Abstract
BRCA1/2 are breast cancer susceptibility genes that are involved in DNA repair and transcriptional control. They are dysregulated in breast cancer, making them attractive therapeutic targets. Here, we performed a systematic multiomics analysis to expound BRCA1/2 functions as prognostic biomarkers in breast cancer. First, using different web-based bioinformatics platforms (Oncomine, TIMER 2.0, UALCAN, and cBioportal), the expression of BRCA1/2 was assessed. Then, the R package was used to analyze the diagnostic value of BRCA1/2 in patients. Next, we determined the relationship between BRCA1/2 mRNA expression and prognosis in patients (PrognoScan Database, R2: Kaplan Meier Scanner and Kaplan–Meier Plotter). Subsequently, the association of BRCA1/2 with mutation frequency alteration and copy number alterations in breast cancer was investigated using the cBioportal platform. After that, we identified known and predicted structural genes and proteins essential for BRCA1/2 functions using GeneMania and STRING db. Finally, GO and KEGG pathway enrichment analyses were performed to elucidate the potential biological functions of the co-expression genes of BRCA1/2. The BRCA1/2 mRNA level in breast cancer tissues was considerably higher than in normal tissues, with AUCs of 0.766 and 0.829, respectively. Overexpression of BRCA1/2 was significantly related to the worse overall survival (p < 0.001) and was correlated to clinicopathological characteristics including lymph nodes, estrogen receptors, and progesterone receptors (p < 0.01). The alteration frequencies of both the gens have been checked, and the results show that BRCA1 and BRCA2 show different alteration frequencies. Their mutation sites differ from each other. GO and KEGG showed that BRCA1/2 was mainly enriched in catalytic activity, acting on DNA, chromosomal region, organelle fission, cell cycle, etc. The 20 most frequently changed genes were closely related to BRCA1/2, including PALB2 and RAD51 relatively. Our study provides suggestive evidence of the prognostic role of BRCA1/2 in breast cancer and the therapeutic target for breast cancer. Furthermore, BRCA1/2 may influence BRCA prognosis through catalytic activity, acting on DNA, chromosomal regions, organelle fission, and the cell cycle. Nevertheless, further validation is warranted.
Keywords: BRCA1/2, breast cancer, multiomics, prognostic biomarkers
1. Introduction
Breast cancer affects a staggering number of 1.7 million women worldwide each year, which is the main leading cause of cancer death in women [1,2]. Five to ten percent of breast cancers are considered to be related to genetic predispositions, and some breast cancers are caused by genetic dominant susceptibility genes, which have a high risk of disease [3].
BRCA1/2 are tumor suppressors that are essential for the faithful repair of double-strand DNA breaks by homologous recombination. However, BRCA1/2 mutation occurs frequently in breast cancer [4]. The tumor suppressor genes BRCA1/2, which are found on chromosomes 17q and 13q, respectively, and encode factors that restrict cell development, were identified in the early 1990s [5,6,7,8,9]. BRCA1 encodes a nuclear phosphoprotein, which acts as a tumor suppressor gene through maintaining genomic stability [3,10]. BRCA1 is also involved in other cellular functions that are important in maintaining genomic integrity, including mitotic spindle assembly, centrosome replication, cell cycle control, and chromatin remodeling at dsDNA break sites [4]. BRCA2 is a 27-exon gene involved in genome stability, particularly in the homologous recombination (HR) pathway, which repairs double-stranded DNA breaks [3]. BRCA2- related cancers, unlike BRCA1, frequently express estrogen and progesterone receptors and have many of the same features as sporadic breast cancer [11]. Women with germline BRCA1 or BRCA2 (BRCA1/2) mutations have a markedly increased risk of breast and ovarian cancer compared with the general population [12,13,14]. PALB2 is a protein-coding gene that is associated with both BRCA1 and BRCA2; it plays a critical role in homologous recombination repair (HRR) through its ability to recruit BRCA2 and RAD51 to DNA breaks [15]. BRCA1 promotes the concentration of PALB2 and BRCA2 at DNA-damage sites, and the interaction between BRCA1 and PALB2 is important for homologous recombination repair [15].
In recent years, BRCA1/2 has attracted considerable attention as a biomarker for predicting cancer prognosis. The identification of biomarkers, such as BRCA1/2, PIK3CA and RSK2, plays an important role in promoting the precise treatment of TNBC [16]. In this study, we assessed the significance of BRCA1/2 expression in breast cancer using multiple online databases and annotation tools. By accessing and analyzing all existing gene expression data, the expression patterns, functions, and prognostic values of BRCA1/2 in breast cancer were comprehensively investigated. These results will facilitate the understanding of the prognostic value of BRCA1/2 in breast cancer in humans.
