to January 31, 2021. Moreover, a manual search was run for reference lists from all articles selected, full-text reviews, and relevant reviews. The search was done using the following terms. For social media (social media OR social networking site OR social network site OR SNS OR online networking site OR “ONS” OR Facebook OR Twitter OR WhatsApp OR WeChat OR Instagram OR Snap chat OR TikTok OR YouTube) AND (addiction OR problematic OR disorder OR pathologic OR dependency OR excessive OR compulsive OR abuse), smartphone (smartphone OR smartphone OR cellular phone OR cell phone OR phone OR cell-phone OR mobile device OR mobile phone) AND (problematic OR problem OR dependence OR dependency OR overuse OR addiction OR excessive OR compulsive), and internet (Internet addiction OR problematic Internet use OR pathological Internet use OR excessive internet use OR Internet dependence OR compulsive Internet use OR compulsive computer use OR virtual addiction OR Internet use OR pathologic use of Internet OR Internet behavioral addiction OR Internet abuse OR Internet overuse OR harmful use of the Internet OR Internet addictive disorder). The mentioned terms were searched (separately and simultaneously) using search functions based on each database (e.g., asterisk, quotation mark) in combination with Boolean “AND” operator with “Fear of missing out” OR “FOMO.”
Study selection, data collection process, and data items
The eligibility of studies was assessed through the following procedure: title screening, abstract screening, full articles screening. Titles and abstracts were screened by M.S. Articles appearing to be potentially relevant were retrieved by M.S. then, independently assessed by M.S, and M.A. Disagreements on eligibility were resolved by consensus among authors (intercoder reliability: Cohen’s Kappa coefficient = 0.91). When the information about the methods or results was omitted, the authors were contacted to obtain missing information. In case of suspicion of duplicates, only the report with the largest sample should be included (Cosci & Fava, 2013; Moher et al., 2009). However, screening revealed no duplicates of sampling at the between-study level. Even so, duplicated outcomes were found at the within-study level (K = 13) for overlapped constructs associated with FoMO (e.g., social media addiction and problematic smartphone use).
Given that each effect size in a meta-analysis should be independent to avoid serial error correlation (Borenstein, Hedges, Higgins, & Rothstein, 2009), the mentioned overlapped effect sizes at the within-study level have been combined. The following assumptions also were made: if not specified, participants were considered without co-occurring psychiatric disorders, neurological, or neurocognitive organic impairment. Please see Appendix A for information on extracted data before the combination.
Quality and bias risk assessment
The quality of each eligible study was assessed independently by two investigators (S.P and G.M.) using “the standard quality assessment criteria for evaluating primary research papers from a variety of fields” (Kmet, Cook, & Lee, 2004) with 14 criteria such as “Question/objective sufficiently described?”, “Results reported in sufficient detail?”, “Conclusions supported by the results?”. The answers might be yes, partial, no, or not applicable (N/A) about the article; the overall score of 28 indicates a high-quality study. Due to the nature of correlational studies, three criteria of intervention studies (items number 5, 6, 7) were scored as N/A; thus, the overall score was 22. By the authors’ consensus, the quality of studies was classified as low risk of bias (i.e., the score equal to or more than 18) and moderate risk of bias (i.e., the score between 16 and 17). Disagreements were resolved by consensus (intercoder reliability: Cohen’s Kappa coefficient = 0.85).
Data analysis
Comprehensive Meta-Analysis Software (CMA-Version 3.3.070) was used to calculate the overall mean effect size (ES), and all analyses were done using the random-effects model. Before the computation, numerous sensitivity analyses using the one-study remove method and cumulative analysis were run to detect the outliers and see if the ES is skewed or robust under different inclusion criteria. The statistics reported were strictly based on Borenstein guidelines (2019) to avoid common mistakes in undertaking meta-analyses.
Although reporting the I 2 as an index of heterogeneity is common, this is a proportion and not an absolute value (Borenstein et al., 2017; Borenstein, 2019), so it only indicates that a percentage of heterogeneity in ESs can be attributed to something other than sampling error, i.e., I 2 = 75% means that the sampling error can explain 25% of heterogeneity, and other factors would explain the remainder. Therefore, it does not provide any indication of the degree of heterogeneity. However, alongside I 2 and Q, we have reported an estimate of between-study heterogeneity, i.e., tau, using a random-effect model (Johnson, 2021). Also, to answer the above question using the Borenstein et al. (2017) formula, we have reported the prediction interval (PI), which can address the true heterogeneity and determine the expected true effect in 95% of akin studies that will be undertaken in the future. Thus, PI of −0.20 to +0.80 means the ESs in some populations would be as low as −0.20, and in some populations as high as +0.80, which is more informative than I 2.
The mixed-effects model (Borenstein et al., 2009) was used to calculate the pooled ESs for subgroups, pooled the ESs in each subgroup by random-effect model, and used the fixed-effect model to check the differences between subgroups. We have reported Q, DF, and the corresponding P-value to pairwise omnibus test or test the subgroup differences’ significance.
We did not use the fail-safe N to assess publication bias, which is no longer recommended (Borenstein, 2019). Instead, we examined the small-study-effect using cumulative analysis (Borenstein, 2019), which if the studies with smaller sample size shows higher ESs can be considered a reason to assume publication bias. Besides, Egger and colleagues’ (1997) regression test was conducted to estimate the extent of heterogeneity (funnel plot asymmetry), which reports an intercept and the corresponding P-value. A significant intercept means smaller studies have shown larger ESs (closer intercept to zero means insufficient evidence of publication bias). However, it is only an indicator and does not explain how ESs would be different without publication bias. Thus, we have also used the trim and fill procedure (Duval & Tweedie, 2000), which assumes there are missed studies that are not included in the meta-analysis, so it will calculate the mean ES after controlling for publication bias. Moreover, bivariate and multiple meta-regression models were tested using Knapp–Hartung procedures and the maximum likelihood method to test if the moderators were significant.
Results
Selection and inclusion of studies
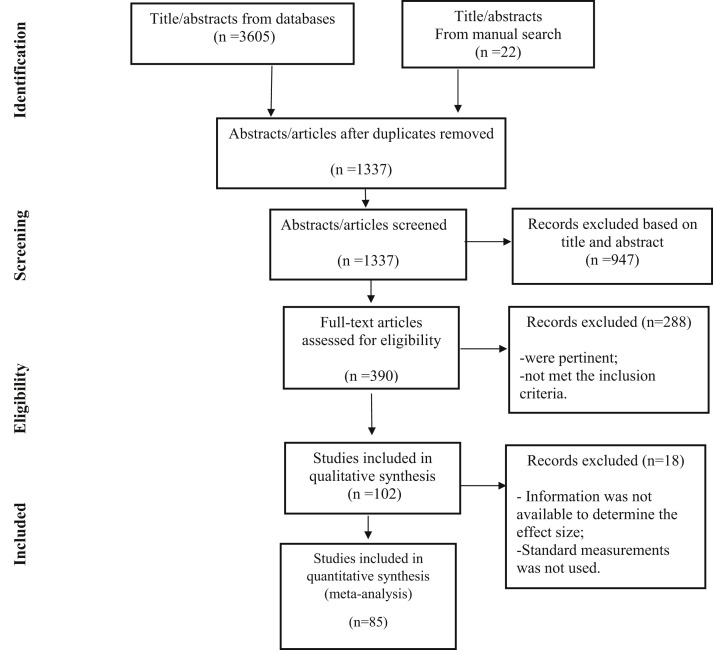
Figure 1 depicts the selection and inclusion of research as a PRISMA chart. Following the duplicated studies exclusion, two independent authors screened the titles and abstracts of 1,337 articles for a primary appraisal. After retrieving 390 articles for full-text screening, 102 studies were eligible for qualitative analysis. Finally, 85 studies were found to meet the inclusion criteria and were included in the quantitative review.
Fig. 1.
Flow diagram of the search
Sensitivity analysis, quality, and risk of bias assessment
Several sensitivity analyses were performed for each subgroup to determine whether the pooled ESs were robust concerning differences in the correlations of interest. The one-study-removed technique revealed that none of the included studies influenced or skewed the final results. However, among 85 articles (86 effect-sizes) included in the analysis, 21 articles had a moderate risk of bias (Alt & Boniel-Nissim, 2018a, 2018b; Barber & Santuzzi, 2017; Barry & Wong, 2020; Burnell, George, Vollet, Ehrenreich, & Underwood, 2019; Buyukbayraktar, 2020; Classen, Wood, & Davies, 2020; Elhai et al., 2016; Fuster, Chamarro, & Oberst, 2017; Hishan, Ramakrishnan, & Qureshi, 2020; McAndrew, 2018; Metin-Orta, 2020; Munawaroh, Nurmalasari, & Sofyan, 2020; O’Connell, 2020; Rahardjo & Mulyani, 2020; Riordan et al., 2020; Rogers & Barber, 2019; Schneider & Hitzfeld, 2019; Sha, Sariyska, Riedl, Lachmann, & Montag, 2019; Sheldon, Antony, & Sykes, 2021; Tang, Hung, Au-Yeung, & Yuen, 2020; Tunc-Aksan & Akbay, 2019) and the rest had a high quality and low risk of bias judged by the authors.
Publication bias assessment
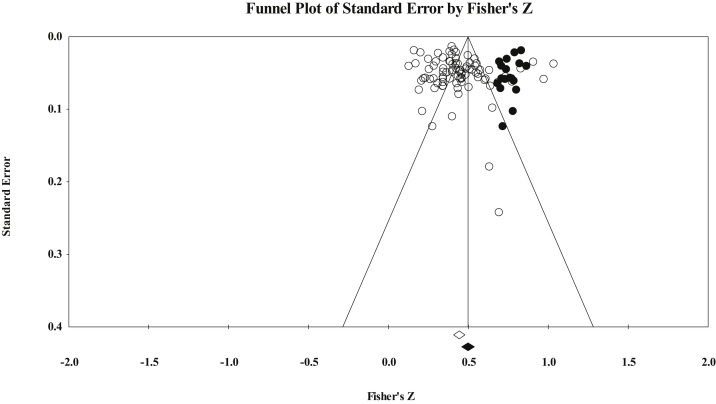
The small-study-effect was first appraised for publication bias, which shows no evidence of bias in this regard. Following this, Egger’s regression test was performed. As seen in Table 1, the results were significant for internet use’s ES (b = 2.16, P = 0.015), indicating that the pooled calculated ES was underestimated. Thus, the adjusted ESs were computed using Duval and Tweedie’s procedure (see Fig. 2 for the funnel plot); by trimming 18 studies to the right of the mean, the adjusted ES for INTERNET USE is significantly different (Q = 104.939, df = 1, P = 0.001) than the pooled ES; however, it would not change the drawn conclusion. Also, the results were significant for Facebook use (b = 4.96, P = 0.022), showing a potential publication bias. Thus, the adjusted ESs were computed; however, the estimated adjusted ES did not change significantly.
Table 1.
Adjusted effect-sizes for publication bias bases on Duval and Tweedie's trim and fill method
| Egger's regression test of publication bias | Adjusted effect-sizes | |||||||||
| B | SE | Ll to Ul | t-value (df) | p-value (1-tailed) | St | r | Ll | Ul | Q-value | |
| Age | −0.71 | 2.85 | [−6.94, 5.50] | 0.251 (12) | 0.402 | - | −0.18 | −0.26 | −0.10 | 312.879 |
| internet use | 2.16 | 0.98 | [0.19, 4.13] | 2.190 (84) | 0.015 | 18(R) | 0.46 | 0.42 | 0.49 | 2693.995 |
| FU | 4.96 | 2.12 | [0.16, 9.76] | 2.339 (9) | 0.022 | - | 0.35 | 0.27 | 0.42 | 139.914 |
| IGU | 26.82 | 8.81 | [−85, 138] | 3.042 (1) | 0.101 | - | 0.49 | 0.32 | 0.64 | 23.908 |
Note. FU = problematic Facebook use, IGU = Instagram use, St = Studies trimmed, R = right of mean.
Fig. 2.
