Abstract
The efficacy of immunoglobulin replacement therapy (IgRT) has been demonstrated for primary immune deficiency diseases and hematological malignancies such as chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or multiple myeloma with hypogammaglobulinemia. Clinical development of anti-B cell therapies including a monoclonal antibody, bispecific antibody, or chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy which could result in severe hypogammaglobulinemia accelerates the argument of prophylactic use of IgRT. Clinical guidelines for CLL describe immunoglobulin administration in patients with a low IgG who have experienced a severe/repeated bacterial infection. The utility in hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) remains unknown. Although an early randomized trial demonstrated that IgRT decreased infection risk and transplant-related mortality after HSCT, subsequent clinical trials could not validate the benefit. Consequently, a meta-analysis did not show the benefit of IgRT in HSCT. Most of the available data derives from matched-related HSCT using myeloablative regimen, and the impact in haploidentical and cord blood transplantation, or reduced-intensity HSCT remains unknown. One crucial issue is that no studies exist for patients with only hypogammaglobulinemia after HSCT. Other challenges are heterogeneous patient characteristics, or immunoglobulin formulation, dosage, schedule, route and duration of IgRT. Without evidence in HSCT, it would be reasonable to follow the guidelines for other diseases with hypogammaglobulinemia.
Subject terms: Translational research, Bone marrow transplantation
Introduction
Prognosis in patients who underwent hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) has improved over the years due to better disease control and decreased complications related to HSCT [1, 2]. The development of novel antibiotics, antifungal agents, or antiviral agents results in a lower incidence of relevant infections after HSCT [3]. However, some infectious diseases remain lethal even in long-survivors, and further improved supportive therapy is warranted [4]. Hypogammaglobulinemia is a susceptible condition to infection, and clinical application of immunoglobulin replacement therapy (IgRT) has been discussed. Without a clear-cut threshold defining hypogammaglobulinemia, the generally accepted definition is serum IgG levels below 700 mg/dL [5]. IgRT application has been focused upon with widespread use of anti-B cell therapy inducing hypogammaglobulinemia [6]. The situation is more complicated in the context of HSCT in that immune status is influenced by immune reconstitution of various immune cells, pre-transplant therapies, or posttransplant immunosuppressive therapies. We comprehensively summarize the latest information about IgRT for hypogammaglobulinemia, and describe a feasible application, especially in HSCT recipients.
Causes and mechanisms of hypogammaglobulinemia
A major component of immunoglobulin is IgG, and it has a central role in protecting against infection through multifactorial actions such as Fc-mediated antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity and complement-dependent cytotoxicity [6]. IgG deficiency is divided into primary immunodeficiency (PID) and secondary immunodeficiency (SID) [5]. A representative PID is X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA) harboring pathogenic variants in Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) gene [7]. SID accounts for most of the IgG deficiency, and derives from both primary disease (e.g., chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or multiple myeloma (MM)), and anti-cancer therapy (e.g., anti-B cell monoclonal antibody, genetically engineered chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy) [6]. In HSCT, the process is explained by multiple factors including primary disease, reconstitution of various immune cells, pre-transplant therapies, or posttransplant immunosuppressive therapies.
CLL and MM are hematologic malignancies more likely to develop hypogammaglobulinemia. CLL cells could suppress the activity of normal plasma cells either by cell contact or by deprivation of soluble factors essential for plasma cell survival [8]. MM cells excessively produce transforming growth factor-b, an immune-suppressive cytokine, resulting in inhibition of normal B-cell proliferation and immunoglobulin production [9]. Additionally, several agents are associated with drug-induced hypogammaglobulinemia. The well-known example is an anti-B cell antibody rituximab, and the possible mechanism of action is total B-cell reduction [6]. According to a study enrolling 211 patients with B-cell lymphoma who received rituximab, hypogammaglobulinemia following the administration was detected in 39% of the patients with initially normal serum immunoglobulin, and the incidence of hypogammaglobulinemia with recurrent non-neutropenic infections was 7% [10]. In a cohort study including over 8500 patients with rituximab, hypogammaglobulinemia (IgG < 600 mg/dL) was observed in 48% before rituximab treatment, and 65% after rituximab, respectively [11].
CAR T-cell therapy targeting CD19 antigen is a novel therapy for refractory/relapsed B-cell malignancies, and cell-based gene therapies such as tisagenlecleucel (tisa-cel) or axicabtagene ciloleucel (axi-cel) are commercially available in the US or Europe [12]. This treatment often induces normal B-cell aplasia and resultant hypogammaglobulinemia through proliferating activated T-cells, which is considered as possible on-target toxicity [13]. Wudhikarn et al. reviewed 60 patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma who received anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy with either tisa-cel or axi-cel, and reported that 44% of the patients had hypogammaglobulinemia (IgG ≤ 400 mg/dL) 30 days after treatment, and an additional 38% of the patients at a later time [14]. According to the phase 1 trial of anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy in patients with refractory/relapsed B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia, 83% of the 24 patients whose IgG was measured at least 30 days after infusion had lower IgG levels (median 415 mg/dL) [15].
