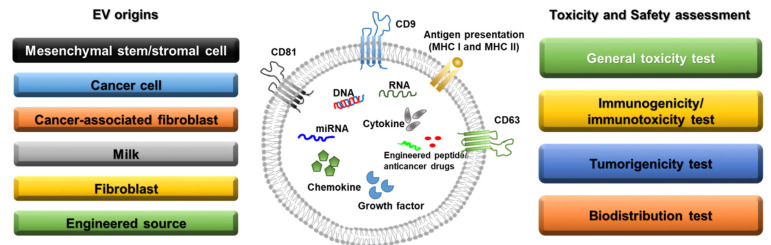
Figure 1.
Sources of extracellular vesicles and toxicity/safety assessments. EVs can originate from mesenchymal stem/stromal cells, cancer cells, cancer-associated fibroblasts, milk, normal fibroblasts, and engineered cells. EVs have a lipid bilayer and can contain transmembrane proteins, antigen presentation proteins, DNA, RNA, miRNA, cytokines, chemokines, growth factors, engineered peptides, and anticancer drugs. Before clinical studies of EVs, general toxicity, immunogenicity, tumorigenicity, and biodistribution tests should be performed in preclinical studies depending on the source of the EVs.