Abstract
Human papillomavirus (HPV) testing using self-collected vaginal specimens is the preferred choice to increase screening uptake. Although the HPV testing results of these samples depend on the cells that naturally exfoliate from the cervical lesion and drift into the vagina, the mechanism of when and how these exfoliated cells mix with the self-collected sample remains unclear. Hence, the study aimed to clarify the relationship between the vaginal drift of HPV-infected cells exfoliated from the cervix, and the menstrual cycle. A total of 180 scraped samples of the cervix and vagina were examined. The exfoliated cells were classified into two categories according to the HPV genotyping results of each sample: sufficient accumulation (same HPV types in cervical and vaginal samples) and insufficient accumulation (fewer HPV types in vaginal samples than in cervical samples, or HPV positivity in cervical samples and HPV negativity in vaginal samples). A moderately strong statistically significant association was observed between exfoliated cell accumulation and the menstrual cycle, and insufficient accumulation was statistically significantly increased at the early proliferative phases. Self-collection of vaginal samples at the early proliferation phase indicates insufficient sample quantities or lower viral load, thereby affecting HPV genotyping.
Keywords: human papillomavirus, cervical cancer screening, self-collection, menstrual cycle
1. Introduction
Due to its greater sensitivity than cytology for detecting precancerous lesions, human papillomavirus (HPV) testing has gradually become the primary method for cervical cancer prevention programs [1,2]. Although cervical cancer screening helps decrease the incidence and mortality rate of cancer, it is still unlikely to resolve the problem of poor screening uptake [3]. In Japan, the participation rate in cervical cancer screening is quite low (approximately 40%) [3,4]. Numerous barriers prevent women from attending a screening; among them are embarrassment regarding the examination, fear of the test result, fear of pain, and lack of time [5]. Therefore, self-collection of vaginal samples for HPV testing has been proposed as an additional strategy to convince unwilling women [6,7,8]. Accumulating evidence reveals that the rate of detection of HPV and cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 2 or worse (CIN2+) in these self-collected specimens is comparable to that in physician-collected specimens [6,9,10,11,12,13].
The sources of HPV positive results in the vaginal sample are cells exfoliated from the female genitalia, including the cervix, and cells of unknown origin that were scraped where the self-sampling instrument contacted them [14]. If vaginal sampling fails to exfoliate a specific cervix, a false-positive result is possible because of other cells exfoliated from the vaginal canal, or a true-positive result because of cells that have naturally exfoliated and drifted away from the cervix. The fact that the HPV testing results of self-collected samples depend on the cells that have drifted away after natural exfoliation from various sites explains why their value is somewhat questionable. Nonetheless, the sensitivity of self-collected samples to CIN2+ is guaranteed to be equivalent to that of physician-collected samples as long as the self-collected samples contain even a small proportion of cells derived from cervical lesions. Hence, self-collection of vaginal samples for HPV testing can possibly be an alternative cervical cancer screening approach for women who are hesitant to undergo pelvic examination at a healthcare clinic. However, the mechanism of when and how exfoliated cells from cervical lesions mix with the self-collected sample remains poorly understood. Further investigation of the cells that exfoliate and drift away from the cervix is important to enhance the reliability of HPV testing using the self-collection approach, which can contribute to increasing the coverage of cervical cancer screening.
Therefore, using the HPV genotyping results of cervical and vaginal samples collected by physicians, this study aimed to clarify the relationship between HPV-infected cells that exfoliate from the cervix and drift into the vagina, and the menstrual cycle.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Specimen Collection
This study used two types of SurePath™ (Becton Dickinson and Company, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) liquid-based cytology (LBC) samples obtained from the cervix and vaginal canal of 324 patients. Prior to the study, these patients were referred for colposcopy because of abnormalities in cervical cytologic screening at the Tokyo Genki Plaza Health Medical Center from 2020 to 2021.
