Abstract
Objectives
Although evidence is accumulating globally, data on outcomes in rheumatic disease and COVID-19 in Ireland are limited. We used data from the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance (C19-GRA) to describe time-varying COVID-19 outcomes for people with rheumatic disease in Ireland.
Methods
Data entered into the C19-GRA provider registry from Ireland between 24 March 2020 and 9 July 2021 were analysed. Differences in the likelihood of hospitalization and mortality according to demographic and clinical variables were investigated using Chi-squared test or Fisher’s exact test, as appropriate. Trends in odds of hospitalization and mortality over time were investigated using logistic regression with the time period as a categorical variable.
Results
Of 212 cases included, 59.4% were female and median age was 58.0 years (range 13–96). Of the 212 cases, 92 (43%) were hospitalized and 22 (10.4%) died. Increasing age, a diagnosis of gout, ever smoking, glucocorticoid use, having comorbidities and specific comorbidities of cancer, cardiovascular and pulmonary disease were more common in those hospitalized. A diagnosis of inflammatory arthritis, csDMARD and/or b/tsDMARD use were less frequent in those hospitalized. Increasing age, a diagnosis of gout, ever smoking, having comorbidities and specific comorbidities of obesity, cardiovascular and pulmonary disease were more common in those who died. Odds of hospitalization or mortality did not change over time.
Conclusion
No temporal trend was observed in either COVID-19-related hospitalization or mortality outcomes for people with rheumatic disease in Ireland.
Keywords: rheumatic disease, COVID-19, biologics, hospitalization
Rheumatology key messages.
The current study includes 212 cases of COVID-19 in people with rheumatic disease reported in Ireland.
Of the COVID-19 cases reported, 43% were hospitalized and 10% died.
COVID-19 outcomes for people with rheumatic disease did not show the temporal improvements observed in the general population.
Introduction
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and the resulting Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) continue to present a global health crisis. Significant improvements in COVID-19 outcomes have been demonstrated over time [1–5]. This may relate to accumulating clinical experience leading to an improvement in care [6] along with beneficial effects of several immunomodulating treatments in severe COVID-19 [7–10]. It is unclear whether outcomes for people with rheumatic disease who develop COVID-19 are also improving, with some studies reporting improved outcomes [4, 11]. Because outcomes following SARS-CoV-2 infection may also vary depending on the geography and ethnicity of affected populations, it is important to explore outcomes in different locations and over time [12–16].
We have previously reported predictors of hospitalization in people with rheumatic disease who developed COVID-19 in the first five months of the pandemic in Ireland [17]. In this study we examine temporal trends in COVID-19 outcomes in people with rheumatic disease in Ireland in the first 16 months of the pandemic.
Methods
COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance
Data regarding individuals with rheumatic disease with COVID-19 are entered into one of two parallel international data portals hosted in the United States and United Kingdom. Details of the C19-GRA registries have been published previously [18, 19].
Data collection
Cases in this study were entered into the C19-GRA provider registry from 24 March 2020 to 9 July 2021. Data were collected on baseline rheumatic disease status including demographic and clinical variables such as age, sex, smoking status, rheumatic disease diagnosis, disease activity (as per the physician’s global assessment (remission, low, moderate or high/severe)), and comorbidities. Medications were categorized as previously described [17]. DMARDs were grouped as conventional synthetic DMARDs (csDMARDs) or biologic DMARDs (bDMARDs) and targeted synthetic DMARDs (tsDMARDs) [18]. Rheumatic diseases were categorized as (i) inflammatory arthritis (IA); (ii) gout; and (iii) vasculitis, connective tissue diseases and all other diagnoses (‘other’). Data collected regarding COVID-19 infection included method of diagnosis, place of diagnosis, COVID-19 symptoms, and outcomes of COVID-19 disease including hospitalization, ventilation and death.
Demographic and clinical continuous variables were reported as median (IQR) and categorical variables as number and percentage (%). Hospitalization and mortality probability were calculated for each category of the key demographic and clinical variables. Differences in the likelihood of hospitalization and mortality according to demographic and clinical variables were investigated using Chi-squared test or Fisher’s exact test, as appropriate.
