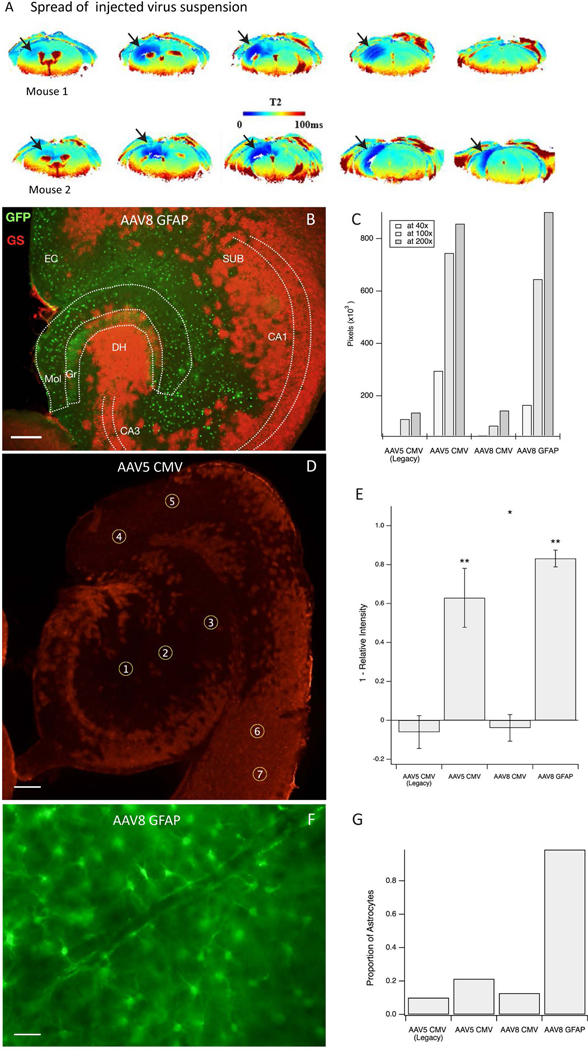
Figure 1. Spatial distribution and astroglial specificity of the knockdown approach.
A. Virus suspension with added superparamagnetic iron oxide (USPIO) nanoparticles was injected into the right hippocampus as a single 0.5 μL bolus, followed by Perfusion Weighted (PW) Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast (DSC) MRI, 4 days later in 2 normal mice. The regions of darker blue coloring in the T2 images (arrows) indicate the presence of USPIO nanoparticles in the parenchyma, reflecting the local spread of the infusion. B. Representative horizonal section of the hippocampal formation of a GSflox/flox mouse injected with AAV8-GFAP-GFP-Cre virus. Immunofluorescence for green fluorescent protein (GFP, green color) represents virus-transfected cells, and immunofluorescence for glutamine synthetase (GS, red color) represents GS-expressing astrocytes. This shows effective deletion of GS by absent GS-immunoreactivity in the virus-transfected (green) cells. C. Area of GS knockout for each virus at various magnifications. AAV5 CMV and AAV8 GFAP outperformed the AAV5 CMV Legacy and AAV8 CMV viruses. D. Example of region-ofinterest (ROI) selection in a horizontal hippocampal section transfected with AAV5 CMV. ROIs 1–5 are placed in areas of knockout whereas ROIs 6–7 are used as control regions to scale intensity measures. Red stained areas are not infected with virus and express GS normally. E. Knockdown efficiency by each of the 4 viruses as assessed by densitometry of GS in the injected brain region. The efficiency is expressed as 1 – relative GS intensity (*p < 0.05 and **p < 0.001). F. Representative field from the hippocampus of a GSflox/flox mouse injected with AAV8-GFAP-GFP-Cre virus and immunostained for green fluorescent protein. Note the characteristic astrocyte morphology of nearly all the transfected cells. G. The proportion of green fluorescent protein-positive cells show astrocyte morphology after transfection with each of the 4 virus types. Scale bars: B, D = 0.2 mm, F = 25 μm. Abbreviations: CA1, CA3, Cornu Ammonis subfields of the hippocampus; DH, dentate hilus; EC, entorhinal cortex; Gr, granule layer of the dentate gyrus; Mol, molecular layer of the dentate gyrus; SUB, subiculum.