2. Results
2.1. BRCA1/2 Expression in Human Breast Cancer
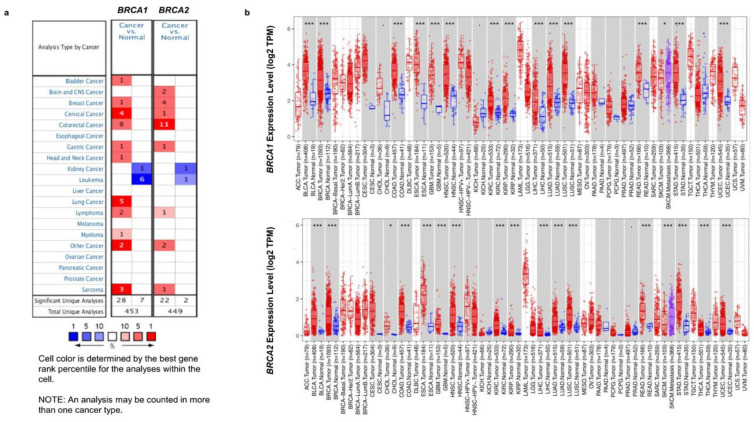
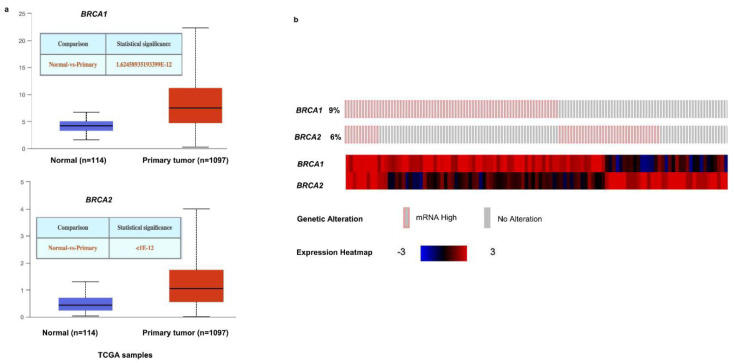
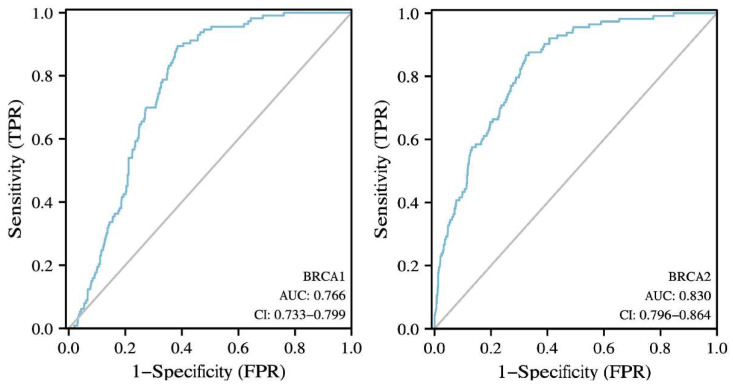
The Oncomine database was used to analyze the mRNA levels of BRCA1/2 between tumor tissues and normal tissues. The results showed that BRCA1/2 were overexpressed in breast cancer as compared to their expression levels in normal tissues (Figure 1a). To further evaluate the differential expression of BRCA1/2, we compared its expression levels in the TCGA dataset using the TIMER2.0 database. As shown in Figure 1b, expression of BRCA1/2 in breast cancer tissues is significantly higher than in normal tissue (Figure 1b). BRCA1 was overexpressed in intraductal cribriform breast adenocarcinoma patients in the TCGA database, with a fold change of 3.454 and a p value of 1.92 × 10−6. BRCA2 was also overexpressed in mucinous breast cancer, with a fold change of 3.750 and a p value of 3.22 × 10−5. The mRNA levels of BRCA2 were significantly increased in patients with invasive ductal breast carcinoma and invasive lobular breast carcinoma, with fold changes of 3.214 and 2.124, and p values of 1.46 × 10−25 and 9.36 × 10−9, respectively (Table 1). Furthermore, it was discovered that the expression of BRCA1/2 mRNA in breast cancer tissues was significantly higher than that in normal tissues (Figure 2a), and the change rates of BRCA1/2 mRNA in BRCA were 9% and 6%, respectively (Figure 2b), and the AUC of BRCA1/2 was 0.766 and 0.830, respectively (Figure 3), using UALCAN, cBioPortal, and the TCGA database.
Figure 1.
Expression of BRCA1/2 mRNA in cancer vs. normal (Oncomine and TCGA database). (a) This graphic generated by Oncomine (https://www.oncomine.org/resource/login.html, accessed on 10 February 2022) indicates the numbers of datasets with statistically significant (p < 0.01) mRNA overexpression (red) or downexpression (blue) of BRCA1/2 (different types of cancer vs. corresponding normal tissue). The threshold was designed with the following parameters: p value of 1 × 10−4, fold change of 2, and gene ranking of 10%. (b) Human BRCA1/2 expression levels in different tumor types from TCGA database were determined by TIMER 2.0 (http://timer.cistrome.org, accessed on 10 February 2022) (* p < 0.05; *** p < 0.001).
Table 1.
The expression of BRCA1/2 in BRCA in the Oncomine database.
| Gene Name | Types of BRCA vs. Normal | Fold Change | t Test | p Value | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BRCA1 | Intraductal Cribriform Breast Adenocarcinoma vs. Normal | 3.454 | 15.862 | 1.92 × 10−6 | TCGA Breast |
| BRCA2 | Mucinous Breast Carcinoma vs. Normal | 3.750 | 9.344 | 3.22 × 10−5 | TCGA Breast |
| Invasive Breast Carcinoma vs. Normal | 2.602 | 9.978 | 5.91 × 10−18 | TCGA Breast | |
| Invasive Ductal Breast Carcinoma vs. Normal | 3.214 | 14.586 | 1.46 × 10−25 | TCGA Breast | |
| Invasive Lobular Breast Carcinoma vs. Normal | 2.124 | 6.314 | 9.36 × 10−9 | TCGA Breast |
TCGA: The Cancer Genome Atlas.
Figure 2.
Expression of BRCA1/2 in BRCA patients. (a) Expression of BRCA1/2 in BRCA based on sample types by UALCAN (http://ualcan.path.uab.edu/index.html, accessed on 10 February 2022). (b) Expression of BRCA1/2 in BRCA by cBioPortal database (https://www.cbioportal.org, accessed on 10 February 2022) (breast invasive carcinoma (TCGA, Cell 2015)).
Figure 3.
The diagnostic value of BRCA1/2 in BRCA patients. The diagnostic value of BRCA1/2 in BRCA patients. AUC: area under curve.
2.2. Clinicopathological Parameters of BRCA1/2 in BRCA Patients
In the TCGA database, overexpression of BRCA1/2 was correlated with clinicopathological features and prognosis of BRCA patients (Table 2). Overexpression of BRCA1 was related to lymph node stage, ER status, PR status and PAM 50 subtypes (p < 0.05). Overexpression of BRCA2 was related to age, lymph node stage, ER stage, PR status, HER-2 status, and PAM 50 subtypes (p < 0.01) (Table 2).
Table 2.