Funnel Plot for the publication bias. The eighteen black nodes (potential studies) trimmed to the right of the mean, suggesting that the pooled ES of FoMO and internet use association is underestimated
Study characteristics
The included studies were published from 2013 to 2021, with the participation of 55,134 individuals (Females = 58.37%) with a mean age of 22.07 (SD = 6.15). Regarding the origin of studies, 45%, 32%, 19%, and 4% were conducted in Asia, Europe, the USA, and Oceania. Data collection was predominantly online (61%), followed by the paper-and-pencil method (25%), and 14% of studies with an unknown data collection modality. Furthermore, 68.23% and 16.47% of the studies were conducted before and after the COVID-19 pandemic, respectively, and the remaining 16.47% were unspecified.
The averaged internal consistency for FoMO (a = 0.83) and internet use measurements (a = 0.85) were acceptable. The spent hours per week on social media was M = 31.71 (SD = 18.15). Moreover, the mean scores and standard deviations (SD) for variables of interest were averaged into a scale of one to ten for the included participants as follows: FoMO = 4.93 (SD = 0.67), internet use = 4.72 (1.36); Facebook use = 4.26 (SD = 1.10), Instagram use = 5.03 (SD = 0.55). For psychological variables scores the mean was as follows: depressive symptoms = 2.89 (SD = 0.73), anxiety symptoms = 2.34 (SD = 0.48), stress symptoms = 3.51 (SD = 0.17), and satisfaction with life = 7 (SD = 0.26).
FoMO and internet use
The association of trait-FoMO with internet use is estimated as r = 0.41 95% CI [0.38, 0.44]. However, given that the Q-value exceeded the df; thus, the mean point estimation no longer fits, and PI values should be granted. As seen in Table 2, the prediction interval suggests that the FoMO- internet use relationship is low as r = 0.11 in some populations and high as r = 0.63 in some populations.
Table 2.
FOMO and internet use, effect-sizes, heterogeneity, and prediction interval
| Effect-sizes and 95% interval | Heterogeneity | Prediction interval | ||||||||
| K | n | r | Ll | Ul | Q-value (df) | I 2 | T 2 | Ll | Ul | |
| Age | 14 | 16,428 | −0.19 | −0.26 | −0.11 | 733.753 (13) | 98.23 | 0.053 | −0.48 | 0.14 |
| internet use | 85 | 55,134 | 0.41 | 0.38 | 0.44 | 1,428.198 (85) | 94.04 | 0.025 | 0.11 | 0.63 |
| FU | 11 | 8,339 | 0.35 | 0.27 | 0.42 | 139.914 (10) | 92.85 | 0.020 | 0.03 | 0.60 |
| IGU | 3 | 1,019 | 0.49 | 0.32 | 0.64 | 23.908 (2) | 91.63 | 0.033 | −0.97 | 0.99 |
Note. PFU = problematic Facebook use, PIGU = problematic Instagram use.
FoMO and social media: Specific to content
The adjusted ES for Facebook use was r = 0.35, 95% CI [0.27, 0.42], and the PI values indicate that in some populations, the ESs are as high as r = 0.60 and in some as trivial as r = 0.03. Also, the adjusted ES for Instagram use was r = 0.49, 95% CI [0.32, 0.64], and the PI values indicate that in some populations, the ESs are as high as r = 0.99 and in some as low as -0.97. However, the omnibus test showed insignificant differences between Facebook and Instagram use (Q = 3.062, df = 1, P = 0.08).
Effect size as a function of FoMO and internet use severity
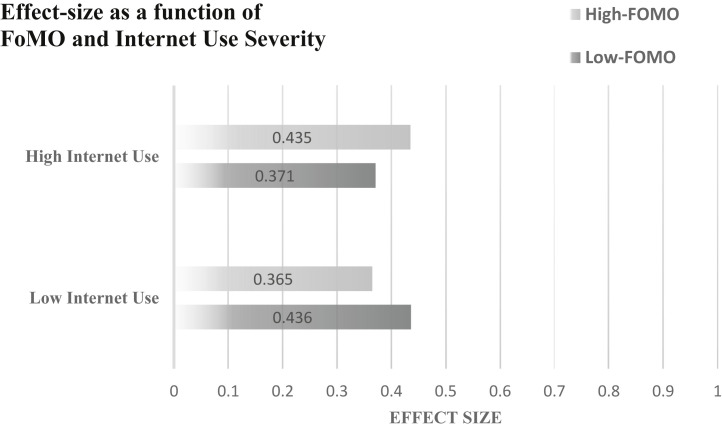
We tested to determine if the association between FoMO and internet use is dependent on the level of each. The effect-size based on low FoMO severity was r = 0.43 and r = 0.37 for low and high internet use severity, averaged in r = 0.40; as well, the ESs based on high FoMO severity was r = 0.36 and r = 0.43 for low and high internet use severity, averaged in r = 0.40. Likewise, the ES based on low internet use severity was r = 0.43 and 0.36 for low and high FoMO severity, averaged in r = 0.40; similarly, the ESs based on high internet use was r = 0.37 and r = 0.43 for low and high FoMO severity, averaged in r = 0.40. As seen, there is no significant interaction between different levels of FoMO and internet use (ps > 0.05), which is depicted in Fig. 3. Moreover, given that the interaction was insignificant, it was worthwhile to determine whether this relationship is linear or curvilinear. Neither the linear (b = 0.022, SE = 0.03, 95% CI [−0.03–0.08], P = 0.465) nor the curvilinear (b = −0.009, SE = 0.02, 95% CI [−0.05–0.04], P = 0.701) association was statistically significant.
Fig. 3.
Effect-size as a function of FoMO and internet use severity. There were no significant differences at any level of severity
FoMO and age
The Adjusted ES for the association of age with FoMO was r = −0.19, 95% CI [−0.26, −0.11], and the PI values indicate that in some populations, the ESs is as high as r = 0.14 and in some as low as r = −0.48.
Categorical moderator analysis
General population versus students
As seen in Table 3, there was no substantial variation in the relationship between FoMO and internet use, FoMO and Instagram use, FoMO and Facebook use, and FoMO and age between general populations and students (P > 0.10).
Table 3.
Pairwise omnibus test comparing general population versus students, adults versus teenagers
| Variables | Effect-sizes and 95% interval | Omnibus test | ||||||
| Participants | K | n | r | Ll | Ul | Q (df) | p-value | |
| Internet use | General population | 28 | 22,747 | 0.44 | 0.38 | 0.50 | 1.60 (1) | 0.20 |
| students | 58 | 32,387 | 0.40 | 0.36 | 0.43 | |||
| Adults | 47 | 24,909 | 0.43 | 0.39 | 0.48 | 2.69 (1) | 0.10 | |
| Teenagers | 39 | 30,225 | 0.38 | 0.35 | 0.42 | |||
| Facebook use | General population | 4 | 3,339 | 0.40 | 0.27 | 0.52 | 1.063 (1) | 0.30 |
| students | 7 | 5,000 | 0.32 | 0.21 | 0.42 | |||
| Adults | 6 | 4,284 | 0.36 | 0.25 | 0.47 | 0.11 (1) | 0.74 | |
| Teenagers | 5 | 4,055 | 0.34 | 0.21 | 0.45 | |||
| Instagram use | General population | 2 | 682 | 0.53 | 0.21 | 0.74 | 0.150 (1) | 0.69 |
| students | 1 | 337 | 0.43* | −0.06 | 0.75 | |||
| Adults | 1 | 377 | 0.43* | −0.06 | 0.75 | 0.15 (1) | 0.70 | |
| Teenagers | 2 | 682 | 0.53 | 0.21 | 0.74 | |||
Note. * = insignificant.
Adults versus teenagers
When comparing adults (>20 years old) to teenagers (13–20 years old), as seen in Table 3, the strengths of the relationship between FoMO and internet use, FoMO and Instagram use, FoMO and Facebook use, and FoMO and age between adults and teenagers were not substantially different (P > 0.10).
High versus low in mean scores
The high or low mean scores in FoMO and internet use or Facebook use have an insignificant effect on the ESs in this regard. However, as seen in Table 4, the level of Instagram use and not the level of FoMO is the only significant moderator of the relationship between FoMO and Instagram use. As a result, the higher the use of Instagram, the stronger the correlation with FoMO, but the opposite was not significant.
Table 4.
Categorical moderator analysis
| Effect-size and Interval 95% | Pairwise omnibus test | |||||
| Moderator | K | r | Ll | Ul | Q-value (df) | p-value |
| Internet Use | ||||||
| Dependent variable means scores | ||||||
| Higher than 5 | 23 | 0.41 | 0.35 | 0.46 | 0.06 (1) | 0.97 |
| Lower than 5 | 63 | 0.41 | 0.38 | 0.45 | ||
| FOMO mean scores | ||||||
| Higher than 5 | 29 | 0.39 | 0.34 | 0.44 | 0.77 (1) | 0.37 |
| Lower than 5 | 57 | 0.42 | 0.38 | 0.46 | ||
| Data collection | ||||||
| In-person | 27 | 0.40 | 0.35 | 0.44 | 0.77 (2) | 0.69 |
| Online | 45 | 0.42 | 0.38 | 0.46 | ||
| Unknown | 14 | 0.40 | 0.28 | 0.50 | ||
| COVID-19 Pandemic | ||||||
| Before | 58 | 0.38 | 0.35 | 0.41 | 9.54 (2) | 0.00 |
| After | 14 | 0.54 | 0.45 | 0.63 | ||
| Unknown | 14 | 0.38 | 0.31 | 0.45 | ||
| Facebook use | ||||||
| Dependent variable mean scores | ||||||
| Higher than 5 | 1.00 | 0.45 | 0.20 | 0.64 | 0.77 (1) | 0.38 |
| Lower than 5 | 10.00 | 0.34 | 0.26 | 0.42 | ||
| FOMO mean scores | ||||||
| Higher than 5 | 5.00 | 0.34 | 0.22 | 0.46 | 0.02 (1) | 0.87 |
| Lower than 5 | 6.00 | 0.36 | 0.24 | 0.46 | ||
| Data collection | ||||||
| In-person | 4.00 | 0.32 | 0.19 | 0.44 | 0.31 (1) | 0.58 |
| Online | 7.00 | 0.37 | 0.27 | 0.46 | ||
| COVID-19 Pandemic | ||||||
| Before | 6 | 0.35 | 0.20 | 0.48 | 1.55 (1) | 0.21 |
| After | 2 | 0.44 | 0.38 | 0.49 | ||
| Instagram use | ||||||
| Dependent variable means scores | ||||||
| Higher than 5 | 1.00 | 0.65 | 0.57 | 0.72 | 23.24 (1) | 0.01 |
| Lower than 5 | 2.00 | 0.40 | 0.34 | 0.46 | ||
| FoMO mean scores | ||||||
| Higher than 5 | 2.00 | 0.53 | 0.21 | 0.74 | 0.15 (1) | 0.70 |
| Lower than 5 | 1.00 | 0.43* | −0.06 | 0.75 | ||
Note. * = insignificant.
Online versus in-person data collection
In this regard, as seen in Table 4, the omnibus test is not significant for FoMO, and internet use relationship and FoMO and Facebook use relationship, suggesting that the effect-sizes are not varied based on the method of data collection. However, it was not applicable to do for Instagram use due to the low numbers of studies.
Before versus after COVID-19 pandemic
The studies’ effect sizes based on their temporality concerning the COVID-19 pandemic were significantly different. Based on Table 4, the conducted researches after the pandemic have demonstrated a stronger correlation between FoMO and internet use. This suggested that the COVID-19 pandemic did moderate the mentioned relationship.
Continuous moderator analysis: Univariate and multiple meta-regression
According to the multicollinearity test, the variance inflation factor (VIF) index ranged from 1.28 to 1.70, indicating that running a multiple meta-regression model is feasible. Next, to determine the power of each covariate to explain the observed heterogeneity before conducting a meta-regression, each covariate was separately included in a univariate meta-regression model. The examined covariates were demographic (temporality of studies (before or after the COVID-19, female proportion, year of publication, and internet use usage time), psychological (depression, anxiety, stress, life satisfaction, severity of internet use and FoMO), and methodological (Cronbach’s alpha and data collection).
