Abstract
Purpose
The aims of this systematic review were to examine the use of radiolunate (RL) or radioscapholunate (RSL) arthrodesis as surgical management for patients with advanced radiocarpal arthritis that failed conservative management and to assess postoperative outcomes.
Methods
We reviewed articles from PubMed, EMBASE, and Web of Science from inception through December 2019. We identified complete manuscripts written in English reporting on RL or RSL arthrodesis for treatment of wrist pathology that included the primary outcomes (pain or grip strength) and at least 2 secondary outcomes (range of motion, patient-reported outcomes, or nonunion). Data pooling was used to calculate weighted averages.
Results
We identified 2,252 articles and selected 13 for inclusion. Across all studies, RSL arthrodesis was performed for 180 patients (49% female; 45 years old) and RL for 94 (87% female; 50 years old). Both procedures exhibited improvements in pain score and grip strength. Both cohorts demonstrated postoperative changes in flexion-extension arc, flexion, extension, ulnar deviation, supination, and pronation after data pooling. The nonunion rate for RSL was 15% versus 2% for RL, whereas the rate of progression to total wrist arthrodesis for RSL and RL was 4% and 0%, respectively.
Conclusions
Both RL and RSL arthrodesis can be successfully used to manage debilitating radiocarpal arthritis by affording patients with pain reduction. Each has its own benefits, in which RSL arthrodesis provides a total arc of motion within the functional demands of most activities of daily living, and RL arthrodesis has low rates of nonunion and progression to total wrist arthrodesis. Further research is needed to compare the 2 surgeries directly and prospectively in comparable patient groups.
Type of study/level of evidence
Therapeutic III.
Key words: Radiolunate arthrodesis, Radiolunate fusion, Radioscapholunate arthrodesis, Radioscapholunate fusion, Wrist arthritis
More than 1 in 10 American adults will experience wrist arthritis in their lifetime.1 The wrist is susceptible to arthritis given its potential for overuse and the high prevalence of distal radius injuries, especially in young, active patients.1,2 Wrist arthritis can be painful and hinder completion of activities of daily living (ADLs).3,4 Etiologies include posttraumatic, degenerative (eg, osteoarthritis), infectious (eg, septic arthritis), congenital (eg, Madelung deformity), inflammatory (eg, rheumatoid arthritis [RA]), and unknown (eg, Kienböck's disease).5, 6, 7 After failure of nonsurgical management, surgical treatment may be pursued to treat pain and decreased motion.8 Perhaps the most important factor in preoperative decision-making is determining which joints to spare.7,9, 10, 11 In many common forms of arthritis, the radiolunate (RL) articulation is spared, allowing for options such as proximal row carpectomy or 4-corner arthrodesis.12, 13, 14, 15, 16 However, when the RL joint is involved, patients are left with limited options, which include but are not limited to RL or radioscapholunate (RSL) arthrodesis, total wrist arthrodesis (TWA), total wrist arthroplasty, or partial wrist denervation.7, 8, 9, 10, 11,17, 18, 19, 20
The RL or RSL arthrodesis maintains midcarpal motion by fusing only arthritic radiocarpal joints.6,21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33 Compared with TWA, RSL and RL usually achieve the minimum range of motion (ROM) necessary to complete ADLs, defined as 5° to 10° of flexion, 30° to 35° of extension, 10° of radial deviation, and 15° of ulnar deviation.22,34, 35, 36 In 1955, Watson-Jones described RSL arthrodesis for radiocarpal degeneration from posttraumatic arthritis, RA, and Kienböck's disease.6,21,37 This procedure has been modified to include excision of the distal pole of the scaphoid with or without triquetrum excision to reduce impingement and improve motion.6,21,22,24,38,39 In 1983, Chamay et al23 proposed RL arthrodesis for patients with RA who specifically have unstable carpal articulation with ulnar misalignment, though it is now commonly used for posttraumatic osteoarthritis, particularly after intraarticular distal radius fracture and Kienböck’s disease.40 Whereas both RL and RSL arthrodesis can be used to treat wrist arthritis, the primary difference is that RSL is the sole option for those with RSL arthritis whereas those with RL arthritis may undergo either procedure.40
With success in many short-term studies, the indications continue to expand for these procedures.41, 42, 43, 44, 45 However, a lack of literature that guides surgical decision-making remains in relation to patient outcomes. Furthermore, decision making may not always be clear-cut and is instead directed by a number of patient-specific factors. The aims of this systematic review were to examine the use of RL or RSL arthrodesis as surgical management for patients with advanced radiocarpal arthritis that failed conservative management and to assess postoperative outcomes. We sought to examine (1) whether RL and RSL are reasonable to consider for radiocarpal arthritis, (2) whether RSL and RL arthrodeses decrease postoperative pain and preserve motion, and (3) what nonunion rates are after RSL and RL arthrodeses.
Materials and Methods
The authors searched studies published from inception to December 2019 within PubMed, Web of Science, and EMBASE to identify citations related to RL or RSL arthrodesis. A medical librarian assisted in creating, verifying, and converting the search terms for use in other databases. Key terms were employed to identify wrist arthritis and its surgical approaches to capture all desired papers (Appendix A, available on the Journal’s Web site at www.jhsgo.org). Two reviewers conducted a title and abstract search to identify articles that were in agreement with predeveloped criteria (Table 1). The same 2 authors then reviewed full-text articles for final inclusion. A third author confirmed all manuscripts and ultimately decided to include or exclude articles if the prior 2 authors had discordant opinions. The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines were followed for study design and manuscript preparation.46
Table 1.