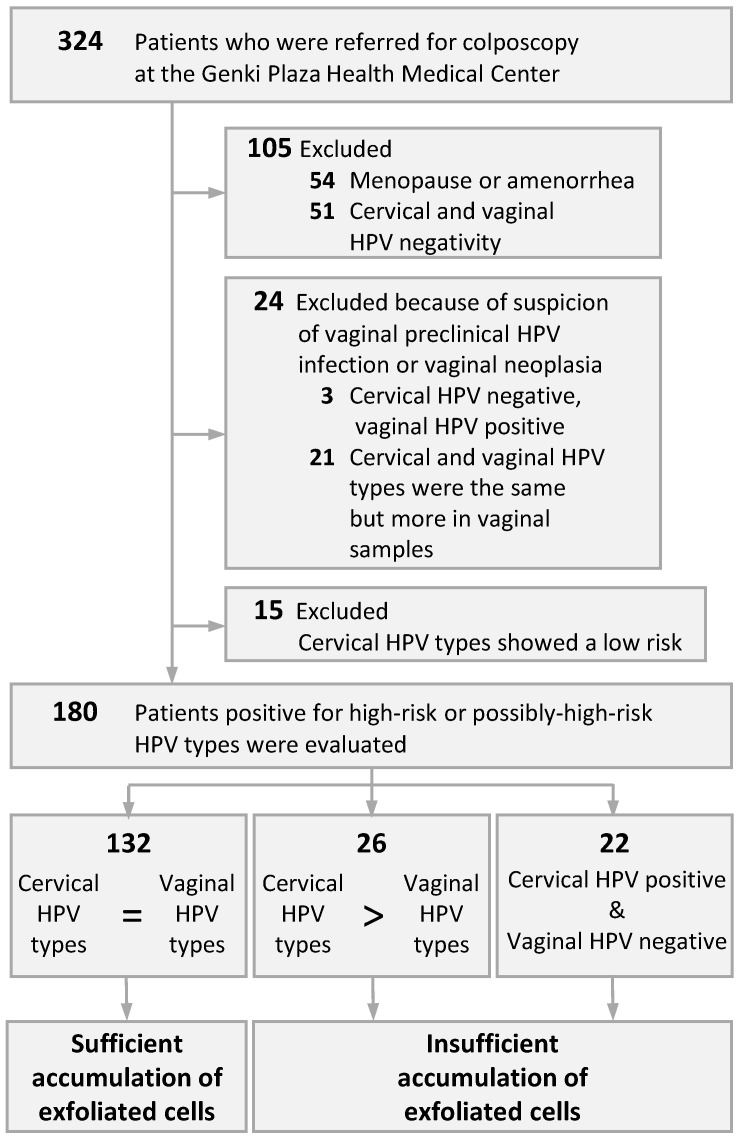
Immediately before colposcopic assessment, a vaginal speculum was inserted into the patient to expose the cervix, and then the endocervix and the portio vaginalis were scraped using an IM sampler instrument (Muto Pure Chemical, Tokyo, Japan), which includes a spatula and a brush, and eluted into a collection vial to collect the cervical sample. Next, with the vaginal speculum open, the bilateral parts from the vaginal fornix to the upper 1/2 of the vaginal canal was scraped and collected using a spatula for the vaginal sample. Written informed consent was obtained from the patients before sample collection. The Ethics Committee on Human Research of Kyorin University approved the study protocol. The protocol was implemented in accordance with the approved guidelines. Patients who had menopause, amenorrhea, or cervical and vaginal HPV negative by HPV genotyping (as described below) were excluded. We also excluded those with suspected vaginal preclinical HPV infection or vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia (VaIN) such as only low-risk (LR) HPV-type positive in cervical samples, HPV negative in cervical samples but HPV positive only in vaginal samples, or HPV positive in both samples but with more HPV types in vaginal samples. In particular, those who were only LR HPV-type positive in the cervical samples were excluded because LR types with suspected vaginal tropism [15] may have contaminated the cervix. Ultimately, 180 patients who had a high-risk (HR) or possibly-high-risk (pHR) HPV-type were evaluated (Figure 1). All patients were nonpregnant women of reproductive age, with a mean age of 36 (range: 22–53) years.
Figure 1.
Stratification of patients by the accumulation of exfoliated cells during the menstrual cycle. HPV, human papillomavirus.
2.2. HPV Genotyping using LBC Samples
DNA from the cell pellet of the LBC samples was isolated using the hot sodium hydroxide method [16]. Cell pellets were lysed with 50 μL of alkaline lysis solution (25 mM NaOH and 0.2 mM ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid [EDTA]; pH, 12.0) for 30 min at 95 °C. Lysed cells were then neutralized with 0.04M Tris-HCl (pH 5.0), centrifuged at 13,200 rpm for 1 min, and directly used as the DNA template. The presence of human β-actin in cells was determined using polymerase chain reaction (PCR), which was an internal standard for genotyping. All HPV genotypes tested positive for human β-actin, demonstrating that we extracted DNA of amplifiable quality from the specimens. HPV genotyping was performed using uniplex E6/E7 PCR, a highly sensitive HPV-PCR method [17]. This method identified E6 or E7 genes of 39 mucosal HPV types, including 13 HR types (HPV16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59, and 68), 11 pHR types (HPV26, 30, 34, 53, 66, 67, 69, 70, 73, 82, and 85), and 15 LR types (HPV6, 11, 40, 42, 44, 54, 55, 61, 62, 71, 74, 81, 84, 89, and 90), from as few as 100 viral copies, with no cross-reactivity across all the HPV genotypes.
2.3. Data Analysis
According to the HPV genotyping results of cervical and vaginal samples, we classified the HPV-infected cells that detached from the cervix and drifted into the vagina into two categories: sufficient and insufficient. HPV detected in the vagina is a possible result of contamination by exfoliated cells from the cervix [15]. Therefore, if the HPV types in the cervical and vaginal samples were the same, we classified these samples as sufficient accumulation of exfoliated cells in the vagina because it suggests that the HPV-infected cells came from the cervix and drifted into the vagina after natural exfoliation. Conversely, insufficient accumulation was considered if the HPV types in the vaginal samples were fewer than those in the cervical samples, or if HPV was positive in the cervical samples but negative in the vaginal samples, suggesting that the exfoliation of the cervical epithelium was suppressed, preventing the HPV-infected cells from drifting into the vagina.