Clinical data of IgRT in non-HSCT setting including COVID-19
(Table 1) The primary purpose for administering IgRT is to reduce the incidence of infections or serious infections through supplying immunoglobulin and elevating internal immunoglobulin levels. To support this rationale, there exists one meta-analysis which examined the association between trough IgG concentration and pneumonia incidence in PID patients [16]. This analysis showed pneumonia incidence declined by 27% with each 100 mg/dL increment in trough IgG levels. The application of IgRT is different depending on the type of primary disease as evidenced by the French PID expert recommendations [17] (Table 2).
Table 1.
Randomized-trial and meta-analysis data of IgRT on HSCT or non-HSCT settings.
| Author | Publication year | Study design | Route of IgRT | Number of patients | Disease | Designated IgG levels in enrollment (Randomized trial) | HSCT/non-HSCT setting | Major clinical outcomes | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gale et al. | 1988 | Placebo-controlled trial | IVIG | 84 | CLL | IgG level <50% of the lower limit of normal | Non-HSCT | Bacterial infectious events: 23 vs. 42, P = 0.01 | [20] |
| Chapel et al. | 1994 | Placebo-controlled trial | IVIG | 82 | MM | No limitation | Non-HSCT | Serious infectious events: 19 in 449 patient-months vs. 38 per 470 patient-months, P = 0.019 | [21] |
| Sullivan et al. | 1990 | Placebo-controlled trial | IVIG | 382 | Acute leukemia, CML, lymphoma, AA, others | No limitation | HSCT | Interstitial pneumonia in serologic CMV-positive cases (13% vs. 22%, P = 0.02); reduced gram-negative septicemia (risk ratio 0.38) and local infection (risk ratio 0.74) | [38] |
| Cordonnier et al. | 2003 | Placebo-controlled trial | IVIG | 200 | Acute leukemia, CML, lymphoma, others | ≥400 mg/dl | HSCT | Severe VOD/SOS incidence: 0% for placebo, 0% for IVIG 50 mg/kg, 4% for IVIG 250 mg/kg, 11% for IVIG 500 mg/kg; P = 0.014 | [39] |
| Raanani et al. | 2009 | Meta-analysis | IVIG | 205 | CLL, MM | Not applicable | Non-HSCT | Major infection events (risk ratio 0.45); clinically-documented infection events (risk ratio 0.49) | [22] |
| Ahn et al. | 2018 | Meta-analysis | IVIG | 3934 | NA | Not applicable | HSCT | Reduced acute GVHD (risk ratio 0.78) and CMV disease (risk ratio 0.52); increased VOD/SOS (risk ratio 3.04) and disease relapse (risk ratio 1.26) | [40] |
| Raanani et al. | 2009 | Meta-analysis | IVIG | 4223 | Acute leukemia, CML, others | Not applicable | HSCT | Increased VOD/SOS (risk ratio 2.73) | [41] |
| Raanani et al. | 2008 | Meta-analysis | IVIG | 1418 | CLL, MM, lymphoma | Not applicable | HSCT/non-HSCT | Increased VOD/SOS (risk ratio 2.73); clinically-documented infection for only CLL/MM cases (risk ratio 0.49); microbiologically-documented infection for only CLL/MM cases (risk ratio 0.71) | [42] |
HSCT hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation, IgRT immunoglobulin replacement therapy, IVIG intravenous immunoglobulin, CLL chronic lymphocytic leukemia, MM multiple myeloma, AA aplastic anemia, CMV cytomegalovirus, VOD veno-occlusive disease, SOS sinusoidal obstruction syndrome, GVHD graft-versus-host disease.
Table 2.
Recommendations about IgRT application based on clinical guidelines.
| Guideline | HSCT/non-HSCT setting | Suitable candidates for IgRT | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| French expert consensus | Non-HSCT | All PID patients | [17] |
| UK expert consensus | Non-HSCT | Patients who suffered from recurrent or severe infection with encapsulated bacteria and had a serum IgG <500 mg/dl | [18] |
| NCCN | Non-HSCT | Patients who had recurrent serious infection with a serum IgG <400 mg/dl | [23] |
| NCCN | Non-HSCT | Patients who had recurrent sinopulmonary infection with a serum IgG <500 mg/dl | [24] |
| ASBMT/CBMT | HSCT | CBT recipients, children who undergo transplantation for inherited or acquired disorders associated with B-cell deficiency, and chronic GVHD patients with recurrent sinopulmonary infections | [46] |
| ASBMT | HSCT | High-risk recipients who undergo unrelated HSCT with IgG <400 mg/dL | [47] |
| NCCN | HSCT | Allo-recipients who had recurrent infection with a seum IgG <400 mg/dl | [48] |
| European expert consensus | HSCT | All allo-recipients (particularly patients with low IgG level (<400 mg/dl) or with GVHD on immunosuppressive treatment) | [50] |
| JSHCT | HSCT | Allo-recipients with pre-transplant IgG <400 mg/dl or with delayed immunoglobulin recovery after HSCT | [51] |
| AAAAI | HSCT | Recipients with IgG <400 mg/dL who had bacteremia or recurrent sinopulmonary infection | [52] |
NCCN National Comprehensive Cancer Network, ASBMT American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation, CBMT Canadian Blood and Marrow Transplant, JSHCT Japanese Society for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation, AAAAI American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology, HSCT hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation, IgRT immunoglobulin replacement therapy, PID primary immunodeficiency, CBT cord blood transplant, GVHD graft-versus-host disease.
