Abstract
Biofilm formation has become a serious health and environmental problem. Mushrooms are now considered a valuable source of bioactive compounds with antimicrobial properties. The lion's mane mushroom (Hericium erinaceus [HE]) has been used as an antimicrobial for ulcers and gastritis in East Asian countries. However, studies on the antibiofilm activities of HE basidiome against biofilm-forming pathogenic bacteria and their bioactive compound profiles are still limited. The purpose of this study was to determine the antibiofilm activity of HE and to identify its phenolic compound profile. The HE inhibitory activities against bacterial growth and biofilm formation were performed against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Salmonella Typhimurium, Proteus mirabilis, and Staphylococcus aureus. Remarkably, P. mirabilis was the most susceptible bacteria to HE. The total phenolic content (TPC) of HE was 1652 ± 1.06 µg/ml, with protocatechuic acid and p-coumaric acid being the most abundant phenolic compounds as determined by high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrophotometry (HPLC-MS). This research highlights the possibility of HE as an antibiofilm agent that can be developed as a nutraceutical and natural food preservative.
Keywords: Biofilm, Hericium erinaceus, pathogenic bacteria, phenolic contents
INTRODUCTION
Biofilms are bacterial communities that are attached to surfaces and covered in an extracellular matrix. With the higher resistance of biofilms to antibiotics compared to planktonic forms, the treatment of infections and food contamination associated with biofilm-forming bacteria has become more challenging.[1,2]
Current research has attempted to identify effective natural compounds for the prevention and control of biofilms. Bioactive phenolic acids have been reported to exhibit antibiofilm activities.[3] Hence, mushrooms have become a topic of interest in drug discovery as potential sources of phenolic compounds with antibiofilm activities. Several solvents have been used to extract natural antibiofilm substances.[4] The methanol extract (ME) of Mycena rosea inhibited Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms by up to 50%.[5] Meanwhile, the ethanol extract (EE) of Marasmius oreades had higher phenolic levels and biofilm inhibition against S. epidermidis and P. aeruginosa by up to 90%.[6] The ethyl acetate extract (EAE) of Hericium sp. WBSP8 showed antibiofilm activity against Candida albicans.[7]
Previous studies have reported HE as a potential antibacterial agent, including its application to relieve gastric ulcers.[8,9] However, research on the antibiofilm activity of EE from HE basidiome against pathogenic biofilm-forming bacteria is still limited. It has been previously noted that ethanol as an extraction solvent displayed better antibiofilm activity. Therefore, the aims of the work were to determine the antibiofilm activity and phenolic compounds of the ethanol extract of HE basidiome, which may increase its potency as a nutraceutical or food preservative.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Bacterial strains
The bacterial strains, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus mirabilis, Salmonella Typhimurium, and Staphylococcus aureus, were maintained in nutrient agar at 4°C for subsequent experiments.
