Abstract
A conjugative IncL/M plasmid (pSEM) conferring resistance to gentamicin, amikacin, kanamycin, sulfonamides, and expanded-spectrum cephalosporins was found in pathogenic strains of Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium. Resistance to aminoglycosides was encoded by a sul1-type class 1 integron (In-t3). An extended-spectrum beta-lactamase gene, blaSHV-5, was identified 3.5 kb downstream of the integrase (intI1) gene of In-t3. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the 5.3-kb blaSHV-5–In-t3 region of pSEM highlighted striking similarities with IncL/M plasmids isolated from nosocomial gram-negative pathogens, conferring resistance to expanded-spectrum cephalosporins and aminoglycosides.
Although antibiotic resistance is becoming a major threat to human health worldwide, information concerning the dissemination and geographical distribution of antibiotic-resistant bacterial pathogens remains scattered (8, 14, 26). During the last decade many hospital outbreaks caused by extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Enterobacteriaceae have been reported, and most of the ESBL-producing strains were found to carry the blaTEM-1, blaTEM-2, and blaSHV-1 gene derivatives (5, 6, 9, 11, 19, 27). These genes are prevalently located on large conjugative plasmids of the incompatibility (Inc) groups IncC, IncFI, IncH12, and IncL/M (3, 5, 7, 13, 18, 20, 23, 28).
More recent reports have highlighted the emergence of ESBL-producing strains endowed with an extremely wide spectrum of antibiotic resistance, including resistance to sulfonamides, trimethoprim, streptomycin, kanamycin, gentamicin, and amikacin (17, 21, 23). However, the molecular mechanisms involved in the acquisition and/or transmission of ESBL-encoding genes are poorly understood.
In previous work we identified an IncL/M plasmid, referred to as pSEM, in eight epidemiologically unrelated, multiple-drug-resistant strains of Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium. This plasmid contains a sul1-type class 1 integron (In-t3) carrying the aacA4, aacC1, and aadA1 gene cassettes and conferring resistance to sulfonamides, kanamycin, gentamicin, and amikacin (29). The streptomycin and spectinomycin-resistance determinant, aadA1, is poorly expressed in In-t3 because it is located in a distal position relative to the main integron promoter Pant (29).
The Salmonella strains harboring pSEM were analyzed in more detail with regard to their antibiotic resistance profile. Microdilution susceptibility tests demonstrated that all eight strains were resistant to ceftazidime (≥16 μg/ml), cefotaxime (≥32 μg/ml), ceftriaxone (≥64 μg/ml), cefamandole (≥32 μg/ml), cefoxitin (≥8 μg/ml), and aztreonam (≥16 μg/ml) but sensitive to imipenem (<4 μg/ml).
To clone the gene responsible for resistance to expanded-spectrum cephalosporins, an EcoRI genomic library was constructed in the pUC18 vector using total DNA extracted from the prototypic Salmonella 202 strain. The library was introduced by transformation in Escherichia coli DH5α competent cells, and selection was performed on Luria-Bertani agar plates containing ceftazidime (4 μg/ml). Plasmids extracted from six independent ceftazidime-resistant transformants contained a 13.5-kb EcoRI insert. The DNA of one randomly selected recombinant plasmid, designated pE135, was used as the template in PCR amplification experiments performed with OS5-OS6 or TEMA-TEMB primer pairs specifically designed to amplify the blaSHV-1 and blaTEM-1 gene derivatives, respectively (2, 15). An amplicon of 795 bp was obtained with the OS5-OS6 primer pair, and its complete sequence unambiguously identified the blaSHV-5 gene (1, 12) (sequence accession no. P37320).