Meanwhile, in terms of secondary hypogammaglobulinemia, the British clinical guidelines for CLL recommend IgRT only when patients suffer from recurrent or severe infection with encapsulated bacteria and had a serum IgG < 500 mg/dL [18] (Table 2). IgRT is given either intravenously (intravenous immunoglobulin, IVIG) or subcutaneously (subcutaneous immunoglobulin, SCIG). Compagno et al. compared the clinical efficacy and toxicity between IVIG (300 mg/kg given every 4 weeks) and SCIG (75 mg/kg per week) in 61 patients, and showed that serum IgG trough level was higher, and incidence of infections and need for antibiotics were lower in the SCIG group (2.3 vs. 1.8 per patient-year; 1.8 vs. 1.4 cycles of antibiotics per patient-year, respectively) [19]. In this study, systemic adverse events such as fever, dyspnea, headache, or nausea were scarce in the SCIG group, and the percentage in patients who required premedications was also lower in the latter (52% vs. 2%). Meanwhile, infusion-site reactions occurred more frequently in the SCIG group (0% vs. 10%).
A placebo-controlled trial of IVIG (400 mg/kg given every 3 weeks) in 84 patients with CLL who had hypogammaglobulinemia or any infection history clearly demonstrated fewer bacterial infections in the IVIG group (23 times vs. 42 times, P = 0.01) [20]. Another randomized trial between IVIG and placebo in 82 patients with MM (400 mg/kg given monthly) showed fewer serious infectious events in the IVIG group (19 in 449 patient-months vs. 38 per 470 patient-months, P = 0.019) [21]. According to the systematic review and meta-analysis about IVIG in patients with CLL and MM, IVIG reduced major infections (risk ratio 0.45) and clinically-documented infections (risk ratio 0.49) [22]. This data comprehensively suggests the clinical utility of IgRT. Conversely, routine IgRT is not recommended in all CLL/MM cases, and the application should be individually considered based on the baseline IgG level or past infection history. The National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) Guidelines about MM or CLL describe IgRT in the setting of recurrent serious infection with a serum IgG < 400 mg/dL or recurrent sinopulmonary infection with a serum IgG < 500 mg/dL, respectively [23, 24] (Table 2). Regarding hypogammaglobulinemia induced by CAR T-cell therapy, Hill et al. propose following application based on serum IgG level: all patients with IgG < 400 mg/dL and those with IgG ≥ 400 mg/dL in case of serious or recurrent bacterial infection [13].
Under the pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), clinical impact of IVIG for the disease is discussed. NCCN advisory committee give no descriptions about IVIG [25]. Clinical studies against COVID-19 are conducted worldwide. Shao et al. showed IVIG from normal human plasma reduced mortality rate at day 28 in patients with critical COVID-19 (P = 0.014) [26]. However, phase 3 trial of IVIG for patients with COVID-19-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome did not prolong ventilation-free days by day 28 as the primary endpoint (P = 0.21) [27]. To expect more powerful action for SARS-CoV-2, hyperimmune anti-COVID-19 IVIG (C-IVIG) is under investigation [28]. In a phase I/II randomized controlled trial of C-IVIG, 50 COVID-19 patients were enrolled, and randomized into four C-IVIG groups (0.15, 0.20, 0.25, 0.30 g/kg) and standard of care only group [29]. 28-day mortality rate as a primary endpoint was lower in the C-IVIG group (relative risk: 0.333 for 0.15 g/kg, 0.5 for 0.20 g/kg, 0.167 for 0.25 g/kg, 0.667 for 0.30 g/kg group) than the control group. Regarding convalescent plasma, there exist randomized trials enrolling patients with COVID-19 who received oxygen for respiratory symptom or patients who suffered from severe COVID-19 pneumonia, respectively [30, 31]. In these trials, convalescent plasma could not exhibit improved clinical outcomes. Consistently, a systematic review and meta-analysis including 10 randomized trials did not show significant clinical benefits (all-cause mortality, length of hospital stay, or mechanical ventilation use) in convalescent plasma group [32]. We should consider the possibility that antibody titter produced against SARS-CoV-2 would be various among COVID-19 convalescent individuals, which results in heterogenous efficacy among formulations. Problems concerned with COVID-19 pandemic evoke the role of IgRT in viral infection.
Current status of IgRT in HSCT recipients
Along with antibiotics, antifungal agents, antiviral agents, acute graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) prophylaxis, IgRT for hypogammaglobulinemia occupies a relevant position in supportive therapies for infection. Several outcomes have been tied to posttransplant hypogammaglobulinemia occurrence. Norlin et al. retrospectively reported that patients with low IgG level (<400 mg/dL) during the first year after HSCT had lower survival rate (54% vs. 71%, P = 0.04) and increased transplant-related mortality (27% vs. 9%, P < 0.01) compared with patients with IgG ≥ 400 mg/dL [33]. In this study, they identified acute GVHD, patient age ≤30 years, female donor-to-male recipient, not receiving anti-thymocyte globulin, and GVHD prophylaxis using cyclosporine and methotrexate are significant factors for posttransplant hypogammaglobulinemia. A similar study identified lymphoid malignancy, a history of previous HSCT, mycophenolate mofetil administration, low pre-transplant IgG level, and grade 2–4 acute GVHD as the risk factors [34]. Frangoul et al. analyzed the incidence and risk factors for hypogammaglobulinemia in pediatric patients and showed that hypogammaglobulinemia (IgG < 500 mg/dL) was observed in 77% of the patients, with lower pre-transplant IgG, younger age, malignant disease as a primary disease, acute GVHD and HSCT from unrelated donors were risk factors [35]. Notably with such a high prevalence of posttransplant hypogammaglobulinemia after HSCT, one might consider an appropriate therapeutic intervention in patients with hypogammaglobulinemia after HSCT [35].
The application of IgRT on HSCT is still controversial (Table 1). Limited to cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection as a common posttransplant complication, a randomized trial in HSCT recipients showed that IVIG reduced symptomatic CMV infection (21% vs. 46%, P = 0.03) and interstitial pneumonia (18% vs. 46%, P = 0.02) [36]. Similarly, a meta-analysis exhibited IVIG reduced fatal CMV infection (risk ratio 0.47), and CMV pneumonia (risk ratio 0.61) [37]. As these studies were published a few decades ago, it should be noted that the clinical application is different from current practice where prophylactic use of antiviral agents such as letermovir, and/or pre-emptive therapy with ganciclovir or foscarnet is utilized. However, these results suggest the possible positive impact of IVIG in managing CMV infection after HSCT and patients with hypogammaglobulinemia and persistent/refractory CMV infection may be candidates for IgRT after HSCT.
Sullivan et al. conducted a placebo-controlled IVIG trial in 382 HSCT recipients [38]. Regardless of baseline IgG level, patients were assigned to IVIG (500 mg/kg given weekly to day 90, then monthly to day 360 after HSCT) or placebo groups. The former group had lower incidences of grade II-IV GVHD (34% vs. 51%, P = 0.005), non-relapse mortality (30% vs. 46%, P = 0.02), or interstitial pneumonia in serologic CMV-positive cases (13% vs. 22%, P = 0.02). In addition, the frequency of Gram-negative septicemia and local infection was lower in the IVIG group (risk ratio 0.38 and 0.74, respectively) but overall survival (OS) rates were similar between the two groups. Cordonnier et al. also conducted a placebo-controlled randomized IVIG trial in 200 HSCT recipients [39]. In this trial, varying IVIG doses (50 mg/kg, 250 mg/kg or 500 mg/kg) or placebo were administrated weekly from day −7 to day 100 after HSCT. This trial excluded patients with pre-transplant hypogammaglobulinemia (<400 mg/dL) at the time of randomization. Cumulative incidences of infection, interstitial pneumonia, GVHD, and transplantation-related mortality, and OS rates were not significantly different between the IVIG and placebo groups. The incidence of severe veno-occlusive disease (VOD)/sinusoidal obstruction syndrome (SOS) was higher along with increased IVIG dose (0% for placebo, 0% for IVIG 50 mg/kg, 4% for IVIG 250 mg/kg, 11% for IVIG 500 mg/kg; P = 0.014). A systematic review and meta-analysis including 3,934 patients about IgRT in the HSCT setting did not demonstrate survival benefit [40]. In this study, risks of acute GVHD and CMV disease were reduced, whereas those of VOD and disease relapse were elevated. Another systematic review and meta-analysis including 4,223 patients in 30 studies exhibited no significant differences in OS or clinically-documented infections [41]. As with the aforementioned analysis, VOD risk was higher in the IVIG group (risk ratio 2.73). According to the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews for HSCT and non-HSCT cases, no survival benefit associated with IgRT was confirmed, whereas a subgroup-analysis with lymphoproliferative disorders cohort showed a lower incidence of clinically and microbiologically-documented infection by IVIG (risk ratio 0.49 and 0.71) [42]. Clinical data using SCIG in HSCT are far more limited compared with IVIG. Pasic et al. administrated SCIG (100 mg/kg/week) for a maximum of 6 months in HSCT recipients with IgG level <700 mg/dL who had one or more infectious complications, and compared clinical outcomes including healthcare resource use, patient satisfaction from a questionnaire, and quality of life with IVIG control cases [43]. While lacking clinical efficacy, SCIG was advantageous in terms of patient satisfaction and healthcare costs ($9756 for SCIG vs. $13,780 for IVIG, P = 0.046).
