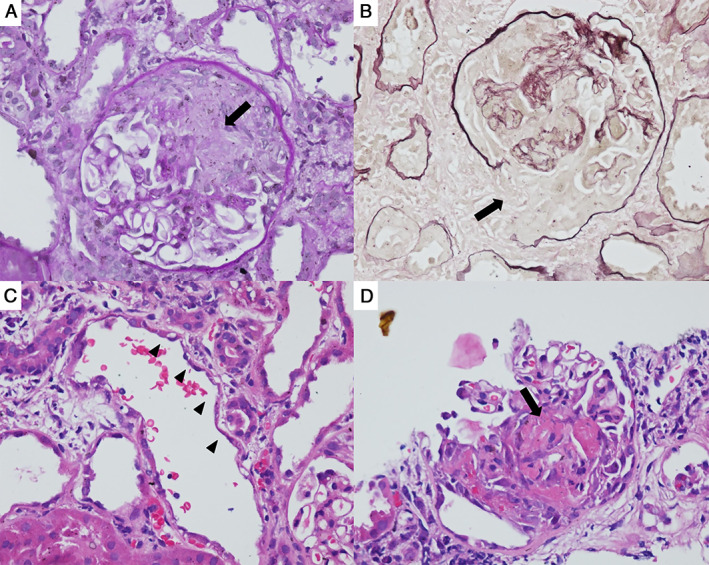
Mass vaccination campaigns to prevent coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19) are occurring worldwide; not surprisingly, reports of rare postvaccination immune‐mediated adverse events, as seen with the influenza vaccination (1), also started to surface, including cases of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)–associated vasculitis (AAV) after receipt of the Pfizer‐BioNTech and Moderna COVID‐19 vaccines (2, 3). Here, we report a case from Brazil of new‐onset AAV temporally associated with inactivated COVID‐19 vaccination. The patient, a previously asymptomatic 78‐year‐old White woman with a medical history of odontogenic maxillary sinusitis resolved after sinus surgery (in 2011), presented with asthenia, low‐grade fever, and a mild dry cough 2 weeks after receiving Sinovac Biotech’s COVID‐19 vaccine (CoronaVac) on March 12, 2021 (second shot on April 5, 2021). Over the weeks, in addition to persistent fever, the patient experienced worsening of fatigue, weight loss, night sweats, and renal dysfunction. Of note, various antibiotics were empirically used until she underwent a kidney biopsy on June 22. At that time, she had leukocytosis, anemia, thrombocytosis, elevated inflammatory biomarkers and serum creatinine (peak at 7.3 vs 0.8 mg/dl on May 1, 2021), cytoplasmic ANCA 1:20 by indirect immunofluorescence (reference: negative), an anti‐proteinase‐3 level of 19 U/ml by fluorescent‐enzyme immunoassay (positive >3 U/ml), a normal complement level, polyclonal hypergammaglobulinemia, and active urinary sediment. The diagnostic workup was negative for COVID‐19 (reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction), antinuclear antibodies (ANA), rheumatoid factor, cryoglobulins, anti‐myeloperoxidase, anti‐phospholipids, anti‐Ro, anti‐La, anti‐Smith (Sm), anti–double‐stranded DNA, anti‐ribonucleoprotein (RNP), anti–glomerular basement membrane, HIV, and hepatitis B and C. Computed tomography (head, chest, paranasal sinuses, and abdomen), echocardiography, and nasal and laryngeal videoendoscopy findings were either normal or nonspecific. Urine and blood culture results were negative. The result of a kidney biopsy (14 glomeruli yielded) was compatible with necrotizing (9 of 14 glomeruli) and crescentic (cellular crescents in 6 of 14 glomeruli) glomerulonephritis. The renal biopsy specimen shows a cellular crescent and break of the glomerular basement membrane (periodic acid–Schiff stain, original magnification ×40) (A), break in Bowman’s capsule (Jones stain, original magnification ×40) (B), an acute tubular injury (hematoxylin–eosin stain, original magnification ×40) (C), and fibrinoid necrosis in the glomerulus capillary loop (hematoxylin–eosin stain, original magnification ×40) (D). Renal immunostaining results were negative for C1q; C3; immunoglobulins A, M, and G; and light chains κ and λ. The patient received high‐dose corticosteroids, pulse cyclophosphamide, and needed hemodialysis for 12 weeks. She is now controlled on low‐dose corticosteroids and mycophenolate mofetil but with chronic renal impairment. To our knowledge, this is the first report of AAV possibly triggered by an inactivated COVID‐19 vaccine.
Supporting information
Disclosure Form
Author disclosures are available at https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/action/downloadSupplement?doi=10.1002%2Facr2.11397&file=acr211397-sup-0001-Disclosureform.pdf.
References
- 1. Zafrir Y, Agmon‐Levin N, Shoenfeld Y. Post‐influenza vaccination vasculitides: a possible new entity. J Clin Rheumatol 2009;15:269–70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Shakoor MT, Birkenbach MP, Lynch M. ANCA‐associated vasculitis following Pfizer‐BioNTech COVID‐19 vaccine. Am J Kidney Dis 2021;78:611–3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Sekar A, Campbell R, Tabbara J, Rastogi P. ANCA glomerulonephritis after the Moderna COVID‐19 vaccination. Kidney Int 2021;100:473–4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Disclosure Form