Trends in the odds of hospitalization and mortality between timing of diagnosis were investigated using logistic regression with hospitalization or mortality as the dependent variable and wave as a categorical predictor. Each case was categorized under a wave using the date of diagnosis as follows: Wave 1 (weeks 10–31), 1 March 2020–1 August 2020; Wave 2 (week 32–47), 2 August 2020–21 November 2020; and Wave 3 (week 48 onwards), 22 November 2020–9 July 2021 [20]. The COVID-19 vaccination programme in Ireland began on 29 December 2020, with 1 million vaccine doses administered by April 2021, and 90% of adults fully vaccinated by September 2021. Appropriate confounders were identified as those demographic and clinical variables that were associated with both the outcome of interest as well as with timing/wave of diagnosis. These confounders were corrected for in each model. The significance of any suspected trend was tested using the ‘contrast’ post-estimation command.
A sensitivity analysis was performed restricting our results to two institutions employing a rigorous case-finding methodology. These institutions contacted all patients requesting that they notify the rheumatology service if they developed COVID-19 (as part of clinical care), all admissions to the institutions with COVID-19 were screened for rheumatic disease cases, and finally all positive SARS-CoV-2 PCR tests were back-referenced against people attending the rheumatology services using medical record linkage.
All statistical analyses were performed using STATA IC15 (StataCorp. 2017. Stata Statistical Software: Release 15. College Station, TX, USA: StataCorp LLC.) and graphs were prepared using GraphPad Prism version 6 for Windows (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA, USA, www.graphpad.com).
This study was approved by the Irish National Research Ethics Committee for COVID-19 (20-NREC-COV-010). The committee waived the need for written informed consent as the data were fully anonymised.
Results
The 212 cases had a median age of 58.0 years (IQR: 45.5–73.0) and the majority were female (59.4%). Most had IA (136/212 64.2%) with the balance having gout (35/212, 16.5%) and CTD or other diagnoses (50/212, 23.6%). The majority of patients (46.2%) were in remission, with 35.6% of cases having low disease activity. Seventy cases (33%) had no comorbidities; among those with comorbidities, cardiovascular and pulmonary diseases were the most prevalent (42% and 17.5%, respectively). Just under half of cases were hospitalized (92/212, 43%) and 22 (10.4%) died.
Hospitalization outcome
Demographic and clinical details according to hospitalization are shown in Table 1. Increasing age, a diagnosis of gout, ever smoking, glucocorticoid use, having comorbidities, and specific comorbidities of cancer and cardiovascular and pulmonary disease were more common in those hospitalized. Patients at either high or low disease activity were more likely to be hospitalized. A diagnosis of IA, csDMARD and/or b/tsDMARD use was less frequent in those hospitalized.
Table 1.
Hospitalisation outcome according to demographic and clinical factors in people with rheumatic disease diagnosed with COVID-19
| All Participants (n = 212) | Not hospitalised (n = 113) | Hospitalised (n = 92) | P-value | Alive (n = 190) | Deceased (n = 22) | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender, n (%) | |||||||
| Female | 126 (59.4) | 72 (59.0) | 50 (41.0) | 0.17 | 114 (90.5) | 12 (9.5) | 0.62 |