Moreover, menstrual cycles were classified into five phases according to the date of the start of the last menstruation, days of menstrual cycle and bleeding period, and cyclic cytologic characteristics of the Pap smear: (1) menstrual phases (days 1–5; numerous red blood cells, leukocytes, and endometrial cells are present); (2) early proliferative phases (days 6–10; intermediate cells with degenerated cytoplasm are predominant, and endometrial cells and histiocytes are noted occasionally); (3) late proliferative phases (days 11–14; smear background is clear, and superficial cells with transparent flat acidophilic cytoplasm and pyknotic nuclei are predominant); (4) early secretory phases (days 15–21; superficial cells with basophil and folded cytoplasm are present, and the proportion of intermediate cells gradually increases); (5) late secretory phases (days 22–28; numerous Döderlein bacilli, leukocytes, and predominant intermediate cells with markedly folded or degraded cytoplasm are present).
Chi-square analysis with cross-tabulation frequencies was performed using Statistical Package for the Social Sciences version 25.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) to determine whether the accumulation of exfoliated cells was significantly different among the five menstrual phases. We also calculated adjusted residuals for each phase to aid in interpretation.
3. Results
Figure 1 illustrates how we classified the accumulated exfoliated cells in 180 patients according to the HPV genotyping results. All patients had no abnormal findings on colposcopic assessments of the vaginal fornix and vaginal canal. Table 1 enumerates the HPV types detected in the cervical and vaginal samples, the evaluation of the concordance of HPV types in each sample, and the menstrual cycle in each patient.
Table 1.
Accumulation of exfoliated cells and menstrual cycle in 180 patients.
| Case | Cervical HPV Types |
Vaginal HPV Types |
Evaluation | Cycles | Case | Cervical HPV Types |
Vaginal HPV Types |
Evaluation | Cycles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 16,52,58,66 | 16,52,58,66 | C = V | L-Pro | 91 | 66 | 66 | C = V | L-Sec |
| 2 | 52,6b | 52,6b | C = V | L-Sec | 92 | 52,42,74 | 52,42,74 | C = V | Mens |
| 3 | 51,58 | 51,58 | C = V | E-Pro | 93 | 52 | 52 | C = V | Mens |
| 4 | 31,81,82 | 81,82 | C > V | E-Pro | 94 | 31,58,74 | 58,74 | C > V | E-Pro |
| 5 | 18 | 18 | C = V | E-Sec | 95 | 16 | 16 | C = V | E-Sec |
| 6 | 67 | Negative | N | L-Sec | 96 | 39,58,53 | 39,58,53 | C = V | E-Sec |
| 7 | 16 | Negative | N | L-Sec | 97 | 51 | 51 | C = V | L-Sec |
| 8 | 52 | 52 | C = V | L-Pro | 98 | 16 | 16 | C = V | L-Pro |
| 9 | 82,90 | 82,90 | C = V | E-Pro | 99 | 59,90 | 59,90 | C = V | E-Sec |
| 10 | 33,52 | 33,52 | C = V | L-Pro | 100 | 52 | Negative | N | L-Sec |
| 11 | 52 | 52 | C = V | L-Pro | 101 | 31,52,69,74 | 31,52,69,74 | C = V | E-Pro |
| 12 | 52,66 | 52,66 | C = V | L-Sec | 102 | 52,6b | 52,6b | C = V | L-Sec |
| 13 | 56 | 56 | C = V | E-Sec | 103 | 16 | 16 | C = V | L-Sec |
| 14 | 16,45,52,40 | 16,45,40 | C > V | E-Pro | 104 | 52 | 52 | C = V | L-Pro |
| 15 | 58 | 58 | C = V | Mens | 105 | 56 | 56 | C = V | E-Sec |
| 16 | 16 | 16 | C = V | L-Pro | 106 | 66 | 66 | C = V | L-Sec |
| 17 | 56,62 | 62 | C > V | L-Sec | 107 | 31,52,58,70 | 31,58,70 | C > V | L-Pro |
| 18 | 52 | 52 | C = V | E-Sec | 108 | 52 | Negative | N | E-Pro |
| 19 | 39,58,53 | 39,58,53 | C = V | E-Sec | 109 | 51,58,82 | 51,58 | C > V | Mens |
| 20 | 16,66 | 16,66 | C = V | L-Sec | 110 | 58 | 58 | C = V | L-Sec |
| 21 | 33 | 33 | C = V | L-Sec | 111 | 16,51,52,56 | 16,51,52,56 | C = V | L-Sec |