Study Inclusion Criteria
| Variable | Inclusion Criteria |
|---|---|
| Article parameters | Original study with primary patient outcomes Human subjects English language publication Published from database inception to December 2019 Randomized controlled trial or prospective nonrandomized trial |
| Treatment | Radiolunate arthrodesis or radioscapholunate arthrodesis |
| Outcomes | Must report preoperative and postoperative changes in either pain score or grip strength OR must report preoperative and postoperative changes in at least 2 of the following: ROM, patient reported outcome, and nonunion |
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
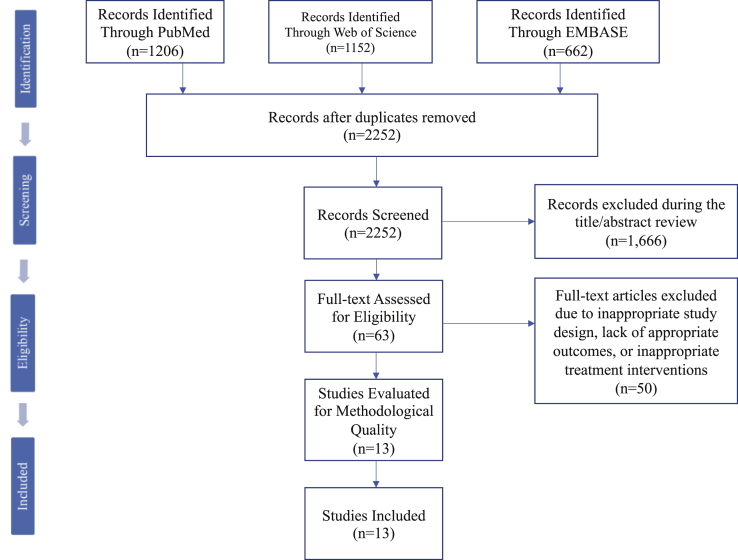
Inclusion was restricted to complete manuscripts published in English that reported on wrist arthritis resulting from trauma, degeneration, infection, inflammation, and congenital malformations, which were treated with either RL or RSL arthrodesis. Publications that did not include at least one primary outcome or 2 secondary outcomes, measured both before and after surgery, were excluded (Table 1). Despite using institutional literary access and those of inter-loan partners, articles were excluded if the full text was not obtained. These were primarily articles published internationally or before 1990 (Fig. 1). Thirteen studies were included for final review (Table 2).6,21,22,24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29,31, 32, 33,47 Eight studies focused on RSL arthrodesis,6,21,22,24,25,27,28,38 3 were on RL arthrodesis,26,31,33 and 2 included both.29,32 Two studies included patient data with slight procedural variations: Ha et al47 included patients with iliac crest bone graft, distal scaphoidectomy, and/or triquetrectomy, whereas Mühldorfer-Fodor et al22 included patients with and without distal scaphoidectomy.22 The study selection process and assessment of quality, using the Methodological Items for Non-Randomized Studies (MINORS) criteria, are detailed in Figure 1 and Table 2, respectively.46,48 The first 2 authors independently assigned MINORS scores to each study, and because all scores were in agreement, no other authors had to settle disputes.
Figure 1.
Attrition flowchart describing the study selection process for inclusion within the systematic review in accordance with Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines.
Table 2.
Quality Scoring of Included Studies Based on MINORS Criteria∗
| Criteria | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ha et al | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 14 | ||||
| Beyermann et al | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 12 | ||||
| Bain et al | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 14 | ||||
| Montoya-Faivre et al | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 13 | ||||
| Mühldorfer-Fodor et al | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 20 |
| Nagy and Büchler | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 13 | ||||
| Prommersberger et al | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 11 | ||||
| Quadlbauer et al | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 13 | ||||
| Raven et al | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 12 | ||||
| Ishikawa et al | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 12 | ||||
| Motomiya et al | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 14 | ||||
| Trieb et al | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 13 | ||||
| Stanley and Boot | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 15 |
All 13 included studies were prospective, nonrandomized trials analyzed with the MINORS criteria. The MINORS tool is composed of 12 criteria: 8 for noncomparative studies and an additional 4 for comparative studies. Criteria for noncomparative studies are (1) stated aim of study, (2) inclusion criteria, (3) collection data, (4) end point of study, (5) unbiased evaluation, (6) follow-up period, (7) loss of follow-up, and (8) prospective calculation of sample size. Additional criteria for comparative studies are (9) reference standard for control group, (10) contemporary groups, (11) baseline equivalence, and (12) statistical analyses. These items are scored as 0 (not reported), 1 (reported but not adequately), or 2 (reported adequately). The global ideal scores for noncomparative and comparative studies are 16 and 24, respectively.
Outcomes of interest and statistical analysis
The primary outcomes extracted were pain and grip strength (GS). Pain was reported using the visual analog scale (VAS), ranging from 0 (no pain) to 100 (worse pain). Whenever pain was reported on a scale of 0 to 10, it was converted to a scale of 0 to 100 for comparison.49,50 Manuscripts reported GS in kilopascals, millimeters of mercury, kilograms, or Newtons. For the purpose of data pooling, predetermined conversion factors were used to convert all GS measurements to kilopascals.51 Pooled outcomes were weighted by the number of cases per study before and after surgery. Weighted preoperative and postoperative means were statistically analyzed for differences using 2-tailed, unequal variance t tests with an alpha significance level of .05.