Of this, the only significant model was the temporality of studies (before or after the COVID-19) which explained 22% of the 94.04% of the ESs heterogeneity on its own (b = 0.20, SE = 0.059, 95% CI [0.08, 0.32], P = 0.001) in the univariate regression model. After controlling the variables listed in Table 5 in the multiple meta-regression model, it remained a significant moderator and explained 15% heterogeneity. However, all of the mentioned variables together in the multiple meta-regression explained 32% heterogeneity. Notwithstanding, the included variables were insignificant in the univariate regression and the multiple meta-regression models except the temporality of studies. So, the actual explained percentage of heterogeneity is 15% after controlling for all of those mentioned above. Nonetheless, 79.93% of the ESs disparities remained unexplained. Table 5 displays the multiple meta-regression model.
Table 5.
Multiple meta-regression model
| Covariates | b | SE | 95%Ll | 95%Ul | p-value-2tailed |
| Intercept | −9.36 | 36.36 | −82.20 | 63.47 | 0.80 |
| Age | 0.003 | 0.004 | −0.006 | 0.011 | 0.53 |
| Female % | 0.001 | 0.002 | −0.002 | 0.004 | 0.54 |
| Year | 0.004 | 0.018 | −0.032 | 0.040 | 0.82 |
| Time Use | 0.0004 | 0.0013 | −0.0021 | 0.0030 | 0.74 |
| Depression | 0.01 | 0.04 | −0.07 | 0.09 | 0.85 |
| Anxiety | 0.07 | 0.12 | −0.18 | 0.32 | 0.57 |
| Stress | 0.11 | 0.12 | −0.13 | 0.36 | 0.36 |
| Life Satisfaction | 0.11 | 0.09 | −0.06 | 0.28 | 0.20 |
| FOMO alpha | 0.10 | 0.46 | −0.82 | 1.02 | 0.83 |
| DV* alpha | 0.42 | 0.53 | −0.64 | 1.48 | 0.43 |
| DV Mean | −0.06 | 0.06 | −0.17 | 0.05 | 0.30 |
| FOMO Mean | 0.003 | 0.05 | −0.10 | 0.11 | 0.95 |
| Data Collection | −0.01 | 0.08 | −0.17 | 0.14 | 0.89 |
| COVID-19 pandemic | 0.20 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.32 | 0.01 |
| Test of the model: Simultaneous test that all coefficients (excluding intercept) are zero | |||||
| F = 1.52, df = 15, 56, p = 0.130 | |||||
| Total between-study variance (intercept only) | |||||
| T 2 = 0.0292, T = 0.1708, I 2 = 94.24%, Q = 1,232.09, df = 71, p = 0.001 | |||||
| Proportion of total between-study variance explained by model | |||||
| R 2 = 0.32 | |||||
Note. DV corresponds to mobile internet use measures.
Discussion
The current study sought to quantify the strength of the association between FoMO and internet use, as the first meta-analysis to our knowledge adhered to the new taxonomy toward unifying the literature on uses of internet, social media and smartphone (Browne et al., 2021; Elhai, Yang, & Levine, 2021; Montag et al., 2019; Moretta et al., 2020; Rumpf et al., 2021; Wu et al., 2021), as well as looking for predisposing variable linking to internet use (Montag et al., 2019).
Although twenty-three percent of the final entered studies were judged to have a moderate risk of bias, sensitivity analysis revealed that this had little impact on the firmness of the findings. Moreover, even though the publication bias was significant for internet use and Facebook use, the adjusted ESs were not different, enabling the study’s findings to be summarized and interpreted.
FoMO and internet use severity: Is there a significant interaction?
The results showed that FoMO and internet use severity interacted insignificantly, suggesting that neither level influences the strength of the trait FoMO- internet use association. While this result was unexpected, Wegman et al. (2017)’s conceptualization of FoMO can explain it. According to the authors, FoMO could be regarded as a stable trait that reflects certain predispositions. Still, there is a specific cognition regarding fear of missing something online, called state-FoMO. They conceptualize that trait-FoMO represents the tendency to develop state-FoMO and other internet-related cognitions. In a test of this theory, state-FoMO and not trait-FoMO is found to mediate the relationship between an individual’s core characteristics and internet-communication disorder (Wegmann et al., 2017). A study by Balta et al. (2020) also supported this idea, as state-FoMO mediates the relationship between trait-FoMO and phubbing behavior as well as Instagram use.
Moreover, it could be used to speculate regarding disparities, the null association for FoMO-Facebook uses among some people, negative and positive association of FoMO-Instagram use among some populations. Since each application can provoke different behavior patterns and provide different reward patterns (Montag et al., 2019), state-FoMO as a specific cognition toward any online activity may correspond to the found notable variations.
Does FoMO’s association with internet use vary across studies?
The heterogeneity of included studies was significant; the strength of this association varied from r = 0.11 to r = 0.63 across different populations, suggested by prediction intervals. It was impossible to determine which people have the lowest or the highest association at the study level, as moderator analysis revealed no differences between adults vs. teenagers and the general population vs. students.
FoMO and internet use: Specific to content
Regarding internet use’s specific content, FoMO had a trivial association with Facebook use in some populations, suggesting that the level of experiencing FoMO is not linked to engaging in Facebook use for some individuals but not for all. However, this trend was different in the case of Instagram use. It was observed that higher FoMO in some people is strongly associated with problematic Instagram use, while in others, it is associated with ending the use of Instagram, which suggests a possible bi-directional association. Besides, given the insignificant difference in Facebook and Instagram uses between teenagers and adults, it can be inferred that their association with FoMO is unrelated to the life stage.
Regarding Instagram use concerning FoMO, we speculate that there is an ambivalent stage, where individuals go back and forth from using more to using less and eventually ’graduating’ into excessive use, is plausible. This thesis is aligned with CIUT. When the state experienced is still not problematic, internet use appears a voluntary coping strategy; when the person feels it may not work, they may disengage. Again, when the negative situations (e.g., unmet needs) remain unchanged, individuals may start re-using. Once this becomes excessive use, FoMO will steadily motivate internet use-specifically Instagram use. The I-PACE model can also explain this ’pre-stage.’ Accordingly, there is an early stage in which frontostriatal circuits are imbalanced. But in the addictive behavior formation stage, the dorsal striatum becomes imbalanced, and by its caudate nucleus corresponds to compulsive behaviors (Maia, Cooney, & Peterson, 2008). Also, these findings, different results for FoMO-Facebook use vs. FoMO-Instagram use indicates the importance of noticing to the used content, it is justified by considering that specific needs, expectations, and rewards could influence the preference in a particular type of application or content (Montag et al., 2019).
FoMO and age: Is FoMO stable across the board?
A significant heterogeneity makes it less relevant to accept the mean effect-size as the estimated strength of the association between trait-FoMO and age. Moreover, this association was not significantly different comparing teenagers vs. adults or between the general populations vs. students (P > 0.50). This implies that some groups may be more vulnerable to experiencing FoMO-prone activities, such as excessive internet use, regardless of their life stage. However, the prediction intervals suggest not whole populations are moving in the same direction. Surprisingly, the finding suggests that FoMO may rise with age in some populations, as well, some people demonstrate a null correlation between FoMO and age.
The association of FoMO and internet use: Looking toward potential moderators
As seen in Tables 3 and 4, several continuous and categorical potential moderators were explored to determine how strength of FoMO- internet use association can vary. The only significant moderator was the temporality of studies, as being conducted after the COVID-19 pandemic has positively increased the mentioned strength. It supports CIUT, as people tend to use internet use to compensate for something out of access, having touch during the pandemic. Also it explain that distress can strengthen the FoMO- internet use association (Kardefelt-Winther, 2014), as people use the internet as a coping strategy to relieve from the experienced negative affectivity.
FoMO and internet use: What do we know and don’t know
In the current study we conducted a quantitative literature review on FoMO and internet use. Based on previous meta-analyses, we knew the quantified strength of the association for FoMO-social media. However, we did not know the strength of this association concerning internet use and if the effect-sizes varied across studies. Additionally, we were unsure whether a bidirectional relationship exists between FoMO and internet use. We also did not know the relationship’s strength between FoMO and age to gain a developmental perspective on it.
In light of the current meta-analysis, we discovered that the effect sizes for FoMO and internet use and FoMO and age vary. Additionally, by examining a meta-analytic interaction and the non-significant effect of FoMO or internet use on the strength of the association, we gained a better understanding of bi-directionality. What we still don’t know is what factors contribute to individuals exhibiting distinct patterns of in the FoMO-internet use association.
Limitations
This review’s strength is that it was performed following existing standards (Borenstein, 2019) and afforded a timely viewpoint on the current status of FoMO and internet use. Despite this, some limitations need to mention before drawing conclusions, which are as follows. (1) All findings should be interpreted in light of the observational nature of the current meta-analysis, as all comparisons made were indirect, and casualties could not be inferred given the cross-sectional design of included studies; (2) As the majority of participants were female (58.37%), young (Mean = 22.07, SD = 6.15), and Asian (45%), followed by 32% Europeans and 19% Americans, findings are confined to these groups; (3) The included studies had, on average, few psychological variables in relation with FoMO- internet use, thus, future studies might want to consider variables such as internet usage motives (Amiel & Sargent, 2004; Bischof-Kastner, Kuntsche, & Wolstein, 2014), emotion dysregulation (Mo, Chan, Chan, & Lau, 2018), social support (Gunuc & Dogan, 2013), impulsivity and obsessive passion (Burnay, Billieux, Blairy, & Larøi, 2015; Lee et al., 2012), limiting moderator analysis, leaving the cause of observed heterogeneity unexplained; (5) The surveyed literature is limited in reporting the used content by the participants in studies, as each participant may have different internet use from other participants.
Conclusions
According to observations so far (1), The strength of the Trait FoMO-internet use association significantly varies from r = 0.11 to r = 0.63; (2) It was not significantly different between the general versus student population or adults versus teenagers; (3) The FoMO- internet use association was independent of their severity, as the interaction was not significant; (4) The association was neither linear nor curvilinear; (5) This association does not appear to be associated with depressive, anxiety, and stress symptoms or by the level of life satisfaction; (6) Given the in-person or online data collection, this association remained stable; (7) The COVID-19 pandemic was the only significant moderator of the FoMO-internet use association, strengthening this relationship; (8) Facebook use was unrelated to FoMO in some populations; (9) Higher FoMO was linked with stopping Instagram use for some individuals; (10) In some populations, FoMO increases with age and is reverse in some populations.
Future directions
In light of this study, the following recommendations were made for consideration (1), Given that effect sizes vary, it should be considered before calculating sample size for studying FoMO and internet use, FoMO-Facebook, and Instagram use; sample size needs the power to detect the least calculated prediction intervals represented in Table 2; (2) Moreover, based on the findings, given no evidence of a linear or curvilinear relationship between FoMO and internet use, future research might want to examine other types of non-linearity, such as the quadratic or cubic relationship between FoMO-internet use, FoMO-Facebook, and Instagram use. Likewise, future studies using the regression method in studying FoMO- internet use need to pay attention to whether the non-linear regression method is more appropriate; (3) Considering users’ different behavior patterns and rewards (Brand et al., 2019), future studies should separate their participants according to their internet usage, and also if they are a passive or an active users (Montag et al., 2019); (4) Future studies must investigate which factors interact with FoMO or moderate its association with internet use and consider state-FoMO when studying the FoMO-internet use, FoMO-Facebook, and Instagram use; (5) It is worth examining the possible bi-directional association of FoMO with Instagram usage through a longitudinal design; (6) Given the significant moderating role of the COVID-19 pandemic, considering state-FoMO and using the daily diary method may shed light on how distress can increase the FoMO- internet use association.
Authors’ contribution
The authors’ roles in the preparation of the study is as follows: Study concept and design: MA, MSp & MSe. Data Curation: MSe & MA. Analysis and interpretation of data: MA & MSe. Statistical analysis: MA & MSe. Drafting the manuscript: MA, MS, SP, GM, MSp, GC. Final edition: MA, MSe, MSp, SP, GS, GM and GS have read and edited the final version of the study. Approval of the version of the manuscript to be published: MA, MSe, MSp, SP, GM, GC.
Funding infromation
The research did not receive any specific grant funding from any public, commercial, or non-profit agencies.
Conflicts of interests
The authors have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have influenced this work.