| 22 | 52 | 52 | C = V | E-Sec | 112 | 58 | 58 | C = V | L-Pro |
| 23 | 52,53,74 | 53,74 | C > V | L-Sec | 113 | 31,71 | 31,71 | C = V | E-Sec |
| 24 | 52,84 | 52,84 | C = V | E-Sec | 114 | 51,82 | 51,82 | C = V | L-Sec |
| 25 | 56 | Negative | N | L-Sec | 115 | 51,53,54 | 51,53,54 | C = V | E-Pro |
| 26 | 51,58 | 58 | C > V | E-Sec | 116 | 39,59,40 | 39,59,40 | C = V | L-Sec |
| 27 | 52,58 | 52 | C > V | L-Sec | 117 | 56,66,74 | 56,66,74 | C = V | L-Pro |
| 28 | 51,58,82 | 51,58,82 | C = V | E-Sec | 118 | 53,66 | 53 | C > V | L-Pro |
| 29 | 56,61,74 | 56,61,74 | C = V | E-Sec | 119 | 66 | 66 | C = V | Mens |
| 30 | 39,71 | 39,71 | C = V | L-Sec | 120 | 58 | 58 | C = V | E-Sec |
| 31 | 16 | 16 | C = V | L-Pro | 121 | 16 | 16 | C = V | L-Pro |
| 32 | 52,54,62,70,90 | 52,54,62,70,90 | C = V | L-Sec | 122 | 58 | 58 | C = V | L-Pro |
| 33 | 39,58 | 58 | C > V | E-Sec | 123 | 16 | 16 | C = V | L-Pro |
| 34 | 53,81,90 | 53,81,90 | C = V | L-Sec | 124 | 58 | 58 | C = V | E-Sec |
| 35 | 51 | Negative | N | E-Pro | 125 | 52 | Negative | N | L-Sec |
| 36 | 52 | Negative | N | E-Pro | 126 | 58 | 58 | C = V | E-Pro |
| 37 | 16 | Negative | N | L-Pro | 127 | 39,51,53,42 | 39,51,53,42 | C = V | E-Sec |
| 38 | 52,56 | 52,56 | C = V | E-Pro | 128 | 68 | 68 | C = V | E-Sec |
| 39 | 31 | 31 | C = V | L-Sec | 129 | 31 | Negative | N | E-Sec |
| 40 | 51,71 | 51,71 | C = V | E-Pro | 130 | 51,71 | 51,71 | C = V | E-Pro |
| 41 | 59,74 | 59,74 | C = V | E-Pro | 131 | 34 | 34 | C = V | L-Sec |
| 42 | 52 | 52 | C = V | E-Sec | 132 | 66,62,81 | 66,62,81 | C = V | L-Sec |
| 43 | 51,82 | 51,82 | C = V | L-Sec | 133 | 82,90 | 82,90 | C = V | Mens |
| 44 | 51 | Negative | N | E-Sec | 134 | 53 | 53 | C = V | L-Sec |
| 45 | 31,74 | 74 | C > V | E-Sec | 135 | 52 | 52 | C = V | L-Sec |
| 46 | 52 | 52 | C = V | E-Sec | 136 | 31 | 31 | C = V | L-Sec |
| 47 | 16 | 16 | C = V | L-Pro | 137 | 62,81,90 | 62,81,90 | C = V | E-Sec |
| 48 | 52 | 52 | C = V | L-Sec | 138 | 18 | Negative | N | L-Sec |
| 49 | 16,52,56 | 52,56 | C > V | E-Sec | 139 | 51 | 51 | C = V | E-Sec |
| 50 | 52,58 | 52 | C > V | E-Sec | 140 | 52 | 52 | C = V | L-Sec |
| 51 | 58,67 | 58,67 | C = V | E-Sec | 141 | 58 | 58 | C = V | E-Pro |
| 52 | 16,31,51,52,58,82,54,70 | 16,31,51,52,58, 82,54,70 |
C = V | L-Pro | 142 | 51,82,62 | 51,82,62 | C = V | E-Sec |
| 53 | 52,6b | 52,6b | C = V | L-Pro | 143 | 51,74 | 74 | C > V | L-Pro |
| 54 | 58 | 58 | C = V | E-Sec | 144 | 53,40,62,81 | 53,40,62,81 | C = V | L-Sec |
| 55 | 53 | 53 | C = V | E-Sec | 145 | 16,39 | 16,39 | C = V | E-Sec |
| 56 | 52,40,81 | 52,40,81 | C = V | Mens | 146 | 67 | Negative | N | E-Sec |
| 57 | 52 | 52 | C = V | L-Sec | 147 | 52 | 52 | C = V | E-Sec |
| 58 | 56,66 | 56,66 | C = V | E-Sec | 148 | 56 | Negative | N | E-Pro |
| 59 | 52,62 | 52,62 | C = V | Mens | 149 | 51,82 | 51,82 | C = V | E-Sec |
| 60 | 51,53,54 | 51,53,54 | C = V | E-Pro | 150 | 31 | 31 | C = V | L-Pro |
| 61 | 56,34 | 34 | C > V | L-Pro | 151 | 51 | Negative | N | L-Sec |
| 62 | 16 | Negative | N | L-Sec | 152 | 31,51,52,58 | 31,58 | C > V | E-Pro |
| 63 | 16,66 | 16,66 | C = V | E-Sec | 153 | 53,74 | 53,74 | C = V | L-Sec |
| 64 | 52,58 | 52,58 | C = V | E-Pro | 154 | 66,40 | 40 | C > V | E-Sec |
| 65 | 52 | Negative | N | E-Pro | 155 | 16,66 | 16,66 | C = V | L-Sec |
| 66 | 51,82 | Negative | N | Mens | 156 | 31 | 31 | C = V | L-Pro |
| 67 | 82 | 82 | C = V | E-Sec | 157 | 58 | 58 | C = V | L-Pro |
| 68 | 68 | 68 | C = V | Mens | 158 | 31,90 | 31,90 | C = V | E-Sec |
| 69 | 45,59,53,62,66,67,81 | 45,59,53,62,66, 67,81 |
C = V | L-Sec | 159 | 58 | 58 | C = V | E-Sec |
| 70 | 51 | 51 | C = V | L-Pro | 160 | 31,33,53,68 | 31,33,53,68 | C = V | E-Pro |