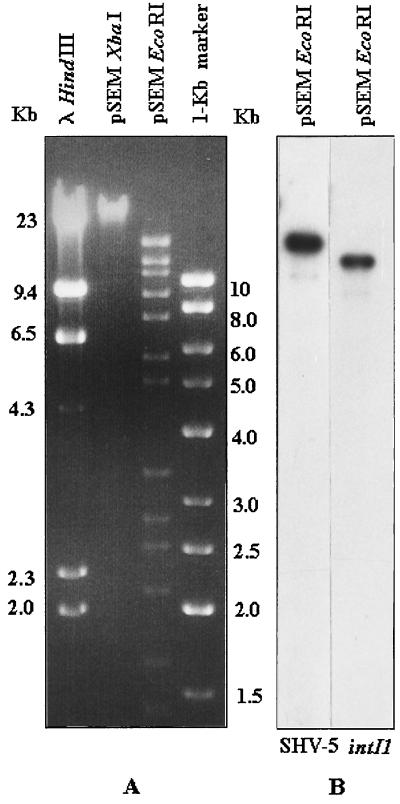
Conjugal transfer of pSEM from S. enterica serotype Typhimurium strain 202 to E. coli CSH26R (29) was associated with transmission of the ceftazidime-resistance determinant, providing direct genetic evidence of the physical link between pSEM and the blaSHV-5 gene. pSEM was purified from the ceftazidime-resistant E. coli 202-24 exconjugant, digested with EcoRI or with XbaI (Fig. 1A), and analyzed by Southern blot hybridization with the blaSHV-5 and int1I gene probes (Fig. 1B). The blaSHV-5 and int1I probes recognized two different EcoRI bands of 13.5 and 12.5 kb, respectively.
FIG. 1.
(A) agarose gel electrophoresis of XbaI- and EcoRI-digested pSEM extracted from E. coli 202-24. HindIII-digested lambda DNA (λ-HindIII) and 1-kb marker (KiloBase DNA marker; Pharmacia Biotech, Milan, Italy) were used as standards. (B) Southern blot hybridization (25) of EcoRI-digested pSEM (electrophoresed as in panel A) with [α-32P]dCTP-labeled blaSHV-5 and intI1 probes. The blaSHV-5 probe was obtained by PCR amplification with the OS5-OS6 primer pair. The intI1 probe was obtained by agarose elution of the 596-bp PvuII-RsaI restriction fragment from the plasmid pACYC184::Tn21 (4).
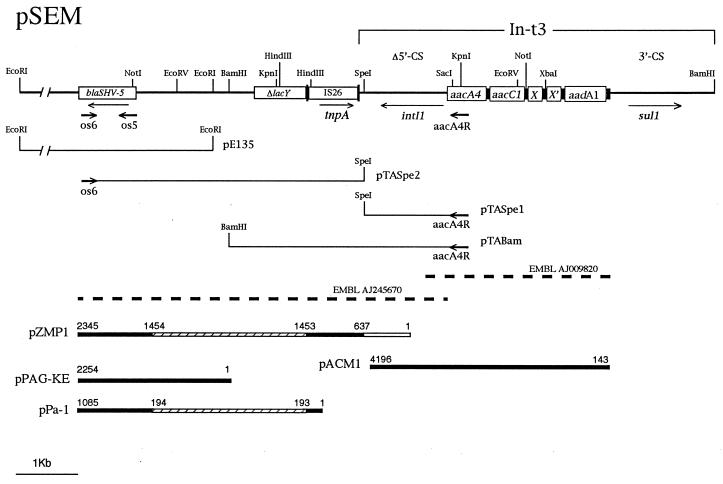
To characterize the blaSHV-5 flanking regions and locate the blaSHV-5 gene relative to the In-t3 position on pSEM, extended PCR amplification experiments were performed on total DNA extracted from S. enterica serotype Typhimurium 202, with the aacA4R-OS5 or aacA4R-OS6 primer pairs. An amplicon of approximately 5.5 kb was obtained only with the aacA4R-OS6 primer pair, indicating that the blaSHV-5 gene was located approximately 3.5 kb downstream of the int1I gene of In-t3. The amplicon was digested with SpeI and BamHI for ligation in the pT-Adv vector, yielding plasmids pTASpe1, pTASpe2, and pTABam. Further subclones of the pTASpe2 construct were obtained by EcoRV and KpnI internal deletions (24). The DNA inserts of these subclones and the blaSHV-5-flanking regions in pE135 were entirely sequenced (25). A consensus map of pSEM, encompassing the In-t3 integron and the blaSHV-5 gene, is shown in Fig. 2.
FIG. 2.