Appendix A
Information of Extracted Data
| Study | Reported Content | population | r | n | COVID-19 | INTERNET USE alpha | FoMO alpha | Female% | age | INTERNET USE x– | FoMO x– | Data Collection |
| Elhai et al., (2016) | smartphone use | general | 0.40 | 308 | pre | 0.95 | 0.84 | 46.4 | 33.15 | 8.47 | 4.25 | online |
| Wolniewicz et al., (2020) | smartphone use | Student | 0.53 | 297 | pre | 0.92 | 0.87 | 72.1 | 19.7 | 4.62 | 4.68 | online |
| Elhai et al., (2018) | smartphone use | Student | 0.51 | 296 | pre | 0.93 | 0.9 | 76.7 | 19.44 | 4.72 | 4.8 | online |
| Elhai et al. (2020) | smartphone use | Student | 0.51 | 316 | pre | 0.86 | 0.89 | 66.8 | 19.21 | 4.57 | 4.52 | online |
| Elhai et al., (2020) | smartphone use | Student | 0.29 | 1,034 | pre | 0.92 | 0.81 | 65.3 | 19.34 | 5.82 | 5.18 | online |
| Long, Wang, Liu, and Lei (2019) | smartphone use | Student | 0.38 | 677 | pre | 0.86 | 0.73 | 41.1 | 16.79 | 5.68 | 5.66 | in-person |
| Wang, Wang, Nie, et al. (2019) | smartphone use | Student | 0.40 | 724 | pre | 0.86 | 0.74 | 56.9 | 16.79 | 5.7 | 5.64 | in-person |
| Lee et al., (2021) | smartphone use | Student | 0.56 | 218 | pre | 0.85 | 0.9 | 57.3 | 19.26 | 4.74 | 5.58 | online |
| Traş and Öztemel (2019) | smartphone use | Student | 0.44 | 608 | pre | 0.85 | 0.83 | 71.87 | 21.34 | 4.74 | 5.57 | in-person |
| Upreti and Musalay (2018) | smartphone use | Student | 0.21 | 300 | pre | 0.85 | 0.84 | 50 | 22.68 | 4.48 | 5.41 | in-person |
| Tugtekin, Barut Tugtekin, Kurt, and Demir (2020) | smartphone use | Student | 0.52 | 469 | pre | 0.85 | 0.83 | 58.4 | 22.68 | 4.74 | 5.32 | in-person |
| Yam and Kumcağız (2020) | smartphone use | Student | 0.62 | 327 | post | 0.91 | 0.88 | 73.08 | 22.68 | 5.08 | 5.12 | online |
| Brown, George, and Rickwood (2021) | smartphone use | general | 0.40 | 528 | Blank | 0.86 | 0.88 | 70 | 20.46 | 5.34 | 5.06 | online |
| Gezgin (2018) | smartphone use | Student | 0.66 | 161 | pre | 0.76 | 0.77 | 41.6 | 16.22 | 4.87 | 4.9 | in-person |
| Gezgin (2018) | smartphone use | Student | 0.05 | 161 | pre | 0.76 | 0.77 | 41.6 | 16.22 | 4.87 | 4.9 | in-person |
| Adelhardt, Markus, and Eberle (2018) | smartphone use | Student | 0.56 | 34 | pre | 0.85 | 0.83 | 50 | 22.68 | 4.74 | 4.89 | in-person |
| Li, Griffiths, Mei, and Niu (2020) | smartphone use | Student | 0.39 | 2,886 | post | 0.9 | 0.82 | 52.04 | 14.79 | 4.74 | 4.89 | in-person |
| Buyukbayraktar (2020) | smartphone use | Student | 0.49 | 610 | Blank | 0.87 | 0.83 | 53.3 | 22.68 | 4.74 | 4.89 | N.S |
| Elhai et al., (2020) | smartphone use | general | 0.72 | 812 | post | 0.85 | 0.83 | 50.1 | 44.45 | 4.73 | 4.89 | online |
| Coco et al., (2020) | smartphone use | Student | 0.40 | 242 | pre | 0.79 | 0.78 | 54.95 | 14.16 | 4.16 | 4.89 | in-person |
| Li, Griffiths, Mei, and Niu (2020) | smartphone use | Student | 0.33 | 1,164 | post | 0.86 | 0.82 | 14.13 | 20.1 | 4.95 | 4.88 | online |
| Coskun and Muslu (2019) | smartphone use | Student | 0.37 | 1,630 | pre | 0.85 | 0.83 | 55 | 22.68 | 4.51 | 4.82 | in-person |
| Tunc-Aksan and Akbay (2019) | smartphone use | Student | 0.42 | 296 | pre | 0.92 | 0.81 | 45.94 | 22.68 | 4.51 | 4.56 | in-person |
| Wolniewicz et al., (2018) | smartphone use | Student | 0.42 | 299 | pre | 0.88 | 0.87 | 57.1 | 20 | 4.5 | 4.4 | N.S |
| Chotpitayasunondh and Douglas (2016) | smartphone use | general | 0.61 | 251 | pre | 0.91 | 0.9 | 63.4 | 27.7 | 4.5 | 4.38 | online |
| Servidio (2021) | smartphone use | Student | 0.35 | 405 | pre | 0.8 | 0.73 | 71.11 | 22.11 | 4.47 | 4.32 | in-person |
| Sha et al., (2019) | smartphone use | general | 0.40 | 2,299 | pre | 0.8 | 0.76 | 39.19 | 30.33 | 4.56 | 4.06 | online |
| Liu and Ma (2020) | smartphone use | Student | 0.36 | 465 | Blank | 0.9 | 0.85 | 69.24 | 18.83 | 5.19 | 4.03 | N.S |
| Gugushvili et al., (2020) | smartphone use | general | 0.42 | 426 | pre | 0.89 | 0.83 | 77 | 26.74 | 2.06 | 3.2 | online |
| Elhai et al., (2020) | smartphone use | Student | 0.40 | 1,097 | post | 0.89 | 0.89 | 81.9 | 19.38 | 6.23 | 4.68 | online |
| O’Connell, (2020) | smartphone use | Student | 0.43 | 253 | Blank | 0.88 | 0.87 | 61 | 22.68 | 4.68 | 5.1 | online |
| Reer, Tang, and Quandt (2019) | social media use | general | 0.30 | 1,865 | pre | 0.81 | 0.87 | 51.5 | 27.65 | 3.84 | 5.22 | online |
| Tsai et al., (2019) | social media use | general | 0.19 | 187 | pre | 0.85 | 0.88 | 36 | 45.37 | 4.74 | 3.99 | online |
| Oberst, Wegmann, Stodt, Brand, and Chamarro (2017) | social media use | general | 0.46 | 1,468 | Blank | 0.79 | 0.83 | 74.31 | 16.59 | 6.63 | 4.26 | online |
| Kacker and Saurav (2020) | social media use | general | 0.12 | 600 | Blank | 0.85 | 0.83 | 44.83 | 22.68 | 2.52 | 6.6 | N.S |
| Shen, Zhang, and Xin (2020) | social media use | Student | 0.43 | 399 | pre | 0.7 | 0.63 | 56.64 | 20.4 | 6.59 | 6.54 | online |
| Sindermann, Yang, Liu, Elhai, and Montag (2021) | social media use | Student | 0.51 | 377 | post | 0.93 | 0.85 | 75.86 | 21.64 | 5.38 | 6.04 | online |
| Hamutoglu, Topal, and Gezgin (2020) | social media use | Student | 0.48 | 845 | Blank | 0.85 | 0.83 | 50 | 22.68 | 7.11 | 5.81 | N.S |
| Wang et al., (2018) | social media use | Student | 0.37 | 832 | pre | 0.78 | 0.8 | 48 | 16.43 | 4.74 | 5.74 | in-person |
| Yin et al., (2021) | social media use | Student | 0.41 | 704 | pre | 0.87 | 0.75 | 57.2 | 16.8 | 5.26 | 5.64 | in-person |
| Classen et al., (2020) | social media use | general | 0.33 | 218 | Blank | 0.8 | 0.8 | 73.85 | 22.68 | 6.86 | 5.4 | online |
| Luo and Liang (2018) | social media use | Student | 0.27 | 68 | pre | 0.85 | 0.88 | 73.5 | 21.1 | 4.74 | 5.1 | in-person |
| Pontes e al., (2018) | social media use | general | 0.68 | 511 | pre | 0.86 | 0.91 | 64.6 | 22.68 | 4.74 | 4.9 | online |
| Blackwell et al., (2017) | social media use | general | 0.46 | 207 | pre | 0.85 | 0.91 | 74.87 | 22.15 | 4.74 | 4.89 | online |
| Lai, Altavilla, Ronconi, and Aceto (2016) | social media use | general | 0.60 | 20 | pre | 0.85 | 0.87 | 45 | 24.1 | 4.74 | 4.89 | in-person |
| Tomczyk & Lizde, (2018) | social media use | Student | 0.50 | 717 | pre | 0.85 | 0.83 | 47 | 13 | 4.74 | 4.89 | in-person |
| Munawaroh et al., (2020) | social media use | Student | 0.57 | 106 | post | 0.85 | 0.83 | 100 | 22.68 | 4.74 | 4.89 | online |
| Liu and Ma (2019) | social media use | Student | 0.56 | 463 | Blank | 0.94 | 0.83 | 74.29 | 19.94 | 4.74 | 4.89 | N.S |
| Alt, (2015) | social media use | Student | 0.54 | 296 | pre | 0.84 | 0.83 | 85.3 | 25.4 | 2.26 | 4.61 | in-person |
| Rozgonjuk, Sindermann, Elhai, and Montag (2020) | social media use | general | 0.47 | 748 | Blank | 0.9 | 0.77 | 55.08 | 38.63 | 3.72 | 4.59 | online |
| Tunc-Aksan and Akbay (2019) | social media use | Student | 0.43 | 296 | Blank | 0.74 | 0.81 | 45.94 | 22.68 | 2.54 | 4.56 | in-person |
| Fabris, Marengo, Longobardi, and Settanni (2020) | social media use | Student | 0.48 | 472 | post | 0.73 | 0.81 | 50 | 13.49 | 4.24 | 4.51 | in-person |
| Fuster et al., (2017) | social media use | general | 0.378 | 5,280 | pre | 0.81 | 0.85 | 76.18 | 15.47 | 2.02 | 4.48 | online |
| Casale, Rugai, and Fioravanti (2018) | social media use | Student | 0.45 | 579 | pre | 0.82 | 0.81 | 54.6 | 22.39 | 3.98 | 4.43 | in-person |
| Barry and Wong (2020) | social media use | general | 0.33 | 419 | pre | 0.86 | 0.88 | 75.89 | 30.29 | 4.74 | 4.26 | online |
| Sha et al., (2019) | social media use | general | 0.39 | 2,299 | pre | 0.88 | 0.76 | 39.19 | 30.33 | 3.6 | 4.06 | online |
| Liu and Ma (2020) | social media use | Student | 0.40 | 465 | Blank | 0.94 | 0.85 | 69.24 | 18.83 | 5.31 | 4.03 | N.S |
| Przybylski et al., (2013) | social media use | general | 0.40 | 2079 | pre | 0.82 | 0.9 | 49.97 | 43.21 | 2.07 | 3.78 | online |
| Wegmann et al., (2017) | social media use | general | 0.20 | 270 | pre | 0.83 | 0.82 | 70.37 | 23.43 | 4.17 | 4.86 | online |
| McAndrew (2018) | social media use | Student | 0.41 | 198 | pre | 0.82 | 0.87 | 86 | 19 | 5.86 | 5.04 | online |
| Tang et al., (2020) | Internet use | Student | 0.75 | 290 | post | 0.86 | 0.74 | 59.3 | 22.68 | 5.5 | 4.94 | online |
| Alt and Boniel-Nissim (2018a, 2018b) | Internet use | Student | 0.32 | 216 | pre | 0.8 | 0.82 | 49 | 22.68 | 4.4 | 5.64 | N.S |
| Metin-Orta, (2020) | Internet use | Student | 0.33 | 322 | Blank | 0.9 | 0.76 | 61.49 | 22.16 | 2.89 | 5.42 | N.S |
| Reyes et al., (2018) | Internet use | general | 0.57 | 1,060 | pre | 0.93 | 0.85 | 60.94 | 25.22 | 3.76 | 4.75 | in-person |
| Kargın, Türkben Polat, & Coşkun Şimşek (2020) | Internet use | Student | 0.33 | 511 | post | 0.85 | 0.83 | 72.6 | 22.68 | 4.74 | 4.65 | N.S |
| Aygar et al., (2019) | Internet use | Student | 0.42 | 463 | pre | 0.85 | 0.83 | 45.1 | 21 | 3.95 | 4.47 | N.S |
| Chotpitayasunondh and Douglas (2016) | Internet use | general | 0.58 | 251 | pre | 0.89 | 0.9 | 63.04 | 27.7 | 3.31 | 4.38 | online |
| Cabrera, Andal, Delariarte, Kallarackal, and Tanganco (2019) | Internet use | Student | 0.53 | 254 | Blank | 0.85 | 0.83 | 62.6 | 22.4 | 4.46 | 3.54 | in-person |
| Sela, Zach, Amichay-Hamburger, Mishali, and Omer (2020) | Internet use | Student | 0.38 | 85 | pre | 0.86 | 0.87 | 41 | 14.04 | 5.07 | 4.88 | online |
| Rahardjo and Mulyani (2020) | Instagram use | general | 0.65 | 259 | Blank | 0.91 | 0.83 | 68.3 | 18.85 | 5.62 | 7.22 | online |
| Sheldon et al., (2021) | Instagram use | Student | 0.43 | 337 | pre | 0.85 | 0.87 | 57.27 | 23.35 | 4.52 | 4.7 | online |
| Balta et al., (2020) | Instagram use | general | 0.38 | 423 | Blank | 0.89 | 0.78 | 53 | 17.15 | 4.97 | 5.25 | online |
| Li et al., (2020) | Social media use- frequency | student | 0.20 | 2,017 | Blank | 0.74 | 0.81 | 50.47 | 20.1 | 4.13 | online | |
| Burnell et al., (2019) | Social media use- frequency | Student | 0.17 | 717 | pre | 0.85 | 0.83 | 69 | 21.47 | 9.66 | 4.82 | online |
| Hamutoglu et al., (2020) | Social media use- frequency | Student | 0.23 | 845 | Blank | 0.85 | 0.83 | 50 | 22.68 | 1.32 | 5.81 | N.S |
| Stead and Bibby (2017) | Social media use- frequency | Student | 0.47 | 495 | pre | 0.89 | 0.84 | 69 | 20.62 | 4.9 | 4.91 | online |
| Gezgin (2018) | Social media use- frequency | Student | 0.43 | 161 | pre | 0.85 | 0.77 | 41.6 | 16.22 | 1.47 | 4.9 | in-person |
| Bloemen and De Coninck (2020) | Social media use- frequency | Student | 0.29 | 831 | pre | 0.85 | 0.7 | 35.9 | 15.94 | 4.74 | 4.89 | online |
| *Gullu and Serin (2020) | Social media use- frequency | general | 0.77 | 702 | post | 0.92 | 0.95 | 53 | 22.68 | 4.74 | 4.89 | N.S |
| Barber and Santuzzi (2017) | Social media use- frequency | Student | 0.30 | 241 | pre | 0.86 | 0.87 | 57.9 | 19.01 | 6.7 | 4.82 | N.S |
| Reyes et al., (2018) | Social media use- frequency | general | 0.41 | 1,060 | pre | 0.93 | 0.85 | 60.94 | 25.22 | 4.68 | 4.75 | in-person |
| Wolniewicz et al., (2018) | Social media use- frequency | Student | 0.12 | 299 | pre | 0.85 | 0.87 | 57.1 | 20 | 2.81 | 4.4 | N.S |
| Rogers and Barber (2019) | Social media use- frequency | Student | 0.21 | 97 | pre | 0.85 | 0.9 | 62 | 19.81 | 8.37 | 4.24 | in-person |
| Buglass, Binder, Betts, and Underwood (2017) | Social media use- frequency | general | 0.25 | 489 | pre | 0.85 | 0.88 | 47 | 20 | 5.08 | 4 | N.S |
| Cabrera et al., (2019) | Social media use- frequency | Student | 0.08 | 254 | Blank | 0.85 | 0.83 | 62.6 | 22.4 | 5.44 | 3.54 | in-person |
| Elhai et al., (2016) | Smartphone use- frequency | general | 0.04 | 308 | pre | 0.86 | 0.84 | 46.4 | 33.15 | 6.9 | 4.25 | online |
| Wolniewicz et al., (2020) | Smartphone use- frequency | Student | 0.18 | 297 | pre | 0.74 | 0.87 | 72.1 | 19.7 | 7.51 | 4.68 | online |
| Elhai et al., (2018) | Smartphone use- frequency | Student | 0.13 | 296 | pre | 0.76 | 0.9 | 76.7 | 19.44 | 7.31 | 4.8 | online |