The presence of secondary outcomes (ROM, patient-reported outcomes, and nonunion rate) varied across studies. All ROM data are reported in degrees, although the plane of motion varied by study. Data were extracted from patient outcome questionnaires such as the Michigan Hand Questionnaire, Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand (DASH) questionnaire, QuickDASH, Mayo Wrist Score (MWS), and Modified Mayo Wrist Score. Nonunion was defined as failed fusion radiographically, although each study varied in the specific time point at which this was assessed. Progression to TWA was also collected but was not a required secondary outcome for inclusion. When reported for each individual study, rates of nonunion and TWA were calculated based on the number of wrists included in the analysis and observed for the specified amount of time as dictated by the authors. Because not all studies reported on the nonunion rate and TWA, only those that included this measure were included in the analysis and were frequency weighted accordingly.
Results
Demographics
Of the 2,252 articles identified, 13 were selected for inclusion (Fig. 1, Table 1, Table 2).6,21,22,24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29,31, 32, 33,47 A total of 274 patients were included across all studies; 180 were treated with RSL arthrodesis and 94 with RL arthrodesis. Patients undergoing RSL compared with RL arthrodesis were younger (age 45 vs 50 years; P = .34), and there were fewer females (49% vs 87%; P = .016) and a shorter overall follow-up (60 vs 91 months; P = .022), respectively (Table 3). Table 4 lists pathology representation by study.
Table 3.
Pooled and Weighted Study Demographics
| Variable | RSL Arthrodesis | RL Arthrodesis |
|---|---|---|
| Patients, n | 180 | 94 |
| Wrists, n | 181 | 100 |
| Mean age at surgery, y (range) | 45 (18–86) | 50 (24–79) |
| Female Patients, n (%) | 88 (49) | 82 (87) |
| Mean follow-up, mo (range) | 60 (18–180) | 91 (34–156) |
Table 4.
Represented Pathologies, by Study
| Author | Pathology |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kienböck's | Madelung Deformity | Osteoarthritis | Posttraumatic | Rheumatoid Arthritis | Malunion | |
| RSL arthrodesis | ||||||
| Bain et al | X | X | X | X | ||
| Beyermann et al | X | |||||
| Ha et al | X | X | X | X | X | |
| Montoya-Faivre et al∗ | X | X | X | X | ||
| Mühldorfer-Fodor et al | X | X | ||||
| Nagy and Büchler | X | X | X | |||
| Prommersberger et al | X | X | ||||
| Quadlbauer et al | X | X | ||||
| Ishikawa et al | X | |||||
| Raven et al† | X | |||||
| RL arthrodesis | ||||||
| Motomiya et al | X | |||||
| Stanley and Boot | X | |||||
| Trieb et al | X | |||||
| Ishikawa et al | X | |||||
| Raven et al† | X | |||||
Included one patient with scapholunate advanced collapse.
Included one patient with psoriatic arthritis.
Pain
Of the 5 studies that reported preoperative and postoperative VAS scores, all had decreased pain after surgery; however, Stanley and Boot33 was the sole study to report this for RL arthrodesis (Table 5).6,25,28,47 For patients undergoing RSL arthrodesis, postoperative VAS scores ranged from 1629 to 42.47 Of those that reported preoperative and postoperative pain, Bain et al6 was the only one to report P values (P < .01). For RL arthrodesis, postoperative VAS scores ranged from 1033 to 14.29 Although Ishikawa et al32 did not collect VAS scores, the authors noted that moderate to severe pain was initially present among 25 patients, and pain was completely resolved in 88% at an average follow-up of 13 years. Given the limited number of studies that reported pain with VAS, weighted means were calculated for RSL during surgery and RL only after surgery (Table 7, Table 8, Table 9).
Table 5.
Individual Study Reported Outcomes
| Author | n | Average Follow-Up, mo | Preoperative VAS | Postoperative VAS | GS (% of Contralateral) | GS (% Change) | Required TWA (%) | Nonunion Rate (%) | Patient-Reported Outcome Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RSL arthrodesis | |||||||||
| Bain et al | 23 | 32 | 64.0 | 28.0† | +48 | 8.7 | 0 | ||
| Beyermann et al | 18 | 19 | 48.6∗ | 27.1∗ | +60∗ | 13.6 | 4.5 | 25.7§ | |
| Ha et al | 17 | 180 | 67.0∗ | 42.0∗ | 65∗ | 11.8 | 0 | ||
| Montoya-Faivre et al | 34 | 53 | 30.0 | 71 | 12.5 | 29 | 44.5§,‖; 57.2¶ | ||
| Mühldorfer-Fodor et al | 35 | 28 | 41.1 | 60∗ | 8.6 | 44‖; 47∗∗ | |||
| Nagy and Büchler | 15 | 96 | 66∗ | 33.3 | 26 | 58¶ | |||
| Prommersberger et al | 18 | 19 | 43.5 | 21.0 | +63∗ | 5.5 | 26§ | ||
| Quadlbauer et al | 11 | 63 | 22.0 | 80∗ | 0 | 27§ | |||
| Ishikawa et al | 6 | 156 | +26 | 0 | |||||
| Raven et al | 4 | 132 | 16.0 | 75†† | |||||
| RL arthrodesis | |||||||||
| Motomiya et al | 22 | 84 | +25‡ | 71¶ | |||||
| Stanley and Boot | 16 | 34 | 50.0∗ | 10.0∗ | +28∗ | 6.3 | |||
| Trieb et al | 27 | 65 | 0 | ||||||
| Ishikawa et al | 16 | 156 | +50† | 0 | |||||
| Raven et al | 19 | 132 | 14.0 | 0 | |||||
P value not recorded.
P < .05.
P < .01.
DASH score.
QuickDASH score.