Consensus map of the antibiotic resistance region of pSEM. Thin arrows show the orientation of genes. Δ5′CS and 3′CS are the 5′ and 3′ conserved region of the In-t3 integron. The short boldface arrows indicate the position and direction of primers used in PCR amplifications. The aacA4R-OS6 amplicon was obtained by the Expand 20 kb PCR system (Boehringer GmbH, Mannheim, Germany). The DNA sequence of the aacA4R primer is: 5′-TGTGACGGAATCGTTGC-3′. Thin bars below the map represent cloned inserts used for sequencing, with the plasmid designation given on the right of each construct. Dashed lines show the In-t3 and In-t3/blaSHV-5 intervening sequences released under EMBL accession no. AJ009820 and AJ245670, respectively. Black thick bars represent pSEM regions homologous to pPAG-KE, pPa-1, pZMP1, and pACM1 plasmids; hatched thick bars are gaps between homologous regions; white thick bars are nonhomologous regions. The numbering is relative to positions of nucleotides in the released plasmid sequences.
Nucleotide sequence comparisons of the 4,379-bp fragment of pTASpe2 revealed striking homologies between pSEM and promiscuous plasmids carrying ceftazidime-resistance determinants in different gram-negative bacteria. The 2,254-bp segment encompassing the blaSHV-5 gene matched a homologous sequence (99.8% identity) on plasmid pPAG-KE from a clinical Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolate (accession no. AF096930) (E. Scoulica, A. Aransay, and I. Tselentis, unpublished results, 1998). In the blaSHV-5-preceding region, two open reading frames (ORFs) were identified on opposite DNA strands; their predicted translation products (277 and 297 amino acids) do not show significant homology with known proteins. However, the pSEM region spanning from nucleotide 2654 to 3456 was 81% identical to the Klebsiella pneumoniae lacY gene (from nucleotide 416 to 1215 of the sequence released under accession no. X14154), encoding the lactose transport protein. A deletion of the first 130 codons and an opale mutation at codon 174 predicted the deduced translation product to be nonfunctional, justifying the cognate gene designation ΔlacY. Interestingly, an IS26 element was found juxtaposed to codon 131 of the ΔlacY pseudogene in the HindIII-SpeI region of the pSEM. This element, which also includes the transposase gene (tnpA) and the inverted repeats (16), is flanked by the 5′ conserved segment (5′CS) region of In-t3 with a 113-bp deletion (Δ5′CS) (10). The IS26 element of pSEM is identical to the IS26 element flanking the blaSHV-2 gene in plasmids pPa-1 from P. aeruginosa and pZMP1 from K. pneumoniae (accession no. AF074954 and X53817, respectively). The location of the blaSHV gene and of the IS26 element differs between pSEM and pPa-1 and pZMP1. In pPa-1 and pZMP1 the IS26 shortly precedes the ATG codon of the blaSHV-2 gene, while in pSEM it is located 2,638 bp upstream of the 5′ end of the blaSHV-5 gene. Insertion sequences closely linked to ESBL genes were previously mapped on other plasmids. This was the case with pCFF04, an IncL/M replicon of 85 kb isolated from K. pneumoniae in France, carrying an IS15 element and the blaTEM-3 gene on a large EcoRI band (17). An IS6100 element was recently described in pACM1, found in Klebsiella oxytoca isolates responsible for a nosocomial outbreak in the United States. This IncL/M plasmid carries the blaSHV-5 gene and a class 1 integron, thereby displaying structural and functional similarity to pSEM (21, 22). Remarkably, both integrons contain the same aacA4, aacC1, and aadA1 gene cassettes and two additional ORFs, ORF X and ORF X′, coding for unknown functions. A unique feature of the class 1 integrons of pSEM and pACM1 is the lack of the conserved BamHI site in the region downstream of the intI1 gene (21). Although the presence of integrons was not described for other IncL/M plasmids, both aadA1 and aacA4 genes were detected by Southern blot hybridization on pCFF04 (17). Uncharacterized genetic determinants for gentamicin and tobramycin resistance were associated with the blaSHV-5 gene in pIBK1, an IncL/M conjugative plasmid of 80 kb isolated at the Innsbruck University Hospital (Innsbruck, Austria) from K. pneumoniae strains responsible for outbreaks in intensive care units (23).
