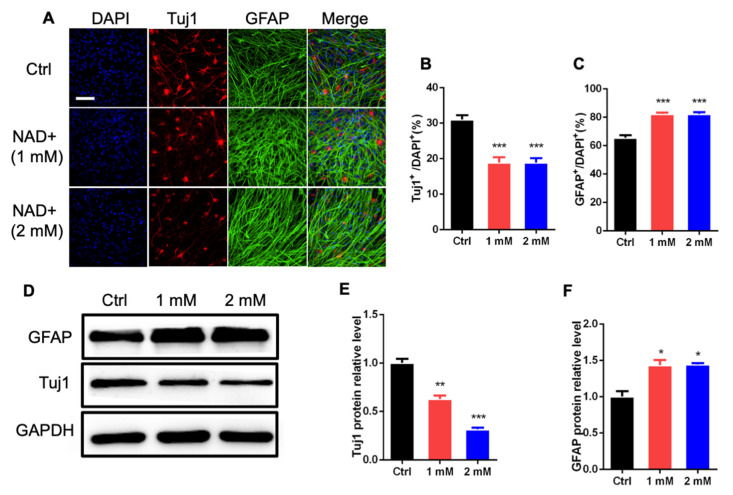
Figure 2.
NAD+ exposure regulates the differentiation of aNSPCs in vitro. (A) Representative immunostaining images of neuronal marker β-III tubulin (Tuj1) and astrocytic marker glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) with Ctrl and NAD+-treated aNSPCs under differentiation conditions. Scale bar, 50 μm. (B,C) Quantification results show that NAD+ exposure decreased the percentage of Tuj1+ cells but increased the percentages of GFAP+ cells under differentiation conditions. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. n = 3 independent experiments, unpaired t-test. (D–F) Western blot assay (D) and quantification results (E,F) show that NAD+ exposure decreased the level of Tuj1, but increased the level of GFAP. GAPDH was used as an internal control. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. n = 3 independent experiments, unpaired t-test; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.