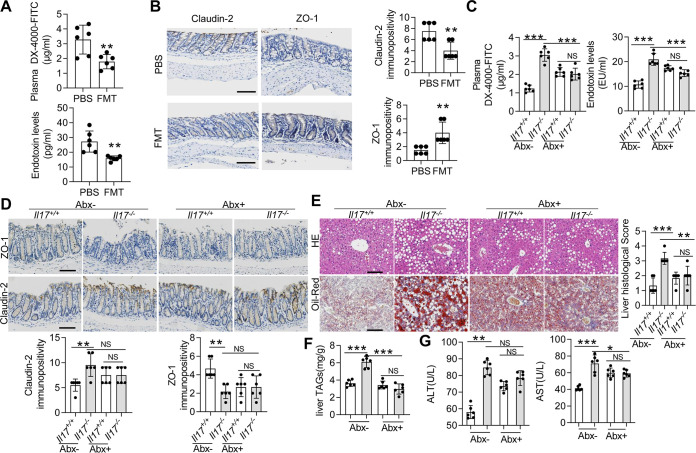
FIG 6.
The gut microbiota promotes high intestinal permeability and hepatic steatosis in Il17−/− mice. After a week of adaptation to an MCD diet, Il17−/− mice were subjected to FMT or were inoculated with PBS by enema. (A) The FITC-dextran levels (upper panel) and plasma LPS concentrations (lower panel) were determined. (B) Immunohistochemical staining for Claudin-2 (left) and ZO-1 (right) in colon sections. Scale bar, 50 μm. The data are expressed as means ± SD. Significance versus the PBS-treated group: *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. Il17−/− and Il17+/+ mice were treated with or without Abx for 4 weeks and then were fed an MCD diet for 3 weeks (n = 5 in each group). (C) FITC-dextran levels (upper panel) and plasma LPS concentrations (lower panel) were determined. (D) Immunohistochemical staining for ZO-1 (upper panel) and Claudin-2 (lower panel). Scale bar, 50 μm. (E) Representative H&E-stained (upper panel) and Oil Red O-stained (lower panel) liver sections. Scale bar, 50 μm. (F) TAG levels in the liver. (G) Serum levels of ALT and AST. The data are expressed as means ± SD. NS, not significant; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.