The finding that pSEM shares common traits with other ESBL-encoding plasmids is also supported by the observation that the EcoRI restriction profile of pSEM is similar to the published EcoRI patterns of pACM1, pCFF04, and pIBK1 IncL/M plasmids (17, 21, 23). The largest EcoRI fragment, which appeared to be the most variable in length (ranging from 13.5 to approximately 20 kb), was reported to contain the ceftazidime resistance determinants in all three plasmids (17, 21, 23). Thus, plasmids pSEM, pPAG-KE, pZMP1, pPa-1, pACM1, pIBK1, and pCFF04 could be members of a family of broad-host-range replicons responsible for resistance to expanded-spectrum cephalosporins in gram-negative pathogens. Common features of these plasmids are the presence of ESBL-encoding genes (SHV or TEM type), likely associated with a sul1-type class 1 integron conferring resistance to aminoglycosides and possibly the IncL/M ori/rep functions. The physical association between insertion sequences and ESBL genes in these plasmids suggests that IS elements could be involved in the assembly of antibiotic resistance islands by gene mobilization. A simple way to generate the gene configuration shown in Fig. 2 is for IS26 to have jumped either into the 5′CS of In-t3 or, from a position adjacent to it, to have deleted adjacent bases. IS26-mediated deletion of adjacent bases could also explain the relationship of pSEM to pZMP1 and pPa-1.
We emphasize that all the ESBL-encoding plasmids described thus far, with the exception of pSEM, originate from bacteria responsible for nosocomial outbreaks. The presence of a genetic relict, i.e., the lactose transport protein pseudogene (ΔlacY), could indicate that pSEM originates from lactose-fermenting bacteria, thus representing a recent acquisition for Salmonella, likely occurring through horizontal transfer. The identification of this family of antibiotic resistance plasmids in enteric bacteria responsible for food-borne and community-acquired infections, such as S. enterica serotype Typhimurium, has serious public health implications. It is of concern that broad-host-range plasmids carrying resistance determinants for a number of clinically relevant new-generation antibiotics are spreading worldwide among bacteria responsible for both nosocomial and community-acquired infections.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to I. Luzzi, A. Pantosti, and A. Cassone for critical reading of the manuscript and to the anonymous reviewers for their constructive criticism. We also thank F. Riccobono for DNA sequencing, and S. Mariotti, I. Benedetti, and S. Arena for excellent technical assistance.
Funding for this work was provided through grants from the Ministero della Sanità, Programmi per la Ricerca Finalizzata 1998 and 1999.
REFERENCES
- 1.Ambler R P, Coulson A F, Frère J M, Ghuysen J M, Joris B, Forsman M, Levesque R C, Tiraby G, Waley S G. A standard numbering scheme for the class A β-lactamases. Biochem J. 1991;276:269–270. doi: 10.1042/bj2760269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Arlet G, Rouveau M, Philippon A. Substitution of alanine for aspartate at position 179 in the SHV-6 extended-spectrum β lactamase. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1997;152:163–167. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1097(97)00196-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bingen E H, Desjardins P, Arlet G, Bourgeois F, Mariani-Kurkdjian P, Lambert-Zechovsky N Y, Denamur E, Philippon A, Elion J. Molecular epidemiology of plasmid spread among extended broad-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates in a pediatric hospital. J Clin Microbiol. 1993;31:179–184. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.2.179-184.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Colonna B, Bernardini M, Micheli G, Maimone F, Nicoletti M, Casalino M. The Salmonella wien virulence plasmid pZM3 carries Tn1935, a multiresistance transposon containing a composite IS1936-kanamycin resistance element. Plasmid. 1988;20:221–231. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(88)90028-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.de Champs C, Sirot D, Chanal C, Poupart M C, Dumas M P, Sirot J. Concomitant dissemination of three extended-spectrum β-lactamases among different Enterobacteriaceae isolated in French hospital. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991;27:441–457. doi: 10.1093/jac/27.4.441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Du Bois S K, Marriott M S, Amyes S G B. TEM- and SHV-derived extended-spectrum β-lactamases: relationship between selection, structure and function. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1995;35:7–22. doi: 10.1093/jac/35.1.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Eisen D, Russell E G, Tymms M, Roper E J, Grayson M L, Turnidge J. Random amplified polymorphic DNA and plasmid analyses used in investigation of an outbreak of multiresistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Clin Microbiol. 1995;33:713–717. doi: 10.1128/jcm.33.3.713-717.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.File T M., Jr Overview of resistance in the 1990s. Chest. 1999;115:3S–8S. doi: 10.1378/chest.115.suppl_1.3s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Gniadkowski M, Palucha A, Grzesiowski P, Hryniewicz W. Outbreak of ceftazidime-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in a pediatric hospital in Warsaw, Poland: clonal spread of the TEM-47 extended-spectrum β-lactamases (ESBL)-producing strain and transfer of a plasmid carrying the SHV-5-like ESBL-encoding gene. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1998;42:3079–3085. doi: 10.1128/aac.42.12.3079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hall R M, Brown H J, Brookes D E, Stokes H W. Integrons found in different locations have identical 5′ ends but variable 3′ ends. J Bacteriol. 1994;176:6286–6294. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.20.6286-6294.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Jacoby G A. Genetics of extended-spectrum beta-lactamases. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1994;13:2–11. doi: 10.1007/BF02390679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Jacoby G A. Extended-spectrum β-lactamases and other enzymes providing resistance to oxymino-β-lactams. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 1997;11:875–887. doi: 10.1016/s0891-5520(05)70395-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Jacoby G A, Sutton L. Properties of plasmids responsible for production of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991;35:164–169. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.1.164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Levy S B. Multidrug resistance-A sign of the times. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:1376–1378. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199805073381909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Mabilat C, Goussard S, Sougakoff W, Spencer R C, Courvalin P. Direct sequencing of the amplified structural gene and promoter for the extended-broad-spectrum β-lactamase TEM-9 (RHH-1) of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Plasmid. 1990;23:27–34. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(90)90041-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Mahillon J, Chandler M. Insertion sequences. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 1998;62:725–774. doi: 10.1128/mmbr.62.3.725-774.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Petit A, Gerbaud G, Sirot D, Courvalin P, Sirot J. Molecular epidemiology of TEM-3 (CTX-1) β-lactamase. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990;34:219–224. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.2.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Philippon A, Arlet G, Lagrange P H. Origin and impact of plasmid-mediated extended-spectrum β-lactamases. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1994;13(Suppl. 1):17–29. doi: 10.1007/BF02390681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Pitout J D D, Thomson K S, Hanson N D, Ehrhardt A F, Moland E S, Sanders C C. β-lactamases responsible for resistance to expanded-spectrum cephalosporins in Klebsiella pneumoniae, Escherichia coli, and Proteus mirabilis isolates recovered in South Africa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1998;42:1350–1354. doi: 10.1128/aac.42.6.1350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Pitout J D D, Thomson K S, Hanson N D, Ehrhardt A F, Coudron P, Sanders C C. Plasmid-mediated resistance to expanded-spectrum cephalosporins among Enterobacter aerogenes strains. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1998;42:596–600. doi: 10.1128/aac.42.3.596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Preston K E, Kacica M A, Limberger R J, Archinal W A, Venezia R A. The resistance and integrase genes of pACM1, a conjugative multiple-resistance plasmid, from Klebsiella oxytoca. Plasmid. 1997;37:105–118. doi: 10.1006/plas.1997.1284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Preston K E, Radomski C C A, Venezia R A. The cassettes and 3′ conserved segment of an integron from Klebsiella oxytoca plasmid pACM1. Plasmid. 1999;42:104–114. doi: 10.1006/plas.1999.1418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Prodinger W M, Fille M, Bauernfeind A, Stemplinger I, Amann S, Pfausler B, Lass-Florl C, Dierich M P. Molecular epidemiology of Klebsiella pneumoniae producing SHV-5 β-lactamase: parallel outbreaks due to multiple plasmid transfer. J Clin Microbiol. 1996;34:564–568. doi: 10.1128/jcm.34.3.564-568.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Rosdahl V T, Pedersen K B, editors. The Copenhagen recommendations. Report from the European Union Conference on “the Microbial Threat” [ http://www.microbial.threat.dk]. Ministry of Health; 1998. and Ministry of Food, Agriculture and Fisheries, Denmark. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Sambrook J E, Fritsch F, Maniatis T. Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. 2nd ed. Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1989. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson A R. DNA sequencing with chain terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1977;74:5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Shannon K, Stapleton P, Xiang X, Johnson A, Beattie H, El Bakri F, Coohson B, French G. Extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae strains causing nosocomial outbreaks of infection in the United Kingdom. J Clin Microbiol. 1998;36:3105–3110. doi: 10.1128/jcm.36.10.3105-3110.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Sirot D L. Extended-spectrum plasmid-mediated beta-lactamases. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1995;36(Suppl. A):19–34. doi: 10.1093/jac/36.suppl_a.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Tosini F, Visca P, Luzzi I, Dionisi A M, Pezzella C, Petrucca A, Carattoli A. Class 1 integron-borne multiple-antibiotic resistance carried by IncFI and IncL/M plasmids in Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1998;42:3053–3058. doi: 10.1128/aac.42.12.3053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]