The relationships between BRCA1/2 expression and clinicopathological features in Breast Cancer.
| Variables | No. | BRCA1 (p Value) | BRCA2 (p Value) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | NS | p < 0.01 | |
| ≤60 | 601 | ||
| >60 | 482 | ||
| T-Stage | NS | NS | |
| T1 | 277 | ||
| T2 | 629 | ||
| T3 | 139 | ||
| T4 | 35 | ||
| N-Stage | p < 0.05 | p < 0.01 | |
| N0 | 514 | ||
| N1 | 358 | ||
| N2 | 116 | ||
| N3 | 76 | ||
| M-Stage | NS | NS | |
| M0 | 902 | ||
| M1 | 20 | ||
| ER status | p < 0.01 | p < 0.001 | |
| − | 240 | ||
| + | 793 | ||
| PR status | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | |
| − | 342 | ||
| + | 688 | ||
| HER2 status | NS | p < 0.01 | |
| − | 558 | ||
| + | 157 | ||
| PAM (50) | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | |
| Lum A | 562 | ||
| Lum B | 204 | ||
| Her 2 | 82 | ||
| Basal | 195 | ||
| Normal | 40 |
T stage: primary tumor, N stage: regional lymph nodes, M stage: distant metastasis, ER status: estrogen receptor, PR status: progesterone receptor, HER2 status: human epidermal growth factor receptor 2, PAM (50): prediction analysis of microarray 50, Lum A: luminal A, Lum B: luminal B, Her2: Her2-enriched, Basal: basal-like, Normal: normal-like, NS: no significance.
2.3. Prognostic Value of BRCA1/2 mRNA Expression in BRCA Patients
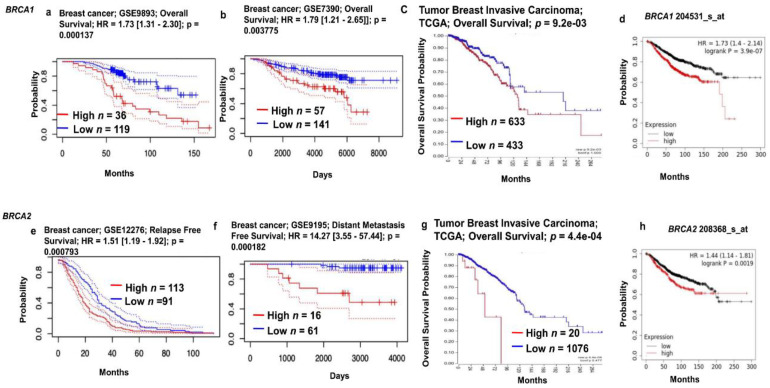
The prognostic value of BRCA1/2 expression in breast cancer was investigated using the PrognoScan, Kaplan–Meier Plotter and R2 databases to explain how BRCA1/2 affects the prognostic characteristics of breast cancer patients and the associations between variations in the expression of BRCA1/2 genes and clinical outcomes. We observed a positive correlation between BRCA1/2 overexpression and poor patient survival in breast cancer (Figure 4, p < 0.01). Kaplan–Meier Plotter’s survival analysis showed that the overall survival of breast cancer patients was poor in both BRCA1/2 overexpression. In PrognoScan and R2-Kaplan Meier Scanner, overexpression of BRCA1/2 was associated with poor prognosis.
Figure 4.
Relationship between BRCA1/2 mRNA expression and clinical outcomes in breast cancer patients (PrognoScan Database, R2: Kaplan Meier Scanner and Kaplan–Meier Plotter). (a,b,e,f) The survival curve comparing the patient with high (red), and low (blue) expression of BRCA1/2 was plotted from the PrognoScan database (http://dna00.bio.kyutech.ac.jp/PrognoScan/, accessed on 10 February 2022) in breast cancer patients. The threshold of cox p value < 0.05. (c,g) The survival curve comparing the patient with high (red) and low (blue) expression of BRCA1/2 was plotted from R2: Kaplan Meier Scanner (https://hgserver1.amc.nl/cgi-bin/r2/main.cgi, accessed on 10 February 2022) in TCGA breast cancer patients. The threshold of cox p value < 0.05. (d,h) The survival curve comparing the patient with high (red) and low (black) expression of BRCA1/2 was plotted from Kaplan–Meier Plotter (https://kmplot.com/analysis/, accessed on 10 February 2022) in breast cancer patients. The threshold of cox p value < 0.05.
2.4. The Relationship of BRCA1/2 Mutations and Copy Number Alterations (CNAs) in Breast Cancer
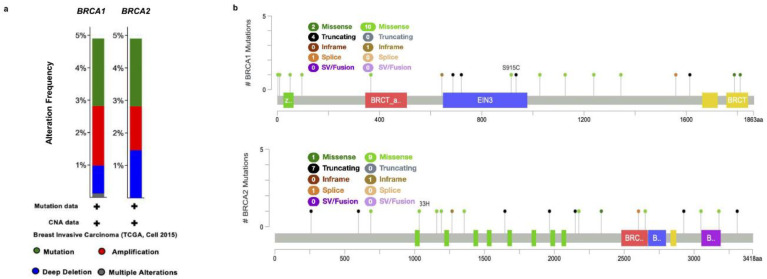
We individually examined the genetic alterations of BRCA1/2 in breast cancer using cBioPortal. Based on the Breast Invasive Carcinoma (TCGA, Cell 2015) samples and studies, with clinical data from 816 patients, we queried the database for BRCA1/2. The results showed that there was a significant difference in BRCA1/2 alteration frequency in breast cancer. As presented in Figure 5, the alteration frequency of BRCA1/2 was determined. It included mutations (green), amplification (red), deep deletions (blue), and multiple alterations (grey) (Figure 5a). Of the queried samples of BRCA1, 76 (9%) samples were associated with an altered gene set or pathway, resulting in a somatic mutation frequency of 2.2%. There were 18 mutation sites detected located from amino acids 0 to 1863 of the BRCA1 protein, including 12 missenses, 4 truncating, and 1 inframe mutation. Of the queried samples of BRCA2, 76 (9%) samples were associated with an altered gene set or pathway, resulting in a somatic mutation frequency of 2.1%. In BRCA2, a total of 19 mutation sites were detected between amino acids 0 to 3418 of the BRCA2 protein, including 10 missenses, 7 truncating, and 1 inframe mutation (Figure 5b).
Figure 5.
BRCA1/2 alteration frequency of mutations and copy number alterations (CNAs) in Breast Cancer (cBioPortal web). (a) The alteration frequency of the BRCA1/2 signature was determined cBioPortal (http://www.cbioportal.org, accessed on 10 February 2022). The alteration frequency included mutations (green), amplifications (red), deep deletions (blue), and multiple alterations (grey). (b) Summary of mutations in BRCA1/2 in BRCA from TCGA, cell 2015.
2.5. Co-Expression Analysis of BRCA1/2
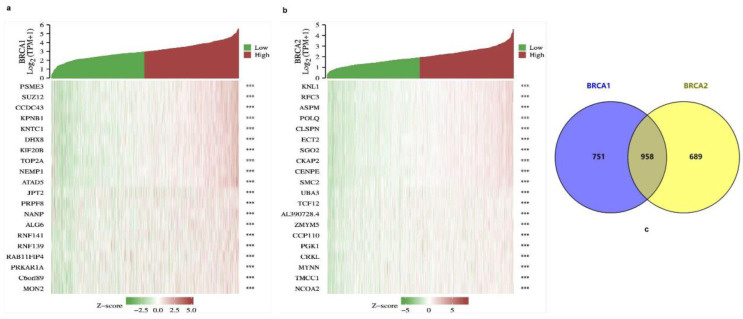
There were 3919 positively correlated genes and 37 negatively correlated genes for BRCA1 in the TCGA transcriptome database, and 3720 positively correlated genes and 340 negatively correlated genes for BRCA2. The top 10 co-expressed genes with positive and negative correlations to BRCA1/2 are shown in the form of heat maps (Figure 6a,b). In addition, the Venn diagram indicates that there were 958 intersections of BRCA1/2 co-expressing genes (Figure 6c).
Figure 6.
Co-expressed genes of BRCA1/2. (a,b) The top 10 genes with positive and negative co-expression of BRCA1/2 in the TCGA database according to heat map and Venn map. (c) Intersection co-expression genes of BRCA1/2. Note: |r| > 0.4 and p < 0.001.
2.6. Analysis of GO and KEGG Pathway for BRCA1/2
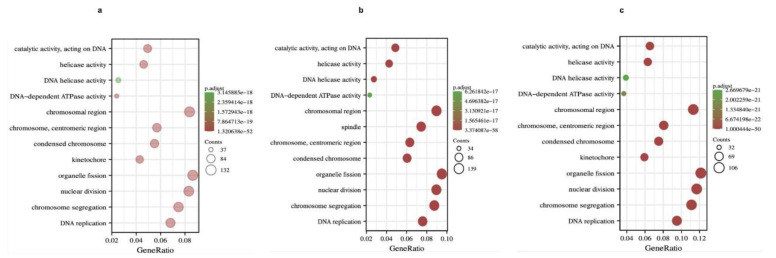
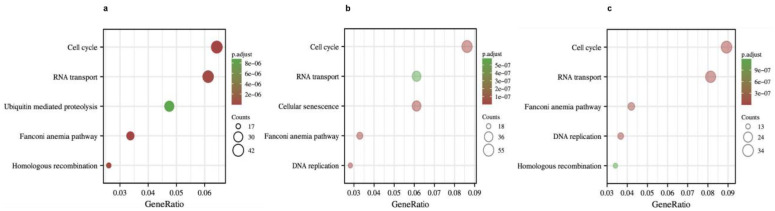
To further understand the potential role of BRCA1/2 in BRCA, GO and KEGG analyses were performed on BRCA1/2 co-expressed genes. The results revealed that BRCA1/2 co-expressed genes were mainly involved in catalytic activity, acting on DNA, chromosomal regions, and organelle fission (Figure 7). KEGG pathway analysis displayed that BRCA1/2 co-expressed genes were enriched in regulating the cell cycle, RNA transport, and the Fanconi anemia pathway (Figure 8).
Figure 7.
GO analysis of BRCA1, BRCA2 co-expression genes, and intersection co-expression genes among BRCA1/2. (a) GO analysis of BRCA1, (b) GO analysis of BRCA2, (c) GO analysis of co-expression genes, and intersection co-expression genes among BRCA1/2. GO: Gene Ontology.
Figure 8.
KEGG pathway enrichment analysis of BRCA1, BRCA2 co-expression genes, and intersection co-expression genes among BRCA1/2. KEGG pathway enrichment analysis of BRCA1 (a), BRCA2 (b) co-expression genes, and intersection co-expression genes among BRCA1/2 (c). KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genome.
2.7. Identification of BRCA1/2 Interacting Genes and Proteins and Genetic Alterations
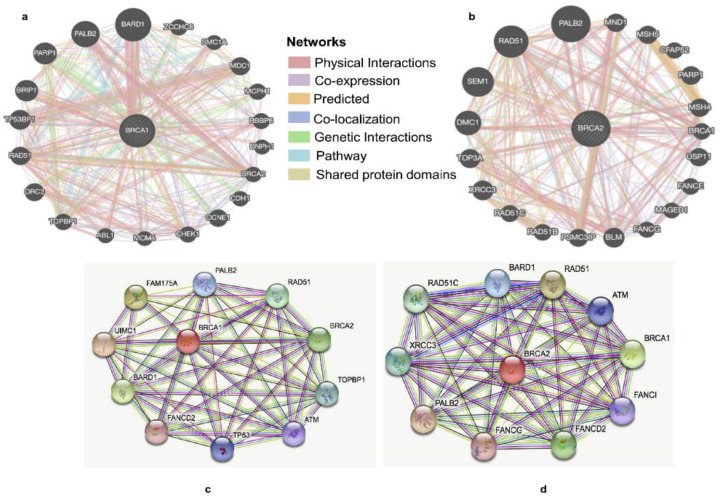
We constructed the gene–gene interaction networks for BRCA1/2 and the altered neighboring genes by using GeneMania. The results showed that 20 of the most frequently altered genes were closely correlated with BRCA1, including PALB2, RAD51, and PARP1 (Figure 9a). There were 20 most frequently altered genes that were closely correlated with BRCA2, including PALB2, RAD51, and SEM1 (Figure 9b). The A protein–protein interaction (PPI) networks of BRCA1/2 were generated using the STRING database. The result of the PPI network of BRCA1 showed that there were 45 edges and 11 nodes, including PALB2, RAD51, and TP53 (Figure 9c). There were 50 edges and 11 nodes in the result of the PPI network of BRCA2, including RAD51, BARD1 and XRCC3 (Figure 9d).