Mayo Wrist Score.
Modified Mayo Wrist Score.
All recorded nonunions occurred in those without distal scaphoidectomy.
Table 7.
Preoperative and Postoperative Weighted Functional Outcome Means, by Surgery Type
| Variable | RSL | RL |
|---|---|---|
| Before surgery | ||
| VAS | 56.2 | |
| GS, kPa | 23.4 | 7.51 |
| GS (% contralateral hand) | ||
| Flexion-extension arc (degrees) | 63 | |
| Flexion (degrees) | 33 | 31 |
| Extension (degrees) | 32 | 31 |
| Radial deviation (degrees) | 10 | 7 |
| Ulnar deviation (degrees) | 15 | 15 |
| Supination (degrees) | 77 | 73 |
| Pronation (degrees) | 80 | 74 |
| After surgery | ||
| VAS | 31.2 | 12.2 |
| GS, kPa | 36.5 | 10.7 |
| GS (% contralateral hand) | 68.4 | |
| Flexion-extension arc (degrees) | 65 | 63 |
| Flexion (degrees) | 26 | 17 |
| Extension (degrees) | 31 | 29 |
| Radial deviation (degrees) | 10 | 8 |
| Ulnar deviation (degrees) | 20 | 16 |
| Supination (degrees) | 82 | 82 |
| Pronation (degrees) | 87 | 80 |
| Rate of nonunion (%) | 15.0 | 2.1 |
| Mean progression to TWA, n∗ | 3.65 (18) | 0 |
Calculated as the percentage of those who progressed to TWA only for studies that included TWA outcomes.
Table 8.
Radioscapholunate Arthrodesis Preoperative and Postoperative Weighted Functional Outcome Means
| Variable | Before Surgery | After Surgery |
|---|---|---|
| VAS | 56.2 | 31.2 |
| GS, kPa | 23.4 | 36.5 |
| GS (% contralateral hand) | 68.4 | |
| Flexion-extension arc (degrees) | 65 | 65 |
| Flexion (degrees) | 33 | 26 |
| Extension (degrees) | 32 | 31 |
| Radial deviation (degrees) | 10 | 10 |
| Ulnar deviation (degrees) | 15 | 20 |
| Supination (degrees) | 77 | 82 |
| Pronation (degrees) | 80 | 87 |
| Rate of nonunion (%) | 15.0 |
Table 9.
Radiolunate Arthrodesis Preoperative and Postoperative Weighted Functional Outcome Means
| Variable | Before Surgery | After Surgery |
|---|---|---|
| VAS | 12.2 | |
| GS, kPa | 7.51 | 10.7 |
| GS (% contralateral hand) | ||
| Flexion-extension arc (degrees) | 69 | 63 |
| Flexion (degrees) | 31 | 17 |
| Extension (degrees) | 31 | 29.1 |
| Radial deviation (degrees) | 7 | 8 |
| Ulnar deviation (degrees) | 15 | 16 |
| Supination (degrees) | 73 | 82 |
| Pronation (degrees) | 73 | 79 |
| Rate of nonunion (%) | 2.1 |
Grip strength
All RSL studies except for that by Raven et al29 included changes in GS (Table 5). Grip strength from individual studies was reported as a percentage of the contralateral hand or percent change after surgery. In the RSL group, GS expressed as a percentage of the contralateral hand ranged from 60%22 to 80%.24 Average change in GS ranged from 48%6 to 63%.28 Neither of the studies that reported P values demonstrated statistical significance.6,32 Of the 3 RL studies that reported GS, percent change ranged from 25%26 to 50%.32 Motomiya et al26 and Ishikawa et al32 were the sole studies to report P values (P < .001 and < .05, respectively). Preoperative weighted averages for GS were 23.4 for RSL versus 7.51 for RL, whereas postoperative values were 36.5 for RSL and 10.7 for RL. All were reported in kilopascals, and none were statistically significant.
Range of motion
Among RSL studies, 5 reported data on ROM (Table 6).24,25,28,29,32 All reported a decrease in flexion and an increase in radial deviation, except for Quadlbauer et al.24 Those authors reported significantly increased extension and supination (P < .05), whereas Ishikawa et al32 reported significantly decreased flexion (P < .01) and Raven et al29 reported significantly increased ulnar deviation (P < .05).
Table 6.
Individual Study Reported Changes in ROM
| Author | n | Average Follow-Up, mo | Δ Flexion (degrees) | Δ Extension (degrees) | Δ Radial Deviation (degrees) | Δ Ulnar Deviation (degrees) | Δ Pronation (degrees) | Δ Supination (degrees) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RSL arthrodesis | ||||||||
| Bain et al | 23 | 32 | ||||||
| Beyermann et al | 18 | 19 | –11‡ | –10‡ | +5‡ | +1‡ | ||
| Ha et al | 17 | 180 | ||||||
| Montoya-Faivre et al | 34 | 53 | ||||||
| Mühldorfer-Fodor et al | 35 | 28 | ||||||
| Nagy and Büchler | 15 | 96 | ||||||
| Prommersberger et al | 18 | 19 | –10‡ | –11‡ | –5‡ | –1n | –1‡ | +1‡ |
| Quadlbauer et al | 11 | 63 | +9 | +18∗ | +11 | +26∗ | ||
| Ishikawa et al | 6 | 156 | –19† | –5 | +3 | –3 | +6 | –6 |
| Raven et al | 4 | 132 | –8 | +20 | +9 | +7∗ | –8 | –12 |
| RL arthrodesis | ||||||||
| Motomiya et al | 22 | 84 | –15† | –3 | +11∗ | |||
| Stanley and Boot | 16 | 34 | ||||||
| Trieb et al | 27 | 65 | +4‡ | +1‡ | +2‡ | +7‡ | +5‡ | |
| Ishikawa et al | 16 | –13† | –6∗ | –8 | +13 | +12∗ | ||
| Raven et al | 19 | –8∗ | +8∗ | +7∗ | –3 | –10 | ||
P < .05.