| Male | 86 (40.6) | 41 (49.4) | 42 (50.6) | 76 (88.4) | 10 (11.6) | ||
| Age (years), n (%) | |||||||
| 18-29 | 8 (3.8) | 6 (85.7) | 1 (14.3) | <0.01a | 8 (100.0) | 0 (0.0) | <0.01a |
| 30-49 | 54 (25.8) | 42 (80.8) | 10 (19.2) | 54 (100.0) | 0 (0.0) | ||
| 50-65 | 67 (32.1) | 46 (70.8) | 19 (29.2) | 62 (92.5) | 5 (7.5) | ||
| >65 | 80 (38.3) | 17 (21.5) | 62 (78.5) | 63 (78.8) | 17 (21.2) | ||
| Most common rheumatic disease diagnoses*, n (%) | |||||||
| Inflammatory arthritisb | 136 (64.2) | 91 (70.0) | 39 (30.0) | <0.01 | 126 (92.7) | 10 (7.3) | 0.05 |
| Gout | 35 (16.5) | 2 (5.7) | 33 (94.3) | <0.01 | 27 (77.1) | 8 (22.9) | 0.01a |
| Connective Tissue Disease and Otherc | 50 (23.6) | 23 (47.9) | 25 (52.1) | 0.25 | 45 (90.0) | 5 (10.0) | 0.29 |
| Disease Activity, n (%) | |||||||
| 1 | 96 (46.2) | 34 (36.6) | 59 (63.4) | <0.01a | 81 (84.4) | 15 (15.6) | 0.19 a |
| 2 | 74 (35.6) | 54 (75.0) | 18 (25.0) | 70 (94.6) | 4 (5.4) | ||
| 3 | 30 (14.4) | 21 (70.0) | 9 (30.0) | 27 (90.0) | 3 (10.01) | ||
| 4 | 5 (2.40) | 1 (20.0) | 4 (80.0) | 5 (100.0) | 0 (0.0) | ||
| No comorbidities, n (%) | 70 (33.0) | 58 (85.3) | 10 (14.7) | <0.01 | 69 (98.6) | 1 (1.4) | <0.01 |
| Most common comorbidities, n (%) | |||||||
| Cancer | 10 (4.3) | 1 (11.1) | 9 (88.9) | 0.01a | 7 (77.8) | 2 (22.2) | 0.24a |
| Cardiovascular diseased | 89 (42.0) | 23 (26.4) | 64 (73.6) | <0.01 | 70 (78.7) | 19 (21.3) | <0.01a |
| Pulmonary diseased | 37 (17.5) | 9 (24.3) | 28 (75.7) | <0.01 | 26 (70.3) | 11 (29.7) | <0.01a |
| Neurological/Neuromuscular/ Psychiatric disease | 10 (4.7) | 3 (30.0) | 7 (70.0) | 0.12 | 8 (80.0) | 2 (20.0) | 0.28a |
| Obesity | 20 (9.4) | 11 (55.0) | 9 (45.0) | 0.99 | 14 (70.0) | 6 (30.0) | <0.01a |
| Smoking status, n (%) | |||||||
| Never | 120 (56.6) | 72 (60.5) | 47 (39.5) | <0.01 | 110 (91.7) | 10 (8.3) | 0.02 |
| Ever | 54 (25.5) | 15 (28.3) | 38 (71.7) | 43 (79.6) | 11 (20.4) | ||
| Unknown | 38 (17.9) | ||||||
| Medication prior to COVID-19 diagnosis, n (%) | |||||||
| Steroids | 33 (15.6) | 11 (34.4) | 21 (65.6) | 0.01 | 26 (78.8) | 7 (21.2) | 0.06 |
| Steroids 10 mg or more | 15 (7.1) | 4 (28.6) | 10 (71.4) | 0.04 | 12 (80.0) | 3 (20.0) | 0.19 |
| csDMARD monotherapye | 61 (28.8) | 39 (67.2) | 19 (32.8) | 0.03 | 56 (91.8) | 5 (8.2) | 0.51 |
| b_tsDMARD (monotherapy or in combination with csDMARD)f | 81 (38.2) | 56 (70.0) | 24 (30.0) | 0.00 | 75 (92.6) | 6 (7.4) | 0.27 |
| No complications, n (%) | 162 (76.4) | 155 (95.7) | 7 (4.3) | <0.01 | 155 (95.7) | 7 (4.3) | <0.01 |
| Most common complications, n (%) | |||||||
| ARDS | 10 (4.7) | 3 (30.0) | 7 (70.0) | <0.01a | 3 (30.0) | 7 (70.0) | <0.01a |
| Sepsis | 9 (4.3) | 4 (44.4) | 5 (55.6) | <0.01a | 4 (44.4) | 5 (55.6) | <0.01a |
| Concominant infection | 14 (6.6) | 9 (64.3) | 5 (35.7) | 0.01a | 9 (64.3) | 5 (35.7) | <0.01a |
| Thromboembolism | 11 (5.2) | 10 (89.6) | 1 (9.1) | 1.00a | 10 (90.9) | 1 (9.1) | 1.00 |
| AKI or renal failure | 7 (3.3) | 2 (28.6) | 5 (71.4) | <0.01a | 2 (28.6) | 5 (71.4) | <0.01a |
| Deceased, n (%) | 22 (10.4) | 0 (0.0) | 22 (100.0) | <0.01 | — | — | |
P-value from Pearson’s χ2 test, unless a=Fisher’s Exact test.
Patients could be diagnosed with more than one rheumatic diseases.
Inflammatory arthritis diagnosis includes: axial spondyloarthritis (including ankylosing spondylitis); PsA; other spondyloarthritis (including reactive arthritis); JIA, oligo; juvenile idiopathic arthritis, poly; systemic JIA; RA; other inflammatory arthritis.