| 71 | 53 | 53 | C = V | L-Pro | 161 | 31,68,67 | 31,68,67 | C = V | E-Sec |
| 72 | 59,74 | 59,74 | C = V | E-Sec | 162 | 56 | 56 | C = V | L-Sec |
| 73 | 51,82 | 51 | C > V | L-Pro | 163 | 52 | 52 | C = V | L-Pro |
| 74 | 52 | Negative | N | E-Pro | 164 | 53 | 53 | C = V | L-Pro |
| 75 | 33,52 | 33 | C > V | E-Pro | 165 | 26,90 | 90 | C > V | L-Sec |
| 76 | 52 | 52 | C = V | E-Sec | 166 | 16 | 16 | C = V | E-Sec |
| 77 | 51,58 | 51 | C > V | L-Pro | 167 | 52,67,74,89 | 52,67,74,89 | C = V | L-Pro |
| 78 | 33 | 33 | C = V | L-Sec | 168 | 66,30 | 66,30 | C = V | E-Sec |
| 79 | 31,90 | 31,90 | C = V | L-Sec | 169 | 16 | 16 | C = V | E-Pro |
| 80 | 39,59,40 | 39,59,40 | C = V | E-Sec | 170 | 52,59 | 59 | C > V | E-Pro |
| 81 | 58 | 58 | C = V | E-Sec | 171 | 16,51,52,61 | 16,51,52,61 | C = V | E-Sec |
| 82 | 51,61,74 | 61,74 | C > V | E-Sec | 172 | 16 | 16 | C = V | E-Pro |
| 83 | 66 | 66 | C = V | E-Sec | 173 | 52,82 | 52,82 | C = V | Mens |
| 84 | 66,40 | 40 | C > V | E-Pro | 174 | 33,52 | Negative | N | E-Pro |
| 85 | 56 | Negative | N | L-Sec | 175 | 58 | 58 | C = V | L-Pro |
| 86 | 59 | 59 | C = V | E-Sec | 176 | 51 | 51 | C = V | E-Pro |
| 87 | 31,52,69,42,55,74 | 31,52,69,42,55, 74 |
C = V | E-Sec | 177 | 82 | 82 | C = V | E-Sec |
| 88 | 52,67,74 | 52,67,74 | C = V | L-Sec | 178 | 18 | 18 | C = V | L-Pro |
| 89 | 16,52 | 16,52 | C = V | L-Pro | 179 | 66 | 66 | C = V | L-Sec |
| 90 | 52 | Negative | N | E-Pro | 180 | 18,31,52,59,67,55,74,90 | 31,52,67,55,74,90 | C > V | L-Sec |
The HPV-type column for each case is shown in the order of the high-risk (HR), possibly-high-risk (pHR), and low-risk (LR) types. Different HPV types in cervical and vaginal samples are highlighted in bold. C = V, HPV types in the cervix and vaginal samples are the same; N, HPV is positive in the cervical samples but negative in the vaginal samples; C > V, the number of HPV types in the vaginal samples was reduced more than in the cervical samples; HPV, human papillomavirus; Mens, menstrual phase; E-Pro, early proliferative phase; L-Pro, late proliferative phase; E-Sec, early secretory phases; L-Sec, late secretory phases.
A total of 132 (73.3%) patients had the same HPV types detected in the cervical samples and vaginal samples, and were thereby classified as a sufficient accumulation of HPV-infected cells of cervical origin.
However, 26 (14.4%) patients had fewer HPV types detected in the vaginal sample than in the cervical sample. Those HPV types detected in cervical samples only were HR and pHR types, which accounted for 76.9% and 23.1%, respectively. Furthermore, 22 (12.2%) patients were HPV positive in the cervix but HPV negative in the vagina. The HPV genotypes detected in the cervical samples were HR type, pHR type, and a mixture of both in 86.4%, 9.1%, and 4.5%, respectively. Both cases were classified as insufficient accumulation of HPV-infected cells of cervical origin.
A chi-square test of independence was conducted between the accumulation of HPV-infected cells and the menstrual cycles. Results showed a moderately strong statistically significant association (χ2(4) = 10.642, p < 0.05) (Cramer’s V = 0.243). Table 2 presents a cross-tabulation of the accumulation of HPV-infected cells and the menstrual cycles. Each category consists of the observed frequencies, total percentage, expected frequencies, and adjusted residuals. Absolute adjusted residuals of >2.576 are highlighted in bold, and one category has >2.576 absolute adjusted residuals, indicating that insufficient accumulation was statistically significantly increased at the early proliferative phases (p < 0.01).
Table 2.
Cross-tabulation of the menstrual cycle phases and the accumulation of exfoliated cells.
| Accumulation of Exfoliated Cells | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sufficient | Insufficient | ||
| Menstrual phases | Frequencies | 9 | 2 |
| Total percentage | 82% | 18% | |
| Expected frequencies | 8.1 | 2.9 | |
| Adjusted residual | 0.7 | −0.7 | |
| Early proliferative phase | Frequencies | 16 | 15 |
| Total percentage | 52% | 48% | |
| Expected frequencies | 22.7 | 8.3 | |
| Adjusted residual | −3.0 * | 3.0 * | |
| Late proliferative phase | Frequencies | 27 | 7 |
| Total percentage | 79% | 21% | |
| Expected frequencies | 24.9 | 9.1 | |
| Adjusted residual | 0.9 | −0.9 | |
| Early secretory phases | Frequencies | 45 | 10 |
| Total percentage | 82% | 18% | |
| Expected frequencies | 40.3 | 14.7 | |
| Adjusted residual | 1.7 | −1.7 | |
| Late secretory phases | Frequencies | 35 | 14 |
| Total percentage | 71% | 29% | |
| Expected frequencies | 35.9 | 13.1 | |
| Adjusted residual | −0.4 | 0.4 | |
Absolute adjusted residuals of > 2.576 are highlighted in bold. * p < 0.01.
4. Discussion
Self-sampling HPV tests must be more consistent and reproducible with minimal false-negative results, considering that women who self-collect are distrustful of the results because they are uncertain whether they have collected the specimen correctly [18]. The present study demonstrated that the accumulation of HPV-infected cells that drifted from the cervical epithelium into the vagina is insufficient at the early proliferative phase. Therefore, self-collection of vaginal samples during the early proliferative phase of the menstrual cycle may lead to insufficient sample quantities and lower viral load, thereby affecting the HPV-DNA detection and genotyping.
The reason why insufficient exfoliated cells accumulate at the early proliferative phase may be that this phase is the period after the vaginal exfoliated cells have been washed away by menstrual blood; in addition, estrogen is gradually affecting the cervical epithelium, and the squamous epithelial layer is in the process of forming [19], resulting in a fewer cells available for exfoliation. The squamous epithelium that has differentiated to the superficial layer forms during the late proliferative phase, when estrogen secretion peaks. At this phase, the high estrogen effect increases the permeability and deformability of the cervical epithelium. This squamous epithelial change theoretically causes a decrease in epithelial cell connectivity [20], suggesting the start of natural exfoliation. At the beginning of the secretory phase, the progesterone effect causes deeper exfoliation of the superficial cells. In the final stage, intermediate cells are degraded and, during menstruation, the endometrium expulsion washes away cells on the cervical epithelium’s surface. Thus, if the physiological changes in the cervix caused by sex hormones are understood, we can infer that a constant number of cervical cells will naturally be exfoliated and accumulate in the vagina during most of the menstrual cycle. More than 70% of the women had the same genotypes in both cervical and vaginal samples; hence, natural cervical exfoliation and drift of the exfoliated cells into the vagina occur during most of the menstrual cycle. However, the timing of self-collection has some effect on the HPV test result.
Fairly et al. [21] investigated the effect of menstrual cycle on HPV detection rates and the size of tampons self-inserted into the vagina. The highest number of cells was collected in the middle of the menstrual cycle (probably the late proliferative to mid-secretory phase). In addition, the frequency of HPV detection was higher in this phase than in the early cycle, when the number of cells was the lowest. This result is consistent with the present study, in which insufficient accumulation of HPV-infected cells was observed during the early phase, when the amount of exfoliation was low. Studies that quantified the HPV copy numbers using daily self-collected vaginal samples showed consistency concerning daily HPV positivity and negativity in women, but HPV and cellular DNA copy numbers varied considerably between collection days [22]. Considering that they used a highly sensitive real-time PCR that can determine positive results for less than 10 copies, HPV results may not be consistent in PCR methods with limits of detection greater than 100 copies. Additionally, the copy numbers of viral and cellular DNA are almost positively correlated. Thus, the timing of self-collection may cause variations in the number of epithelial cells and HPV-infected cells in the sample, affecting the results of HPV testing.
However, Sherman et al. [23] found that the frequency of HPV positive results obtained by low-sensitivity Hybrid Capture 2 in physician-collected cervical samples was not related to the date of the last menstrual period. In another study, HPV typing results from similar samples were consistent regardless of the menstrual cycle. Given that the physician-collected cervical samples used in these studies mainly contain cells that have been scraped from cervical lesions, and only a portion of the cells have exfoliated naturally, any variation in the number of cells in the sample caused by the timing of collection may hardly affect the HPV testing results [24]. Therefore, the period of time when few cells have accumulated in the vagina should be considered because self-collection must target HPV-infected cells that have naturally exfoliated.