P < .01.
P value not recorded.
Among RL arthrodeses, all except Stanley and Boot33 reported ROM. Trieb et al31 did not report significance. All studies demonstrated significantly decreased postoperative flexion.26,29,32 Both Motomiya et al26 and Ishikawa et al32 found significantly increased supination. Raven et al29 reported significantly increased ulnar deviation as well as increased radial deviation (P < .05), whereas Ishikawa et al32 reported decreased radial deviation (P < .05) (Table 6).
Patient-reported outcomes
Measures of patient-reported outcomes varied widely across studies (Table 5). Of those used, higher DASH and QuickDASH scores indicate greater disability, whereas higher MWS and Modified Mayo Wrist Score indicate better overall functioning. Multiple RSL studies reported patient DASH scores, which ranged from 25.725 to 4422 at a follow-up of 19 and 28 months, respectively. Montoya-Faivre et al21 reported a QuickDASH average of 44.5 at 53 months for RSL.21 The MWS for RSL ranged from 57.221 to 5827 at 53 and 96 month follow-up, respectively. The sole MWS for RL was 71 at 84 months.26 In addition to collecting the DASH score, Quadlbauer et al24 reported Michigan Hand Questionnaire scores of 70 at an average follow-up of 63 months for RSL.24 Nagy and Büchler27 collected an additional measure called the Wrist Score, which resulted in a score of 56 at 96 months for RSL.27 Of the included studies on RL, only Motomiya et al26 compared preoperative and postoperative MWS, which were 37 versus 71 (P < .001). Pooled analysis of patient outcomes was unachievable owing to the heterogeneity of reported measures.
Nonunion and reoperation
Studies that reported nonunion rates are detailed in Table 5. In the RSL group, rates of nonunion ranged from 0% within multiple studies to 75% by Raven et al.6,24,27,29,47 Among RL arthrodeses, Raven et al29 and Trieb et al31 both reported 0% nonunion whereas Stanley and Boot33 had the maximum of 6%. The weighted rates of nonunion for RSL and RL were 15% and 2%, respectively. The weighted mean progression to TWA for RSL and RL arthrodesis were 4% and 0%, respectively (Table 7).
Discussion
In the setting of advanced degenerative changes of the radiocarpal joints, patients often experience considerable limitations in ADLs that are resistant to nonsurgical treatment.52, 53, 54 If the degenerative changes spare the midcarpal articulations, RL and RSL arthrodesis represent promising options for patients to improve pain and function.6,21,22,24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29,31, 32, 33,47 Compared with TWA,20,55,56 RL and RSL arthrodesis maintain wrist motion at or above the level of functional wrist motion required to perform most ADLs.35 Compared with TWA, RL and RSL arthrodesis minimally alter articulations, preserving surface area if the need arises for further surgical intervention. When deciding between these 2 operations, the decision has historically been based on the extent of the pathology and surgeon preference.57 Given the paucity of systematic reviews or randomized controlled trials examining the 2 procedures, we sought to review the literature comprehensively to assess postoperative pain, function, and long-term success as measured by nonunion and patient outcomes.
Regarding postoperative pain scores, both studies on RL and RSL arthrodesis demonstrated reductions in VAS scores. Both groups of studies had short and long-term interval follow-up, suggesting that the pain relief initially achieved persisted into the future. For every RL or RSL study that reported VAS pain scores, change in VAS exceeded the minimal clinically significant change of 11 (on a 100-point scale) that is widely accepted for RA patients with chronic pain.58,59
Both surgeries exhibited improvement in GS. Only RL arthrodesis had multiple studies reporting statistically significant increases in GS. It should be noted that Stanley and Boot33 reported average GS much lower than all other studies. Because the study by Stanley and Boot is the earliest one in our review, it is possible that technological limitations or measurement variations could account for the lower values, misleadingly lowering pooled preoperative and postoperative GS values.33,60 Furthermore, the low overall perioperative GS reported in the RL cohort could be attributed to the greater percentage of females represented.61 This decreased GS could also be related to the systemic impacts of RA seen in all patients in the RL group.
Postoperative ROM was an additional marker of function. We predicted that both surgeries would result in decreased ROM owing to the fusing of wrist bones that these procedures employ.23,37 Alternatively, the data demonstrated a combination of both statistically significant increases and decreases in wrist ROM after surgical intervention among individual studies. Generally, RL studies displayed more statistically significant instances of decreased ROM. Patients who experienced RSL arthrodesis demonstrated more instances of increased ROM. Only 2 of the 4 RL postoperative weighted averages met the ROMs deemed necessary for completion of ADLs, whereas all pooled averages for RSL fell within or above these minimal parameters.22,34, 35, 36
Success was evaluated by subjective and objective standardized measures, including patient outcome surveys, nonunion rates, and progression to TWA. Although multiple RL studies had no cases of nonunion,29,31 several RSL studies demonstrated multiple cases of nonunion, which Nagy and Büchler27 deemed unacceptable for modern surgeries. These findings challenge those of prior studies suggesting that a single articulation with a small surface area is more susceptible to nonunion; instead, they recommend incorporating adjacent carpals to increase the chance of successful union.62, 63, 64, 65
This study had limitations. Because of the small number of studies that met inclusion criteria, we chose to include the studies of Ha et al47 and Mühldorfer-Fodor et al,26 even though they included variations of RSL arthrodesis. Thus, it is difficult to say whether some of the significance found in these results resulted from the variation in surgical technique. In addition, we included studies with MINORS scores of 11 and 12, which are at higher risk for bias, to avoid further reducing the sample size.48 Through pooling of the study demographics, the sex disparity across cohorts became evident and could limit the generalizability of the results. Furthermore, studies were inconsistent in their reporting of preoperative and postoperative outcomes, which weakened the strength of the comparisons. Because 4 studies reported solely on the rheumatoid wrist, generalizability is decreased because the diversity in wrist arthritis etiologies was largely skewed.26,31, 32, 33 Finally, this was not a meta-analysis owing to the large heterogeneity among studies that resulted in an insufficient sample size to compare outcome measures directly using tests of significance. This was partially mitigated by data pooling throughout the study; however, this does not make up for the lack of randomized studies and disparities in outcome reporting.