| Elhai et al., (2020) | Smartphone use- frequency | Student | 0.20 | 1,034 | pre | 0.82 | 0.81 | 65.3 | 19.34 | 7.63 | 5.18 | online |
| Schneider and Hitzfeld (2019) | Internet use- frequency | general | 0.54 | 278 | Blank | 0.9 | 0.8 | 74 | 26.78 | 4.96 | 6.54 | online |
| Traş and Öztemel (2019) | Internet use- frequency | Student | 0.22 | 608 | pre | 0.85 | 0.83 | 71.87 | 21.34 | 4.74 | 5.57 | in-person |
| Franchina, Vanden Abeele, Van Rooij, Lo Coco, and De Marez (2018) | Facebook use | Student | 0.16 | 2,663 | pre | 0.82 | 0.83 | 57.1 | 14.87 | 4.88 | 6.22 | in-person |
| Fang, Wang, Wen, and Zhou (2020) | Facebook use | Student | 0.45 | 501 | post | 0.81 | 0.79 | 70.66 | 19.6 | 6.37 | 6.1 | in-person |
| Uram and Skalski (2020) | Facebook use | general | 0.43 | 309 | post | 0.86 | 0.89 | 59 | 25.11 | 4.82 | 5.57 | online |
| Traş and Öztemel (2019) | Facebook use | Student | 0.15 | 608 | pre | 0.85 | 0.83 | 71.87 | 21.34 | 4.74 | 5.57 | in-person |
| Beyens, Frison, and Eggermont (2016) | Facebook use | Student | 0.50 | 402 | pre | 0.78 | 0.84 | 57 | 16.41 | 4.74 | 5 | in-person |
| Riordan et al., (2020) | Facebook use | Student | 0.28 | 198 | pre | 0.85 | 0.83 | 80.8 | 19.7 | 4.74 | 4.89 | online |
| Sheldon et al., (2021) | Facebook use | Student | 0.39 | 337 | pre | 0.85 | 0.87 | 57.27 | 23.35 | 3.82 | 4.7 | online |
| Błachnio and Przepiórka (2018) | Facebook use | general | 0.45 | 360 | pre | 0.87 | 0.78 | 64 | 22.22 | 4.1 | 4.6 | online |
| Can and Satici (2019) | Facebook use | general | 0.43 | 371 | pre | 0.93 | 0.78 | 59.83 | 33.65 | 3.47 | 4.58 | online |
| Sha et al., (2019) | Facebook use | general | 0.31 | 2,299 | pre | 0.9 | 0.76 | 39.19 | 30.33 | 2.68 | 4.06 | online |
| Dempsey et al., (2019) | Facebook use | Student | 0.25 | 291 | pre | 0.85 | 0.87 | 57.6 | 20.03 | 2.54 | 4.41 | online |
| Reer et al., (2019) | Age | general | −0.15 | 1,865 | pre | 0.81 | 0.87 | 51.5 | 27.65 | 3.84 | 5.22 | online |
| Wolniewicz et al., (2020) | Age | Student | −0.16 | 297 | pre | 0.74 | 0.87 | 72.1 | 19.7 | 7.51 | 4.68 | online |
| Elhai et al., (2018) | Age | Student | −0.16 | 296 | pre | 0.93 | 0.9 | 76.7 | 19.44 | 4.72 | 4.8 | online |
| Tsai et al., (2019) | Age | general | −0.44 | 187 | pre | 0.85 | 0.88 | 36 | 45.37 | 4.74 | 3.99 | online |
| Schneider and Hitzfeld (2019) | Age | general | −0.41 | 278 | Blank | 0.9 | 0.8 | 74 | 26.78 | 4.96 | 6.54 | online |
| Wang et al., (2018) | Age | Student | −0.05 | 832 | pre | 0.78 | 0.8 | 48 | 16.43 | 4.74 | 5.74 | in-person |
| Classen et al., (2020) | Age | general | 0.05 | 218 | Blank | 0.8 | 0.8 | 73.85 | 22.68 | 6.86 | 5.4 | online |
| Stead and Bibby (2017) | Age | Student | −0.13 | 495 | pre | 0.89 | 0.84 | 69 | 20.62 | 4.9 | 4.91 | online |
| Rozgonjuk et al., (2020) | Age | general | −0.32 | 748 | Blank | 0.9 | 0.77 | 55.08 | 38.63 | 3.72 | 4.59 | online |
| Fabris et al., (2020) | Age | Student | 0.03 | 472 | post | 0.73 | 0.81 | 50 | 13.49 | 4.24 | 4.51 | in-person |
| Fuster et al., (2017) | Age | general | −0.08 | 5,280 | pre | 0.81 | 0.85 | 76.18 | 15.47 | 2.02 | 4.48 | online |
| Sha et al., (2019) | Age | general | −0.31 | 2,299 | pre | 0.9 | 0.76 | 39.19 | 30.33 | 2.68 | 4.06 | online |
| Przybylski et al., (2013) | Age | general | −0.37 | 2,079 | pre | 0.82 | 0.9 | 49.97 | 43.21 | 2.07 | 3.78 | online |
| Elhai et al., (2020) | Age | Student | −0.01 | 1,097 | post | 0.89 | 0.89 | 81.9 | 19.38 | 6.23 | 4.68 | online |
References
- (An asterisk indicates that the study was included in the meta-analysis) [Google Scholar]
- * Adelhardt, Z. , Markus, S. , & Eberle, T. (2018). Teenagers’ reaction on the long-lasting separation from smartphones, anxiety and fear of missing out. Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Social Media and Society, 212–216. 10.1145/3217804.3217914. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- * Alt, D. (2015). College students’ academic motivation, media engagement and fear of missing out. Computers in Human Behavior , 49, 111–119. 10.1016/j.chb.2015.02.057. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- * Alt, D. , & Boniel-Nissim, M. (2018a). Links between adolescents’ deep and surface learning approaches, problematic Internet use, and fear of missing out (FOMO). Internet Interventions , 13, 30–39. 10.1016/j.invent.2018.05.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alt, D. , & Boniel-Nissim, M. (2018b). Parent–Adolescent communication and problematic internet use: The mediating role of Fear Of Missing Out (FOMO). Journal of Family Issues , 39(13), 3391–3409. [Google Scholar]
- Al‐Saggaf, Y. , & O’Donnell, S. B. (2019). Phubbing: Perceptions, reasons behind, predictors, and impacts. Human Behavior and Emerging Technologies , 1(2), 132–140. [Google Scholar]
- Amiel, T. , & Sargent, S. L. (2004). Individual differences in internet usage motives. Computers in Human Behavior , 20(6), 711–726. [Google Scholar]
- Andreassen, C. S. , Torsheim, T. , Brunborg, G. S. , & Pallesen, S. (2012). Development of a Facebook addiction scale. Psychological Reports , 110(2), 501–517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- * Aygar, H. , Goktas, S. , Zencirci, S. A. , Alaiye, M. , Onsuz, M. F. , & Metintas, S. (2019). Association between fear of missing out in social media and problematic internet use in university students. Dusunen Adam , 32(4), 302–308. 10.14744/DAJPNS.2019.00044. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Baker, Z. G. , Krieger, H. , & LeRoy, A. S. (2016). Fear of missing out: Relationships with depression, mindfulness, and physical symptoms. Translational Issues in Psychological Science , 2(3), 275. [Google Scholar]
- * Balta, S. , Emirtekin, E. , Kircaburun, K. , & Griffiths, M. D. (2020). Neuroticism, trait fear of missing out, and phubbing: The mediating role of state fear of missing out and problematic Instagram use. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction , 18(3), 628–639. 10.1007/s11469-018-9959-8. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- * Barber, L. K. , & Santuzzi, A. M. (2017). Telepressure and college student employment: The costs of staying connected across social contexts. Stress and Health , 33(1), 14–23. 10.1002/smi.2668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- * Barry, C. T. , & Wong, M. Y. (2020). Fear of missing out (FoMO): A generational phenomenon or an individual difference? Journal of Social and Personal Relationships , 37(12), 2952–2966. 10.1177/0265407520945394. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- * Beyens, I. , Frison, E. , & Eggermont, S. (2016). “I don’t want to miss a thing”: Adolescents’ fear of missing out and its relationship to adolescents’ social needs, Facebook use, and Facebook related stress. Computers in Human Behavior , 64, 1–8. 10.1016/j.chb.2016.05.083. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Bischof-Kastner, C. , Kuntsche, E. , & Wolstein, J. (2014). Identifying problematic internet users: Development and validation of the internet motive questionnaire for adolescents (IMQ-A). Journal of Medical Internet Research , 16(10), e230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Błachnio, A. , & Przepiórka, A. (2018). Facebook intrusion, fear of missing out, narcissism, and life satisfaction: A cross-sectional study. Psychiatry Research , 259, 514–519. 10.1016/j.psychres.2017.11.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell, D. , Leaman, C. , Tramposch, R. , Osborne, C. , & Liss, M. (2017a). Extraversion, neuroticism, attachment style and fear of missing out as predictors of social media use and addiction. Personality and Individual Differences , 116, 69–72. [Google Scholar]
- * Blackwell, D. , Leaman, C. , Tramposch, R. , Osborne, C. , & Liss, M. (2017). Extraversion, neuroticism, attachment style and fear of missing out as predictors of social media use and addiction. Personality and Individual Differences , 116, 69–72. 10.1016/j.paid.2017.04.039. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- * Bloemen, N. , & De Coninck, D. (2020). Social media and fear of missing out in adolescents: The role of family characteristics. Social Media+ Society , 6(4), 2056305120965517. 10.1177/2056305120965517. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Borenstein, M. (2019). Common mistakes in meta-analysis and how to avoid them : Biostat Inc. [Google Scholar]
- Borenstein, M. , Hedges, L. V. , Higgins, J. P. T. , & Rothstein, H. R. (2009). Introduction to meta-analysis . Chichester, UK: Wiley. [Google Scholar]
- Borenstein, M. , Higgins, J. P. , Hedges, L. V. , & Rothstein, H. R. (2017). Basics of meta‐analysis: I 2 is not an absolute measure of heterogeneity. Research Synthesis Methods , 8(1), 5–18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand, M. , Wegmann, E. , Stark, R. , Müller, A. , Wölfling, K. , Robbins, T. W. , & Potenza, M. N. (2019). The Interaction of Person-Affect-Cognition-Execution (I-PACE) model for addictive behaviors: Update, generalization to addictive behaviors beyond internet-use disorders, and specification of the process character of addictive behaviors. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews , 104, 1–10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand, M. , Young, K. S. , Laier, C. , Wolfling, K. , & Potenza, M. N. (2016). Integrating psychological and neurobiological considerations regarding the development and maintenance of specific internet-use disorders: An Interaction of Person-Affect Cognition-Execution (I-PACE) model. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews , 71, 252–266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkmann, S. (2019). The joy of missing out: The art of self-restraint in an age of excess : John Wiley & Sons. [Google Scholar]
- Browne, D. T. , May, S. S. , Colucci, L. , & Rumpf, H. J. (2021). Developmental and family considerations in internet use disorder taxonomy. Commentary on: How to overcome taxonomical problems in the study of Internet use disorders and what to do with “smartphone addiction”?(Montag et al., 2020). Journal of Behavioral Addictions , 9(4), 920–923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- * Brown, P. M. , George, A. M. , & Rickwood, D. J. (2021). Rash impulsivity, reward seeking and fear of missing out as predictors of texting while driving: Indirect effects via mobile phone involvement. Personality and Individual Differences , 171, 110492. 10.1016/j.paid.2020.110492. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- * Buglass, S. L. , Binder, J. F. , Betts, L. R. , & Underwood, J. D. (2017). Motivators of online vulnerability: The impact of social network site use and FOMO. Computers in Human Behavior , 66, 248–255. 10.1016/j.chb.2016.09.055. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Burnay, J. , Billieux, J. , Blairy, S. , & Larøi, F. (2015). Which psychological factors influence internet addiction? Evidence through an integrative model. Computers in Human Behavior , 43, 28–34. [Google Scholar]
- * Burnell, K. , George, M. J. , Vollet, J. W. , Ehrenreich, S. E. , & Underwood, M. K. (2019). Passive social networking site use and well-being: The mediating roles of social comparison and the fear of missing out. Cyberpsychology: Journal of Psychosocial Research on Cyberspace , 13(3) article 5 10.5817/CP2019-3-5. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- * Buyukbayraktar, C. G. (2020). Predictive relationships among smartphone addiction, fear of missing out and interaction anxiousness. European Journal of Educational Sciences , 7(2), 1–16. 10.19044/ejes.v7no2a1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- * Cabrera, G. A. , Andal, A. B. A. , Delariarte, C. F. , Kallarackal, M. V. , & Tanganco, G. J. S. (2019). Fear of missing out and social networking site usage: Predictors of problematic internet use among college students. Asia Pacific Journal of Academic Research in Social Sciences , 4. [Google Scholar]