One attractive approach is the IgRT application based on IgG level monitoring. Howel et al. retrospectively compared clinical outcomes after HSCT between patients who received routine IVIG (200 mg/kg weekly) and those who received IVIG when serum IgG level became below 400 mg/dL [44]. While the incidences of GVHD, VOD, or documented infections were comparable between the two groups, total IVIG dosage and the cost were 6940 g vs. 1896 g and $924,408 vs. $252,547, respectively. They suggested that IVIG application according to the individual IgG level was a cost-effective approach. Aiming at reducing unnecessary IVIG usage, a stewardship IVIG program was carried out in the US [45]. In this program, the clinical application of IVIG was limited to designated two situations: (1) IgG < 400 mg/dL following autologous HSCT and CAR T-cell therapy; (2) IgG < 400 mg/dL with a history of a bacterial infection within the last 3 months. IVIG dosage was reduced from 4902 g in 86 patients to 1777 g in 55 patients, and the saved cost was $44,700. In terms of infection occurrence, this strategy reasonably excluded patients at low risk from IVIG application, which is considered as cost-beneficial.
Several guidelines describe issue statements about IgRT (Table 2). American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (ASBMT) and Canadian Blood and Marrow Transplant Group statements do not support routine prophylaxis, and refer umbilical cord blood transplant (CBT) recipients, children who undergo transplantation for inherited or acquired disorders associated with B-cell deficiency, and chronic GVHD patients with recurrent sinopulmonary infections as potential candidates for IgRT [46]. According to 2009 ASBMT guidelines for preventing infectious complications, routine IVIG for bacterial infection prophylaxis is not recommended, and high-risk recipients who undergo unrelated HSCT with IgG < 400 mg/dL may be a candidate for IgRT [47]. Similarly, the latest NCCN Guidelines about prevention and treatment of cancer-related infections recommend IgRT in allo-recipients with IgG < 400 mg/dL and recurrent infections. Meanwhile, patients without such risk factors or autologous recipients are not applicable to IgRT [48]. According to the long-term follow-up after HSCT manual by Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center and Seattle Cancer Care Alliance, IgRT is considered from day 100 through 1-year after HSCT in the following situations: (1) MM, CLL or low-grade lymphoma patients; (2) PID patients; (3) patients who underwent HLA-haploidentical transplantation or CBT under severe hypogammaglobulinemia; (4) pediatric patients with unrelated donors, or patients with ongoing infections or chronic GVHD under severe hypogammaglobulinemia [49]. HSCT recipients with chronic GVHD beyond 1-year with recurrent sinopulmonary infections and persistent hypogammaglobulinemia are also applicable to IgRT. In European expert consensus about treating secondary IgG deficiency in patients with hematological malignancy, 83% of the experts agree with the statement that all patients with allogeneic HSCT are candidates for IgRT, particularly in patients with low IgG levels (<400 mg/dL) or with GVHD on immunosuppressive treatment [50]. Consistently, the Japanese Society for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation guidelines do not support routine IgRT for all allo-recipients, and recommend that IgRT is considered in patients with pre-transplant IgG < 400 mg/dL or those with delayed immunoglobulin recovery after HSCT [51]. American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology working group has recently issued similar recommendation (not routine use for IgRT, IgG < 400 mg/dL with bacteremia or recurrent sinopulmonary infection) [52]. To assess posttransplant immune reconstitution, the guidance suggests CD4+ T-cell count in addition to serum IgG.
Conclusions and future directions
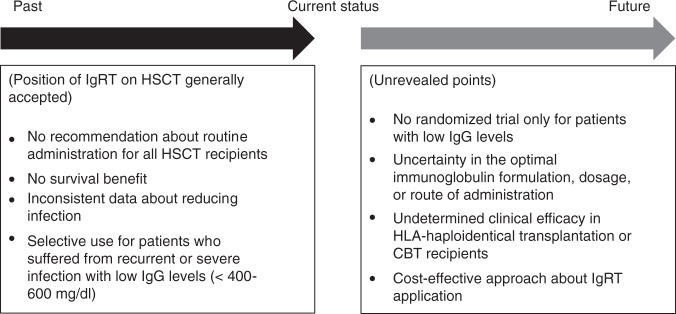
Clinical data of IgRT in the HSCT setting are not yet as robust. We summarized available data about the clinical impact of IgRT (Fig. 1). In both HSCT and non-HSCT settings, no data has demonstrated the OS prolongation effect of IgRT [20–22, 37–42]. Randomized trials and meta-analysis for CLL or MM patients in the non-HSCT setting have revealed that IgRT reduced infectious events [20–22]. While some studies for HSCT recipients showed lower infection incidence in patients with IgRT, this result was not validated in other studies [37–42]. Studies conducted decades ago showed a significant benefit in the management of CMV with the use of IgRT. Although CMV management has significantly changed, IgRT might be beneficial in patients with refractory CMV infection.