This study demonstrates that RL and RSL are safe, effective approaches to managing debilitating radiocarpal arthritis.65 This systematic review provides a unique contribution to the current body of literature because of the summative exploration it offers. Radioscapholunate arthrodesis appears to produce a total arc of motion within the functional demands of most ADLs. Radiolunate arthrodesis appears to be associated with low rates of both nonunion and progression to TWA. Both surgeries yield pain reduction. Given the lack of conclusive findings, the decision regarding which surgery to pursue should be patient-centered and consider the individual’s unique situation. Our hope is that this systematic review prompts further exploration of these 2 motion-sparing surgical techniques with prospective, randomized controlled trials to compare outcomes directly.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Mia White, MILS, AHIP and the Emory Woodruff Health Sciences Center Library informationists for their assistance in preparing and editing our search strategy.
Footnotes
Declaration of interests: No benefits in any form have been received or will be received by the authors related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article.
Supplementary Data
References
- 1.Akhondi H., Panginikkod S. Wrist arthritis, In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK531497/ [PubMed]
- 2.Lameijer C.M., Ten Duis H.J., Vroling D., Hartlief M.T., El Moumni M., van der Sluis C.K. Prevalence of posttraumatic arthritis following distal radius fractures in non-osteoporotic patients and the association with radiological measurements, clinician and patient-reported outcomes. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2018;138(12):1699–1712. doi: 10.1007/s00402-018-3046-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Nelson D.L., Mitchell M.A., Groszewski P.G., Pennick S.L., Manske P.R. In: Schuind F., An K.N., Cooney W.P., Garcia-Elias M., editors. Vol. 256. Springer; Boston, MA: 1994. Wrist range of motion in activities of daily living. (Advances in the Biomechanics of the Hand and Wrist. NATO ASI Series (Series A: Life Sciences)). [Google Scholar]
- 4.Haugen I.K., Englund M., Aliabadi P., et al. Prevalence, incidence and progression of hand osteoarthritis in the general population: the Framingham Osteoarthritis Study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70(9):1581–1586. doi: 10.1136/ard.2011.150078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Dahlhamer J., Lucas J., Zelaya C., et al. Prevalence of chronic pain and high-impact chronic pain among adults—United States, 2016. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2018;67(36):1001–1006. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6736a2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bain G.I., Ondimu P., Hallam P., Ashwood N. Radioscapholunate arthrodesis—a prospective study. Hand Surg. 2009;14(2-3):73–82. doi: 10.1142/S021881040900427X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Campbell C.C., Neustein T.M., Daly C.A., Wagner E.R. Surgical treatment of wrist arthritis in young patients. JBJS Rev. 2020;8(3) doi: 10.2106/JBJS.RVW.19.00078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kitay A., Wolfe S.W. Scapholunate instability: current concepts in diagnosis and management. J Hand Surg Am. 2012;37(10):2175–2196. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2012.07.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Srnec J.J., Wagner E.R., Rizzo M. Total wrist arthroplasty. JBJS Rev. 2018;6(6):e9. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.RVW.17.00123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wagner E.R., Bravo D., Elhassan B., Moran S.L. Factors associated with improved outcomes following proximal row carpectomy: a long-term outcome study of 144 patients. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2016;41(5):484–491. doi: 10.1177/1753193415597096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Wagner E.R., Werthel J.D., Elhassan B.T., Moran S.L. Proximal row carpectomy and 4-corner arthrodesis in patients younger than age 45 years. J Hand Surg Am. 2017;42(6):428–435. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2017.03.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Balk M.L., Imbriglia J.E. Proximal row carpectomy: ndications, surgical technique, and long-term results. Oper Tech Orthop. 2003;13(1):42–47. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Vanhove W., De Vil J., Van Seymortier P., Boone B., Verdonk R. Proximal row carpectomy versus four-corner arthrodesis as a treatment for SLAC (scapholunate advanced collapse) wrist. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2008;33(2):118–125. doi: 10.1177/1753193408087116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Traverso P., Wong A., Wollstein R., Carlson L., Ashmead D., Watson H.K. Ten-year minimum follow-up of 4-corner fusion for SLAC and SNAC wrist. Hand (N Y) 2017;12(6):568–572. doi: 10.1177/1558944716681949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Vesnaver A., Claudio M., Megaro A., Galli S., Ferrari P.R.F. Treatment of SNAC SLAC with 4-corner arthrodesis. J Orthop Traumatol. 2011;12:S74–S75. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Zimmermann M.S., Weiss A.P.C., Gotha H. Failure of proximal row carpectomy (PRC) and fourcorner fusion (4CF) in patients younger than 50: Level 3 evidence. J Hand Surg Am. 2012;37(8):31–32. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Strauch R.J. Scapholunate advanced collapse and scaphoid nonunion advanced collapse arthritis—update on evaluation and treatment. J Hand Surg Am. 2011;36(4):729–735. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2011.01.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Laulan J., Marteau E., Bacle G. Wrist osteoarthritis. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2015;101(suppl 1):S1–S9. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2014.06.