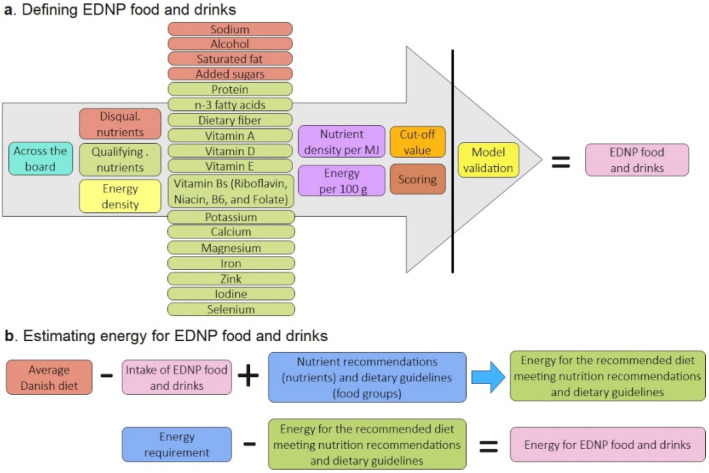
Figure 1.
(a) An across-the-board nutrient profiling model including nutrient and energy density was used to define energy-dense, nutrient-poor (EDNP) food and drinks. The visual model was adapted from Verhagen and Van den Berg [13]. (b) The average Danish diet without EDNP food and drinks was used to model recommended diets that meet the dietary guidelines and nutrient recommendations. The amount of energy for EDNP food and drinks was defined as the energy requirement for different age and sex groups minus the energy needed to meet a recommended diet.