- * Can, G. , & Satici, S. A. (2019). Adaptation of fear of missing out scale (FoMOs): Turkish version validity and reliability study. Psicologia: Reflexão e Crítica , 32. 10.1186/s41155-019-0117-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casale, S. , & Fioravanti, G. (2020). Factor structure and psychometric properties of the Italian version of the fear of missing out scale in emerging adults and adolescents. Addictive Behaviors , 102, 106179. 10.1016/j.addbeh.2019.106179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- * Casale, S. , Rugai, L. , & Fioravanti, G. (2018). Exploring the role of positive metacognitions in explaining the association between the fear of missing out and social media addiction. Addictive Behaviors , 85, 83–87. 10.1016/j.addbeh.2018.05.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazzulino, F. , Burke, R. V. , Muller, V. , Arbogast, H. , & Upperman, J. S. (2014). Cell phones and young drivers: A systematic review regarding the association between psychological factors and prevention. Traffic Injury Prevention , 15, 234–242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, C. , Lau, Y. C. , Chan, L. , & Luk, J. W. (2021). Prevalence of social media addiction across 32 nations: Meta-analysis with subgroup analysis of classification schemes and cultural values. Addictive Behaviors , 117, 106845. 10.1016/j.addbeh.2021.106845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, C. , & Li, A. Y. L. (2014). Internet addiction prevalence and quality of (real) life: A meta-analysis of 31 nations across seven world regions. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking , 17(12), 755–760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- * Chotpitayasunondh, V. , & Douglas, K. M. (2016). How “phubbing” becomes the norm: The antecedents and consequences of snubbing via smartphone. Computers in Human Behavior , 63, 9–18. 10.1016/j.chb.2016.05.018. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- * Classen, B. , Wood, J. K. , & Davies, P. (2020). Social network sites, fear of missing out, and psychosocial correlates. Cyberpsychology: Journal of Psychosocial Research on Cyberspace , 14(3) Article 4 10.5817/CP2020-3-4. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- * Coco, G. L. , Salerno, L. , Franchina, V. , La Tona, A. , Di Blasi, M. , & Giordano, C. (2020). Examining bi-directionality between Fear of Missing Out and problematic smartphone use. A two-wave panel study among adolescents. Addictive Behaviors , 106, 106360. 10.1016/j.addbeh.2020.106360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosci, F. , & Fava, G. A. (2013). Staging of mental disorders: Systematic review. Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics , 82(1), 20–34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- * Coskun, S. , & Muslu, G. K. (2019). Investigation of problematic mobile phones use and fear of missing out (FoMO) level in adolescents. Community Mental Health Journal , 55(6), 1004–1014. 10.1007/s10597-019-00422-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crook, C. (2014). The joy of missing out: Finding balance in a wired world : New Society Publishers. [Google Scholar]
- Demirci, K. , Akgönül, M. , & Akpinar, A. (2015). Relationship of smartphone use severity with sleep quality, depression, and anxiety in university students. Journal of Behavioral Addictions , 4(2), 85–92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- * Dempsey, A. E. , O’Brien, K. D. , Tiamiyu, M. F. , & Elhai, J. D. (2019). Fear of missing out (FoMO) and rumination mediate relations between social anxiety and problematic Facebook use. Addictive Behaviors Reports , 9, 100150. 10.1016/j.abrep.2018.100150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duval, S. , & Tweedie, R. (2000). Trim and fill: A simple funnel-plot-based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics , 56, 455–463. 10.1111/j.0006-341X.2000.00455.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egger, M. , Davey Smith, G. , Schneider, M. , & Minder, C. (1997). Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ , 315(7109), 629–634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elhai, J. D. , Dvorak, R. D. , Levine, J. C. , & Hall, B. J. (2017). Problematic smartphone use: A conceptual overview and systematic review of relations with anxiety and depression psychopathology. Journal of Affective Disorders , 207, 251–259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- * Elhai, J. D. , Gallinari, E. F. , Rozgonjuk, D. , & Yang, H. (2020). Depression, anxiety and fear of missing out as correlates of social, non-social and problematic smartphone use. Addictive Behaviors , 105, 106335. 10.1016/j.addbeh.2020.106335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elhai, J. D. , Levine, J. C. , Alghraibeh, A. M. , Alafnan, A. A. , Aldraiweesh, A. A. , & Hall, B. J. (2018). Fear of missing out: Testing relationships with negative affectivity, online social engagement, and problematic smartphone use. Computers in Human Behavior , 89, 289–298. [Google Scholar]
- * Elhai, J. D. , Levine, J. C. , Alghraibeh, A. M. , Alafnan, A. A. , Aldraiweesh, A. A. , & Hall, B. J. (2018a). Fear of missing out: Testing relationships with negative affectivity, online social engagement, and problematic smartphone use. Computers in Human Behavior , 89, 289–298. 10.1016/j.chb.2018.08.020. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Elhai, J. D. , Levine, J. C. , Dvorak, R. D. , & Hall, B. J. (2016). Fear of missing out, need for touch, anxiety and depression are related to problematic smartphone use. Computers in Human Behavior , 63, 509–516. [Google Scholar]
- * Elhai, J. D. , McKay, D. , Yang, H. , Minaya, C. , Montag, C. , & Asmundson, G. J. (2021). Health anxiety related to problematic smartphone use and gaming disorder severity during COVID‐19: Fear of missing out as a mediator. Human Behavior and Emerging Technologies , 3(1), 137–146. 10.1002/hbe2.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- * Elhai, J. D. , Yang, H. , Fang, J. , Bai, X. , & Hall, B. J. (2020). Depression and anxiety symptoms are related to problematic smartphone use severity in Chinese young adults: Fear of missing out as a mediator. Addictive Behaviors , 101, 105962. 10.1016/j.addbeh.2019.04.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elhai, J. D. , Yang, H. , & Levine, J. C. (2021). Applying fairness in labeling various types of internet use disorders: Commentary on How to overcome taxonomical problems in the study of internet use disorders and what to do with “smartphone addiction” Journal of Behavioral Addictions , 9(4), 924–927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elhai, J. D. , Yang, H. , & Montag, C. (2020). Fear of missing out (FOMO): Overview, theoretical underpinnings, and literature review on relations with severity of negative affectivity and problematic technology use. Brazilian Journal of Psychiatry . 10.1590/1516-4446-2020-0870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- * Elhai, J. D. , Yang, H. , Rozgonjuk, D. , & Montag, C. (2020). Using machine learning to model problematic smartphone use severity: The significant role of fear of missing out. Addictive Behaviors , 103, 106261. 10.1016/j.addbeh.2019.106261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- * Fabris, M. A. , Marengo, D. , Longobardi, C. , & Settanni, M. (2020). Investigating the links between fear of missing out, social media addiction, and emotional symptoms in adolescence: The role of stress associated with neglect and negative reactions on social media. Addictive Behaviors , 106, 106364. 10.1016/j.addbeh.2020.106364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- * Fang, J. , Wang, X. , Wen, Z. , & Zhou, J. (2020). Fear of missing out and problematic social media use as mediators between emotional support from social media and phubbing behavior. Addictive Behaviors , 107, 106430. 10.1016/j.addbeh.2020.106430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez, D. P. , Kuss, D. J. , & Griffiths, M. D. (2020). Short-term abstinence effects across potential behavioral addictions: A systematic review. Clinical Psychology Review , 76, 101828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fioravanti, G. , Casale, S. , Benucci, S. B. , Prostamo, A. , Falone, A. , Ricca, V. , & Rotella, F. (2021). Fear of missing out and social networking sites use and abuse: A meta-analysis. Computers in Human Behavior , 106839. [Google Scholar]
- * Franchina, V. , Vanden Abeele, M. , Van Rooij, A. J. , Lo Coco, G. , & De Marez, L. (2018). Fear of missing out as a predictor of problematic social media use and phubbing behavior among Flemish adolescents. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health , 15(10), 2319. 10.3390/ijerph15102319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- * Fuster, H. , Chamarro, A. , & Oberst, U. (2017). Fear of missing out, online social networking and mobile phone addiction: A latent profile approach. Aloma: Revista de Psicologia, Ciències de l’Educació i de l’Esport , 35(1), 22–30. 10.51698/aloma.2017.35.1.22-30. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- * Gezgin, D. M. (2018). Understanding patterns for smartphone addiction: Age, sleep duration, social network use and fear of missing out. Cypriot Journal of Educational Science , 13(2), 166–177. https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4688-043X. [Google Scholar]
- Gil, F. , Chamarro, A. , & Oberst, U. (2015). PO-14: Addiction to online social networks: A question of “fear of missing out”? Journal of Behavioral Addictions , 4(S1), 51–52. [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths, M. D. (1996). Internet addiction: An issue for clinical psychology? Clinical Psychology Forum , 97, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths, M. D. (1998). Internet addiction: Does it really exist?. In Gackenbach J. (Ed.), Psychology and the internet: Intrapersonal, interpersonal, and transpersonal implications . New York: Academic Press. [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths, M. D. (2021). Internet use disorders: What’s new and what’s not?: Commentary on: How to overcome taxonomical problems in the study of Internet use disorders and what to do with “smartphone addiction”?(Montag et al., 2019). Journal of Behavioral Addictions , 9(4), 934–937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- * Gugushvili, N. , Täht, K. , Rozgonjuk, D. , Raudlam, M. , Ruiter, R. , & Verduyn, P. (2020). Two dimensions of problematic smartphone use mediate the relationship between fear of missing out and emotional well-being. Cyberpsychology: Journal of Psychosocial Research on Cyberspace , 14(2). 10.5817/CP2020-2-3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- *Gullu, B. F. , & Serin, H. (2020). The relationship between Fear of Missing Out (FoMO) levels and cyberloafing behaviour of teachers. Journal of Education and Learning , 9(5), 205–214. 10.5539/jel.v9n5p205. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Gunuc, S. , & Dogan, A. (2013). The relationships between Turkish adolescents’ Internet addiction, their perceived social support and family activities. Computers in Human Behavior , 29(6), 2197–2207. [Google Scholar]