Mushroom samples and extraction
Basidiome samples were collected from Marayat Farm, Pathumthani, Thailand, from February–March 2021 and identified at the Department of Microbiology, Kasetsart University, Thailand, as HE (Voucher No. HE-01). Basidiome samples (200 g) were cleaned and air-dried before extraction. The samples were soaked in 800 mL of 96% ethanol (1:4, w/v) for 7 days at 25°C in the dark. The extract was concentrated at 40°C in a rotary evaporator, then freeze-dried, and stored at −20°C.[10]
Disk diffusion assay
Aliquots of 100 µl bacterial suspension (108 CFU/ml) were spread onto sterile Mueller–Hinton Agar (MHA) plates. After that, 6 mm filter paper disks were impregnated with 10 µl HE (200 mg/ml) or ampicillin as a positive control in 5% DMSO. The disks were placed on MHA surfaces and incubated at 37°C for 24 h, followed by a zone of inhibition (ZOI) measurement.[11]
Biofilm quantification assay
A biofilm quantification analysis was performed using the crystal violet assay (CVA). About 200 µl of bacterial culture in Mueller–Hinton broth (108 CFU/ml) was inoculated into 96-well microplates and incubated at 37°C for 42 h. The suspensions were then discarded and rinsed with 250 µl NaCl followed by ethanol. The microplates were then dried and subsequently added to 100 µl of 0.1% crystal violet for 15 min of incubation. The stain was then excluded and rinsed with distilled water before being treated with 200 µl of 30% glacial acetic acid. The absorbance was taken at 550 nm using a microplate spectrophotometer.[6] The biofilm-forming bacteria were distinguished using the cutoff OD (ODc). The ODc is three standard deviations higher than the average of the negative control OD at 550 nm. The classifications were as follows: no biofilm producers (OD ≤ ODc), weak (O. Dc < O. D. ≤2 × ODc), moderate (2 ODc < OD ≤ (4 × ODc), and strong (4 × ODc < OD).[12]
Antibiofilm assay
In brief, a 195 µl bacterial suspension (108 CFU/ml) and 5 µl HE were added into 96-well microplates at 3.375–100 mg/ml following incubation at 37°C for 42 h. The antibiofilm activities were measured using the CVA assay by comparing the absorbance of treatments with the negative control.[7]
Total phenolic content
The total phenolic content (TPC) was calculated using Folin–Ciocalteu as described by Nowacka et al.[13]
Phenolic compound analysis using high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrophotometry
The HE (0.1 g/mL) was dissolved in ethanol: water (20:80) and filtered with a 0.22 µm LC disk. Aliquots of 10 µL were injected into an HPLC Agilent 1200 series with a C-18 column operated at 30°C using mobile phase: (A) 0.1% formic acid in H2O and (B) 0.1% formic acid in acetonitrile with a flow rate of 0.2 ml/min at 280 nm. The MS analysis was conducted using an Agilent 6420 according to the method by Li et al. Identification was accomplished through comparison with commercial standards and library databases.[14]
Statistical test
The experiments were repeated three times and the findings were given as mean ± standard deviation. The statistical analysis was carried out in SPSS version 22 (IBM, USA), with a significance value of P < 0.05, using one-way ANOVA followed by Duncan's multiple range test.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Antibacterial activity of Hericium erinaceus
The antibacterial activities of HE against biofilm-forming bacteria are shown in Table 1. The highest ZOI was found against S. aureus (11.7 mm), followed by P. mirabilis (6 mm). It revealed that HE did not show sufficient antibacterial activity to inhibit the growth or kill the tested pathogens compared to the positive control.
Table 1.
Zone of inhibition of Hericium erinaceus (mm±standard deviation)
| Treatments | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | S. Typhimurium | Proteus mirabilis | Staphylococcus aureus |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HE | 0a | 0a | 6±0a | 11.7±0.25a |
| C (+) (ampicillin) | 23.3±1.25b | 17.3±0b | 23.3±0.5b | 38.3±0.25b |
Means notated by different letters differ significantly (P<0.05). HE: Hericium erinaceus
Biofilm quantification assay
The results showed that P. aeruginosa and S. Typhimurium were considered strong biofilm producers, while P. mirabilis and S. aureus were moderate biofilm producers [Table 2].
Table 2.
Classifications of biofilm-forming bacteria used in this study
| Bacterial strains | Gram-staining | Classification |
|---|---|---|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Gram-negative | Strong |
| S. Typhimurium | Gram-negative | Strong |
| Proteus mirabilis | Gram-negative | Moderate |
| Staphylococcus aureus | Gram-positive | Moderate |
The Gram-negative bacteria in this study were mostly classified as strong producers. Pili and natural conjugative plasmids attached to surfaces might improve the biofilm formation of Gram-negative bacteria.[15] However, both Gram bacteria may form biofilms of similar properties.[16]
Antibiofilm evaluation of Hericium erinaceus
The antibiofilm activities of HE are presented in Figure 1. In general, HE exhibited antibiofilm activities against all the tested bacteria. Therefore, although HE did not show significant antibacterial activity, it revealed antibiofilm potential. This result was similar to a study of M. oreades EE that exhibited low antibacterial effects but high antibiofilm activity against E. coli, P. aeruginosa, S. aureus, and S. epidermidis.[6]
Figure 1.
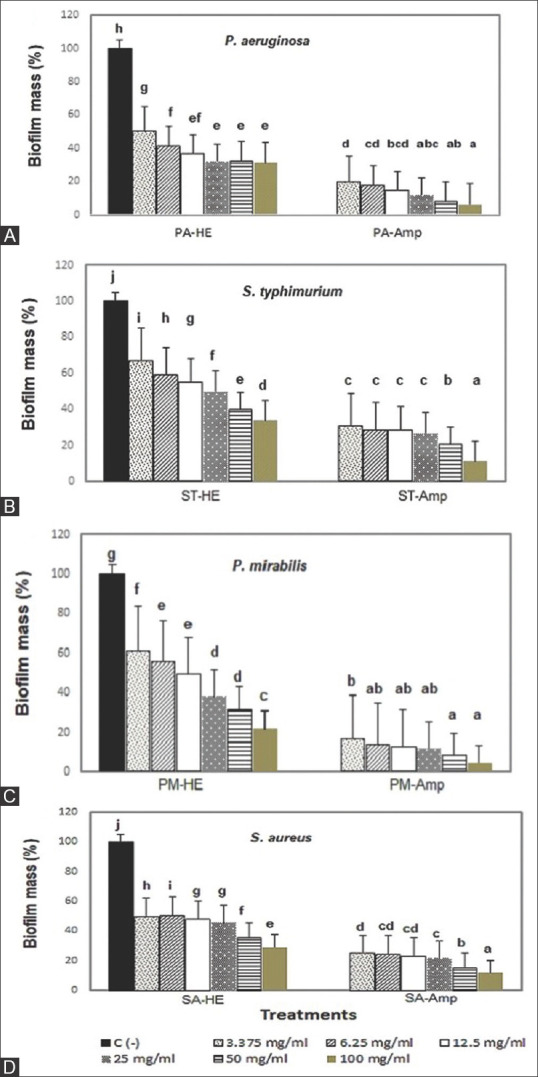
Biofilm inhibition of Hericium erinaceus against (A) PA: Pseudomonas aeruginosa, (B) ST: S. Typhimurium, (C) PM: Proteus mirabilis, (D) SA: Staphylococcus aureus, Amp: Ampicillin. Means notated by different letters differ significantly (P < 0.05)
The minimum biofilm inhibitory concentration (MBIC50) of HE against P. aeruginosa was 6.25 mg/ml, while concentrations of >12.5 mg/ml were not significantly different. It might be related to P. aeruginosa resistance to HE at higher concentrations. P. aeruginosa is a Gram-negative, strong biofilm producer associated with bacteremia pneumonia and urinary tract infections (UTIs) due to its high antibiotic resistance.[6,17] The MBIC50 of HE against S. Typhimurium was 25 mg/ml, with significant differences at higher concentrations. S. Typhimurium is a food-borne biofilm-forming pathogen and is the causative agent of enteric fever infection.[18,19]
The moderate biofilm producer, P. mirabilis, is a prevalent source of respiratory, gastrointestinal, and UTIs.[20] S. aureus is a Gram-positive bacteria responsible for nosocomial and chronic wound infections.[21,22] These moderate biofilm producers were shown to be more vulnerable to the antibiofilm compounds of HE with an MBIC50 of 12.5 mg/ml and a significant difference (P < 0.05) between concentration treatments.
Table 3 shows the antibiofilm evaluation of HE using the CVA at higher concentrations than MBIC50 (100 mg/ml). The darker color of the wells revealed that the bacteria were strong biofilm producers. A lighter color after the treatments showed that the antibiofilm was more effective. The biofilm inhibition of HE at 100 mg/ml against P. aeruginosa and S. typhimurium was 68.81% and 68.88%, respectively, whereas for P. mirabilis and S. aureus, it was 78.18% and 70.77%, respectively. Therefore, P. mirabilis is the most susceptible strain.