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.O’Shaughnessy M.A., Wagner E.R., Berger R.A., Kakar S. Buying time: long-term results of wrist denervation and time to repeat surgery. Hand (N Y) 2019;14(5):602–608. doi: 10.1177/1558944718760031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wagner E.R., Elhassan B.T., Kakar S. Long-term functional outcomes after bilateral total wrist arthrodesis. J Hand Surg Am. 2015;40(2) doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2014.10.032. 224.e221–228.e221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Montoya-Faivre D., Pomares G., Calafat V., Dap F., Dautel G. Clinical and radiological outcomes following radioscapholunate fusion. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2017;103(7):1093–1098. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2017.07.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Mühldorfer-Fodor M., Ha H.P., Hohendorff B., Löw S., Prommersberger K.J., van Schoonhoven J. Results after radioscapholunate arthrodesis with or without resection of the distal scaphoid pole. J Hand Surg Am. 2012;37(11):2233–2239. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2012.08.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Chamay A., Della Santa D., Vilaseca A. Radiolunate arthrodesis: factor of stability for the rheumatoid wrist. Ann Chir Main. 1983;2(1):5–17. doi: 10.1016/s0753-9053(83)80073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Quadlbauer S., Leixnering M., Jurkowitsch J., Hausner T., Pezzei C. Volar radioscapholunate arthrodesis and distal scaphoidectomy after malunited distal radius fractures. J Hand Surg Am. 2017;42(9) doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2017.05.031. 754.e751–754.e758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Beyermann K., Prommersberger K.J., Lanz U. Radioscapholunate fusion following comminuted fractures of the distal radius. Eur J Trauma. 2000;26(4):169–175. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Motomiya M., Iwasaki N., Minami A., Matsui Y., Urita A., Funakoshi T. Clinical and radiological results of radiolunate arthrodesis for rheumatoid arthritis: 22 wrists followed for an average of 7 years. J Hand Surg Am. 2013;38(8):1484–1491. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2013.05.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Nagy L., Büchler U. Long-term results of radioscapholunate fusion following fractures of the distal radius. J Hand Surg Br. 1997;22(6):705–710. doi: 10.1016/s0266-7681(97)80429-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Prommersberger K.J., Beyermann K., Lanz U. Radioscapholunate arthrodesis. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2003;15(4):445–462. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Raven E.E.J., Ottink K.D., Doets K.C. Radiolunate and radioscapholunate arthrodeses as treatments for rheumatoid and psoriatic arthritis: long-term follow-up. J Hand Surg Am. 2012;37(1):55–62. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2011.10.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Sturzenegger M., Büchler U. Radio-scapho-lunate partial wrist arthrodesis following comminuted fractures of the distal radius. Ann Chir Main Memb Super. 1991;10(3):207–216. doi: 10.1016/s0753-9053(05)80285-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Trieb K., Machacek P., Hofstaetter S.G., Panotopoulos J., Wanivenhaus A. Radio-lunate arthrodesis in rheumatoid arthritis: outcome and techniques. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013;133(5):729–734. doi: 10.1007/s00402-013-1729-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ishikawa H., Murasawa A., Nakazono K. Long-term follow-up study of radiocarpal arthrodesis for the rheumatoid wrist. J Hand Surg Am. 2005;30(4):658–666. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2005.02.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Stanley J.K., Boot D.A. Radio-lunate arthrodesis. J Hand Surg Br. 1989;14(3):283–287. doi: 10.1016/0266-7681_89_90082-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Brumfield R.H., Champoux J.A. A biomechanical study of normal functional wrist motion. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1984;187:23–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Palmer A.K., Werner F.W., Murphy D., Glisson R. Functional wrist motion: a biomechanical study. J Hand Surg Am. 1985;10(1):39–46. doi: 10.1016/s0363-5023(85)80246-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Yajima H., Kobata Y., Shigematsu K., Kawamura K., Takakura Y. Radiocarpal arthrodesis for osteoarthritis following fractures of the distal radius. Hand Surg. 2004;9(2):203–209. doi: 10.1142/s0218810404002297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Watson-Jones R. 4th ed. Livingstone; Edinburgh: 1955. Fractures and joint injuries; p. 928. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Harrison R.K., DiMeo T., Klinefelter R.D., Ruff M.E., Awan H.M. Multi-modal pain control in ambulatory hand surgery. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ) 2018;47(6) doi: 10.12788/ajo.2018.0042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Garcia-Elias M., Lluch A., Ferreres A., Papini-Zorli I., Rahimtoola Z.O. Treatment of radiocarpal degenerative osteoarthritis by radioscapholunate arthrodesis and distal scaphoidectomy. J Hand Surg Am. 2005;30(1):8–15. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2004.09.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.McGuire D.T., Bain G.I. Radioscapholunate fusions. J Wrist Surg. 2012;1(2):135–140. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1330071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Jüsten H.P., Wessinghage D. Radiolunate arthrodesis in rheumatoid wrist—the modified Chamay technique with broadening of indications. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb. 2003;141(3):316–321. doi: 10.1055/s-2003-40091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Martini A.K. Indications and technique of partial arthrodesis of the carpus. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb. 1992;130(3):175–180. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1040135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Meuli H.C. Indications for arthrodesis and arthroplasty in late complications following wrist injuries. Z Unfallmed Berufskr. 1974;67(2):126–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Unglaub F., Langer M.F., Unglaub J.M., et al. (Partial) fusion of the wrist: indications and surgical procedures. Unfallchirurg. 2017;120(6):513–526. doi: 10.1007/s00113-017-0356-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Allieu Y. Development of surgical indications in the treatment of rheumatoid wrist: report on experience based on 603 surgical cases, 1968-1994. Ann Chir Main Memb Super. 1997;16(3):179–197. doi: 10.1016/s0753-9053(97)80001-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Moher D., Liberati A., Tetzlaff J., Altman D.G., Group P. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Int J Surg. 2010;8(5):336–341. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2010.02.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Ha N.B., Phadnis J., MacLean S.B.M., Bain G.I. Radioscapholunate fusion with triquetrum and distal pole of scaphoid excision: long-term follow-up. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2018;43(2):168–173. doi: 10.1177/1753193417724139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Slim K., Nini E., Forestier D., Kwiatkowski F., Panis Y., Chipponi J. Methodological index for non-randomized studies (minors): development and validation of a new instrument. ANZ J Surg. 2003;73(9):712–716. doi: 10.1046/j.1445-2197.2003.02748.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Breivik H., Borchgrevink P.C., Allen S.M., et al. Assessment of pain. Br J Anaesth. 2008;101(1):17–24. doi: 10.1093/bja/aen103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Haefeli M., Elfering A. Pain assessment. Eur Spine J. 2006;15(suppl 1):S17–S24. doi: 10.1007/s00586-005-1044-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Neumann S., Kwisda S., Krettek C., Gaulke R. Comparison of the grip strength using the Martin-Vigorimeter and the JAMAR-dynamometer: establishment of normal values. In Vivo. 2017;31(5):917–924. doi: 10.21873/invivo.11147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Wang S., Wang X., Liu Y., Sun X., Tang Y. Ultrasound-guided intra-articular triamcinolone acetonide injection for treating refractory small joints arthritis of rheumatoid arthritis patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 2019;98(33) doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000016714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Cushman D.M., Ofek E., Syed R.H., et al. Comparison of varying corticosteroid type, dose, and volume for the treatment of pain in small- and intermediate-size joint injections: a narrative review. PM R. 2019;11(7):758–770. doi: 10.1016/j.pmrj.2018.09.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Paulus H.E., Di Primeo D., Sharp J.T., et al. Patient retention and hand-wrist radiograph progression of rheumatoid arthritis during a 3-year prospective study that prohibited disease modifying antirheumatic drugs. J Rheumatol. 2004;31(3):470–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Adey L., Ring D., Jupiter J.B. Health status after total wrist arthrodesis for posttraumatic arthritis. J Hand Surg Am. 2005;30(5):932–936. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2005.06.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Field J., Herbert T.J., Prosser R. Total wrist fusion: a functional assessment. J Hand Surg Br. 1996;21(4):429–433. doi: 10.1016/s0266-7681(96)80039-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Burns L.R., Housman M.G., Booth R.E., Koenig A.M. Physician preference items: what factors matter to surgeons? Does the vendor matter? Med Devices (Auckl) 2018;11:39–49. doi: 10.2147/MDER.S151647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Wolfe F., Michaud K. Assessment of pain in rheumatoid arthritis: minimal clinically significant difference, predictors, and the effect of anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy. J Rheumatol. 2007;34(8):1674–1683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Hawker G.A., Mian S., Kendzerska T., French M. Measures of adult pain: Visual Analog Scale for Pain (VAS Pain), Numeric Rating Scale for Pain (NRS Pain), McGill Pain Questionnaire (MPQ), Short-Form McGill Pain Questionnaire (SF-MPQ), Chronic Pain Grade Scale (CPGS), Short Form-36 Bodily Pain Scale (SF-36 BPS), and Measure of Intermittent and Constant Osteoarthritis Pain (ICOAP) Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2011;63(suppl 11):S240–S252. doi: 10.1002/acr.20543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Weinstock-Zlotnick G., Bear-Lehman J., Yu T.Y. A test case: does the availability of visual feedback impact grip strength scores when using a digital dynamometer? J Hand Ther. 2011;24(3):266–275. doi: 10.1016/j.jht.2011.01.004. [quiz: 276] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Puh U. Age-related and sex-related differences in hand and pinch grip strength in adults. Int J Rehabil Res. 2010;33(1):4–11. doi: 10.1097/MRR.0b013e328325a8ba. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Hom S., Ruby L.K. Attempted scapholunate arthrodesis for chronic scapholunate dissociation. J Hand Surg Am. 1991;16(2):334–339. doi: 10.1016/s0363-5023(10)80122-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Larsen C.F., Jacoby R.A., McCabe S.J. Nonunion rates of limited carpal arthrodesis: a meta-analysis of the literature. J Hand Surg Am. 1997;22(1):66–73. doi: 10.1016/S0363-5023(05)80181-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Krakauer J.D., Bishop A.T., Cooney W.P. Surgical treatment of scapholunate advanced collapse. J Hand Surg Am. 1994;19(5):751–759. doi: 10.1016/0363-5023(94)90178-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Wysocki R.W., Cohen M.S. Complications of limited and total wrist arthrodesis. Hand Clin. 2010;26(2):221–228. doi: 10.1016/j.hcl.2009.11.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.