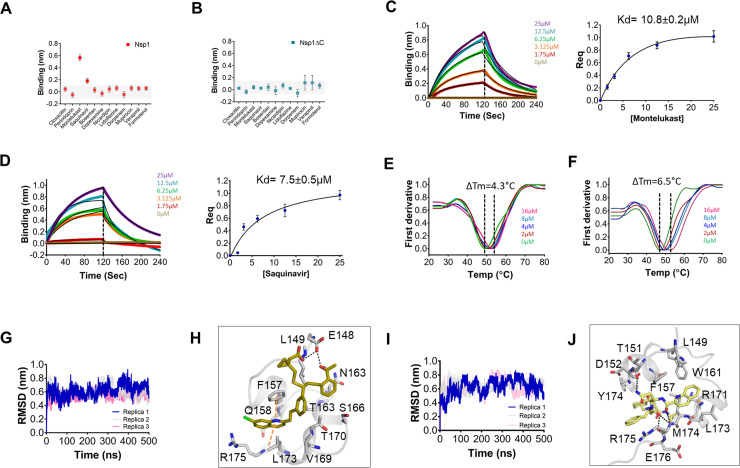
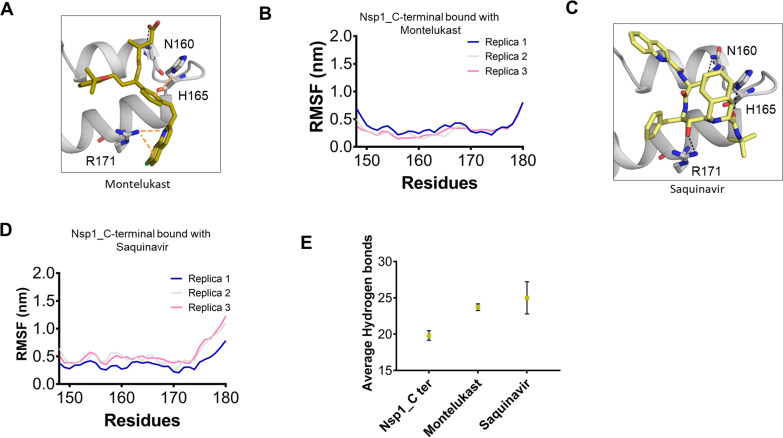
Figure 1. Screening and binding kinetics and molecular simulation dynamics runs of drugs against C-terminal helices of Nsp1 (Nsp1-C-ter).
(A and B) Bio-layer interferometry (BLI) analysis for the initial screening of binding of the drugs with the (A) non-structural protein 1 (Nsp1) and (B) C-terminal helices truncated Nsp1 (Nsp1∆C) proteins. (C and D) The kinetic behaviors of (C) montelukast and (D) saquinavir monitored using BLI by incubating increasing concentration of the drug molecule (0–25 µM) on the protein-bound sensors. Montelukast shows a binding constant (KD) of 10.8 ± 0.8 µM, while saquinavir binds with Nsp1-C-ter with a KD value of 7.5 ± 0.5 µM. (Error bars represent standard deviation of three replicates in (C) and (D). (E and F) Nanoscale differential scanning fluorometry (NanoDSF) experiments to evaluate the change in the melting temperature of the Nsp1 by incubating increasing concentration of (E) montelukast and (F) saquinavir. (The experiments were performed in three replicates.)) (G) Simulation runs with montelukast show stable root mean square deviation (RMSD) values for all replica throughout all molecular dynamic simulation trajectories for 500 ns. (H) The analysis of binding mode of montelukast at the end of 500 ns shows stable binding with C-terminal helices. The residues E148 and L149 form H-bonds with montelukast, while F157 and L173 forms base stacking interactions. (I) Simulation runs with saquinavir show stable pattern in RMSD values throughout in all molecular dynamic simulation trajectories for 500ns. (J) The analysis of binding mode of saquinavir at the end of 500 ns shows stable binding with the C-terminal helices. The residues T151, M174, and R175 form H-bonds with saquinavir, while R171 forms base stacking interactions.