Table 3.
Antibiofilm evaluation of Hericium erinaceus using a crystal violet assay (100 mg/ml)
| Gram staining | Bacteria | C (−) | HE | C (+) (ampicillin) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gram-negative | Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
|
|

|
| Gram-negative | S. Typhimurium |
|

|

|
| Gram-negative | Proteus mirabilis |
|
|

|
| Gram-positive | Staphylococcus aureus |
|

|

|
HE: Hericium erinaceus
Bioactive phenolic compounds of Hericium erinaceus
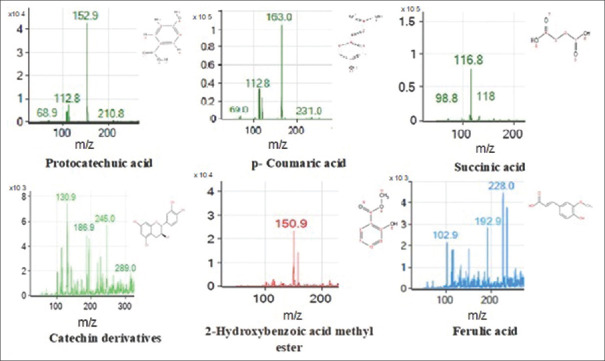
The phenolic compounds in the HE with a potential antibiofilm effect were identified using high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrophotometry (HPLC-MS), as shown by the peak chromatograms, mass spectra, and identified compounds in Figures 2 and 3 and Table 4.
Figure 2.
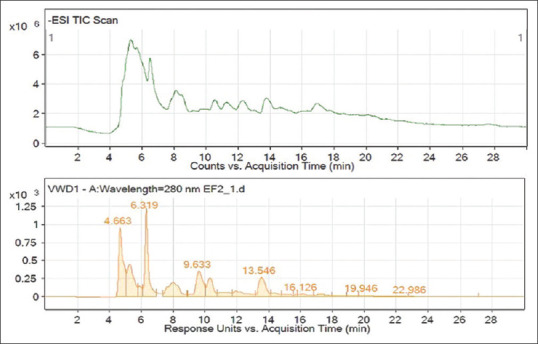
Chromatogram of high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrophotometry of Hericium erinaceus
Figure 3.
Mass spectra (m/z) of phenolic compounds of Hericium erinaceus
Table 4.
Bioactive compounds of Hericium erinaceus
| RT (min) | Identified compounds | m/z, (M−H)− | Molecular formula | Contents (µg/ml) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.663 | Protocatechuic acid | 153 | C7H6O4 | 352.94±2.37 |
| 6.319 | p-coumaric acid | 163 | C9H8O3 | 42.05±0.05 |
| 9.633 | Succinic acid | 118 | C4H6O4 | ND |
| 13.546 | Catechin derivatives | 289 | C15H14O6 | 7.96±0.20 |
| 16.126 | 2-hydroxybenzoic acid methyl ester | 151 | C8H8O3 | Trace |
| 19.946 | Ferulic acid | 193 | C10H10O4 | Trace |
| Total phenolic | 1652±1.06 |
ND: Not determined, RT: Retention time
The HE contained a high TPC (1652 ± 1.06 µg/ml) [Table 4], which was higher than in the HE ME from Portugal (288.25 ± 2.48 µg/100 g).[23] The HE also demonstrated different phenolic compound profiles compared to previous reports. Protocatechuic acid (352.94 µg/ml) and p-coumaric acid (42.05 µg/ml) were the major phenolic compounds of HE, while 2-hydroxybenzoic acid methyl ester and ferulic acid were found as traces. Catechin and succinic acid were also found in the extract. Previous studies found that p-coumaric acid (138.02 µg/100 g), gallic acid (76.25 µg/100 g), and p-hydroxybenzoic acid (73.99 µg/100 g) were major components in HE ME.[22] HE chloroform extract from Korea comprised ferulic acid (245.83 µg/g), 4-hydroxybenzoic acid (10.88 µg/g), and 4-coumaric acid (2.88 µg/g).[14] These variations could be attributed to the origin of the mushroom strains, cultivation conditions, and solvent used for extraction.