Figure 9.
Identification of BRCA1/2 interacting genes and proteins. (a,b) The gene–gene interaction network of BRCA1/2 was constructed using GeneMania. (c,d) The protein–protein interaction network of BRCA1/2 was generated using STRING db.
3. Discussion
The prognostic importance of BRCA1/2 in breast cancer was investigated in this research. BRCA1/2 are high-risk breast cancer susceptibility genes with 11–12-fold elevated relative risks in the general population for women [17]. A previous study showed that the probability of breast cancer in BRCA1 mutation carriers is 57–65%, while the probability of breast cancer in BRCA2 mutation carriers is 45–49% [4]. In the past, many studies have explored the relationship between BRCA1/2 mutation and survival. However, due to the relatively low mutation rate, detection rate, and survival bias of BRCA1/2 mutation carriers, the evidence of low survival rate of BRCA1/2 mutation carriers is still inconclusive [18]. With the aim of comprehensively covering the topic of the prognostic role of BRCA1/2 mutations in breast cancer, in this study, we first analyzed the expression of BRCA1/2 in breast cancer tissues and normal tissues. The results showed that BRCA1/2 were overexpressed in breast cancer tissues than in normal tissues, and we obtained the relationship of BRCA1/2 expression, mutation, and survival data in breast cancer from TCGA data analysis, which further verified the above results.
A previous study has reported that BRCA1 and BRCA2 carriers have varied clinical characteristics [19]. Herein, our study found that overexpression of BRCA1 was related to lymph node stage, ER status, PR status and PAM 50 subtypes (p < 0.05), and overexpression of BRCA2 was related to age, lymph node stage, ER stage, PR status, HER-2 status, and PAM 50 subtypes (p < 0.01).
The prognostic role of BRCA1/2 mutational status in breast cancer patients is unclear. According to previous research, BRCA1/2 mutation carriers had a higher risk of mortality from breast cancer (HR 1.44, 95% CI: 1.05–1.97) and distant metastases (HR 1.82, 95% CI: 1.05–3.16) than sporadic/BRCA-negative individuals [20]. The estimated average cumulative risk of breast cancer to age 70 years was estimated to be 52% (95% CI, 26–69%) for BRCA1 mutation carriers and 47% (95% CI, 29–60%) for BRCA2 mutation carriers [21]. Nevertheless, whether BRCA1/2 mutations are associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer remains controversial. Some studies suggest that breast cancer BRCA1/2 mutation carriers have poorer overall survival (OS) [5,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30]. Other studies have shown that BRCA1/2 mutation carriers have better survival than non-carriers [5,31,32,33]. Several studies have showed that BRCA1/2 mutations occur at scattered sites and occur as missense mutations, of which will especially influence those situated in exon-encoding domains that interact with BRCA1-binding proteins, such as BARD1, BRIP1 and PALB2, which (along with RAD51C, RAD51D and possibly RAP80 and FAM175A, encoding Abraxas) are also breast and/or ovarian cancer-susceptibility genes [34,35].
In this study, we found that overexpression of BRCA1/2 was significantly related to worse overall survival (p < 0.001). As a result, these genes might be used as novel anticancer targets. GO analysis showed that BRCA1/2 co-expressed genes were mainly involved in catalytic activity, acting on DNA, chromosomal regions, and organelle fission. KEGG pathway analysis displayed that BRCA1/2 co-expressed genes were enriched in regulating the cell cycle, RNA transport, and the Fanconi anemia pathway. In gene–gene interaction networks, 20 of the most frequently altered genes were closely correlated with BRCA1, including PALB2, RAD51, and PARP1. There were 20 most frequently altered genes that were closely correlated with BRCA2, including PALB2, RAD51, and SEM1. In the PPI network, there were 45 edges and 11 nodes in BRCA1, including PALB2, RAD51, and TP53. There were also 50 edges and 11 nodes in BRCA2, including RAD51, BARD1 and XRCC3. PALB2 was initially identified as a protein that interacts with BRCA2 and plays a crucial role in the BRCA2 genome caretaker function and was subsequently shown to also interact with BRCA1 [15,36,37,38]. Biallelic germline loss-of-function mutations in PALB2 cause Fanconi’s anemia, whereas monoallelic loss-of-function mutations are associated with an increased risk of breast cancer [39]. RAD51 is a strand transferase that helps DNA strands exchange with undamaged homologous chromatids by polymerizing nucleoprotein filaments on single-stranded DNA [40,41]. Overexpression of RAD51 is associated with tumor aggressiveness and is known to confer treatment resistance in a variety of tumors, including breast cancer [42]. PARP1 has been shown to interact with DNA polymerase α and multiprotein DNA replication complexes [43,44,45]. BRCA1 and BARD1 both bind DNA and interact with RAD51, and BRCA1-BARD1 enhances the recombinase activity of RAD51 [35].
The present study used a systematic multiomics approach to investigate BRCA1/2 functions as prognostic biomarkers in breast cancer. Although we investigated the correlation between BRCA1/2 and breast cancer patients, some limitations remain. Nevertheless, there is a lack of in-depth insight into the relevant mechanisms involved, and further research is required. Overall, our study provides suggestive evidence of the prognostic role of BRCA1/2 in breast cancer and the therapeutic target for breast cancer. Furthermore, BRCA1/2 may influence BRCA prognosis through catalytic activity, acting on DNA, chromosomal regions, organelle fission, and the cell cycle. Nevertheless, further validation is warranted.
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Patient Datasets
The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database (https://www.cancer.gov/about-nci/organization/ccg/research/structural-genomics/tcga, accessed on 10 February 2022) is a publicly funded project initiated by the United States government with the goal of classifying and discovering the major genomic alterations that cause cancer to create a comprehensive The Cancer Genome Atlas database that includes more than 20,000 molecular characterizations of primary cancers and matched normal samples for 33 cancer types [46]. It was used to download all the raw data for BRCA1/2, including transcriptome RNA-seq data and clinical information.