The strength of this study is that all cervical and vaginal samples were carefully collected by a single gynecologist sequentially on the same day of examination; thus, cross-contamination caused by collection was unlikely. Vaginal sampling also included the distal vagina to maximize the evaluation of the accumulation of naturally exfoliated cells drifting from the cervical epithelium. In the present study, we used a highly sensitive PCR method to detect wide-ranging HPV genotypes in both samples and subsequently detected periods with insufficient accumulation of exfoliated cells according to the results of HPV negativity or genotype reduction in the vaginal samples. Of note, all patients associated with vaginal preclinical HPV infection or VaIN were excluded. We believe that the result of undetected HR or pHR types in the vaginal samples indicates that these oncogenic genotypes have tropism [15] for the cervical epithelium and that the HPV-infected cells have not exfoliated from the cervix. This study also had some limitations. First, when the same HPV genotypes were detected in the cervical and vaginal samples, we determined that HPV-infected cells naturally exfoliated from the cervix and reached the vagina. Considering that more than 70% of the patients had the same HPV-type detected in both samples, having the same type that infected each epithelium seems unlikely. However, these two anatomical locations are attached close to each other. Furthermore, although no vaginal lesions were found by colposcopy, the HR type HPV-infected cells present in the vagina were possibly sampled after adhering to the cervix and were then classified as exfoliated cell accumulation. Although most samples with discordant cervical and vaginal HPV test results suggesting insufficient cell accumulation were collected in the early proliferative phase, this finding may have a limited value. Second, our statistics and inferences were restricted because of the limited number of samples included in this study. In addition, this study only speculated about the impact of self-collected samples on HPV testing according to cell exfoliation results obtained in a small population of women who visited for a detailed examination. Further validation studies using self-collected samples in a larger study population are needed to clarify the impact of the timing of each self-collection during the menstrual cycle on HPV testing.
5. Conclusions
The HPV genotyping results of the cervical and vaginal samples revealed that the accumulation of exfoliated cells in the vagina is insufficient at the early proliferative phase of the menstrual cycle. This finding provides new insights for standardization of the optimal timing for self-collection and contributes to the growing literature on the effect on HPV test results in self-collected samples.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.O. (Mitsuaki Okodo) and K.O.; methodology, M.O. (Mitsuaki Okodo), K.O., M.F. and Y.I.; validation, M.O. (Mitsuaki Okodo) and K.O.; formal analysis, M.O. (Mitsuaki Okodo) and K.T. (Koji Teruya); investigation, M.O. (Mitsuaki Okodo), K.T. (Kazumasa Tanabe), C.I. and Y.I.; resources, M.F. and M.O. (Mizue Oda); data curation, M.O. (Mitsuaki Okodo), K.O., K.T. (Koji Teruya) and H.K.; writing—original draft preparation, M.O. (Mitsuaki Okodo); writing—review and editing, M.O. (Mitsuaki Okodo), K.O., M.F., H.K. and M.O. (Mizue Oda); visualization, K.O.; supervision, M.O. (Mitsuaki Okodo); project administration, M.O. (Mitsuaki Okodo) and M.O. (Mizue Oda), All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Funding information is not available.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of Human Research of Kyorin University (2020-39, 17 March 2021).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data and material that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Saslow D., Solomon D., Lawson H.W., Killackey M., Kulasingam S.L., Cain J., Garcia F.A., Moriarty A.T., Waxman A.G., Wilbur D.C. American Cancer Society, American Society for Colposcopy and Cervical Pathology, and American Society for Clinical Pathology screening guidelines for the prevention and early detection of cervical cancer. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2012;62:147–172. doi: 10.3322/caac.21139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Wright T.C., Stoler M.H., Behrens C.M., Sharma A., Zhang G., Wright T.L. Primary cervical cancer screening with human papillomavirus: End of study results from the ATHENA study using HPV as the first-line screening test. Gynecol. Oncol. 2015;136:189–197. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2014.11.076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Aoki E.S., Yin R., Li K., Bhatla N., Singhal S., Ocviyanti D., Saika K., Suh M., Kim M., Termrungruanglert W. National screening programs for cervical cancer in Asian countries. J. Gynecol. Oncol. 2020;31:e55. doi: 10.3802/jgo.2020.31.e55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Center for Cancer Control and Information Services. [(accessed on 31 January 2022)]. Available online: https://ganjoho.jp/en/index.html.
