Abstract
Central venous catheterization interventions are used in various clinics for diagnostic and treatment purposes. Establishing vascular access is a difficult and critical step, especially in critically ill pediatric patients. Complications include ventricular arrhythmia, air embolism, carotid artery puncture, cardiac tamponade, pneumothorax, hemothorax, artery-vein laceration, thoracic duct injury, and catheter malposition can be observed in patients after central venous catheterization interventions. In this case report, a pediatric case was discussed, in which a central venous catheter was inserted without the usage of imaging methods and without confirming the location and was used, even though no blood return was obtained. It was aimed to draw attention to subdural effusions and spinal canal interventions, which is a rare complication of central venous catheterization interventions.
How to cite this article
Misirlioglu M, Horoz OO, Yildizdas D, Ekinci F, Yontem A, Pehlivan UA. A Rare Complication of Central Venous Catheterization Interventions: Subdural Effusion. Indian J Crit Care Med 2022;26(3):384–386.
Keywords: Central venous catheter, Children, Complication, Subdural effusion
Introduction
Central venous catheterization (CVC) interventions are applied to the internal jugular vein, femoral vein, or subclavian vein in intensive care units, operating rooms, emergency services, and other services for diagnostic and treatment purposes.1 Complications such as ventricular arrhythmia, air embolism, carotid artery puncture, cardiac tamponade, pneumothorax, hemothorax, artery-vein laceration, thoracic duct injury, and catheter malposition can be observed in patients after CVC interventions.2,3 In this case report, it was discussed that the catheter tip was monitored in cranial computed tomography (CT) upon the development of increased intracranial pressure findings in the patient due to the insertion without using imaging methods after the recurrent interventions, and it was aimed to draw attention to spinal canal interventions and subdural effusions, a rare complication of CVC interventions.
Case Description
A 4-month-old male patient, who was directed to our hospital from another center due to respiratory distress and difficulty in breathing, was hospitalized to be operated on for the diagnosis of a laryngocele. It was discovered that he was born weighing 2300 g in the 36th week of gestation, had a history of hypoxia due to not crying after being born, was intubated for about 2 months due to respiratory distress, and had an operation history due to esophageal atresia.
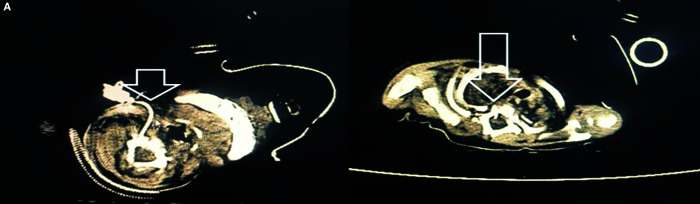
In the direct laryngoscopic examination performed at our hospital, which was done for respiratory distress, it was learned that the cystic formation was totally excised following the monitoring of the internal laryngocele. In this case, a central venous catheter was inserted into the right internal jugular vein due to the difficulty encountered by anesthesiology in establishing peripheral vascular access during the operation under general anesthesia. The patient was put in a 20–30° Trendelenburg position and 20–30° contralateral head rotation to the preferred central line side. The line was then inserted using the seldinger technique; a blunt guide wire was passed through the needle, then the needle was removed. A dilating device was passed over the guide wire to expand the tract. Finally, the central line itself was then passed over the guide wire, which was then removed.4 Due to worsening in the general condition, bradycardia, hypertension, somnolence, and low glasgow coma scale score, the pediatric patient was admitted to our intensive care unit, and cranial imaging was performed. As a result of the cranial CT, it was seen that the central venous catheter tip extended into the C2 vertebra from the right foramen vertebralis in the spinal canal, and a subdural effusion was reported (Fig. 1). During the operation, it was learned that no blood return was achieved from the lumen of the catheter, which was inserted with difficulty without using ultrasonography (USG) or fluoroscopy. After the catheter was removed in our intensive care unit, the catheter was inserted by using USG without complication in the left internal jugular vein, and magnetic resonance (MR) angiography was performed to evaluate the complication of the previous procedure. It was observed that the vertebral arteries were intact and not ruptured. Prophylactically, vancomycin and amikacin were added to the treatment due to the intervention in the spinal cord. The increased intracranial pressure of the patient decreased, and his subdural distance was reported to be at the width compatible with his age in the control cranial CT performed 2 days later. On the 13th day of the admission to the intensive care unit, the patient, whose general condition was good and vitals were stable, was transferred to the service without any complication for the completion of his treatment.
Figs 1A and B.
