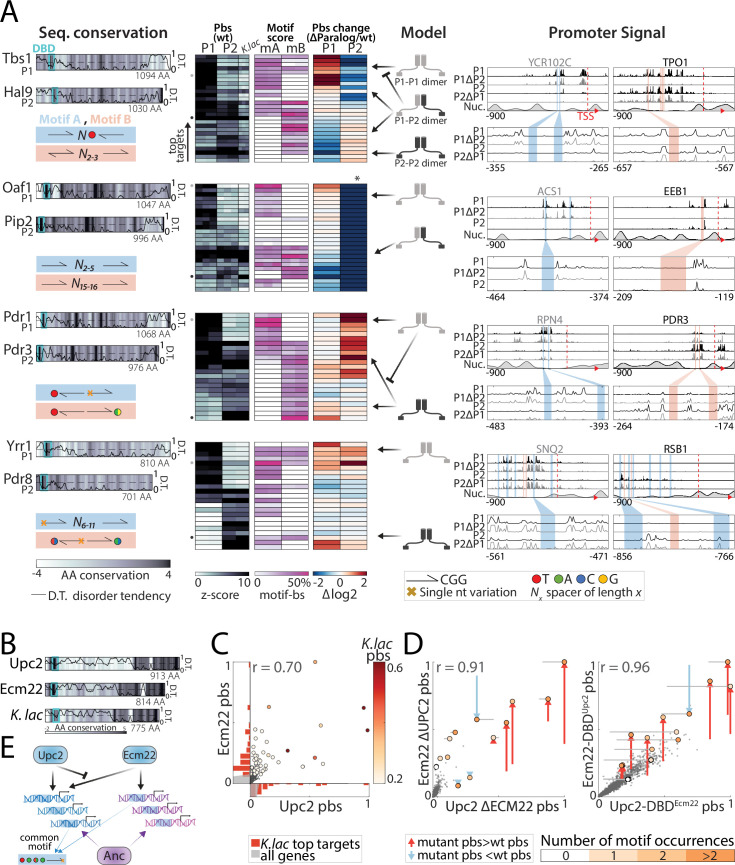
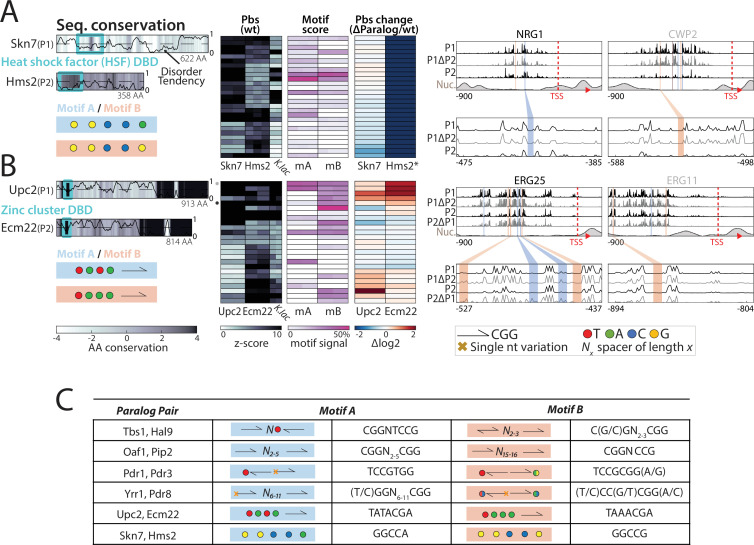
Figure 8. Divergence of zinc cluster transcription factor (TF) paralogs correlates with changes in motif preferences.
(A) Dimerization and changes in motif preferences may explain divergence of zinc cluster paralogs: Zinc cluster paralogs vary in sequence and localized at different variants of their characteristic motif. Shown on the left with pairwise amino acid (AA) sequence conservation shown as color-code, DNA-binding domain (DBD) position indicated as cyan box, and disorder tendency (Mészáros et al., 2018) shown as black line; motif symbols indicated on the bottom (see Figure 8—figure supplement 1 for motif sequences). For each pair, top-bound promoters were selected, and peak-proximal motifs defined. Shown, as indicated, are promoter-binding signal (pbs, z-score, columns correspond to individual repeats), percentage of total promoter signal 50 bases around the indicated motifs (columns correspond to individual repeats), and binding change upon paralog deletion (log2, mean; *: indicates loss of binding specificity after paralog deletion). Suggested models explaining divergence, and the signal on exemplary promoters (indicated by small gray and black dots next to the pbs panel) are also shown. (B–E) Upc2/Ecm22 diverge through DNA-binding competition: shown in (B) are the disorder tendency (Mészáros et al., 2018) and pairwise sequence conservation of Upc2-Ecm22 along the respective protein length and that of their K. lactis ortholog with Upc2 (Figure 6—figure supplement 1). Promoter-binding preferences in the indicated backgrounds are shown in (C–D). (C) Large dots indicate top 50 K. lactis targets, color-coded by binding signal. Distribution of these targets across the Upc2/Ecm22 binding preferences are shown as histograms (red, gray: all promoters). Note that Upc2 and Ecm22 bind comparably to strong K. lactis targets, while Ecm22 dominates on low-intermediate targets. (D) Large dots indicate Upc2 and Ecm22 top 20 targets (in wild-type background), colors indicate the number of occurrences of the known in vitro motif (TA(T/A)ACGA) and arrows show change in binding relative to the wild-type. (E) Suggested model: Ecm22 and Upc2 bind a common motif, but Upc2 outcompetes Ecm22 on Upc2’s share of ancestral targets.