Connective tissue disease and other diagnoses include: NCA-associated vasculitis (e.g. GPA, EGPA); other vasculitis including Kawasaki disease; anti-phospholipid antibody syndrome; autoinflammatory syndrome (including TRAPS, CAPS, FMF); Behcet’s; Chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis; GCA; IgG4-related disease; inflammatory myopathy (e.g. DM, PM); IBM; mixed connective tissue disease; ocular inflammation; PMR; sarcoidosis; SS; SLE; SSC; undifferentiated CTD; localized scleroderma (morphea); other.
Cardiovascular diseases include: cerebrovascular disease; CVD; hypertension; diabetes; and renal disease. Pulmonary diseases include asthma; COPD; and interstitial lung disease.
csDMARD monotherapy includes: antimalarials (including HCQ, chloroquine, mepacrine/quinacrine); apremilast; AZA/6-MP; ciclosporin; leflunomide; MTX; MMF/mycophenolic acid; SSZ; tacrolimus; thalidomide/lenalidomide.
b/tsDMARD thrapy includes: abatacept; belimumab; CD-20 inhibitors (including rituximab, ofatumumab); CYC; IL-1 inhibitors (including anakinra, canakinumab, rilonacept); IL-6 inhibitors (including tocilizumab, sarilumab); IL-12 inhibitors (ustekinumab); IL 23 inhibitors (guselkumab, risankizumab); IL-17 inhibitors (including secukinumab, ixekizumab); JAK inhibitors (including tofacitinib, baricitinib, upadacitinib); TNF-inhibitors (including infliximab, etanercept, adalimumab, golimumab, certolizumab and biosimilars); rituximab within the last 12 months. Bold values indicates the significance of P < 0.05.
Mortality outcome
Demographic and clinical details according to mortality are shown in Table 1. Increasing age, a diagnosis of gout, ever smoking, having comorbidities and specific comorbidities of obesity, cardiovascular and pulmonary disease were more common in those who died.
Hospitalization and mortality outcomes according to wave of diagnosis
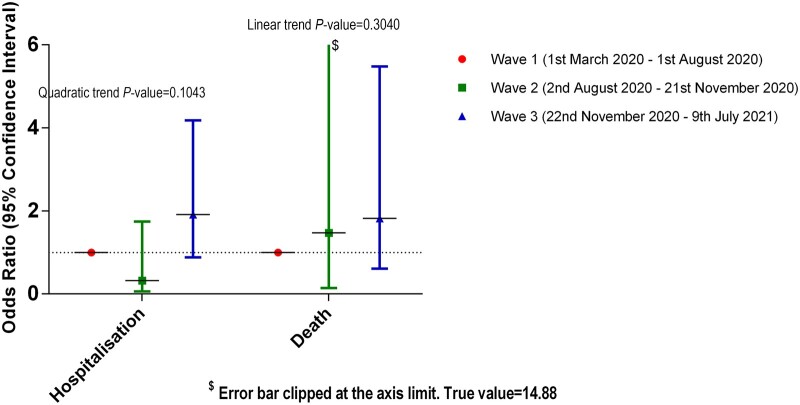
The majority of people (n = 115, 54.2%) were diagnosed during the first wave of the pandemic in Ireland, with 8.9% (n = 19) in the second wave and 36.3% (n = 77) in the third wave. Hospitalization occurred in 49/115 (44.1%) during the first wave, 2/19 (11.1%) during the second wave and 41/77 (54%) during the third wave. Death occurred in 10/115 (8.7%) during the first wave, 1/19 (5.3%) during the second wave and 11/77 (14.3%) during the third wave. A diagnosis of IA, disease activity, cardiovascular disease or obesity was differentially represented in the three waves (Supplementary Table S1, available at Rheumatology online). They were thus inserted as confounders, along with age and gender, in the logistic regression model investigating the odds of hospitalisation across waves. Likewise, disease activity, cardiovascular disease and obesity were both added as confounders, along with age and gender, in the respective model for mortality.
Cases diagnosed during wave 2 displayed a decrease in the likelihood of hospitalisation compared with wave 1, whereas cases diagnosed during wave 3 had increased hospitalisation odds compared with wave 1, but all changes were non-significant, as was the quadratic trend in the odds for hospitalisation between the three waves.
In terms of mortality, cases diagnosed in each successive wave demonstrated again non-statistically significant increased likelihoods of mortality, and a non-statistically increasing linear trend in the odds of mortality across waves (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
Odds for hospitalisation and mortality according to wave of diagnosis
The sensitivity analysis restricting our results to the two institutions with rigorous case-finding methodology, reporting 59% of cases, did not alter the overall results.