- 5.Waller J., Bartoszek M., Marlow L., Wardle J. Barriers to cervical cancer screening attendance in England: A population-based survey. J. Med. Screen. 2009;16:199–204. doi: 10.1258/jms.2009.009073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Arbyn M., Verdoodt F., Snijders P.J., Verhoef V.M., Suonio E., Dillner L., Minozzi S., Bellisario C., Banzi R., Zhao F.-H. Accuracy of human papillomavirus testing on self-collected versus clinician-collected samples: A meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:172–183. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70570-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Verdoodt F., Jentschke M., Hillemanns P., Racey C., Snijders P., Arbyn M. Reaching women who do not participate in the regular cervical cancer screening programme by offering self-sampling kits: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials. Eur. J. Cancer. 2015;51:2375–2385. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2015.07.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sultana F., Mullins R., English D.R., Simpson J.A., Drennan K.T., Heley S., Wrede C.D., Brotherton J.M., Saville M., Gertig D.M. Women’s experience with home-based self-sampling for human papillomavirus testing. BMC Cancer. 2015;15:849. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1804-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Zhao F.-H., Lewkowitz A.K., Chen F., Lin M.J., Hu S.-Y., Zhang X., Pan Q.-J., Ma J.-F., Niyazi M., Li C.-Q. Pooled analysis of a self-sampling HPV DNA test as a cervical cancer primary screening method. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2012;104:178–188. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djr532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Polman N.J., Ebisch R.M., Heideman D.A., Melchers W.J., Bekkers R.L., Molijn A.C., Meijer C.J., Quint W.G., Snijders P.J., Massuger L.F. Performance of human papillomavirus testing on self-collected versus clinician-collected samples for the detection of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia of grade 2 or worse: A randomised, paired screen-positive, non-inferiority trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20:229–238. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30763-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Sargent A., Fletcher S., Bray K., Kitchener H.C., Crosbie E.J. Cross-sectional study of HPV testing in self-sampled urine and comparison with matched vaginal and cervical samples in women attending colposcopy for the management of abnormal cervical screening. BMJ Open. 2019;9:e025388. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-025388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Inturrisi F., Aitken C.A., Melchers W.J., van den Brule A.J., Molijn A., Hinrichs J.W., Niesters H.G., Siebers A.G., Schuurman R., Heideman D.A. Clinical performance of high-risk HPV testing on self-samples versus clinician samples in routine primary HPV screening in the Netherlands: An observational study. Lancet Regional Health-Eur. 2021;11:100235. doi: 10.1016/j.lanepe.2021.100235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Flores C.A., Gutierrez G.G., Leon J.O., Rodriguez D.C., Sørbye S. Self-collected versus clinician-collected cervical samples for the detection of HPV infections by 14-type DNA and 7-type mRNA tests. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021;21:504. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-06189-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Belinson J.L., Hu S., Niyazi M., Pretorius R.G., Wang H., Wen C., Smith J.S., Li J., Taddeo F.J., Burchette R.J. Prevalence of type-specific human papillomavirus in endocervical, upper and lower vaginal, perineal and vaginal self-collected specimens: Implications for vaginal self-collection. Int. J. Cancer. 2010;127:1151–1157. doi: 10.1002/ijc.25144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Castle P.E., Schiffman M., Bratti M.C., Hildesheim A., Herrero R., Hutchinson M.L., Rodriguez A.C., Wacholder S., Sherman M.E., Kendall H. A population-based study of vaginal human papillomavirus infection in hysterectomized women. J. Infect. Dis. 2004;190:458–467. doi: 10.1086/421916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Truett G., Heeger P., Mynatt R., Truett A., Walker J., Warman M. Preparation of PCR-quality mouse genomic DNA with hot sodium hydroxide and tris (HotSHOT) Biotechniques. 2000;29:52–54. doi: 10.2144/00291bm09. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Okodo M., Okayama K., Teruya K., Sasagawa T. Uniplex E6/E7 PCR method detecting E6 or E7 genes in 39 human papillomavirus types. J. Med. Virol. 2018;90:981–988. doi: 10.1002/jmv.25017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Guan Y., Castle P.E., Wang S., Li B., Feng C., Ci P., Li X., Gravitt P., Qiao Y.-L. A cross-sectional study on the acceptability of self-collection for HPV testing among women in rural China. Sex. Transm. Infect. 2012;88:490–494. doi: 10.1136/sextrans-2012-050477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Koss L.G., Melamed M.R. Koss’ Diagnostic Cytology and Its Histopathologic Bases. Volume 1 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia, PA, USA: 2006. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Gorodeski G.I. Estrogen modulation of epithelial permeability in cervical-vaginal cells of premenopausal and postmenopausal women. Menopause. 2007;14:1012. doi: 10.1097/gme.0b013e3180587eb5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Fairley C.K., Robinson P.M., Chen S., Tabrizi S.N., Garland S.M. The detection of HPV DNA, the size of tampon specimens and the menstrual cycle. Sex. Transm. Infect. 1994;70:171–174. doi: 10.1136/sti.70.3.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Sanner K., Wikström I., Gustavsson I., Wilander E., Lindberg J.H., Gyllensten U., Olovsson M. Daily self-sampling for high-risk human papillomavirus (HR-HPV) testing. J. Clin. Virol. 2015;73:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2015.09.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Sherman M., Carreon J., Schiffman M. Performance of cytology and human papillomavirus testing in relation to the menstrual cycle. Br. J. Cancer. 2006;94:1690–1696. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Gustavsson I., Aarnio R., Berggrund M., Hedlund-Lindberg J., Sanner K., Wikström I., Enroth S., Olovsson M., Gyllensten U. Randomised study of HPV prevalence and detection of CIN2+ in vaginal self-sampling compared to cervical specimens collected by medical personnel. Int. J. Cancer. 2019;144:89–97. doi: 10.1002/ijc.31637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The data and material that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.