4.2. Transcript Expression Analysis Using Oncomine Platform
The Oncomine database (https://www.oncomine.org/resource/login.html, accessed on 10 February 2022) is a web-based data mining platform that includes 264 separate datasets and aims to collect, standardize, evaluate, and distribute transcriptomic cancer data for biomedical research [47]. The expression levels of BRCA1/2 in breast cancer were retrieved from the Oncomine platform. The p value 1 × 10−4, fold-change 2, and gene ranking in the top 10% were used to calculate the fold change in the expression of BRCA1/2 in clinical cancer specimens compared to normal controls. The co-expression profile of the BRCA1/2 in breast cancer was shown as a heat map.
4.3. TIMER 2.0 Analysis
Tumor IMmune Estimation Resource 2.0 (http://timer.cistrome.org, accessed on 10 February 2022) is a comprehensive resource for systematical analysis of immune infiltrates across diverse cancer types [48]. In this study, TIMER2.0 was used to determine the expression of BRCA1/2 in breast cancer and normal tissues across all TCGA cohorts.
4.4. Expression of BRCA1/2 in BRCA Based on Sample Types by UALCAN
Data on TCGA have been used for BRCA1/2 expression analysis. There are 1211 patients enrolled in this data profile, including 114 of normal and 1097 of tumors in patients with breast cancer. The analysis was performed on the online tool of UALCAN based on sample types. UALCAN (http://ualcan.path.uab.edu, accessed on 10 February 2022) is a user-friendly, interactive web portal for analyzing TCGA gene expression data in depth [49].
4.5. Analysis of Gene Expression and Mutation Alterations Using cBioPortal
The cBioPortal for Cancer Genomics (http://www.cbioportal.org, accessed on 10 February 2022) is a well-known and frequently used online website that allows large-scale cancer genomics datasets to be visualized, analyzed, and downloaded [50]. In our study, cBioPortal was used to analyze the frequency of mutations and copy number alterations of BRCA1/2 with appropriate parameter settings.
4.6. Correlation Analysis of BRCA1/2 and Breast Cancer Stage
The ggplot2 program was used to perform a correlation analysis of BRCA1/2 expression and cancer stage. The ROC curve for diagnosis analysis was created using R packages. This section’s clinical data were obtained from the TCGA database.
4.7. Prognosis Analysis Using PrognoScan
PrognoScan (http://dna00.bio.kyutech.ac.jp/PrognoScan/, accessed on 10 February 2022) is a widely used online database for meta-analysis of the prognostic significance of genes [51]. In this study, PrognoScan was used to analyze the association of BRCA1/2 expression with the survival in breast cancer patients.
4.8. Survival Analysis Using Kaplan–Meier Plotter
The Kaplan–Meier plotter (https://kmplot.com/analysis/, accessed on 10 February 2022) is an online application tool that can evaluate the impact of the expression of more than 54,000 genes on the survival of 21 different cancer types [52]. It was used to analyze the relationship between BRCA1/2 expression and the survival of patients with breast cancer in this study.
4.9. Survival and Correlation Analysis Using R2
R2 (https://hgserver1.amc.nl/cgi-bin/r2/main.cgi, accessed on 10 February 2022) is an online tool that can be used for a variety of genomics research and visualization tasks. In this study, we used R2 platform to analyze the correlations between BRCA1/2 expression and the survival of patients with breast cancer.
4.10. GO and KEGG Enrichment Analysis
To investigate probable biological activities and signaling pathways influenced by BRCA1/2, we used the package R “cluster profile” to perform Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analyses on co-expressed genes. GO analysis is a commonly used method for large-scale functional enrichment research; gene functions can be classified into biological process (BP), cellular component (CC), and molecular function (MF).
4.11. Analysis of BRCA1/2 Interacting Genes and Proteins
The GeneMANIA database (http://www.genemania.org, accessed on 10 February 2022) was applied to construct the gene–gene interaction network of BRCA1/2. The STRINGdb analysis tool (https://string-db.org/cgi/input.pl, accessed on 10 February 2022) is a database of known and predicted protein interactions and was used to construct a protein–protein interaction (PPI) network of BRCA1/2.
4.12. Statistical Analysis
R (v.3.6.3) was used to perform the statistical analysis. Differences between groups were compared using the Wilcoxon rank-sum test or Student’s t test, as appropriate. Pearson or Spearman correlation tests, as appropriate, were used to determine correlations. Survival curves were generated using PrognoScan, the Kaplan–Meier Plotter, and the R2. All results were shown as p values of the log-rank test. They were created, and log-rank tests were performed to identify the significance of the difference between the survival curves, and differences with a p < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Konkuk University.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.Y.J. and K.S.P.; methodology, K.S.P.; validation, T.Y.J.; formal analysis, T.Y.J.; investigation, S.E.N.; data curation, Y.B.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, T.Y.J.; writing—review and editing, T.Y.J. and K.S.P.; visualization, T.Y.J.; supervision, W.S.P.; project administration, I.J.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets created and/or analyzed during this investigation are available to the public. In the Materials and Methods section, each portal’s persistent web link has been supplied.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Statement of Ethics
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.De Santis C., Siegel R., Bandi P., Jemal A. Breast cancer statistics, 2011. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2011;61:409–418. doi: 10.3322/caac.20134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Sakamoto K., Schmidt J.W., Wagner K.U. Mouse models of breast cancer. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015;1267:47–71. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2297-0_3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Apostolou P., Fostira F. Hereditary breast cancer: The era of new susceptibility genes. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013;2013:747318. doi: 10.1155/2013/747318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Narod S.A., Salmena L. BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations and breast cancer. Discov. Med. 2011;12:445–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Zhu Y., Wu J., Zhang C., Sun S., Zhang J., Liu W., Zhang Z., Huang J. BRCA mutations and survival in breast cancer: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 2016;7:70113–70127. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hall J.M., Lee M.K., Newman B., Morrow J.E., Anderson L.A., Huey B., King M.-C. Linkage of early-onset familial breast cancer to chromosome 17q21. Science. 1990;250:1684–1689. doi: 10.1126/science.2270482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Narod S.A., Feunteun J., Lynch H.T., Watson P., Conway T., Lynch J., Lenoir G.M. Familial breast-ovarian cancer locus on chromosome 17q12-q23. Lancet. 