An earlier report demonstrated that the protocatechuic acid and p-hydroxybenzoic acid of Inonotus obliquus EE contributed to antibiofilm against P. aeruginosa by affecting the bacterial flagella and pili surface attachment, particularly their swimming and twitching ability.[24] Furthermore, ferulic acid and catechin of M. oreades EE disrupted P. aeruginosa and MRSA biofilms by inhibiting the bacterial motility and physicochemical changes on the surfaces.[6,25] Catechin eradicated the preformed biofilm by decreasing the biomolecule production in the exopolysaccharide biofilms.[26] Succinic acid in Lentinus edodes has been reported as a weak antibiofilm against oral bacteria.[27]
There have been few studies on the antibiofilm activity of edible or medicinal mushrooms. This research adds significant information about the antibiofilm of mushrooms that might be useful for health, environmental, and industrial applications.
CONCLUSION
The ethanol extract of HE basidiome had potential antibiofilm activities against pathogenic bacteria, with P. mirabilis being the most susceptible. In the HE basidiome, proteocatechuic acid and p-coumaric acid were the major phenolic compounds.
Financial support and sponsorship
Faculty of Science, Kasetsart University, Thailand; International SciKU Branding (ISB), Faculty of Science, Kasetsart University; Kasetsart University Research and Development Institute (KURDI) and the Agricultural Research Development Agency (Public Organization).
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
REFERENCES
- 1.Lu L, Hu W, Tian Z, Yuan D, Yi G, Zhou Y, et al. Developing natural products as potential anti-biofilm agents. Chin Med. 2019;14:11. doi: 10.1186/s13020-019-0232-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Simões M, Simões LC, Vieira MJ. A review of current and emergent biofilm control strategies. LWT. 2010;43:573–83. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Silva S, Costa EM, Horta B, Calhau C, Morais RM, Pintado MM. Anti-biofilm potential of phenolic acids: The influence of environmental pH and intrinsic physico-chemical properties. Biofouling. 2016;32:853–60. doi: 10.1080/08927014.2016.1208183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Mishra R, Panda AK, De Mandal S, Shakeel M, Bisht SS, Khan J. Natural anti-biofilm agents: Strategies to control biofilm-forming pathogens. Front Microbiol. 2020;11:566325. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.566325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Alves MJ, Ferreira IC, Lourenço I, Costa E, Martins A, Pintado M. Wild mushroom extracts as inhibitors of bacterial biofilm formation. Pathogens. 2014;3:667–79. doi: 10.3390/pathogens3030667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Shomali N, Onar O, Karaca B, Demirtas N, Cihan AC, Akata I, et al. Antioxidant, anticancer, antimicrobial, and antibiofilm properties of the culinary-medicinal fairy ring mushroom, Marasmius oreades (Agaricomycetes) Int J Med Mushrooms. 2019;21:571–82. doi: 10.1615/IntJMedMushrooms.2019030874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Song X, Gaascht F, Schmidt-Dannert C, Salomon CE. Discovery of antifungal and biofilm preventative compounds from Mycelial cultures of a unique North American Hericium sp.fungus. Molecules. 2020;25:E963. doi: 10.3390/molecules25040963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sokol S, Golak SI, Sobieralski K, Siwulski M, Górka K. Biology, cultivation, and medicinal functions of the mushroom Hericium erinaceum. Acta Mycol. 2015;50:1–18. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Liu JH, Li L, Shang XD, Zhang JL, Tan Q. Anti-Helicobacter pylori activity of bioactive components isolated from Hericium erinaceus. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016;183:54–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.09.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Bach F, Zielinski AA, Helm CV, Maciel GM, Pedro AC, Stafussa AP, et al. Bio compounds of edible mushrooms: In vitro antioxidant and antimicrobial activities. LWT. 2019;107:214–20. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Wong KH, Sabaratnam V, Abdullah N, Kuppusamy UR, Naidu M. Effects of cultivation techniques and processing on antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of Hericium erinaceus (Bull.: Fr.) Pers. extracts. Food Technol Biotechnol. 2009;47:47–55. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Fasciana T, Gargano ML, Serra N, Galia E, Arrigo I, Tricoli MR, et al. Potential activity of albino Grifola frondosa Mushroom extract against biofilm of meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Fungi (Basel) 2021;7:551. doi: 10.3390/jof7070551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Nowacka N, Nowak R, Drozd M, Olech M, Los R, Malm A. Analysis of phenolic constituents, antiradical and antimicrobial activity of edible mushrooms growing wild in Poland. LWT. 2014;59:689–94. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Li H, Park S, Moon B, Yoo YB, Lee YW, Lee C. Targeted phenolic analysis in Hericium erinaceum and its antioxidant activities. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2012;21:881–8. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ghigo JM. Natural conjugative plasmids induce bacterial biofilm development. Nature. 2001;412:442–5. doi: 10.1038/35086581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ruhal R, Kataria R. Biofilm patterns in gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Microbiol Res. 2021;251:126829. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2021.126829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Lee K, Yoon SS. Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm, a programmed bacterial life for fitness. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017;27:1053–64. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1611.11056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Krishna D, Dhanashree B. Antibiogram, virulence genes, and biofilm-forming ability of clinical Salmonella enterica serovars: An In vitro study. Microb Drug Resist. 2021;27:871–8. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2020.0419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hakimi Alni R, Ghorban K, Dadmanesh M. Combined effects of Allium sativum and Cuminum cyminum essential oils on planktonic and biofilm forms of Salmonella typhimurium isolates. 3 Biotech. 2020;10:315. doi: 10.1007/s13205-020-02286-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wasfi R, Hamed SM, Amer MA, Fahmy LI. Proteus mirabilis biofilm: Development and therapeutic strategies. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020;10:414. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Suresh MK, Biswas R, Biswas L. An update on recent developments in the prevention and treatment of Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. Int J Med Microbiol. 2019;309:1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2018.11.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kwiecinski JM, Jacobsson G, Horswill AR, Josefsson E, Jin T. Biofilm formation by Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates correlates with the infection type. Infect Dis (Lond) 2019;51:446–51. doi: 10.1080/23744235.2019.1593499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Heleno SA, Barros L, Martins A, Queiroz MJ, Morales P, Fernández-RV, et al. Chemical composition, antioxidant activity and bioaccessibility studies in phenolic extracts of two Hericium wild edible species. LWT. 2015;63:475–81. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Glamočlija J, Ćirić A, Nikolić M, Fernandes Â, Barros L, Calhelha RC, et al. Chemical characterization and biological activity of Chaga (Inonotus obliquus), a medicinal “mushroom”. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015;162:323–32. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.12.069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Borges A, Saavedra MJ, Simões M. The activity of ferulic and Gallic acids in biofilm prevention and control of pathogenic bacteria. Biofouling. 2012;28:755–67. doi: 10.1080/08927014.2012.706751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lahiri D, Nag M, Dutta B, Mukherjee I, Ghosh S, Dey A, et al. Catechin as the most efficient bioactive compound from Azadirachta indica with antibiofilm and anti-quorum sensing activities against dental biofilm: An in vitro and in silico study. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2021;193:1617–30. doi: 10.1007/s12010-021-03511-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Papetti A, Signoretto C, Spratt DA, Pratten J, Lingström P, Zaura E, et al. Components in Lentinus edodes mushroom with anti-biofilm activity directed against bacteria involved in caries and gingivitis. Food Funct. 2018;9:3489–99. doi: 10.1039/c7fo01727h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]