To the Editor:
The article recently published by Simón et al reports a case of bilateral psoas muscle hematoma due to SARS-CoV-2 infection in a critically ill patient1.
We have recently identified 2 cases that share similar characteristics.
The patients are 2 men, aged 64 and 78 years, who required anticoagulation and postural changes to prone position in the context of ICU treatment for severe SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia. On days 30 and 37 after diagnosis, respectively, both patients presented sudden anemia with no apparent signs of external bleeding. CT angiographies were requested, which found right retroperitoneal hematomas measuring 7 × 14 × 22.5 cm and 15 × 13 × 17 cm (Fig. 1 A and 2A) and signs of active bleeding from branches of the lumbar L1, iliolumbar and iliac circumflex arteries (Fig. 1B), and lumbar L3-4 and iliolumbar arteries (Fig. 2 B), which were embolized. The subsequent evolution of both patients was satisfactory.
Fig. 1.
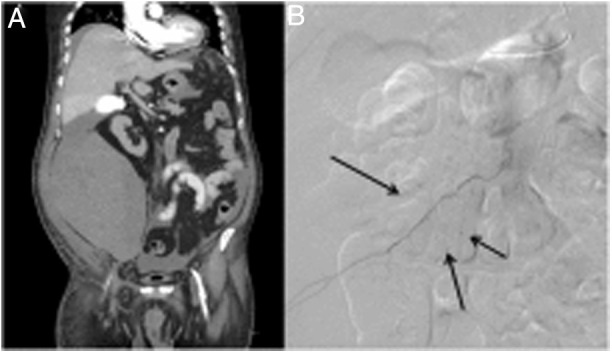
A) Right retroperitoneal hematoma; B) Active arterial bleeding from the lumbar L1, iliolumbar and circumflex iliac branches (arrows).
Fig. 2.
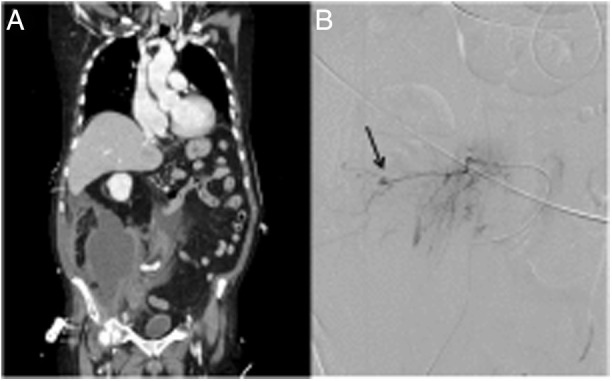
A) Right retroperitoneal hematoma; B) Active arterial bleeding from lumbar L3-4 and iliolumbar branches (arrow).
Other authors in our setting, such as, Pardal-Fernández et al, have also reported several cases of retroperitoneal bleeding with involvement of the psoas in patients with severe SARS-CoV22, infection. Similarly, they have studied the pathogenesis of this infrequent condition, emphasizing that the most relevant circumstance in these patients could be, the anticoagulation indicated in order to minimize the intense thrombotic effects of the virus, which are a consequence of the endotheliitis, proinflammatory state derived from their binding to angiotensin-converting enzyme receptors in the microvascular endothelium. In addition, they refer to prolonged prone positions, postural changes as, favoring retroperitoneal bleeding.
The patient profile usually includes severe COVID infection, with the need for anticoagulation and prolonged ICU hospitalization3, 4. Symptoms at presentation may include abdominal pain, anemia, lumbar polyneuropathy with motor deficits in the lower extremities, tachycardia, or hypotension, even in exceptional circumstances such as ECMO therapy5.
Depending on the degree of hemodynamic impact, the initial treatment must include the withdrawal or a reduced dose of anticoagulants and fluid resuscitation. The need for vasoactive drugs and transfusion support should be assessed. Several experiences of definitive management based on angioembolization have been described with favorable results, which was also our experience with our patients4, 5.
There is a well-known relationship between SARS-CoV-2 and thrombotic phenomena. However, we feel it is necessary to make this condition of spontaneous retroperitoneal hemorrhages known, as they are probably the result of anticoagulant use or consumptive coagulopathies. Publications about this rare complication are scarce and isolated in most cases. It would be interesting to plan a systematic review of the international literature to obtain greater levels of evidence.
Conflict of interests
None of the authors have conflicts of interests to declare.
Footnotes
Please cite this article as: Perfecto A, Villalabeitia I, Sendino P, Sarriugarte A. Hematoma retroperitoneal espontáneo en pacientes con neumonía bilateral grave por SARS-CoV-2. Cir Esp. 2022;100:387–388.
References
- 1.Simón E., Charco L.M., Jiménez J.M. Hematoma del músculo psoas bilateral por infección SARS-CoV-2 en paciente crítico. Cir Esp. 2021 doi: 10.1013/j.ciresp.2021.02.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Pardal-Fernández J.M., García-García J., Gutiérrez-Rubio J.M., Segura T. Plexo-neuropatía por hematoma en iliopsoas en 4 pacientes COVID. Med Clin (Barc) 2021;156:410–417. doi: 10.1016/j.medcli.2020.11.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Javid A, Kazemi R., Dehghani M., Bahrami H. Catastrophic retroperitoneal hemorrhage in COVID-19 patients under anticoagulant prophylaxis. Urol Case Rep. 2021;36:101561. doi: 10.1016/j.eucr.2021.101568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Patel I., Akoluk A., Douedi S., Upadhyaya V., Mazahir U., Costanzo E., et al. Life-threatening psoas hematoma due to retroperitoneal hemorrhage in a COVID-19 patient on enoxaparin treated with arterial embolization: A case report. J Clin Med Res. 2020;12:458–461. doi: 10.14740/jocmr4256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Shao-Hui G., Sheng-Mei Z., Yong-Xing Y. Giant retroperitoneal hematoma during extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in a patient with coronavirus disease-2019 pneumonia. JCVA. 2020:2839–2840. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2020.05.039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