1991;338:82–83. doi: 10.1097/00006254-199203000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hall J.M., Friedman L., Guenther C., Lee M.K., Weber J.L., Black D.M., King M.C. Closing in on a breast cancer gene on chromosome 17q. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1992;50:1235–1242. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Wooster R., Neuhausen S.L., Mangion J., Quirk Y., Ford D., Collins N., Nguyen K., Seal S., Tran T., Averill D., et al. Localization of a breast cancer susceptibility gene, BRCA2, to chromosome 13q12-13. Science. 1994;265:2088–2090. doi: 10.1126/science.8091231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Claus E.B., Risch N., Thompson W.D. Genetic analysis of breast cancer in the cancer and steroid hormone study. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1991;48:232–242. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Foulkes W.D. BRCA1 and BRCA2: Chemosensitivity, treatment outcomes and prognosis. Fam. Cancer. 2006;5:135–142. doi: 10.1007/s10689-005-2832-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Rebbeck T.R., Friebel T., Lynch H.T., Neuhausen S.L., van’t Veer L., Garber J.E., Evans G.R., Narod S.A., Isaacs C., Matloff E., et al. Bilateral prophylactic mastectomy reduces breast cancer risk in BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers: The PROSE Study Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004;22:1055–1062. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2004.04.188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ford D., Easton D.F., Stratton M., Narod S., Goldgar D., Devilee P., Bishop T., Weber B., Lenoir G., Chang-Claude J., et al. Genetic heterogeneity and penetrance analysis of the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes in breast cancer families. The Breast Cancer Linkage Consortium. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1998;62:676–689. doi: 10.1086/301749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Easton D.F., Narod S.A., Ford D., Steel M. The genetic epidemiology of BRCA1. Breast Cancer Linkage Consortium. Lancet. 1994;344:761. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(94)92256-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Zhang F., Ma J., Wu J., Ye L., Cai H., Xia B., Yu X. PALB2 links BRCA1 and BRCA2 in the DNA-damage response. Curr. Biol. 2009;19:524–529. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2009.02.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Huynh M.-M., Pambid M.R., Jayanthan A., Dorr A., Los G., Dunn S.E. The dawn of targeted therapies for triple negative breast cancer (TNBC): A snapshot of investigational drugs in phase I and II trials. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs. 2020;29:1199–1208. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2020.1818067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Easton D.F., Pharoah P.D., Antoniou A.C., Tischkowitz M., Tavtigian S.V., Nathanson K.L., Devilee P., Meindl A., Couch F.J., Southey M., et al. Gene-panel sequencing and the prediction of breast-cancer risk. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015;372:2243–2257. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsr1501341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.van den Broek A.J., Schmidt M.K., van’t Veer L.J., Tollenaar R.A., van Leeuwen F.E. Worse breast cancer prognosis of BRCA1/BRCA2 mutation carriers: What’s the evidence? A systematic review with meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0120189. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Yoshida R. Hereditary breast and ovarian cancer (HBOC): Review of its molecular characteristics, screening, treatment, and prognosis. Breast Cancer. 2021;28:1167–1180. doi: 10.1007/s12282-020-01148-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Baretta Z., Mocellin S., Goldin E., Olopade O.I., Huo D. Effect of BRCA germline mutations on breast cancer prognosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine. 2016;95:e4975. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000004975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Milne R.L., Osorio A., Cajal T.R., Vega A., Llort G., de la Hoya M., Diez O., Alonso M.C., Lazaro C., Blanco I., et al. The average cumulative risks of breast and ovarian cancer for carriers of mutations in BRCA1 and BRCA2 attending genetic counseling units in Spain. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008;14:2861–2869. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-4436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hamann U., Sinn H.P. Survival and tumor characteristics of German hereditary breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2000;59:185–192. doi: 10.1023/A:1006350518190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Robson M.E., Chappuis P.O., Satagopan J., Wong N., Boyd J., Goffin J.R., Hudis C., Roberge D., Norton L., Bégin L.R., et al. A combined analysis of outcome following breast cancer: Differences in survival based on BRCA1/BRCA2 mutation status and administration of adjuvant treatment. Breast Cancer Res. 2004;6:R8–R17. doi: 10.1186/bcr658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Moller P., Evans D.G., Reis M.M., Gregory H., Anderson E., Maehle L., Lalloo F., Howell A., Apold J., Clark N., et al. Surveillance for familial breast cancer: Differences in outcome according to BRCA mutation status. Int. J. Cancer. 2007;121:1017–1020. doi: 10.1002/ijc.22789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Nilsson M.P., Hartman L., Idvall I., Kristoffersson U., Johannsson O.T., Loman N. Long-term prognosis of early-onset breast cancer in a population-based cohort with a known BRCA1/2 mutation status. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014;144:133–142. doi: 10.1007/s10549-014-2842-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Loman N., Johannsson O., Bendahl P.-O., Dahl N., Einbeigi Z., Gerdes A.-M., Borg A., Olsson H. Prognosis and clinical presentation of BRCA2-associated breast cancer. Eur. J. Cancer. 2000;36:1365–1373. doi: 10.1016/S0959-8049(00)00098-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Arun B., Bayraktar S., Liu D.D., Barrera A.M.G., Atchley D., Pusztai L., Litton J.K., Valero V., Meric-Bernstam F., Hortobagyi G.N., et al. Response to neoadjuvant systemic therapy for breast cancer in BRCA mutation carriers and noncarriers: A single-institution experience. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011;29:3739–3746. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.35.2682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Huzarski T., Byrski T., Gronwald J., Górski B., Domagala P., Cybulski C., Oszurek O., Szwiec M., Gugała K., Stawicka M., et al. Ten-year survival in patients with BRCA1-negative and BRCA1-positive breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013;31:3191–3196. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.45.3571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Tryggvadottir L., Olafsdottir E.J., Olafsdottir G.H., Sigurdsson H., Johannsson O.T., Bjorgvinsson E., Alexiusdottir K., Stefansson O.A., Agnarsson B.A., Narod S.A., et al. Tumour diploidy and survival in breast cancer patients with BRCA2 mutations. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2013;140:375–384. doi: 10.1007/s10549-013-2637-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Sambiasi D., Lambo R., Pilato B., Tommasi S., Trojano G., Kardhashi A., Digennaro M., Trojano V., Simone G., Paradiso A. BRCA1/2 and clinical outcome in a monoinstitutional cohort of women with hereditary breast cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2014;31:365–369. doi: 10.3892/or.2013.2802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Marcus J.N., Watson P., Page D.L., Narod S.A., Lenoir G.M., Tonin P., Linder-Stephenson L., Salerno G., Conway T.A., Lynch H.T. Hereditary breast cancer: Pathobiology, prognosis, and BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene linkage. Cancer. 1996;77:697–709. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19960215)77:4<697::AID-CNCR16>3.0.CO;2-W. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Veronesi A., De Giacomi C., Magri M.D., Lombardi D., Zanetti M., Scuderi C., Dolcetti R., Viel A., Crivellari D., Bidoli E., et al. Familial breast cancer: Characteristics and outcome of BRCA 1-2 positive and negative cases. BMC Cancer. 2005;5:70. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-5-70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Gonzalez-Angulo A.M., Timms K.M., Liu S., Chen H., Litton J.K., Potter J., Lanchbury J.S., Stemke-Hale K., Hennessy B.T., Arun B.K., et al. Incidence and outcome of BRCA mutations in unselected patients with triple receptor-negative breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011;17:1082–1089. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Foulkes W.D., Shuen A.Y. In brief: BRCA1 and BRCA2. J. Pathol. 2013;230:347–349. doi: 10.1002/path.4205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Zhao W., Steinfeld J.B., Liang F., Chen X., Maranon D.G., Ma C.J., Kwon Y., Rao T., Wang W., Sheng C., et al. BRCA1-BARD1 promotes RAD51-mediated homologous DNA pairing. Nature. 2017;550:360–365. doi: 10.1038/nature24060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Lee A.S., Ang P. Breast-cancer risk in families with mutations in PALB2. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014;371:1650–1651. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1410673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Xia B., Sheng Q., Nakanishi K., Ohashi A., Wu J., Christ N., Liu X., Jasin M., Couch F.J., Livingston D.M. Control of BRCA2 cellular and clinical functions by a nuclear partner, PALB2. Mol. Cell. 2006;22:719–729. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.05.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Sy S.M., Huen M.S., Zhu Y., Chen J. PALB2 regulates recombinational repair through chromatin association and oligomerization. J. Biol. Chem. 2009;284:18302–18310. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.016717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Tischkowitz M., Xia B. PALB2/FANCN: Recombining cancer and Fanconi anemia. Cancer Res. 2010;70:7353–7359. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-1012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Lee J.O., Kang M.J., Byun W.S., Kim S.A., Seo I.H., Han J.A., Moon J.W., Kim J.H., Kim S.J., Lee E.J., et al. Metformin overcomes resistance to cisplatin in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cells by targeting RAD51. Breast Cancer Res. 2019;21:115. doi: 10.1186/s13058-019-1204-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.San Filippo J., Sung P., Klein H. Mechanism of eukaryotic homologous recombination. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2008;77:229–257. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.77.061306.125255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Hong K.J., Hsu M.C., Hung W.C. RECK impedes DNA repair by inhibiting the erbB/JAB1/Rad51 signaling axis and enhances chemosensitivity of breast cancer cells. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015;5:2422–2430. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Xiao G., Lundine D., Annor G.K., Canar J., Ellison V., Polotskaia A., Donabedian P.L., Reiner T., Khramtsova G., Olopade O.I., et al. Gain-of-Function Mutant p53 R273H Interacts with Replicating DNA and PARP1 in Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2020;80:394–405. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-1036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Simbulan C.M., Suzuki M., Izuta S., Sakurai T., Savoysky E., Kojima K., Miyahara K., Shizuta Y., Yoshida S. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase stimulates DNA polymerase alpha by physical association. J. Biol. Chem. 1993;268:93–99. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)54119-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Simbulan-Rosenthal C.M., Rosenthal D.S., Hilz H., Hickey R., Malkas L., Applegren N., Wu Y., Bers A.G., Smulson M.E. The expression of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase during differentiation-linked DNA replication reveals that it is a component of the multiprotein DNA replication complex. Biochemistry. 1996;35:11622–11633. doi: 10.1021/bi953010z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Tomczak K., Czerwińska P., Wiznerowicz M. The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA): An immeasurable source of knowledge. Contemp. Oncol. 2015;19:A68. doi: 10.5114/wo.2014.47136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Rhodes D.R., Yu J., Shanker K., Deshpande N., Varambally R., Ghosh D., Barrette T., Pander A., Chinnaiyan A.M. ONCOMINE: A cancer microarray database and integrated data-mining platform. Neoplasia. 2004;6:1–6. doi: 10.1016/S1476-5586(04)80047-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Li T., Fu J., Zeng Z., Cohen D., Li J., Chen Q., Li B., Liu X.S. TIMER2.0 for analysis of tumor-infiltrating immune cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020;48:W509–W514. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Chandrashekar D.S., Bashel B., Balasubramanya S.A.H., Creighton C.J., Ponce-Rodriguez I., Chakravarthi B.V.S.K., Varambally S. UALCAN: A Portal for Facilitating Tumor Subgroup Gene Expression and Survival Analyses. Neoplasia. 2017;19:649–658. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2017.05.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Cerami E., Gao J., Dogrusoz U., Gross B.E., Sumer S.O., Aksoy B.A., Jacobsen A., Byrne C.J., Heuer M.L., Larsson E., et al. The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2012;2:401–404. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Mizuno H., Kitada K., Nakai K., Sarai A. PrognoScan: A new database for meta-analysis of the prognostic value of genes. BMC Med. Genom. 2019;2:18. doi: 10.1186/1755-8794-2-18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Lanczky A., Nagy A., Bottai G., Munkacsy G., Szabo A., Santarpia L., Gyorffy B. miRpower: A web-tool to validate survival-associated miRNAs utilizing expression data from 2178 breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2016;160:439–446. doi: 10.1007/s10549-016-4013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets created and/or analyzed during this investigation are available to the public. In the Materials and Methods section, each portal’s persistent web link has been supplied.