Catheter view in cranial CT sections (arrow shows catheter)
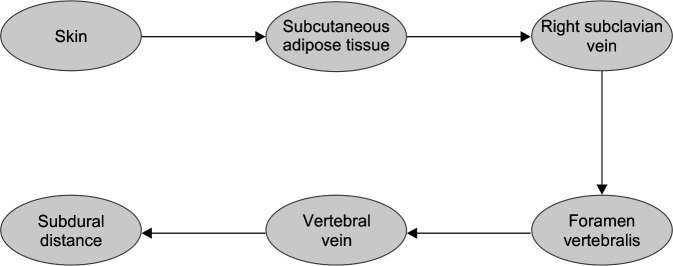
We thought that the passage way of the catheter is skin, subcutaneous adipose tissue, right subclavian vein, foramen vertebralis, vertebral vein, and possibly subdural distance.
Conclusion
CVC is a method used as a result of interventions in the femoral, internal jugular, and subclavian veins for many reasons, such as invasive hemodynamic monitoring, parenteral nutrition, blood collection, drug and fluid treatment, and use of blood and blood products.1 Various complications may develop during CVC. While mechanical complications are observed at a frequency of 5–19%, infectious complications can be seen at a frequency of 5–26% and thromboembolic complications at a frequency of 2–26%.4 Arterial puncture, vascular injuries, catheter malposition, pneumothorax, hemothorax, air embolism, subcutaneous hematoma, and arrhythmias are among the mechanical complications seen with CVC.4,5
In the literature, in the radiography of the first pediatric case (11 week), in whom a central venous catheter wanted to be inserted for parenteral nutrition but intervened in the spinal canal, the catheter tip was observed at the C6 level and in the extradural space.6 Another case was a 9-month-old female infant with a diagnosis of low cardiac output syndrome. Because of local infection, a new catheter was inserted, but aspiration of the distal lumen of the catheter yielded only a small amount of serosanguineous fluid. A CT scan confirmed that the central venous catheter tip had been placed in the intrathecal space.7 In another case that was followed due to trauma at the age of 17, it was reported that the catheter was observed to be in the anterior epidural space in the cervical spinal canal after the catheter insertion.8 However, in the PubMed-based search that we made in the childhood age-group, we did not encounter a case that developed effusion as a result of the treatments used following the direct spinal canal intervention and provided here iatrogenically. In our case, it was also seen that the central venous catheter tip inserted on the right side was at the C2 level and extended from the right neuronal foramen into the spinal canal. We thought that the guide wire used, due to fragility in the vascular structure of infants, was at the C2 level after dissection in the vascular wall. The passageway of the catheter was skin, subcutaneous adipose tissue, right subclavian vein, foramen vertebralis, vertebral vein, and possibly subdural distance. This case developed an effusion as a result of the treatments used following the direct spinal canal intervention and provided here iatrogenically (Flowchart 1).
Flowchart 1.
Flow diagram of the catheter probably followed to reach the spinal canal
Mechanical complications occur due to various reasons, such as recurrent failed interventions, misdirection of the puncture needle, sending the guide wire before suctioning blood and breaking of the wire.4,9 In order to reduce these complications, the person performing the intervention has to be experienced in this field or new practitioners need to perform the intervention in the company of experienced people. The American Board of Internal Medicine does not provide clear recommendations on the number of procedures to be performed by a physician being trained to be considered qualified but recognizes that there is a learning curve that varies between individuals and procedures. It is estimated that 10–20 punctures are required for the training physician to feel comfortable performing the procedure.4 In the literature, another review states that insertion of a catheter by a physician who has performed 50 or more catheterizations is half as likely to result in a mechanical complication as that of an insertion by a physician who has performed fewer than 50 catheterizations.10
The use of USG in interventions significantly reduces catheter-related complications, especially in new practitioners.11,12 The safest method to prevent intervention complications is to perform the procedure with accompanying USG, fluoroscopy, or X-ray imaging. Fluoroscopy is often used in procedures by interventional radiology. In order to increase the success rate of catheterization procedures and reduce the rate of complications, it is recommended to insert the catheter by imaging the central vein and adjacent structures to be inserted by using USG. After catheter placement, the blood from all lumens should be checked by aspiration and examined for complications with X-ray imaging.13,14 The dynamic or static method is preferred during the insertion of a catheter under the guidance of USG. In the dynamic method, the intervention is performed while imaging the target vascular structure on the screen. In the static method, the vascular structure to be intervened and the formations around it are imaged by USG before the procedure and after marking, USG is put away, and the intervention is performed.15
Although the inability of blood aspiration from the catheter lumen is usually thought to be for more benign conditions, such as occlusion of the catheter tip, it should be kept in mind that there may be an intervention in the spinal canal and subdural effusion may develop in the case of not achieving blood return after inserting the catheter in the internal jugular vein; it should not be used if no blood return is achieved. As a result, although CVC has technical difficulties and complications, the rate of complications will be decreased when inserted under appropriate conditions with accompanying USG and experienced people.