- Hamonniere, T. , & Varescon, I. (2018). Metacognitive beliefs in addictive behaviours: A systematic review. Addictive Behaviors , 85, 51–63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- * Hamutoglu, N. B. , Topal, M. , & Gezgin, D. M. (2020). Investigating direct and indirect effects of social media addiction, social media usage and personality traits on FOMO. International Journal of Progressive Education , 16(2), 248–261. 10.29329/ijpe.2020.241.17. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Hishan, S. S. , Ramakrishnan, S. , & Qureshi, M. I. (2020). Smartphone addiction, fear of missing out, and perceived competence as predictors of social media addiction of adolescents. Journal of Critical Reviews , 7(16), 1172–1181. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, B. T. (2021). Toward a more transparent, rigorous, and generative psychology. Psychological Bulletin , 147(1), 1–15. 10.1037/bul0000317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Kacker, P. , & Saurav, S. (2020). Correlation of missing out (fomo), anxiety and aggression of young adults. International Journal of Research-Granthaalayah , 8(5), 132–138. 10.29121/granthaalayah.v8.i5.2020.107. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Kardefelt-Winther, D. (2014). A conceptual and methodological critique of internet addiction research: Towards a model of compensatory internet use. Computers in Human Behavior , 31, 351–354. 10.1016/j.chb.2013.10.059. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- * Kargın, M. , Türkben Polat, H. , & Coşkun Şimşek, D. (2020). Evaluation of internet addiction and fear of missing out among nursing students. Perspectives in Psychiatric Care , 56(3), 726–731. 10.1111/ppc.12488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karsay, K. , Schmuck, D. , Matthes, J. , & Stevic, A. (2019). Longitudinal effects of excessive smartphone use on stress and loneliness: The moderating role of self-disclosure. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking , 22(11), 706–713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King, A. L. S. , Valença, A. M. , Silva, A. C. , Sancassiani, F. , Machado, S. , & Nardi, A. E. (2014). Nomophobia: Impact of cell phone use interfering with symptoms and emotions of individuals with panic disorder compared with A control group. Clinical Practice and Epidemiology in Mental Health , 10, 28–35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmet, L. M. , Cook, L. S. , & Lee, R. C. (2004). Standard quality assessment criteria for evaluating primary research papers from a variety of fields . [Google Scholar]
- Ko, C. H. , Yen, J. Y. , Yen, C. F. , Chen, C. S. , & Chen, C. C. (2012). The association between internet addiction and psychiatric disorder: A review of the literature. European Psychiatry , 27(1), 1–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuss, D. J. , & Griffiths, M. D. (2017). Social networking sites and addiction: Ten lessons learned. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health , 14(3), 311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, M. , Lee, J. Y. , Won, W. Y. , Park, J. W. , Min, J. A. , Hahn, C. , … Kim, D. J. (2013). Development and validation of a smartphone addiction scale (SAS). PloS One , 8(2), e56936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- * Lai, C. , Altavilla, D. , Ronconi, A. , & Aceto, P. (2016). Fear of missing out (FOMO) is associated with activation of the right middle temporal gyrus during inclusion social cue. Computers in Human Behavior , 61, 516–521. 10.1016/j.chb.2016.03.072. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H. W. , Choi, J. S. , Shin, Y. C. , Lee, J. Y. , Jung, H. Y. , & Kwon, J. S. (2012). Impulsivity in internet addiction: A comparison with pathological gambling. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking , 15(7), 373–377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- * Lee, S. , McDonough, I. M. , Mendoza, J. S. , Brasfield, M. B. , Enam, T. , Reynolds, C. , & Pody, B. C. (2021). Cellphone addiction explains how cellphones impair learning for lecture materials. Applied Cognitive Psychology , 35(1), 123–135. 10.1002/acp.3745. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- * Li, L. , Griffiths, M. D. , Mei, S. , & Niu, Z. (2020). Fear of missing out and smartphone addiction mediates the relationship between positive and negative affect and sleep quality among Chinese university students. Frontiers in Psychiatry , 11, 877. 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- * Li, L. , Griffiths, M. D. , Niu, Z. , & Mei, S. (2020). The trait-state fear of missing out scale: Validity, reliability, and measurement invariance in a Chinese sample of university students. Journal of Affective Disorders , 274, 711–718. 10.1016/j.jad.2020.05.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- * Liu, C. , & Ma, J. L. (2019). Adult attachment orientations and social networking site addiction: The mediating effects of online social support and the fear of missing out. Frontiers in Psychology , 10, 2629. 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.02629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- * Liu, C. , & Ma, J. (2020). Social support through online social networking sites and addiction among college students: The mediating roles of fear of missing out and problematic smartphone use. Current Psychology , 39(6), 1892–1899. 10.1007/s12144-018-0075-5. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Long, J. , Liu, T. Q. , Liao, Y. H. , Qi, C. , He, H. Y. , Chen, S. B. , & Billieux, J. (2016). Prevalence and correlates of problematic smartphone use in a large random sample of Chinese undergraduates. BMC Psychiatry , 16(1), 1–12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- * Long, J. , Wang, P. , Liu, S. , & Lei, L. (2019). Materialism and adolescent problematic smartphone use: The mediating role of fear of missing out and the moderating role of narcissism. Current Psychology , 1–9. 10.1007/s12144-019-00526-0. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- * Luo, J. , & Liang, L. (2018 April). Exploring the relationships among university students’ media multitasking, personality and academic performance: A quantitative study. In International scientific conference: Lodging the theory in social and educational practice (pp. 1–10). [Google Scholar]
- Maia, T. , Cooney, R. , & Peterson, B. (2008). The neural bases of obsessive–compulsive disorder in children and adults. Development and Psychopathology , 20(4), 1251–1283. 10.1017/S0954579408000606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- * McAndrew, C. J. (2018). Social media and negative aspects of well-being: Does FOMO play a role? Bridges: A Journal of Student Research , 12(12), 3. https://digitalcommons.coastal.edu/bridges/vol12/iss12/3. [Google Scholar]
- * Metin-Orta, I. (2020). Fear of missing out, internet addiction and their relationship to psychological symptoms. Addicta: The Turkish Journal on Addictions , 7(1), 67–73. 10.15805/addicta.2020.7.1.0070. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Mo, P. K. , Chan, V. W. , Chan, S. W. , & Lau, J. T. (2018). The role of social support on emotion dysregulation and internet addiction among Chinese adolescents: A structural equation model. Addictive Behaviors , 82, 86–93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moher, D. , Liberati, A. , Tetzlaff, J. , Altman, D. G. , Altman, D. , Antes, G. , … Tugwell, P. (2009). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement (Chinese edition). Journal of Chinese Integrative Medicine , 7(9), 889–896. [Google Scholar]
- Montag, C. , Wegmann, E. , Sariyska, R. , Demetrovics, Z. , & Brand, M. (2019). How to overcome taxonomical problems in the study of Internet use disorders and what to do with “smartphone addiction”. Journal of Behavioral Addictions , 1–7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno, M. A. , Jelenchick, L. , Cox, E. , Young, H. , & Christakis, D. A. (2011). Problematic internet use among US youth: A systematic review. Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine , 165(9), 797–805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta, T. , Chen, S. , & Potenza, M. N. (2020). Mobile and non-mobile internet use disorder: Specific risks and possible shared pavlovian conditioning processes: Commentary on: How to overcome taxonomical problems in the study of Internet use disorders and what to do with “smartphone addiction”?(Montag et al., 2019). Journal of Behavioral Addictions , 9(4), 938–941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- * Munawaroh, E. , Nurmalasari, Y. , & Sofyan, A. (2020 August). Social network sites usage and fear of missing out among female Instagram user. In 2nd international seminar on guidance and counseling 2019 (ISGC 2019 (pp. 140–142): Atlantis Press. [Google Scholar]
- * O’Connell, C. (2020). How FOMO (Fear of missing out), the smartphone, and social media may be affecting university students in the Middle East. North American Journal of Psychology , 22(1). [Google Scholar]
- * Oberst, U. , Wegmann, E. , Stodt, B. , Brand, M. , & Chamarro, A. (2017). Negative consequences from heavy social networking in adolescents: The mediating role of fear of missing out. Journal of Adolescence , 55, 51–60. 10.1016/j.adolescence.2016.12.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- * Pontes, H. M. , Taylor, M. , & Stavropoulos, V. (2018). Beyond “Facebook addiction”: The role of cognitive-related factors and psychiatric distress in social networking site addiction. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking , 21(4), 240–247. 10.1089/cyber.2017.0609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- * Przybylski, A. K. , Murayama, K. , DeHaan, C. R. , & Gladwell, V. (2013). Motivational, emotional, and behavioral correlates of fear of missing out. Computers in Human Behavior , 29(4), 1841–1848. 10.1016/j.chb.2013.02.014. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- * Rahardjo, W. , & Mulyani, I. (2020). Instagram addiction in teenagers: The role of type D personality, self-esteem, and fear of missing out. Psikohumaniora: Jurnal Penelitian Psikologi , 5(1), 29–44. 10.21580/pjpp.v5i1.4916. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- * Reer, F. , Tang, W. Y. , & Quandt, T. (2019). Psychosocial well-being and social media engagement: The mediating roles of social comparison orientation and fear of missing out. New Media & Society , 21(7), 1486–1505. 10.1177/1461444818823719. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- * Reyes, M. E. S. , Marasigan, J. P. , Gonzales, H. J. Q. , Hernandez, K. L. M. , Medios, M. A. O. , & Cayubit, R. F. O. (2018). Fear of missing out and its link with social media and problematic internet use among Filipinos. North American Journal of Psychology , 20(3). [Google Scholar]
- * Riordan, B. C. , Cody, L. , Flett, J. A. , Conner, T. S. , Hunter, J. , & Scarf, D. (2020). The development of a single item FoMO (fear of missing out) scale. Current Psychology , 39(4), 1215–1220. 10.1007/s12144-018-9824-8. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, J. A. , & David, M. E. (2020). The social media party: Fear of missing out (FOMO), social media intensity, connection, and well-being. International Journal of Human–Computer Interaction , 36(4), 386–392. [Google Scholar]