Discussion
This is the largest and most detailed report of people with rheumatic disease and COVID-19 from Ireland. We have previously reported associations of clinical features with hospitalisation [17]. We did not identify any reduction in odds for hospitalisation or mortality over time. This lack of change in odds of hospitalisation and mortality over time was in contrast to other data where clear improvements in COVID-19 outcomes have been demonstrated for non-rheumatic disease patients over time [1, 2, 21]. Likely contributors are better general care measures as well as targeted treatments such as glucocorticoids and tocilizumab [7, 8]. One explanatory hypothesis may be that people with rheumatic diseases, who may be receiving long-term immunomodulating treatments, may be less likely to benefit from the use of these treatments in the setting of subsequent severe COVID-19. Alternatively, our small sample size may have limited ability to demonstrate a change. The roll-out of the COVID-19 vaccine in Ireland occurred in conjunction with the third COVID-19 wave and may have impacted on our findings.
Previous studies in rheumatic disease patients have suggested some improvement in outcomes over time [4, 5, 11]. A cohort study from Boston of 143 rheumatic disease patients demonstrated a reduction in rates of mechanical ventilation, but not of hospitalisation or mortality, over time [11]. An exposure scored matched analysis study of 8540 rheumatic disease patients using the US TriNetX electronic health record database reported a reduction in the risks of hospitalisation, mechanical ventilation and mortality when comparing a late cohort to an early cohort [4]. The findings of these studies, and the current work, must be interpreted with cognizance of the limitations, including selection bias, unmeasured confounders and possible artefact related to the identification of milder cases over time as testing capacity expanded [5].
Our study has several limitations. While this is the largest study of people with rheumatic disease and COVID-19 from Ireland, the statistical power of our study is limited by the low number of cases; we did not undertake multivariable analyses due to this. The C19-GRA is a physician-entered registry and is limited by selection bias with a likely tendency to report more severe cases. There is also the possibility that the reporting of cases varied over time potentially influencing our results. However, restricting our data to the two institutions with rigorous case ascertainment did not alter the overall findings. The C19-GRA is also a case-based registry with no denominator population, therefore inferences cannot be made about the incidence of COVID-19 in people with rheumatic diseases. Additionally, the C19-GRA is by design restricted to people with rheumatic disease and COVID-19; therefore, comparisons cannot be made to people with non-rheumatic disease and COVID-19 nor to rheumatic disease in the absence of COVID-19.
In conclusion, our findings demonstrate no difference in hospitalisation or mortality in patients with rheumatic disease across the first three COVID-19 waves in Ireland.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank all rheumatology providers who entered data into the registry.
R.C., C.L., K.L., J.G.R., R.K., A.D.F., J.J.C., P.OC., R.M.F., R.H.M., D.J.K., N.A., F.S. and G.M.M. contributed to data collection, data quality control, data analysis and interpretation. They drafted, and revised, the manuscript critically for important intellectual content and gave final approval of the version to be published. E.N. and C.A.D. contributed to the analysis and interpretation of the data. They drafted, and revised, the manuscript critically for important intellectual content and gave final approval of the version to be published. P.C.R., J.W.L. and R.G. directed the work and contributed to the analysis and interpretation of the data. They drafted, and revised, the manuscript critically for important intellectual content and gave final approval of the version to be published.
Funding: No specific funding was received from any bodies in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors to carry out the work described in this article.
Disclosure statement: The views expressed here are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent the views of the ACR, the EULAR, and the (UK) National Health Service (NHS), the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) or the (UK) Department of Health. R.C.: Speaker’s bureau: Janssen, Roche, Sanofi, Abbvie, Elena. E.N.: Speaker’s bureau: AbbVie Eli-Lilly, Gilead, Celltrion, Pfizer, Sanofi. P.C.R.: Speaker’s bureau: UCB, Roche, Pfizer, Gilead, Janssen, Novartis, Eli Lilly, Abbvie; Grant/research support from: Abbvie, UCB, Novartis, Janssen, Pfizer. J.W.L.: Grant/research support from: Pfizer. R.G.: Speaker’s bureau: Pfizer, Cornerstones, Janssen, Novartis, Abbvie. The other authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Ethics: Irish National Research Ethics Committee for COVID-19 (20-NREC-COV-010).
Data sharing statement: Request for access to data from the registry should be made to the Data Access and Sharing Committee of the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance.
Data availability statement
The data underlying this article are available on reasonable request to the corresponding author.
Supplementary data
Supplementary data are available at Rheumatology online.
Contributor Information
Richard Conway, Department of Rheumatology, St. James’s Hospital; Clinical Medicine, Trinity College Dublin, Dublin, Ireland.
Elena Nikiphorou, Department of Rheumatology, ; Centre for Rheumatic Diseases, King’s College London, London, UK.
Christiana A Demetriou, Department of Primary Care and Population Health, University of Nicosia Medical School, Nicosia, Cyprus.
Candice Low, Department of Rheumatology, St. Vincent’s University Hospital.
Kelly Leamy, Department of Rheumatology, Mater Misericordiae Hospital, Dublin.
John G Ryan, Department of Rheumatology, Cork University Hospital, Wilton.
Ronan Kavanagh, Department of Rheumatology, Galway Clinic, Galway.
Alexander D Fraser, Department of Rheumatology, University Hospitals Limerick; Graduate Entry Medical School, University of Limerick, Limerick.
John J Carey, Department of Rheumatology, Galway University Hospitals; School of Medicine, National University of Ireland Galway, Galway.
Paul O’Connell, Department of Rheumatology, Beaumont Hospital; School of Medicine, Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland.
Rachael M Flood, Clinical Medicine, Trinity College Dublin, Dublin, Ireland; Department of Rheumatology, Tallaght University Hospital.
Ronan H Mullan, Clinical Medicine, Trinity College Dublin, Dublin, Ireland; Department of Rheumatology, Tallaght University Hospital.
David J Kane, Clinical Medicine, Trinity College Dublin, Dublin, Ireland; Department of Rheumatology, Tallaght University Hospital.
Nicola Ambrose, Department of Rheumatology, Blackrock Clinic, Dublin, Ireland.
Frances Stafford, Department of Rheumatology, Blackrock Clinic, Dublin, Ireland.
Philip C Robinson, University of Queensland Faculty of Medicine, Brisbane, Australia.
Jean W Liew, Section of Rheumatology, Boston University School of Medicine, Boston, MA, USA.
Rebecca Grainger, Department of Medicine, University of Otago, Wellington, New Zealand.
Geraldine M McCarthy, Department of Rheumatology, Mater Misericordiae Hospital, Dublin.
the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance:
Brahim Dahou, Rosana Quintana, Gimena Gómez, Karen Roberts, Roberto Miguel Baez, Vanessa Castro Coello, María J Haye Salinas, Federico Nicolas Maldonado, Alvaro Andres Reyes Torres, Gelsomina Alle, Romina Tanten, Hernán Maldonado Ficco, Romina Nieto, Carla Gobbi, Yohana Tissera, Cecilia Pisoni, Alba Paula, Juan Alejandro Albiero, Maria Marcela Schmid, Micaela Cosatti, Maria Julieta Gamba, Carlevaris Leandro, María Alejandra Cusa, Noelia German, Veronica Bellomio, Lorena Takashima, Mariana Pera, Karina Cogo, Maria Soledad Gálvez Elkin, María Alejandra Medina, Veronica Savio, Ivana Romina Rojas Tessel, Rodolfo Perez Alamino, Marina Laura Werner, Sofía Ornella, Luciana Casalla, Maria de la Vega, María Severina, Mercedes García, Luciana Gonzalez Lucero, Cecilia Romeo, Sebastián Moyano, Tatiana Barbich, Ana Bertoli, Andrea Baños, Sandra Petruzzelli, Carla Matellan, Silvana Conti, Ma Alicia Lazaro, Gustavo Fabián Rodriguez Gil, Fabian Risueño, Maria Isabel Quaglia, Julia Scafati, Natalia Lili Cuchiaro, Jonathan Eliseo Rebak, Susana Isabel Pineda, María Elena Calvo, Eugenia Picco, Josefina Gallino Yanzi, Pablo Maid, Debora Guaglianone, Julieta Silvana Morbiducci, Sabrina Porta, Natalia Herscovich, José Luis Velasco Zamora, Boris Kisluk, Maria Sol Castaños Menescardi, Rosana Gallo, María Victoria Martire, Carla Maldini, Cecilia Goizueta, Sabrina Solange de la Vega Fernandez, Carolina Aeschlimann, Gisela Subils, Eva Rath, Yves Piette, Mieke Devinck, Bea Maeyaert, Francinne Machado Ribeiro, Sandra Lucia Euzebio Ribeiro, Marcelo Pinheiro, Sebastián Ibáñez, Anne-Marie Chassin-Trubert, Lingli Dong, Lui Cajas, Marko Bareic, Branimir Anic, Melanie-Ivana Culo, Tea Ahel