Fig. 1. Current position of IgRT on HSCT and unrevealed points about the application.
IgRT immunoglobulin replacement therapy, HSCT hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation, HLA human leukocyte antigen, CBT cord blood transplant.
Concerning the clinical impact of IgRT in HSCT, several points should be elucidated. Firstly, one large limitation in discussing the application of IgRT on HSCT, is that no trials exist for only patients with hypogammaglobulinemia, although the benefit of IVIG should be the largest in patients with hypogammaglobulinemia after HSCT. Secondary, immunoglobulin formulation, dosage, or route of administration are heterogenous in respective studies. Thirdly, most of the clinical data is derived from patients who underwent matched related HSCT, and clinical efficacy of IgRT for patients with HLA-haploidentical transplantation or CBT has not been fully examined. Finally, to develop an effective use of limited medical resources, a cost-effective approach such as IVIG stewardship program is desired [45].
Author contributions
AO and SF designed the outline for the paper and wrote the first draft; KCS, BNS and HE critically reviewed and revised the paper; all authors reviewed the final paper and agreed with its content.
Competing interests
SF received a research grant from CSL Behring K.K.
Footnotes
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
These authors contributed equally: Akihiro Ohmoto, Shigeo Fuji.
References
- 1.McDonald GB, Sandmaier BM, Mielcarek M, Sorror M, Pergam SA, Cheng GS, et al. Survival, nonrelapse mortality, and relapse-related mortality after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: Comparing 2003-2007 versus 2013-2017 cohorts. Ann Intern Med. 2020;172:229–39. doi: 10.7326/M19-2936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Penack O, Peczynski C, Mohty M, Yakoub-Agha I, Styczynski J, Montoto S, et al. How much has allogeneic stem cell transplant-related mortality improved since the 1980s? A retrospective analysis from the EBMT. Blood Adv. 2020;4:6283–90. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020003418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Cooper JP, Storer BE, Granot N, Gyurkocza B, Sorror ML, Chauncey TR, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation with non-myeloablative conditioning for patients with hematologic malignancies: Improved outcomes over two decades. Haematologica. 2021;106:1599–607. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2020.248187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Holmqvist AS, Chen Y, Wu J, Battles K, Bhatia R, Francisco L, et al. Assessment of late mortality risk after allogeneic blood or marrow transplantation performed in childhood. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4:e182453. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.2453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Patel SY, Carbone J, Jolles S. The expanding field of secondary antibody deficiency: causes, diagnosis, and management. Front Immunol. 2019;10:33. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ueda M, Berger M, Gale RP, Lazarus HM. Immunoglobulin therapy in hematologic neoplasms and after hematopoietic cell transplantation. Blood Rev. 2018;32:106–15. doi: 10.1016/j.blre.2017.09.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Pal Singh S, Dammeijer F, Hendriks RW. Role of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase in B cells and malignancies. Mol Cancer. 2018;17:57. doi: 10.1186/s12943-018-0779-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Forconi F, Moss P. Perturbation of the normal immune system in patients with CLL. Blood. 2015;126:573–81. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-03-567388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Pratt G, Goodyear O, Moss P. Immunodeficiency and immunotherapy in multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol. 2007;138:563–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2007.06705.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Casulo C, Maragulia J, Zelenetz AD. Incidence of hypogammaglobulinemia in patients receiving rituximab and the use of intravenous immunoglobulin for recurrent infections. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2013;13:106–11. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2012.11.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Barmettler S, Ong MS, Farmer JR, Choi H, Walter J. Association of immunoglobulin levels, infectious risk, and mortality with rituximab and hypogammaglobulinemia. JAMA Netw Open. 2018;1:e184169. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2018.4169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Gudiol C, Lewis RE, Strati P, Kontoyiannis DP. Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy for the treatment of lymphoid malignancies: is there an excess risk for infection? Lancet Haematol. 2021;8:e216–28. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(20)30376-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hill JA, Giralt S, Torgerson TR, Lazarus HM. CAR-T—and a side order of IgG, to go?—immunoglobulin replacement in patients receiving CAR-T cell therapy. Blood Rev. 2019;38:100596. doi: 10.1016/j.blre.2019.100596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wudhikarn K, Palomba ML, Pennisi M, Garcia-Recio M, Flynn JR, Devlin SM, et al. Infection during the first year in patients treated with CD19 CAR T cells for diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Blood Cancer J. 2020;10:79. doi: 10.1038/s41408-020-00346-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Park JH, Romero FA, Taur Y, Sadelain M, Brentjens RJ, Hohl TM, et al. Cytokine release syndrome grade as a predictive marker for infections in patients with relapsed or refractory B-Cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated with chimeric antigen receptor T cells. Clin Infect Dis. 2018;67:533–40. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciy152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Orange JS, Grossman WJ, Navickis RJ, Wilkes MM. Impact of trough IgG on pneumonia incidence in primary immunodeficiency: a meta-analysis of clinical studies. Clin Immunol. 2010;137:21–30. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2010.06.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Aguilar C, Malphettes M, Donadieu J, Chandesris O, Coignard-Biehler H, Catherinot E, et al. Prevention of infections during primary immunodeficiency. Clin Infect Dis. 2014;59:1462–70. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciu646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Oscier D, Dearden C, Eren E, Fegan C, Follows G, Hillmen P, et al. Guidelines on the diagnosis, investigation and management of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 2012;159:541–64. doi: 10.1111/bjh.12067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Compagno N, Cinetto F, Semenzato G, Agostini C. Subcutaneous immunoglobulin in lymphoproliferative disorders and rituximab-related secondary hypogammaglobulinemia: a single-center experience in 61 patients. Haematologica. 2014;99:1101–6. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2013.101261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Gale RP, Chapel HM, Bunch C, Rai KR, Foon K, Courter SG, et al. Intravenous immunoglobulin for the prevention of infection in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. A randomized, controlled clinical trial. N Engl J Med. 1988;319:902–7. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198810063191403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Chapel HM, Lee M, Hargreaves R, Pamphilon DH, Prentice AG. Randomised trial of intravenous immunoglobulin as prophylaxis against infection in plateau-phase multiple myeloma. The UK Group for Immunoglobulin Replacement Therapy in Multiple Myeloma. Lancet. 1994;343:1059–63.. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(94)90180-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Raanani P, Gafter-Gvili A, Paul M, Ben-Bassat I, Leibovici L, Shpilberg O. Immunoglobulin prophylaxis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and multiple myeloma: systematic review and meta-analysis. Leuk Lymphoma. 2009;50:764–72. doi: 10.1080/10428190902856824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. Multiple myeloma (version 3.2022). https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/myeloma.pdf.
- 24.NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (version 1.2022). https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/cll.pdf.
- 25.NCCN: Cancer and COVID-19 Vaccination. (version 5.0). 2022. https://www.nccn.org/docs/default-source/covid-19/2021_covid-19_vaccination_guidance_v5-0.pdf?sfvrsn=b483da2b_74.
- 26.Shao Z, Feng Y, Zhong L, Xie Q, Lei M, Liu Z, et al. Clinical efficacy of intravenous immunoglobulin therapy in critical ill patients with COVID-19: a multicenter retrospective cohort study. Clin Transl Immunol. 2020;9:e1192. doi: 10.1002/cti2.1192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Mazeraud A, Jamme M, Mancusi RL, Latroche C, Megarbane B, Siami S, et al. Intravenous immunoglobulins in patients with COVID-19-associated moderate-to-severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (ICAR): multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2022;10:158–66. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00440-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Vandeberg P, Cruz M, Diez JM, Merritt WK, Santos B, Trukawinski S, et al. Production of anti-SARS-CoV-2 hyperimmune globulin from convalescent plasma. Transfusion. 2021;61:1705–9. doi: 10.1111/trf.16378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ali S, Uddin SM, Shalim E, Sayeed MA, Anjum F, Saleem F, et al. Hyperimmune anti-COVID-19 IVIG (C-IVIG) treatment in severe and critical COVID-19 patients: A phase I/II randomized control trial. EClinicalMedicine. 2021;36:100926. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Bégin P, Callum J, Jamula E, Cook R, Heddle NM, Tinmouth A, et al. Convalescent plasma for hospitalized patients with COVID-19: an open-label, randomized controlled trial. Nat Med. 2021;27:2012–24. doi: 10.1038/s41591-021-01488-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Simonovich VA, Burgos Pratx LD, Scibona P, Beruto MV, Vallone MG, Vázquez C, et al. A randomized trial of convalescent plasma in Covid-19 severe pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:619–29. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2031304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Janiaud P, Axfors C, Schmitt AM, Gloy V, Ebrahimi F, Hepprich M, et al. Association of convalescent plasma treatment with clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2021;325:1185–95. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.2747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Norlin AC, Sairafi D, Mattsson J, Ljungman P, Ringdén O, Remberger M. Allogeneic stem cell transplantation: low immunoglobulin levels associated with decreased survival. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2008;41:267–73. doi: 10.1038/sj.bmt.1705892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Arai Y, Yamashita K, Mizugishi K, Kondo T, Kitano T, Hishizawa M, et al. Risk factors for hypogammaglobulinemia after allo-SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2014;49:859–61. doi: 10.1038/bmt.2014.