- Rod, N. H. , Dissing, A. S. , Clark, A. , Gerds, T. A. , & Lund, R. (2018). Overnight smartphone use: A new public health challenge? A novel study design based on high-resolution smartphone data. PLoS One , 13(10), e0204811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- * Rogers, A. P. , & Barber, L. K. (2019). Addressing FoMO and telepressure among university students: Could a technology intervention help with social media use and sleep disruption?. Computers in Human Behavior , 93, 192–199. 10.1016/j.chb.2018.12.016. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- * Rozgonjuk, D. , Sindermann, C. , Elhai, J. D. , & Montag, C. (2020). Fear of missing out (FoMO) and social media’s impact on daily-life and productivity at work: Do WhatsApp, Facebook, Instagram, and Snapchat use disorders mediate that association? Addictive Behaviors , 110, 106487. 10.1016/j.addbeh.2020.106487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumpf, H. J. , Browne, D. , Brandt, D. , & Rehbein, F. (2021). Addressing taxonomic challenges for internet use disorders in light of changing technologies and diagnostic classifications: Commentary on: “How to overcome taxonomical problems in the study of internet use disorders and what to do with “smartphone addiction”?” (Montag et al., 2020). Journal of Behavioral Addictions , 9(4), 942–944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, E. J. , Choi, K. S. , Seo, J. S. , & Nam, B. W. (2004). The relationships of Internet addiction, depression, and suicidal ideation in adolescents. Taehan Kanho Hakhoe Chi , 34(1), 102–110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- * Schneider, F. M. , & Hitzfeld, S. (2019). I ought to put down that phone but I phub nevertheless: Examining the predictors of phubbing behavior. Social Science Computer Review . 10.1177/0894439319882365. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- * Sela, Y. , Zach, M. , Amichay-Hamburger, Y. , Mishali, M. , & Omer, H. (2020). Family environment and problematic internet use among adolescents: The mediating roles of depression and fear of missing out. Computers in Human Behavior , 106, 106226. 10.1016/j.chb.2019.106226. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- * Servidio, R. (2021). Self-control and problematic smartphone use among Italian University students: The mediating role of the fear of missing out and of smartphone use patterns. Current Psychology , 40(8), 4101–4111. 10.1007/s12144-019-00373-z. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- * Sha, P. , Sariyska, R. , Riedl, R. , Lachmann, B. , & Montag, C. (2019). Linking internet communication and smartphone use disorder by taking a closer look at the Facebook and WhatsApp applications. Addictive Behaviors Reports , 9, 100148. 10.1016/j.abrep.2018.100148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- * Sheldon, P. , Antony, M. G. , & Sykes, B. (2021). Predictors of problematic social media use: Personality and life-position indicators. Psychological Reports , 124(3), 1110–1133. 10.1177/0033294120934706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- * Shen, Y. , Zhang, S. , & Xin, T. (2020). Extrinsic academic motivation and social media fatigue: Fear of missing out and problematic social media use as mediators. Current Psychology , 1–7. 10.1007/s12144-020-01219-9. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- * Sindermann, C. , Yang, H. , Liu, T. , Elhai, J. D. , & Montag, C. (2021). WeChat—its problematic use and relations with the big five personality traits and fear of missing out. Journal of Technology in Behavioral Science , 6(2), 397–405. 10.1007/s41347-020-00179-y. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Sohn, S. , Rees, P. , Wildridge, B. , Kalk, N. J. , & Carter, B. (2019). Prevalence of problematic smartphone usage and associated mental health outcomes amongst children and young people: A systematic review, meta-analysis and GRADE of the evidence. BMC Psychiatry , 19(1), 1–10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spada, M. M. (2014). An overview of problematic Internet use. Addictive Behaviors , 39(1), 3–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starcevic, V. , King, D. L. , Delfabbro, P. H. , Schimmenti, A. , Castro-Calvo, J. , Giardina, A. , & Billieux, J. (2021). “Diagnostic inflation” will not resolve taxonomical problems in the study of addictive online behaviours: Commentary on: How to overcome taxonomical problems in the study of Internet use disorders and what to do with “smartphone addiction”?(Montag et al., 2020). Journal of Behavioral Addictions , 9(4), 915–919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Statista.com (2021). Number of smartphone users worldwide from 2016 to 2021 (in billions). Retrieved September 02, 2021, from https://www.statista.com/statistics/330695/number-of-smartphoneusers-worldwide/.
- * Stead, H. , & Bibby, P. A. (2017). Personality, fear of missing out and problematic internet use and their relationship to subjective well-being. Computers in Human Behavior , 76, 534–540. 10.1016/j.chb.2017.08.016. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Tandon, A. , Dhir, A. , Almugren, I. , AlNemer, G. N. , & Mäntymäki, M. (2021). Fear of missing out (FoMO) among social media users: A systematic literature review, synthesis, and framework for future research. Internet Research . [Google Scholar]
- * Tang, G. , Hung, E. P. , Au-Yeung, H. K. C. , & Yuen, S. (2020). Politically motivated internet addiction: Relationships among online information exposure, internet addiction, FOMO, psychological well-being, and radicalism in massive political turbulence. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health , 17(2), 633. 10.3390/ijerph17020633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- * Tomczyk, Ł. , & Selmanagic-Lizde, E. (2018). Fear of Missing Out (FOMO) among youth in Bosnia and Herzegovina—scale and selected mechanisms. Children and Youth Services Review , 88, 541–549. 10.1016/j.childyouth.2018.03.048. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Traş, Z. , & Öztemel, K. (2019). Examining the relationships between Facebook intensity, fear of missing out, and smartphone addiction. Addicta , 6, 91–113. 10.15805/addicta.2019.6.1.0063. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi, A. (2017). Impact of internet addiction on mental health: An integrative therapy is needed. Integrative Medicine International , 4(3–4), 215–222. [Google Scholar]
- * Tsai, H. Y. S. , Hsu, P. J. , Chang, C. L. , Huang, C. C. , Ho, H. F. , & LaRose, R. (2019). High tension lines: Negative social exchange and psychological well-being in the context of instant messaging. Computers in Human Behavior , 93, 326–332. 10.1016/j.chb.2018.12.034. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- * Tugtekin, U. , Barut Tugtekin, E. , Kurt, A. A. , & Demir, K. (2020). Associations between fear of missing out, problematic smartphone use, and social networking services fatigue among young adults. Social Media+ Society , 6(4). 10.1177/2056305120963760. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- * Tunc-Aksan, A. , & Akbay, S. E. (2019). Smartphone addiction, fear of missing out, and perceived competence as predictors of social media addiction of adolescents. European Journal of Educational Research , 8(2), 559–566. 10.12973/eujer.8.2.559. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- * Upreti, A. , & Musalay, P. (2018). Fear of missing out, mobile phone dependency and entrapment in undergraduate students. In Applied psychology readings (pp. 39–56). Singapore: Springer. 10.1007/978-981-10-8034-0_3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- * Uram, P. , & Skalski, S. (2020). Still logged in? The link between Facebook addiction, FoMO, self-esteem, life satisfaction and loneliness in social media users. Psychological Reports . 10.1177/0033294120980970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van-Den-Eijnden, R. , Doornwaard, S. , & Ter Bogt, T. (2017). OP-117: Are smartphone dependence symptoms related to FOMO, craving and withdrawal symptoms during smartphone abstinence? Findings from a natural experiment. Journal of Behavioral Addictions , 6(S1), 56–57. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S. (2021). Investigating consumer’s fear of missing out and social media fatigue: An extended literature review [Doctoral dissertation]. Auckland University of Technology. [Google Scholar]
- * Wang, P. , Wang, X. , Nie, J. , Zeng, P. , Liu, K. , Wang, J. , … Lei, L. (2019). Envy and problematic smartphone use: The mediating role of FOMO and the moderating role of student-student relationship. Personality and Individual Differences , 146, 136–142. 10.1016/j.paid.2019.04.013. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J. , Wang, P. , Yang, X. , Zhang, G. , Wang, X. , Zhao, F. , … Lei, L. (2019). Fear of missing out and procrastination as mediators between sensation seeking and adolescent smartphone addiction. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction , 17(4), 1049–1062. [Google Scholar]
- * Wang, P. , Xie, X. , Wang, X. , Wang, X. , Zhao, F. , Chu, X. , … Lei, L. (2018). The need to belong and adolescent authentic self-presentation on SNSs: A moderated mediation model involving FoMO and perceived social support. Personality and Individual Differences , 128, 133–138. 10.1016/j.paid.2018.02.035. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- * Wegmann, E. , Oberst, U. , Stodt, B. , & Brand, M. (2017). Online-specific fear of missing out and Internet-use expectancies contribute to symptoms of Internet-communication disorder. Addictive Behaviors Reports , 5, 33–42. 10.1016/j.abrep.2017.04.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein, A. , Dorani, D. , Elhadif, R. , Bukovza, Y. , Yarmulnik, A. , & Dannon, P. (2015). Internet addiction is associated with social anxiety in young adults. Annals of Clinical Psychiatry , 27(1), 4–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- We are Social (2018). Digital in 2018 in western Asia. Retrivied from https://www.slideshare.net/wearesocial/digital-in-2018-in-western-asia-part-1-northwest86865983.
- * Wolniewicz, C. A. , Rozgonjuk, D. , & Elhai, J. D. (2020). Boredom proneness and fear of missing out mediate relations between depression and anxiety with problematic smartphone use. Human Behavior and Emerging Technologies , 2(1), 61–70. 10.1002/hbe2.159. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- * Wolniewicz, C. A. , Tiamiyu, M. F. , Weeks, J. W. , & Elhai, J. D. (2018). Problematic smartphone use and relations with negative affect, fear of missing out, and fear of negative and positive evaluation. Psychiatry Research , 262, 618–623. 10.1016/j.psychres.2017.09.058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y. L. , Lin, S. H. , & Lin, Y. H. (2021). Two-dimensional taxonomy of internet addiction and assessment of smartphone addiction with diagnostic criteria and mobile apps. Journal of Behavioral Addictions , 9(4), 928–933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yali, Z. H. A. N. G. , Sen, L. I. , & Guoliang, Y. U. (2021). The relationship between social media use and fear of missing out: A meta-analysis. Acta Psychologica Sinica , 53(3), 273. [Google Scholar]
- * Yam, F. C. , & Kumcağız, H. (2020). Adaptation of general phubbing scale to Turkish culture and investigation of phubbing levels of university students in terms of various variables. Addicta: The Turkish Journal on Addictions , 7(1), 48–60. 10.5152/addicta.2020.19061. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- * Yin, L. , Wang, P. , Nie, J. , Guo, J. , Feng, J. , & Lei, L. (2021). Social networking sites addiction and FoMO: The mediating role of envy and the moderating role of need to belong. Current Psychology , 40(8), 3879–3887. 10.1007/s12144-019-00344-4. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Young, K. (1996). Psychology of computer use: XL. Addictive use of the internet: A case that breaks the stereotype. Psychological Reports , 79, 899–902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young, K. S. (1997, August). What makes the internet addictive: Potential explanations for pathological Internet use. In 105th annual conference of the American Psychological Association (Vol. 15, pp. 12–30). Chicago. [Google Scholar]
- Yuxiang, Z. , Xuanhui, Z. , & Xiaokang, S. (2017). Fear of missing out (FoMO) in mobile social media context: Review and prospect. Library and Information Service , 61(8), 133. [Google Scholar]