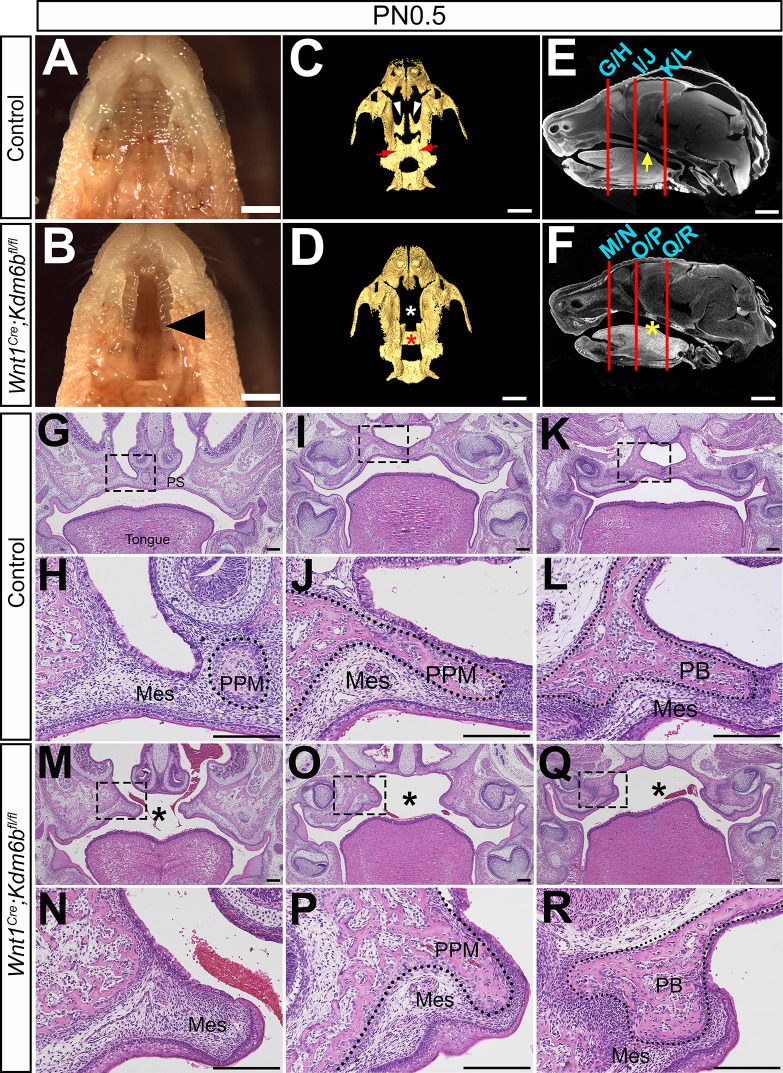
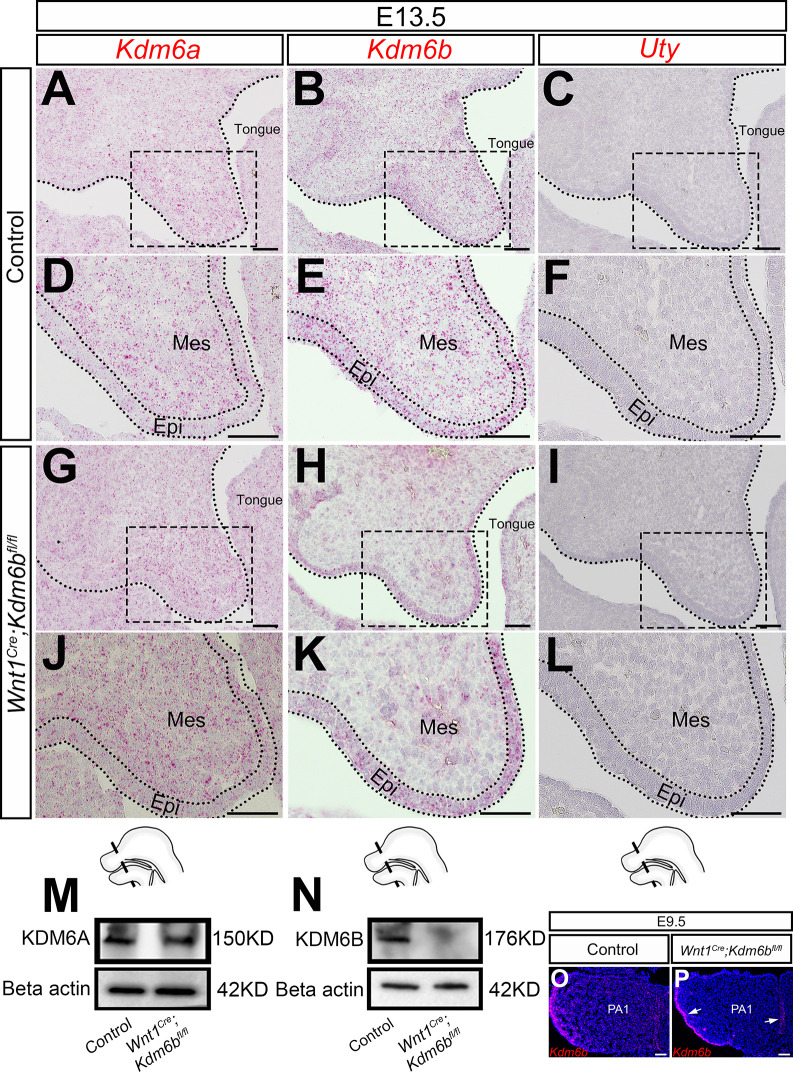
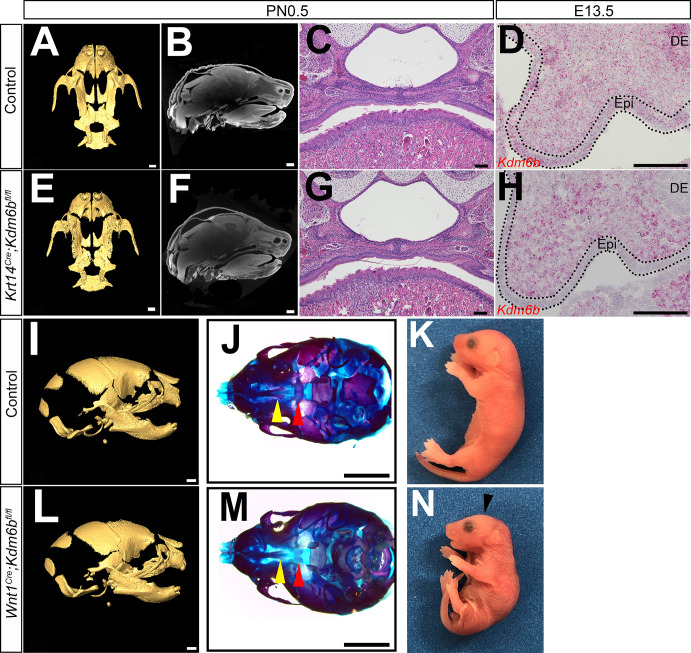
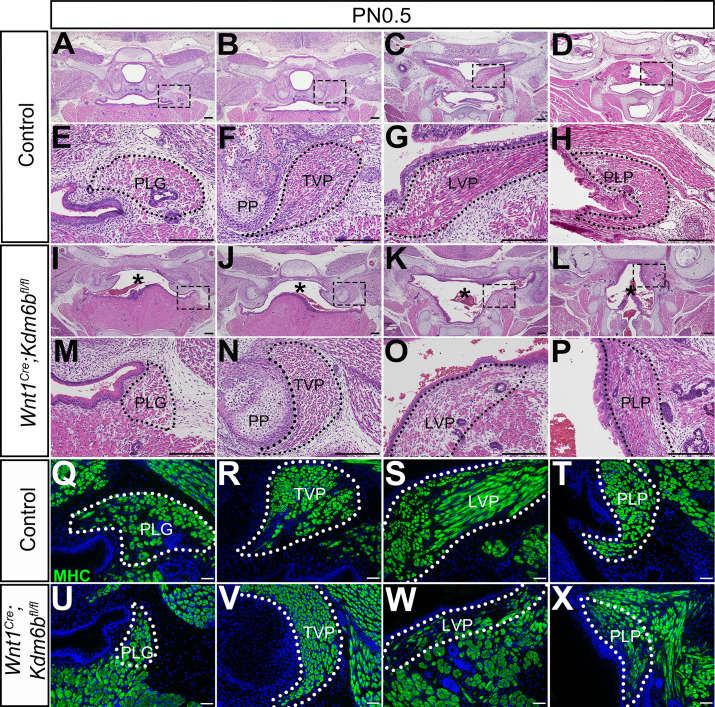
Figure 1. Loss of Kdm6b in cranial neural crest (CNC)-derived cells results in cleft palate.
(A, B) Whole-mount oral view shows complete cleft palate phenotype in Wnt1Cre;Kdm6bfl/fl mice. Arrowhead in (B) indicates the cleft palate. Scale bar: 2 mm. (C, D) CT imaging reveals that the palatine process of the maxilla and palatine bone (PB) is missing in Wnt1Cre;Kdm6bfl/fl mice. White arrowheads in (C) indicate the palatine process of maxilla (PPM) in control mice, and red arrows indicate the PB. White asterisk in (D) indicates the missing PPM in Wnt1Cre;Kdm6bfl/fl mice, and red asterisk in (D) indicates the missing PB in Kdm6b mutant mice. Scale bars: 1 mm. (E, F) Sagittal views of CT images demonstrate the locations of HE sections in (G–R). Red lines indicate the locations of sections. Yellow arrow in (E) indicates palatal shelf, and yellow asterisk in (F) indicates cleft. Scale bars: 1 mm. (G–R) Histological analysis of control and Wnt1Cre;Kdm6bfl/fl mice. (H, J, L, N, P, R) are magnified images of boxes in (G, I, K, M, O, Q), respectively. Asterisks in (M, O, Q) indicate cleft in Kdm6b mutant mice. Scale bar: 200 µm. Mes: mesenchyme.