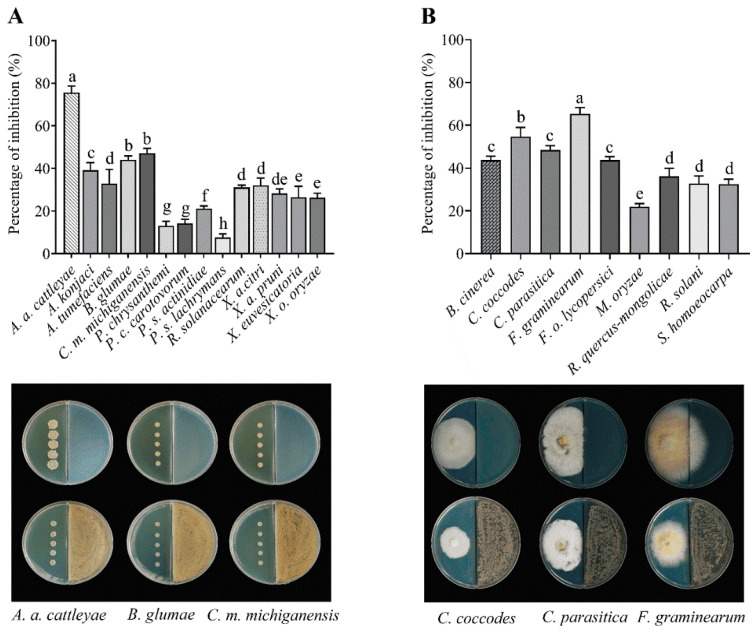
Figure 2.
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) produced by Streptomyces sp. AN090126 inhibited the cell growth of plant pathogenic bacteria (A) and the mycelial growth of fungi (B) in bioassays of the VOCs. The assay was conducted on the I-plate system; the left part was inoculated by pathogens and the right part was Streptomyces sp. AN090126. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation of three independent triplicates. Means denoted by different letters are considered statistically different (p < 0.05) according to Duncan’s multiple range test. VOCs, volatile organic compounds; A. a. cattleyae, A. avenae subsp. cattleyae; C. m. michiganensis, C. michiganensis subsp. michiganensis; P. c. carotovorum, P. carotovorum subsp. carotovorum; P.s. actinidiae, P. syringae pv. actinidiae, P. s. lachrymans, P. syringae pv. lachrymans; X. a. citri, X. arboricola pv. citri; X. a. pruni, X. axonopodis pv. citri, X. o. oryzae, X. oryzae pv. oryzae; F. o. lycopersici, F. oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici.