Figure 2.
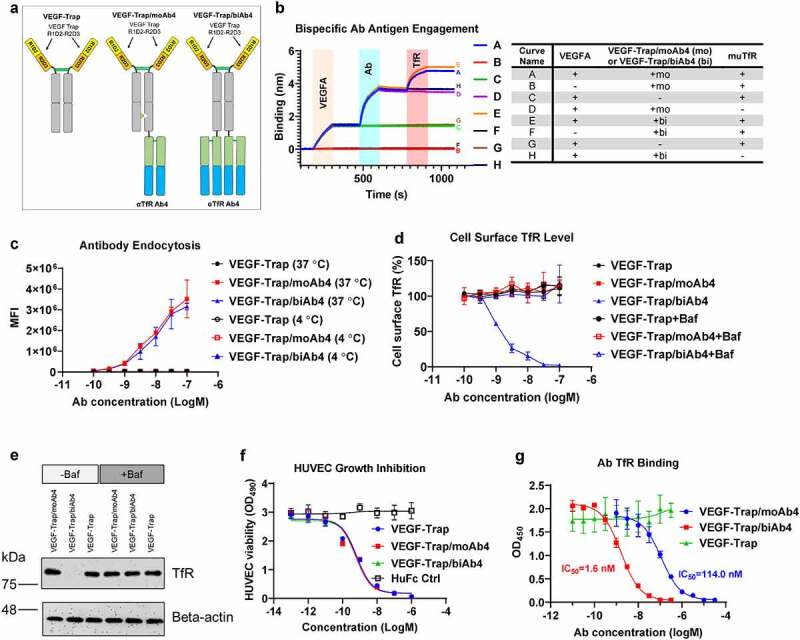
Characterization of VEGF-Trap/αTfR bispecific antibodies. a. Design of VEGF-Trap and VEGF-Trap/αTfR bispecific antibodies. In the VEGF-Trap/moAb4 design, knob-into-hole mutations were introduced to promote heterodimerization. The αTfR Fab was fused to the C-terminus of the CH3. Although not depicted, the human Fc regions contain LALAPG mutations to abolish Fc-mediated immune effector functions. b. Sandwich BLI assay showing the incorporation of both VEGF-Trap and αTfR into the bispecific constructs. The corresponding proteins involved in each curve were labeled in the shaded area and are detailed in the table next to the BLI diagram. c. αTfR bispecific antibodies showed dose-dependent endocytosis in Bend.3 cells. MFI is the mean fluorescent intensity of live cells, n = 3 independent repeats. d. VEGF-Trap/biAb4 showed dose-dependent reduction of cell surface muTfR level. The reduction of TfR surface level by VEGF-Trap/biAb4 was the result of lysosomal degradation. The cell surface level of TfR was measured by flow cytometry using a non-competing antibody against muTfR, n = 3 independent repeats. Baf is bafilomycin A1 at 100 nM. e. Western blotting showing the reduced level of total TfR in Bend.3 cells by VEGF-Trap/biAb4 treatment. The reduction of TfR level by VEGF-Trap/biAb4 was the result lysosomal degradation. Baf is bafilomycin A1 at 100 nM. f. VEGF-Trap/αTfR bispecific antibodies showed similar potency in inhibiting VEGFA-mediated HUVEC proliferation compared to VEGF-Trap, n = 3 independent repeats. g. Titration curves showing dose-dependent binding of TfR by VEGF-Trap/αTfR bispecific antibodies. VEGF-Trap/biAb4 showed significantly stronger binding to TfR than that of VEGF-Trap/moAb4, n = 3 independent repeats. Data points with error bars represent mean ± SD.