Highlights
Establishing vascular access is a difficult and critical step, especially in critically ill pediatric patients.
The dynamic or static method is preferred during the insertion of a catheter under the guidance of USG.
The location of the catheter should be confirmed using a radiological method during central venous catheter placement, and the catheter should only be used after blood return is obtained.
Footnotes
Source of support: Nil
Conflict of interest: None
Orcid
Merve Misirlioglu https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9554-841X
Ozden Ozgur Horoz https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7590-650X
Dincer Yildizdas https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0739-5108
Faruk Ekinci https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6675-3150
Ahmet Yontem https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9982-3010
Umur Anil Pehlivan https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5871-0695
References
- 1.Ruesch S, Walder B, Tramer MR. Complications of central venous catheters: internal juguler versus subclavian access–a systematic review. Crit Care Med. 2002;30(2):454–460. doi: 10.1097/00003246-200202000-00031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bagwell CE, Salzberg AM, Sonnino RE, Haynes JH. Potentially lethal complications of central venous catheter placement. J Pediatr Surg. 2000;35(5):709–713. doi: 10.1053/jpsu.2000.6029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Dogan N, Becit N, Kizilkaya M, Unlu Y. A rare complication due to central venous cannulatıon. Turkish J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2004;12:135–137. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Eisen LA, Narasimhan M, Berger JS, Mayo PH, Rosen MJ, Schneider RF. Mechanical complications of central venous catheters. J Intensive Care Med. 2006;21(1):40–46. doi: 10.1177/0885066605280884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Alemohammad M. Central venous catheter insertion problem solving using intravenous catheter: technical communication. Tehran Univ Med J. 2013;70(11):724–728. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Skinner TA, Mather SJ. Inadvertent extradural insertion of an internal jugular catheter in an infant. Br J Anaesth. 1995;75(6):790–793. doi: 10.1093/bja/75.6.790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Fujita Y, Sobue K, Hattori T, Takeuchi A, Tsuda T, Katsuya H. Inadvertent intrathecal cannulation in an infant, demonstrated by three-dimensional computed tomography: a rare complication of internal jugular vein catheterization. J Anesth. 2006;20:122–125. doi: 10.1007/s00540-005-0383-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Gemma M, Tommasino C, Cipriani A, Calvi MR, Gerevini S. Cannulation of the cervical epidural venous plexus: a rare complication of retrograde internal jugular vein catheterization. Anesthesiology. 1999;90(1):308–311. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199901000-00039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Schummer W, Schummer C, Fröber R. Internal jugular vein and anatomic relationship at the root of the neck. Anesth Analg. 2003;96:1540–1541. doi: 10.1213/01.ane.0000072448.11064.d8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.McGee DC, Gould MK. Preventing complications of central venous catheterization. N Engl J Med. 2003;348(12):1123–1133. doi: 10.1056/nejmra011883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Tolunay O, Okuyan MK, Celik T, Mert KM, Gulek B, Celik U. Use of ultrasound for central venous catheterization in pediatric intensive care unit; a single center experience. J Pediatr Emerg Intensive Care Med. 2015;2(3):127–132. doi: 10.5505/cayb.2015.68077. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Randolph AG, Cook DJ, Gonzales CA, Pribble CG. Ultrasound guidance for placement of central venous catheters: a metaanalysis of the literature. Crit Care Med. 1996;24(12):2053–2058. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199612000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Central Venous Access, Rupp SM, Apfelbaum JL, Blitt C, Caplan RA, Connis RT, Domino KB, et al. Practice guidelines for central venous access: a report by the American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Central Venous Access. Anesthesiology. 2012;116(3):539–573. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e31823c9569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Stone MB, Nagdev A, Murphy MC, Sisson CA. Ultrasound detection of guide wire position during central venous catheterization. Am J Emerg Med. 2010;28(1):82–84. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2008.09.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Resnick JR, Cydulka RK, Donato J, Jones RA, Werner SL. Success of ultrasound-guided peripheral intravenous access with skin marking. Acad Emerg Med. 2008;15(8):783–793. doi: 10.1111/j.1553-2712.2008.00174.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]