Pavelic, Kristina Kovacevic Stranski, Boris Karanovic, Jiri Vencovsky, Marta Píchová, Maria Filkova, Hesham Hamoud, Dimitrios Vassilopoulos, Gabriela Maria Guzman Melgar, Ho So, Márta Király, Mahdi Vojdanian, Alexandra Balbir-Gurman, Fatemah Abutiban, Julija Zepa, Inita Bulina, Loreta Bukauskiene, Beatriz Elena Zazueta-Montiel, Angel Alejandro Castillo-Ortiz, Erick Zamora-Tehozol, David Vega-Morales, Diana Cervántes Rosete, Eduardo Martín-Nares, Tatiana Sofia Rodriguez-Reyna, Marina Rull Gabayet, Deshiré Alpízar-Rodríguez, Fedra Irazoque, Xochitl Jimenez, Lenny Geurts-van Bon, Theo Zijlstra, Monique Hoekstra, Nasra Al-Adhoubi, Babur Salim, Enrique Giraldo, Ariel Salinas, Manuel Ugarte-Gil, Jaroslaw Nowakowski, Samar Al-Emadi, Richard Conway, Rachael Flood, Geraldine McCarthy, Ioana Felea, Ileana Filipescu, Simona Rednic, Laura Groseanu, Maria Magdelena Tamas, Vanda Mlynarikova, Martina Skamlova, Martin Zlnay, Dagmar Miceková, Lubica Capova, Zelmira Macejova, Emoke Tenová, Helena Raffayova, Gabriela Belakova, Eva Strakova, Marieta Sencarová, Sona lnayová, Anna Sabová, Daniela Spisakova, Mária Oetterová, Olga Lukacova, Martina Bakosova, Alojzija Hocevar, Natalia de la Torre-Rubio, Juan José Alegre Sancho, Montserrat Corteguera Coro, Juan Carlos Cobeta Garcia, Maria Carmen Torres Martin, Jose Campos, Jose A Gomez Puerta, Gozd Kubra Yardimci, Servet Akar, Ozan Cemal Icacan, Selda Çelik, Viktoriia Vasylets, Su-Ann Yeoh, Claire Vandevelde, Sasha Dunt, Jane Leeder, Elizabeth Macphie, Rosaria Salerno, Christine Graver, Katie Williams, Sheila O'Reilly, Kirsty Devine, Jennifer Tyler, Elizabeth Warner, James Pilcher, Samir Patel, Elena Nikiphorou, Laura Chadwick, Caroline Mulvaney Jones, Beverley Harrison, Lucy Thornton, Diana O'Kane, Lucia Fusi, Audrey Low, Sarah Horton, Shraddha Jatwani, Sara Baig, Hammad Bajwa, Vernon Berglund, Angela Dahle, Walter Dorman, Jody Hargrove, Maren Hilton, Nicholas Lebedoff, Susan Leonard, Jennifer Morgan, Emily Pfeifer, Archibald Skemp, Jeffrey Wilson, Anne Wolff, Eduardo Cepeda, Kristin D'Silva, Tiffany Hsu, Naomi Serling-Boyd, Jeffrey Sparks, Derrick Todd, Zachary Wallace, Denise Hare, Cassandra Calabrese, Christopher Adams, Arezou Khosroshahi, Adam Kilian, Douglas White, Melanie Winter, Theodore Fields, Caroline Siegel, Nicole Daver, Melissa Harvey, Neil Kramer, Concetta Lamore, Suneya Hogarty, Karen Yeter, Leanna Wise, Faizah Siddique, Byung Ban, Tamar Tanner, Eric Ruderman, William Davis, Robert Quinet, Evangeline Scopelitis, Karen Toribio Toribio, Tameka Webb-Detiege, Jerald Zakem, Khurram Abbass, Gilbert Kepecs, Lilliam Miranda, Michael Guma, Ammar Haikal, Sushama Mody, Daric Mueller, Arundathi Jayatilleke, JoAnn Zell, Alison Bays, Kathryn Dao, Ezzati Fatemeh, Deborah Parks, David Karp, and Guillermo Quiceno
References
- 1. Anesi GL, Jablonski J, Harhay MO, Atkins JH. et al. Characteristics, outcomes, and trends of patients with COVID-19-related critical illness at a learning health system in the United States. Ann Intern Med 2021;174:613–21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Roth GA, Emmons-Bell S, Alger HM. et al. Trends in patient characteristics and COVID-19 in-hospital mortality in the United States during the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA Network Open 2021;4:e218828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Yeates EO, Nahmias J, Chinn J. et al. Improved outcomes over time for adult COVID-19 patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome or acute respiratory failure. PLoS One 2021;16:e0253767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Jorge A, D'Silva KM, Cohen A. et al. Temporal trends in severe COVID-19 outcomes in patients with rheumatic disease: a cohort study. Lancet Rheumatol 2021;3:e131–e7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Gianfrancesco MA, Robinson PC.. Changing COVID-19 outcomes in patients with rheumatic disease-are we really getting better at this? Lancet Rheumatol 2021;3:e88–e90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Smith V, Devane D, Nichol A, Roche D.. Care bundles for improving outcomes in patients with COVID-19 or related conditions in intensive care - a rapid scoping review. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2020;12:Cd013819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.RECOVERY Collaborative Group, Horby P, Lim WS. et al. Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19. New Engl J Med 2021;384:693–704. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32678530/ [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.RECOVERY Collaborative Group. Tocilizumab in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial. Lancet 2021;397:1637–45. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33933206/ [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Guimarães PO, Quirk D, Furtado RH. et al. Tofacitinib in patients hospitalized with Covid-19 pneumonia. New Engl J Med 2021;385:406–15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Kalil AC, Patterson TF, Mehta AK. et al. Baricitinib plus remdesivir for hospitalized adults with Covid-19. New Engl J Med 2021;384:795–807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Serling-Boyd N, D'Silva KM, Hsu TY. et al. Coronavirus disease 2019 outcomes among patients with rheumatic diseases 6 months into the pandemic. Ann Rheum Dis 2021;80:660–6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Mazumder A, Arora M, Sra MS, Gupta A. et al. Geographical variation in case fatality rate and doubling time during the COVID-19 pandemic. Epidemiol Infect 2020;148:e163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Scirè CA, Carrara G, Zanetti A. et al. COVID-19 in rheumatic diseases in Italy: first results from the Italian registry of the Italian Society for Rheumatology (CONTROL-19. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2020;38:748–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. D'Silva KM, Jorge A, Cohen A. et al. COVID-19 outcomes in patients with systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases compared to the general population: a US multicenter, comparative cohort study. Arthritis Rheumatol 2021;73:914–20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.FAI2R/SFR/SNFMI/SOFREMIP/CRI/IMIDIATE consortium and contributors. Severity of COVID-19 and survival in patients with rheumatic and inflammatory diseases: data from the French RMD COVID-19 cohort of 694 patients. Ann Rheum Dis 2021;80:527–38. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7712850/ [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Pang R, Zhao J, Gan Z. et al. Evolution of COVID-19 in patients with autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Aging 2020;12:23427–35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Conway R, Nikiphorou E, Demetriou CA. et al. Predictors of hospitalization in patients with rheumatic disease and COVID-19 in Ireland: data from the COVID-19 global rheumatology alliance registry. Rheumatol Adv Pract 2021;5:rkab031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Gianfrancesco M, Hyrich KL, Al-Adely S. et al. Characteristics associated with hospitalisation for COVID-19 in people with rheumatic disease: data from the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance physician-reported registry. Ann Rheum Dis 2020;79:859–66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Gianfrancesco MA, Hyrich KL, Gossec L. et al. Rheumatic disease and COVID-19: initial data from the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance provider registries. Lancet Rheumatol 2020;2:e250–3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lima V. The Pandemic One Year on: Trends and Statistics Between Three Waves of the COVID-19 Pandemic in Ireland. Available from: https://publicpolicy.ie/papers/the-pandemic-one-year-on-trends-and-statistics-between-three-waves-of-the-covid-19-pandemic-in-ireland/ (17 December 2021, date last accessed).
- 21. Conway RP, Byrne DG, O’Riordan DMR. et al. Emergency medical admissions and COVID-19: impact on 30-day mortality and hospital length of stay. Ir J Med Sci 2021;doi:10.1007/s11845-021-02752-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The data underlying this article are available on reasonable request to the corresponding author.