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Frangoul H, Min E, Wang W, Chandrasekhar R, Calder C, Evans M, et al. Incidence and risk factors for hypogammaglobulinemia in pediatric patients following allo-SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013;48:1456–9. doi: 10.1038/bmt.2013.76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Winston DJ, Ho WG, Lin CH, Bartoni K, Budinger MD, Gale RP, et al. Intravenous immune globulin for prevention of cytomegalovirus infection and interstitial pneumonia after bone marrow transplantation. Ann Intern Med. 1987;106:12–8. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-106-1-12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Bass EB, Powe NR, Goodman SN, Graziano SL, Griffiths RI, Kickler TS, et al. Efficacy of immune globulin in preventing complications of bone marrow transplantation: a meta-analysis. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1993;12:273–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Sullivan KM, Kopecky KJ, Jocom J, Fisher L, Buckner CD, Meyers JD, et al. Immunomodulatory and antimicrobial efficacy of intravenous immunoglobulin in bone marrow transplantation. N Engl J Med. 1990;323:705–12. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199009133231103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Cordonnier C, Chevret S, Legrand M, Rafi H, Dhédin N, Lehmann B, et al. Should immunoglobulin therapy be used in allogeneic stem-cell transplantation? A randomized, double-blind, dose effect, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. Ann Intern Med. 2003;139:8–18. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-139-1-200307010-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Ahn H, Tay J, Shea B, Hutton B, Shorr R, Knoll GA, et al. Effectiveness of immunoglobulin prophylaxis in reducing clinical complications of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Transfusion. 2018;58:2437–52. doi: 10.1111/trf.14656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Raanani P, Gafter-Gvili A, Paul M, Ben-Bassat I, Leibovici L, Shpilberg O. Immunoglobulin prophylaxis in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:770–81. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.16.8450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Raanani P, Gafter-Gvili A, Paul M, Ben-Bassat I, Leibovici L, Shpilberg O. Immunoglobulin prophylaxis in hematological malignancies and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008;4:CD006501. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006501.pub2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Pasic I, Alanazi W, Dranitsaris G, Lieberman L, Viswabandya A, Kim DDH, et al. Subcutaneous immunoglobulin in allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant patients: a prospective study of feasibility, safety, and healthcare resource use. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther. 2021. 10.1016/j.hemonc.2021.01.001. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 44.Howell JE, Gulbis AM, Champlin RE, Qazilbash MH. Retrospective analysis of weekly intravenous immunoglobulin prophylaxis versus intravenous immunoglobulin by IgG level monitoring in hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. Am J Hematol. 2012;87:172–4. doi: 10.1002/ajh.22229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Derman BA, Schlei Z, Parsad S, Mullane K, Knoebel RW. Changes in intravenous immunoglobulin usage for hypogammaglobulinemia after implementation of a stewardship program. JCO Oncol Pract. 2021;17:e445–3. doi: 10.1200/OP.20.00312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Bhella S, Majhail NS, Betcher J, Costa LJ, Daly A, Dandoy CE, et al. Choosing Wisely BMT: American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation and Canadian Blood and Marrow Transplant Group’s list of 5 tests and treatments to question in blood and marrow transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018;24:909–13. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2018.01.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Tomblyn M, Chiller T, Einsele H, Gress R, Sepkowitz K, Storek J, et al. Guidelines for preventing infectious complications among hematopoietic cell transplantation recipients: a global perspective. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2009;15:1143–238. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2009.06.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. Prevention and treatment of cancer-related infections (version 1.2021) https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/infections.pdf. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 49.Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center and Seattle Cancer Care Alliance. Long-term follow-up after hematopoietic stem cell transplant general guidelines for referring physicians (version October 01.2021). https://www.fredhutch.org/content/dam/www/research/patient-treatment-and-support/ltfu/LTFU_HSCT_guidelines_physicians.pdf.
- 50.Jolles S, Michallet M, Agostini C, Albert MH, Edgar D, Ria R, et al. Treating secondary antibody deficiency in patients with haematological malignancy: European expert consensus. Eur J Haematol. 2021;106:439–49. doi: 10.1111/ejh.13580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.The Japan Society for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Post-transplant infectious control guidelines (version 4.2017). (in Japanese) https://www.jstct.or.jp/uploads/files/guideline/01_01_kansenkanri_ver04.pdf.
- 52.Otani IM, Lehman HK, Jongco AM, Tsao LR, Azar A, Tarrant T, et al. Practical guidance for the diagnosis and management of secondary hypogammaglobulinemia: a work group report of the AAAAI primary immunodeficiency and altered immune response committees. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022. 10.1016/j.jaci.2022.01.025. [DOI] [PubMed]