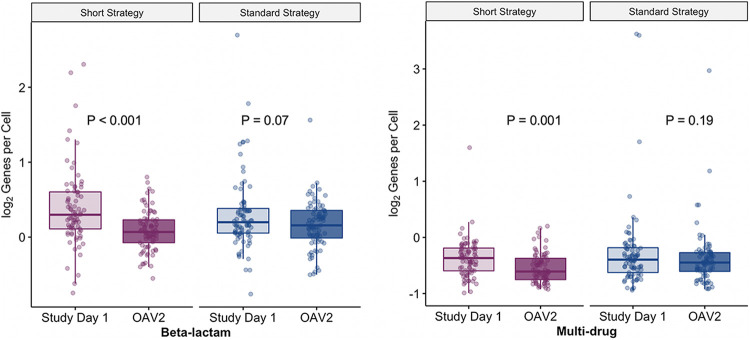
FIG 3.
Comparison of abundances of beta-lactam and multidrug efflux resistance genes per prokaryotic cell (RGPC) at the enrollment visit and end of the study by treatment strategy (n = 158). Boxplots of beta-lactam (left) and multidrug efflux (right) resistance genes per prokaryotic cell (RGPC) in throat swabs from 158 participants at the enrollment visit and end of the study stratified by treatment strategy. The line reflects the median RGPC, lower and upper hinges correspond to the first and third quartiles, respectively, and upper and lower whiskers extend from the hinge to the highest value that is within 1.5× interquartile range of the hinge. A one-sided Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used to assess statistically significant differences (alpha level <0.05) between the numbers of RGPC in participants at enrollment (study day 1) and at the end of the study (outcome assessment visit 2 [OAV2]); participants were stratified by assignment to a short course (light and dark purple) or standard course (light and dark blue) strategy. FDR-adjusted P values are shown. Log2 normalized RGPC data were used for visualization.